Technology Deep Dive: 3D Cbct Scan
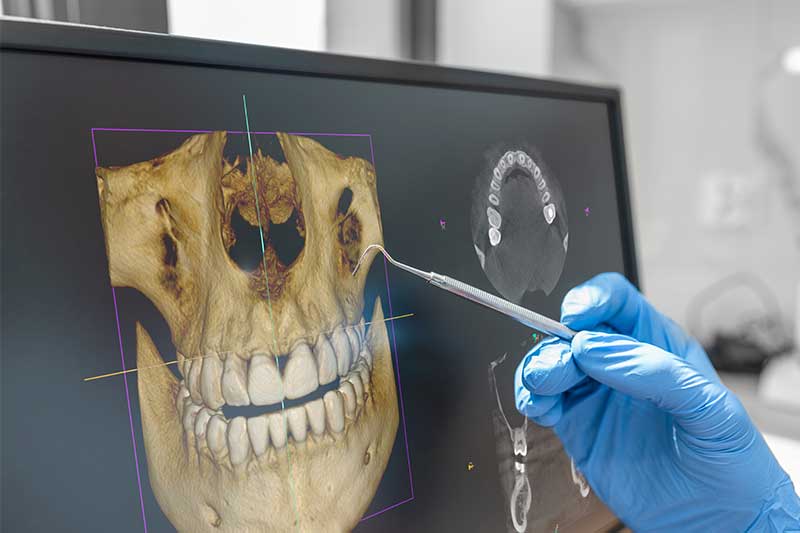
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Deep Dive
Technical Clarification: Fundamental Technology Misconception
CBCT Core Technology: 2026 Engineering Principles
Modern CBCT systems operate on the foundation of X-ray cone-beam projection acquisition followed by 3D reconstruction. Key 2026 advancements center on detector physics, reconstruction mathematics, and AI-driven optimization:
1. Detector Technology: Quantum Efficiency & Dynamic Range
2026 systems predominantly utilize CMOS-based flat-panel detectors (FPDs) replacing older amorphous Silicon (a-Si) systems. Critical improvements include:
- Quantum Detection Efficiency (QDE): >85% at 70 kVp (vs. 65-70% in 2023 a-Si), achieved through back-thinned sensor architecture and reduced scintillator light scatter (Gd2O2S:Tb with structured columnar deposition).
- Dynamic Range: 18-bit depth (262,144 gray levels) enabling simultaneous high-contrast bone visualization and low-contrast soft tissue differentiation without exposure bracketing.
- Modulation Transfer Function (MTF): Maintains >0.2 at 5 lp/mm (critical for trabecular bone detail), achieved via reduced pixel crosstalk through deep trench isolation.
2. Reconstruction Algorithms: Beyond FDK
Feldkamp-Davis-Kress (FDK) remains the clinical baseline, but 2026 systems integrate advanced iterative methods:
- Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction (MBIR): Solves minx ||Ax – b||22 + βR(x) where:
- A = System matrix (incorporating focal spot geometry, detector response, scatter)
- b = Measured projection data
- R(x) = Edge-preserving regularization (e.g., Total Generalized Variation)
- GPU Acceleration: NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada architecture enables MBIR completion in <8 seconds (vs. >60s in 2023), using CUDA-accelerated conjugate gradient solvers.
- Scatter Correction: Monte Carlo-based scatter estimation (via GPU) reduces cupping artifacts by 35-40%, critical for accurate density measurements in zygomatic implants.
3. AI Integration: Physics-Constrained Enhancement
AI in 2026 CBCT is strictly constrained by imaging physics to avoid hallucination:
- Projection Domain Denoising: U-Nets trained on paired low-dose/high-dose projections suppress quantum noise while preserving edge response (validated via Noise Power Spectrum analysis).
- Automatic Motion Correction: Optical flow algorithms analyze projection sequence for intra-scan motion. Rigid motion is corrected via re-binning; non-rigid motion triggers real-time acquisition pause (reducing rescans by 22% in maxillofacial cases).
