Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dental implants posts
In the rapidly evolving landscape of dental healthcare, dental implants posts stand out as a critical component in restorative dentistry. As international B2B buyers seek to enhance their product offerings, understanding the nuances of dental implant posts becomes essential. These fixtures not only support prosthetic teeth but also play a pivotal role in ensuring patient satisfaction and long-term success of dental procedures.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview tailored for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Kenya. Within this framework, we will explore the various types of dental implant posts, including endosteal and subperiosteal options, along with the materials used, such as titanium and zirconia, which directly influence biocompatibility and durability. Furthermore, we will delve into manufacturing processes and quality control standards that ensure reliability and safety in dental practices.
Understanding the cost structures associated with dental implants is crucial for strategic sourcing decisions. We will provide insights into supplier dynamics, highlighting both local and international manufacturers, enabling buyers to make informed choices. Additionally, a dedicated FAQ section will address common queries, ensuring clarity and confidence in your procurement strategy.
By empowering you with this knowledge, this guide aims to streamline your sourcing process, enhance your competitive edge, and ultimately contribute to the success of your dental practice in a global market.
Understanding dental implants posts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endosteal Implants | Inserted directly into the jawbone; most common type. | General dentistry, oral surgery | Pros: High success rate, strong foundation. Cons: Requires sufficient bone density. |
| Subperiosteal Implants | Placed under the gum but above the jawbone; used when bone is insufficient. | Patients with bone loss, specialized cases | Pros: Minimal bone alteration needed. Cons: Higher cost, complex surgical procedure. |
| Zygomatic Implants | Anchored in the zygomatic bone; used for severe bone loss. | Advanced dental restoration | Pros: No need for bone grafting. Cons: Specialized training required for placement. |
| Mini Implants | Smaller diameter, less invasive; used for temporary or transitional solutions. | Temporary restorations, orthodontics | Pros: Easier placement, quicker recovery. Cons: Less stability for long-term solutions. |
| All-on-4 Implants | Four implants support a full arch of teeth; efficient for patients with limited bone. | Full mouth restorations | Pros: Reduces need for bone grafts, quicker procedure. Cons: Limited to specific cases. |
Endosteal Implants
Endosteal implants are the most prevalent type of dental implants, inserted directly into the jawbone. They are suitable for patients with adequate bone density and are commonly used in general dentistry and oral surgery. For B2B buyers, it’s crucial to ensure that the implant systems offered are compatible with various prosthetic solutions, as this can enhance the versatility of treatment plans. Additionally, buyers should consider the quality of materials used, as this affects the long-term success rate of the implants.
Subperiosteal Implants
Subperiosteal implants are placed beneath the gum tissue but above the jawbone, making them ideal for patients who have experienced significant bone loss. These implants are particularly relevant in specialized cases where traditional implants may not be feasible. B2B buyers should focus on the surgical protocols and training provided by manufacturers, as these implants require a more complex surgical approach. Understanding the cost implications and potential for increased patient satisfaction can also guide purchasing decisions.
Zygomatic Implants
Zygomatic implants are anchored in the zygomatic bone and are designed for patients with severe bone loss in the upper jaw. This type of implant eliminates the need for bone grafting, making it a preferred option for advanced dental restorations. B2B buyers must ensure that their teams are adequately trained in the placement of zygomatic implants, as specialized techniques are necessary. Additionally, evaluating the availability of supporting materials and post-operative care products can enhance the overall service offering.
Mini Implants
Mini implants are characterized by their smaller diameter, making them less invasive and suitable for temporary or transitional solutions. They are often used in orthodontics or as part of a larger dental restoration plan. For B2B buyers, the ease of placement and quicker recovery times associated with mini implants can be attractive selling points. However, it’s essential to weigh these benefits against their reduced stability compared to traditional implants, especially for long-term applications.
All-on-4 Implants
All-on-4 implants utilize four strategically placed implants to support a full arch of teeth, making them an efficient solution for patients with limited bone. This method significantly reduces the need for bone grafts and can streamline the treatment process. B2B buyers should consider the technology and support systems offered by manufacturers, as these can influence the overall success of the procedure. Understanding the specific patient demographics that benefit from this approach can also aid in targeted marketing strategies.
Related Video: 3 Types of Dental Implants and Surface treatments explained!