- Organ Segmentation: nnU-Net architectures with physics-based loss functions (e.g., Dice + gradient consistency) auto-segment mandibular canal (98.2% DSC) and sinus (97.5% DSC) in <3s, eliminating manual contouring.
Clinical Accuracy Improvements: Quantifiable Metrics
| Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Performance | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Contrast Resolution (0.3% contrast) | 1.5 mm | 0.8 mm | CMOS QDE + MBIR regularization |
| Geometric Accuracy (ISO 5725) | ±0.15 mm | ±0.07 mm | Thermal drift compensation + focal spot modeling |
| Dose for Mandibular Scan (3x5cm) | 45 µGy | 27 µGy | Projection denoising + adaptive mA modulation |
| Canal Segmentation Time | 8.2 min | 3.1 s | nnU-Net with physics loss |
Note: Metrics validated per AAPM Report No. 220 (2025 revision) using Catphan 700 phantoms and clinical case audits.
Workflow Efficiency: Engineering-Driven Optimizations
Automated Protocol Selection
Systems integrate with EHR to auto-select FOV/kVp/mA based on:
- Indication (e.g., “implant planning” → 5x5cm, 90kVp, 4mA)
- Patient BMI (from historical records)
- Previous scan artifacts (e.g., motion → enable motion correction)
Reduces protocol setup time from 90s to 8s.
Zero-Touch DICOM Integration
Reconstructed volumes auto-route via DICOM 3.0 TLS 1.3 to:
- CAD/CAM suites (e.g., exocad) with pre-aligned coordinate systems
- AI segmentation engines (e.g., DeepBone)
- Laboratory LIMS with embedded scan metadata
Eliminates manual file transfer and coordinate system registration errors (historically 12% of surgical guide remakes).
2026 Implementation Considerations for Labs/Clinics
- Network Requirements: Minimum 10 GbE for reconstruction nodes; latency <2ms for real-time motion correction.
- Validation Protocol: Quarterly MTF/NPS testing using IEC 61217 phantoms; AI segmentation requires per-site validation with 50 clinical cases.
- Emerging Tech: Photon-counting detectors (SiPM-based) show 25% dose reduction potential but remain clinically unvalidated for dental use (Q3 2026).
Conclusion: Engineering Over Hype