Key Industrial Applications of dental implants posts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dental implants posts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Replacement of missing teeth with implants | Improved patient satisfaction and retention | Quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and supplier reliability |
| Dental Laboratories | Custom fabrication of prosthetics | Enhanced precision and reduced turnaround time | Material quality, technological capabilities, and cost-effectiveness |
| Orthodontic Practices | Support for orthodontic devices | Increased treatment effectiveness and patient comfort | Compatibility with existing systems, durability, and design flexibility |
| Medical Equipment Suppliers | Integration into surgical kits | Streamlined operations and improved surgical outcomes | Regulatory certifications, sourcing from reputable manufacturers, and logistical efficiency |
| Research Institutions | Development of new implant technologies | Innovation and competitive advantage | Collaboration with manufacturers, access to cutting-edge materials, and intellectual property considerations |
Dental Clinics
In dental clinics, dental implant posts serve as a reliable solution for replacing missing teeth. By providing a stable foundation for crowns and bridges, these implants enhance patient satisfaction and retention. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize sourcing implants that comply with local regulatory standards and ensure quality assurance. Additionally, understanding the post-surgical support and warranty offered by suppliers is crucial for maintaining high patient care standards.
Dental Laboratories
Dental laboratories utilize dental implant posts for the custom fabrication of prosthetics. The precision of these implants is vital for creating accurate and functional dental solutions. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing high-quality materials that facilitate efficient production processes is essential. Key considerations include the technological capabilities of suppliers, turnaround times, and the cost-effectiveness of the materials used in the fabrication process.
Orthodontic Practices
In orthodontic practices, dental implant posts can be integral in supporting various orthodontic devices, such as retainers and braces. This application increases treatment effectiveness and enhances patient comfort by providing a stable anchorage point. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Kenya should focus on sourcing implants that are compatible with their current systems and offer durability. Furthermore, the design flexibility of the implants can play a significant role in meeting diverse patient needs.
Medical Equipment Suppliers
For medical equipment suppliers, integrating dental implant posts into surgical kits can streamline operations and improve surgical outcomes. This application requires a deep understanding of regulatory certifications and the sourcing of products from reputable manufacturers. B2B buyers should evaluate the logistics of supplier operations to ensure timely delivery and reliable support, which are critical for maintaining the efficiency of surgical procedures.
Research Institutions
Research institutions leverage dental implant posts for the development of new implant technologies. This application is pivotal for driving innovation and gaining a competitive advantage in the dental market. International buyers in this sector must consider collaborations with manufacturers that provide access to cutting-edge materials and technologies. Additionally, understanding the implications of intellectual property rights in the development process is essential for fostering successful partnerships.
Related Video: Project ‘Poo Zoo’ uses animal dung to save at-risk species | REUTERS
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dental implants posts
When selecting materials for dental implant posts, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to consider the specific properties and applications of each material. This section delves into four common materials used in dental implants, providing insights into their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse regions.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is renowned for its excellent biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand physiological conditions, including temperature variations and mechanical stress.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of titanium makes it a preferred choice for long-term implants. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can impact overall project costs. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring precise machining and finishing processes.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is compatible with various media, including bone and soft tissue, facilitating osseointegration. Its corrosion resistance ensures longevity in the oral environment.
Specific Considerations:
International buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM F136 standards for titanium alloys. In regions like Saudi Arabia and Kenya, local regulations may dictate specific certifications, making it essential to verify supplier compliance.
Zirconia
Key Properties:
Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its aesthetic appeal and high strength. It offers excellent fracture toughness and resistance to wear.
Pros & Cons:
Zirconia provides a superior aesthetic solution, making it ideal for anterior implants. However, it can be more brittle than titanium, leading to potential failure under high stress. The manufacturing process is complex and may require specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Zirconia is particularly suitable for patients with metal allergies, as it is metal-free. Its compatibility with soft tissues promotes healing, although its rigidity may not be ideal for all applications.
Specific Considerations:
Buyers in Europe and South America should look for compliance with ISO 6872 standards for dental ceramics. Additionally, understanding local preferences for aesthetics can influence material choice.
Cobalt-Chromium Alloys
Key Properties:
Cobalt-chromium alloys are characterized by high strength, excellent wear resistance, and good corrosion resistance. They can withstand high mechanical loads, making them suitable for various dental applications.
Pros & Cons:
These alloys are durable and can be manufactured with precision, but they are heavier than titanium and zirconia. The cost is generally moderate, but the complexity of the manufacturing process can increase overall expenses.
Impact on Application:
Cobalt-chromium is compatible with various media, including bone and dental cement. Its strength makes it suitable for load-bearing applications, but its weight may be a disadvantage for some patients.