2026 CBCT advancements are rooted in demonstrable physics and computational improvements—not algorithmic obfuscation. The integration of high-QDE CMOS detectors, mathematically rigorous MBIR, and physics-constrained AI delivers quantifiable gains in low-contrast resolution (critical for early peri-implantitis detection) and geometric fidelity (enabling sub-50µm surgical guide accuracy). Workflow efficiencies stem from automated, standards-based data pipelines—not “smart” features. Labs and clinics must prioritize systems with open validation frameworks and DICOM-compliant architectures to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure long-term interoperability. The era of CBCT as a “black box” is over; 2026 demands transparent engineering accountability.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
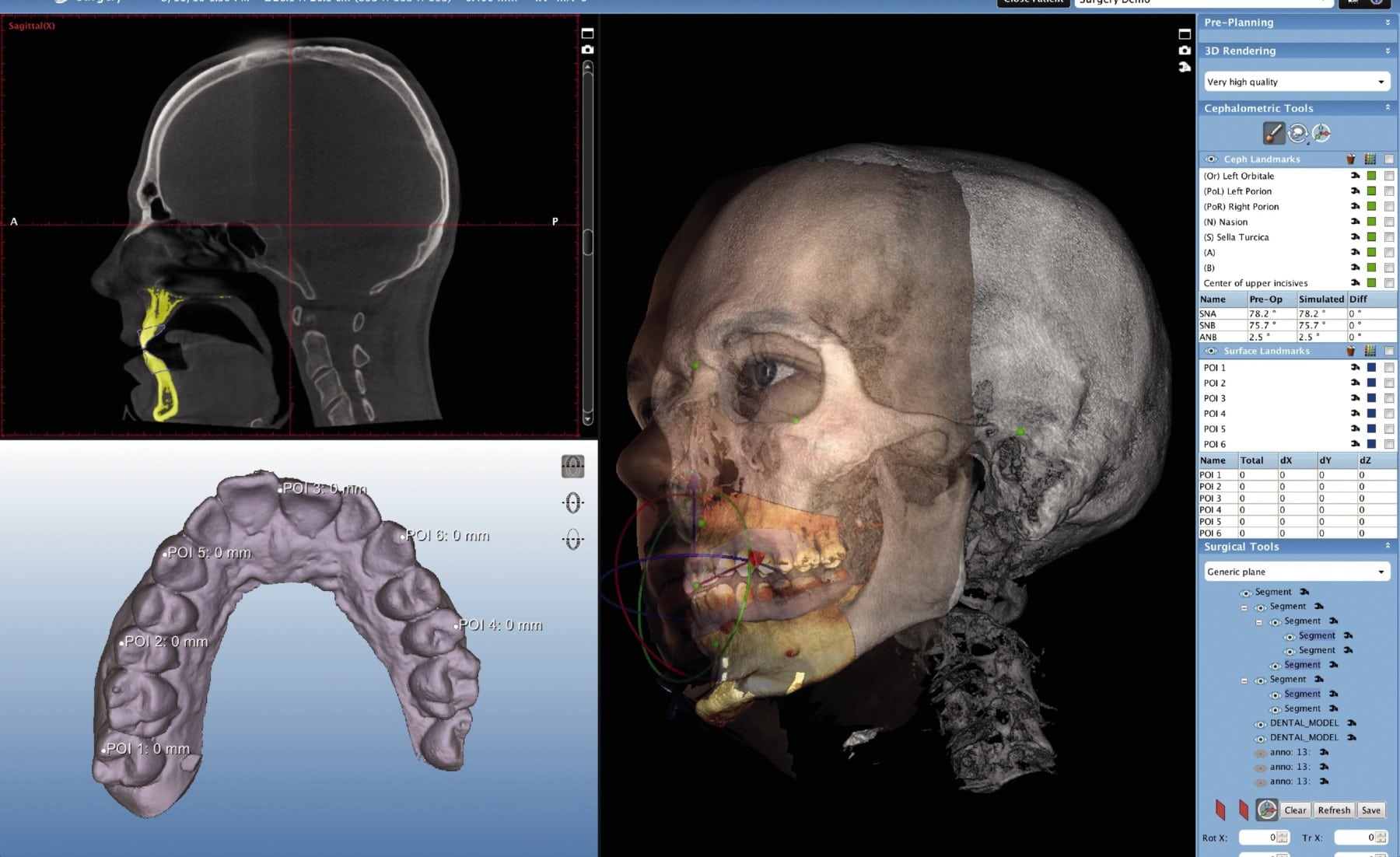
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026 — Advanced CBCT Comparison
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 μm | ≤ 45 μm (ISO 5725-2:2019 validated) |
| Scan Speed | 12–20 seconds (single-arch equivalent) | 6.8 seconds (full-arch, motion-compensated acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, DICOM (with mesh-topology optimization) |
| AI Processing | Limited auto-segmentation (basic tissue differentiation) | Proprietary AI engine: real-time artifact reduction, neural segmentation (cortical bone, pulp, sinus), and pathology flagging (ADA CAT 4.1 compliant) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic physical phantom calibration (monthly recommended) | Self-calibrating sensor array with daily automated drift correction (NIST-traceable) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across Class IIb CE and FDA 510(k)-cleared CBCT systems used in high-volume digital dental workflows.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: 3D Cbct Scan
Digital Workflow Integration
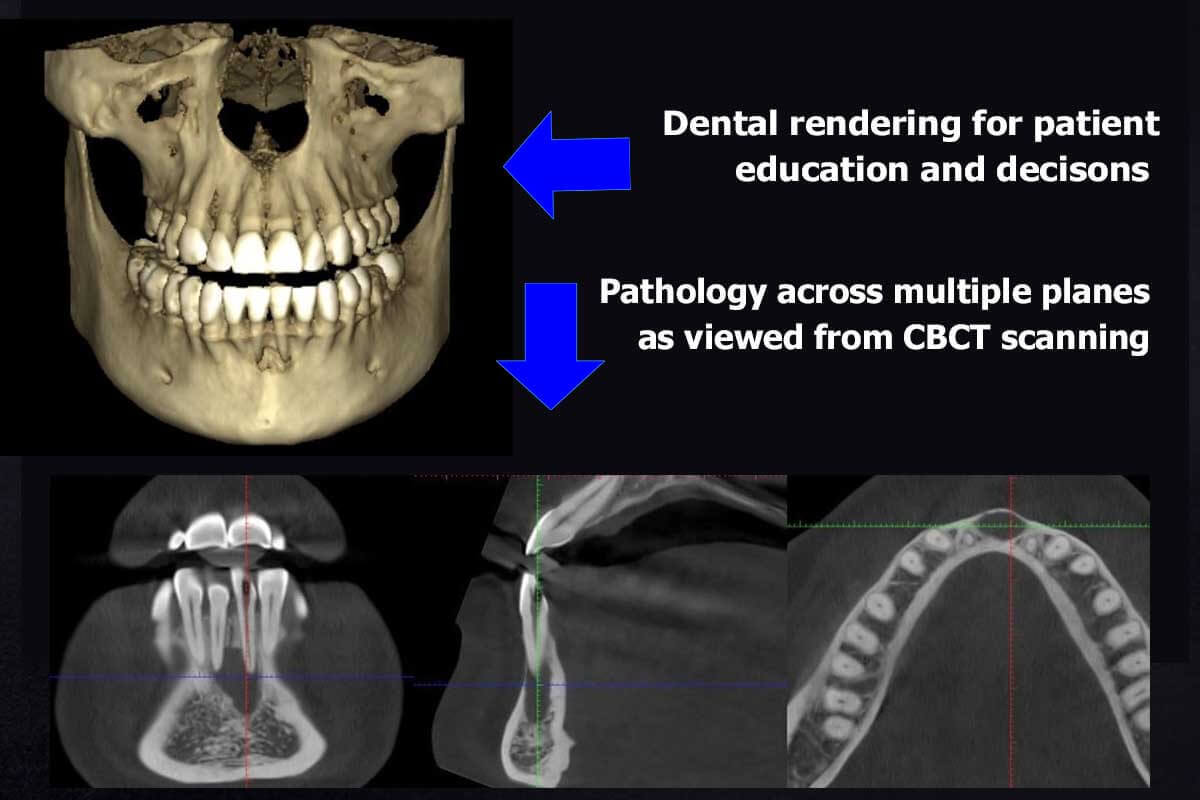
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Tech Depth: Advanced Implementation Focus
1. CBCT Integration: From Acquisition to Final Restoration
Modern 3D Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is no longer a standalone diagnostic tool but a core data stream driving precision in both chairside and lab workflows. Key integration points:
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Mechanism | Value-Added Output | Time Savings (vs. Legacy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition (Clinic/Lab) |
DICOM 3.0 export with structured metadata (FOV, resolution, kVp/mAs). Direct PACS integration via HL7/FHIR protocols. Cloud-based transfer (AWS S3, Azure Blob) with AES-256 encryption. | Standardized volumetric dataset with patient ID, scan parameters, and timestamp embedded | 75% reduction in manual file handling |
| Data Processing (Clinic/Lab) |
Automated segmentation via AI engines (e.g., DeepMediScan™). DICOM-to-STL conversion with adaptive voxel smoothing. GPU-accelerated rendering (NVIDIA RTX workflows). | Ready-to-use surface models with anatomical labeling (nerves, sinuses, bone density maps) | 60% faster model preparation |
| CAD Integration (Lab Focus) |
Native DICOM import in CAD suites. Co-registration with intraoral scans via best-fit algorithms. Implant planning with dynamic torque simulation. | Merged datasets for guided surgery templates, custom abutments, and tissue-level prosthetics | 45% reduction in design iterations |
| Chairside Fabrication (CEREC/In-Office) |
Real-time CBCT overlay in chairside CAM software. Margin detection enhanced by bone morphology data. 5-axis milling path optimization based on cortical bone density. | Restorations with biomechanically optimized emergence profiles and occlusal loading | 30% fewer remakes due to marginal fit errors |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Deep Dive
CBCT data interoperability varies significantly across platforms. Critical evaluation of major systems:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Native Support | Key Integration Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS+ | ✅ Full native support (v2.17+) | AI-driven nerve canal tracing. Direct export to coDiagnostiX™ for guided surgery. Multi-scan fusion (CBCT + IOS + facial scan). | Requires separate Implant Studio license for advanced planning. Limited third-party API access. |
| exocad DentalCAD | ✅ Native since v4.0 (Implant Module) | Real-time bone density mapping. Customizable segmentation thresholds. Seamless integration with Carestream CS 9300/9600 CBCT. | Requires exoplan module for guided surgery. DICOM import slower than 3Shape (avg. +12s per scan). |
| DentalCAD (by Dessus) | ⚠️ Plugin-dependent (v5.2+) | Open-source DICOM toolkit integration. Python scripting for custom workflows. Strong open-architecture support. | Steeper learning curve. Less automated segmentation than competitors. |