Specific Considerations:
International buyers should consider compliance with ASTM F75 standards. In regions like the Middle East, awareness of local preferences for material weight and aesthetics can guide selection.
Polymer-Based Materials
Key Properties:
Polymers, particularly PEEK (polyether ether ketone), are lightweight and flexible, offering good biocompatibility and chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Polymers are cost-effective and can be manufactured easily, but they may not provide the same level of strength as metals. Their flexibility can be advantageous in certain applications, but it may also lead to wear over time.
Impact on Application:
PEEK is compatible with soft tissues and can be used in temporary implants or in conjunction with other materials. However, its lower mechanical strength limits its use in permanent applications.
Specific Considerations:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ISO 10993 for biocompatibility. In regions like Africa, where cost efficiency is paramount, polymer-based materials may present a viable option.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for dental implants posts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Permanent dental implants | Excellent biocompatibility | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic anterior implants | Superior aesthetic appearance | Brittle under high stress | Med |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloys | Load-bearing dental applications | High strength and wear resistance | Heavier than titanium | Med |
| Polymer-Based Materials | Temporary or flexible implants | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with regional preferences and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dental implants posts
Manufacturing dental implants posts is a multifaceted process that requires precision, adherence to international standards, and a commitment to quality assurance. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section will break down the manufacturing stages, key techniques involved, and the quality control measures that ensure the reliability of dental implants.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of dental implants involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets both functional and safety standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing dental implants is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include titanium and zirconia, chosen for their biocompatibility and strength. Manufacturers typically follow these steps:
- Material Selection: Choosing high-grade titanium (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V) or zirconia based on the implant design and intended application.
- Material Treatment: Processes like surface cleaning and polishing to remove any contaminants that might affect the implant’s performance.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming the implant posts. This can involve several techniques:
- CNC Machining: Precision machining techniques are employed to shape the implant posts accurately. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines provide high precision, ensuring that each implant meets strict dimensional tolerances.
- Additive Manufacturing: Some manufacturers are beginning to adopt 3D printing technology for creating complex geometries and customized implants.
3. Assembly
While many implants are single-piece designs, some may require assembly, particularly those with modular components. Key activities include:
- Component Fitting: Ensuring that any modular parts fit securely and maintain the intended functionality.
- Initial Quality Checks: Conducting visual inspections and basic functional tests before proceeding to finishing processes.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage is critical for ensuring the implants are ready for sterilization and use. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as sandblasting, acid etching, or anodization to enhance osseointegration and reduce bacterial colonization.
- Final Inspection: A thorough examination of the finished product for defects or inconsistencies.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of dental implants is governed by a series of international standards and industry-specific regulations. Understanding these can help buyers assess supplier reliability.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is essential for manufacturers aiming for consistency and customer satisfaction.
- ISO 13485: Specifically for medical devices, this standard ensures that manufacturers adhere to stringent quality controls throughout the product lifecycle.
- CE Marking: For companies operating in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
Industry-Specific Certifications
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI): Ensures that manufacturers meet U.S. standards, which can be critical for markets in North America.
- API (American Petroleum Institute): Relevant for implants used in specific applications, ensuring that materials and processes meet industry benchmarks.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated into each stage of the manufacturing process through various checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive review of the finished products before they are released to the market.
Common Testing Methods
To ensure the implants meet the required standards, several testing methods are employed:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and hardness.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Evaluating how the implant interacts with biological tissues, often mandated by ISO 10993.
- Sterilization Validation: Ensuring that the sterilization process effectively eliminates all potential contaminants.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must employ strategies to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers effectively:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed reports on quality control measures, including testing results and certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to verify compliance and quality assurance practices can provide an additional layer of confidence.
Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to consider the following nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding these can prevent delays in product acceptance and market entry.
- Cultural Considerations: Building relationships and understanding local business practices can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Ensuring that suppliers have robust logistics capabilities is crucial, especially for regions with less developed infrastructure.
By gaining insight into the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for dental implants, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality expectations and regulatory requirements. Understanding these elements not only aids in supplier selection but also enhances the overall safety and efficacy of dental implants used in various markets.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dental implants posts Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Dental Implants Posts
When sourcing dental implant posts, it is essential to grasp the comprehensive cost structure involved. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the price. Titanium and zirconia are common materials used for dental implants, each with different cost implications. High-quality materials often come with a premium, but they ensure durability and biocompatibility.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the region and the level of expertise required for manufacturing. Skilled labor may demand higher wages, particularly in regions with advanced manufacturing capabilities.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize these expenses.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost but is necessary for producing specialized implant designs. Buyers should consider whether the investment in custom tooling aligns with their volume needs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure product reliability. The costs associated with QC, including testing and compliance with international standards, should be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the origin and destination. Consideration of Incoterms is crucial as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better prices.
Key Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of dental implant posts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate favorable terms based on volume.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the benefits of customization outweigh the associated costs.
-
Material Quality/Certifications: Implants with higher quality materials and relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may incur higher prices but provide long-term value through enhanced performance and patient safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their quality assurance processes, while less-known suppliers might offer lower prices at higher risks.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly affect total costs. For instance, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) includes shipping and insurance, which can lead to higher upfront costs but lower risks during transit.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage suppliers in negotiations with a clear understanding of your requirements and budget constraints. Leverage volume commitments to secure better pricing.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial purchasing costs, evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, potential failures, and the long-term performance of the implants.
-
Explore Regional Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing from regional suppliers may reduce logistics costs and lead times.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends can provide insights into pricing fluctuations and emerging suppliers, enabling better purchasing decisions.
-
Prioritize Quality Over Cost: While cost is a critical factor, prioritizing quality can lead to better patient outcomes and reduced long-term costs associated with failures or replacements.
Disclaimer
The prices and analysis provided are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable to conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments before making purchasing decisions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dental implants posts
When engaging in the procurement of dental implant posts, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed decisions. This section outlines the key specifications and common jargon that can significantly impact purchasing strategies.
Key Technical Properties of Dental Implant Posts
-
Material Grade
– Dental implant posts are commonly made from titanium or zirconia. Titanium, particularly grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), is favored for its strength, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance. In contrast, zirconia is preferred for its aesthetic qualities. Selecting the appropriate material grade is essential for ensuring longevity and compatibility with the patient’s biological environment. -
Surface Treatment
– The surface of dental implants may undergo various treatments such as sandblasting, acid etching, or coating with bioactive materials. These treatments enhance osseointegration, the process by which the implant bonds with the bone. Understanding surface treatments can help buyers select implants that offer better clinical outcomes, thus improving patient satisfaction. -
Diameter and Length
– Implant posts come in various diameters and lengths, typically ranging from 3.0 mm to 5.0 mm in diameter and 8 mm to 16 mm in length. The choice of dimensions affects the stability and distribution of forces on the implant. Buyers must consider the anatomical conditions of the patient when selecting the appropriate size to ensure optimal performance. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in the dimensions of the dental implant post. Tight tolerances are critical for ensuring proper fit with abutments and prosthetics. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications can help in minimizing complications during the installation process and ensuring the reliability of the final product. -
Load Capacity
– Load capacity is the maximum force that an implant can withstand without failure. This property is vital for ensuring that the implant can support the functional demands placed upon it, particularly in molar areas where chewing forces are highest. Buyers should prioritize implants with proven load capacities to ensure durability and reduce the risk of implant failure.
Common Trade Terms in Dental Implant Procurement
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s product. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality standards and potential customization options for dental implant posts, ensuring that they source reliable and compliant products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and reduced excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers request price proposals from suppliers for specific products. For dental implants, issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare costs, lead times, and terms across multiple suppliers, leading to more informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping and insurance responsibilities. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to mitigate risks and ensure smooth logistics when importing dental implants from different regions. -
CE Marking
– CE marking indicates that a product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in Europe, ensuring that dental implants have CE marking is crucial for regulatory compliance and market acceptance. -
Biocompatibility
– Biocompatibility refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response when applied within the body. This property is vital for dental implants to minimize adverse reactions. Buyers should prioritize products that have been thoroughly tested for biocompatibility to ensure patient safety and implant success.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of dental implant procurement more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance both clinical outcomes and business operations.
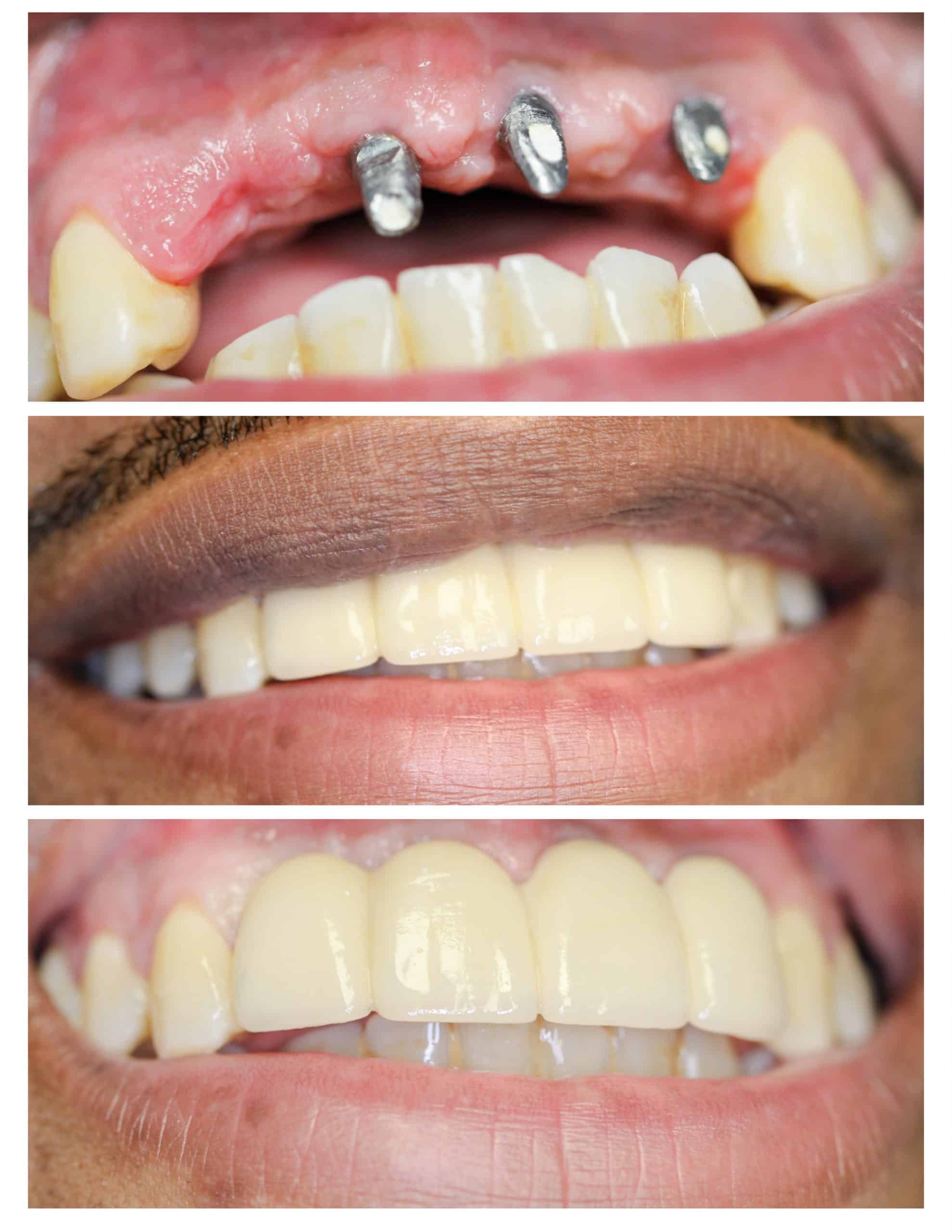
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the dental implants posts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The dental implants posts sector is experiencing significant growth driven by an increasing global demand for dental restoration solutions. Factors such as an aging population, rising awareness of oral health, and advancements in dental technology are propelling this market forward. In regions like Africa and South America, emerging economies are witnessing a surge in dental tourism, which further fuels the demand for high-quality dental implants.
Key trends shaping the market include the adoption of digital technologies, such as 3D printing and CAD/CAM systems, which enhance the precision and customization of dental implants. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence in treatment planning and patient management is becoming commonplace. For international B2B buyers, understanding the technological landscape is crucial for identifying suppliers that can offer innovative solutions at competitive prices.
Sourcing trends are also evolving, with a noticeable shift towards direct relationships with manufacturers rather than intermediaries. This approach not only reduces costs but also allows for better quality control and faster response times. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe are increasingly focused on sourcing from regions that can provide both quality assurance and cost-effectiveness, while also considering the logistical implications of supply chains.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a central concern in the dental implants posts sector, with environmental impacts from manufacturing processes drawing scrutiny. As B2B buyers, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their commitment to sustainable practices, including waste reduction, energy efficiency, and the use of eco-friendly materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure that the materials used in dental implants are sourced responsibly. This includes verifying that suppliers adhere to international labor standards and engage in fair trade practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC certification for materials can help buyers identify suppliers committed to sustainability.
Furthermore, the demand for “green” dental materials is on the rise. Biocompatible materials that minimize environmental impact while ensuring patient safety are gaining traction. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who are innovating in this space, as these collaborations not only reflect a commitment to sustainability but also cater to a growing consumer base that values ethical practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of dental implants has its roots in ancient civilizations, where rudimentary forms of tooth replacement were utilized. However, modern dental implants began to take shape in the 20th century with the introduction of titanium as a biocompatible material. This breakthrough allowed for osseointegration, where the implant integrates with the jawbone, providing a stable foundation for prosthetic teeth.
Over the past few decades, the sector has witnessed significant technological advancements, including the development of computer-guided implant surgery and the use of advanced imaging techniques. Today, the dental implants posts market is characterized by a focus on customization, patient-specific solutions, and an increasing emphasis on sustainability, shaping a future that aligns with the ethical considerations of modern B2B buyers.
Related Video: Dental Implants Cost Guide – 9 Factors Influencing What You Pay
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dental implants posts
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers for dental implants posts?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, quality certifications, and production capacity. Investigate their reputation through reviews and testimonials from other international buyers. Assess compliance with international standards, such as ISO and CE markings. Additionally, consider their ability to provide customization options and their responsiveness to inquiries. This thorough evaluation helps ensure you partner with a reliable supplier who meets your specific needs. -
Can I customize dental implants posts to suit specific market needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for dental implants posts, allowing you to tailor products to your market’s demands. This may include variations in size, material, and design features. It’s crucial to discuss your requirements during initial negotiations and request samples to evaluate quality before placing larger orders. Customization can help you differentiate your offerings in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for dental implants posts?
MOQs for dental implants posts can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times may also differ based on production schedules and customization requirements, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. When negotiating, clarify these terms upfront to ensure they align with your inventory and sales strategies. Understanding MOQs and lead times helps manage cash flow and maintain adequate stock levels. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted by suppliers of dental implants posts?
Most suppliers accept a variety of payment methods, including bank transfers, letters of credit, and payment platforms like PayPal. However, the preferred method may depend on your location and the supplier’s policies. Always negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as partial payments upfront and the balance upon delivery. Establishing secure payment methods fosters trust and ensures smooth transactions throughout the procurement process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for dental implants posts?
To ensure quality assurance, request relevant certifications from your suppliers, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices or CE marking for compliance with European standards. Conduct audits or inspections if possible, or hire third-party services to evaluate manufacturing practices. Additionally, ask for test reports that validate product performance and safety. These steps help mitigate risks associated with substandard products and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing dental implants posts internationally?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Assess the supplier’s ability to handle shipping logistics, including customs clearance and delivery timelines. Familiarize yourself with import regulations specific to your country, as well as potential tariffs or duties. Collaborating with reliable freight forwarders can streamline the process and reduce delays. Additionally, consider incoterms to clearly define responsibilities for shipping costs and risks. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers over dental implants posts?
Establishing clear communication and documentation practices is vital for managing disputes. Always have a contract that outlines terms, responsibilities, and quality expectations. In the event of a disagreement, initiate discussions to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods. Building strong relationships with suppliers can also mitigate disputes, fostering a collaborative environment for resolving conflicts. -
What trends should I be aware of in the dental implants market that could affect sourcing decisions?
Stay informed about emerging trends such as advancements in implant technology, increasing demand for biocompatible materials, and shifts toward digital dentistry solutions. Additionally, monitor regional market growth and regulatory changes that may impact sourcing strategies. Engaging in industry forums or trade shows can provide insights into these trends, helping you make informed sourcing decisions that align with market demands and consumer preferences.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dental implants posts
In the competitive landscape of dental implants, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for success. By prioritizing quality and reliability in suppliers, B2B buyers can ensure that the dental implants they procure meet the highest standards of performance and safety. Key takeaways include the importance of building strong relationships with manufacturers, leveraging regional advantages, and staying informed about global market trends that influence pricing and availability.
Investing time in evaluating suppliers based on their certifications, technological advancements, and customer service can yield substantial long-term benefits. Buyers should also consider diversifying their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical uncertainties, particularly in dynamic markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As we look ahead, the dental implant market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for dental health solutions. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to act strategically—embrace innovation, explore new partnerships, and commit to sustainable sourcing practices. By doing so, you position your business to not only thrive in the present but also lead in the future of dental implant solutions.