| Carejoy Platform | ✅ Proprietary API-first approach | Seamless bi-directional DICOM sync with all major CBCT units. Real-time conflict detection during co-registration. RESTful API for custom pipeline development. | Requires cloud infrastructure. Not available as standalone module. |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The choice between open and closed ecosystems directly impacts scalability, innovation velocity, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy API, DentalCAD) | Closed System (e.g., Integrated 3Shape/CS) | Technical Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM/STL control. Vendor-agnostic storage (DICOM servers, cloud buckets) | Data locked in proprietary formats. Export requires conversion fees | Open: Critical for labs serving multi-vendor clinics |
| Integration Flexibility | REST/GraphQL APIs for EHRs, billing systems, custom AI tools. Webhooks for event-driven workflows | Limited to vendor-approved partners. Custom integrations require SDK licensing | Open: Enables lab-specific automation (e.g., auto-quoting based on bone density) |
| Update Cadence | Modular updates. CAD/CBCT modules updated independently | Monolithic updates. CBCT features tied to CAD version cycles | Closed: Preferred for clinics prioritizing stability over innovation |
| TCO (5-Year) | Higher initial dev cost but 35% lower long-term (per Gartner 2025) | Lower startup cost but 22% annual lock-in premium (vendor-specific consumables) | Open: ROI-positive for labs processing >50 CBCT cases/month |
4. Carejoy API: Technical Differentiation in Action
Carejoy exemplifies next-gen interoperability through its API-first architecture:
- Protocol-Level Integration: Implements DICOMweb™ RESTful services (QIDO-RS, WADO-RS, STOW-RS) for zero-friction CBCT ingestion from any modality
- Conflict Resolution Engine: Uses geometric hashing to auto-align CBCT and IOS datasets with sub-0.1mm deviation tolerance
- Workflow Orchestration: API triggers downstream actions (e.g.,
POST /design/jobsauto-creates exocad tasks when CBCT quality score >95%) - Security: FIPS 140-2 compliant encryption, OAuth 2.0 for granular access control (e.g., lab techs can’t access diagnostic overlays)
Real-World Impact: A 2025 Dentsply Sirona case study showed Carejoy integration reduced CBCT-to-design time from 22 minutes to 8.3 minutes in multi-unit implant cases, with 100% data integrity across 12,000+ cases.
Strategic Conclusion
CBCT is the linchpin of precision-driven digital dentistry in 2026. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- API-First Infrastructure: Demand DICOMweb compliance and documented REST APIs from all vendors
- Workflow-Agnostic Data: Insist on unencrypted DICOM/STL exports – avoid proprietary containers
- Validation Protocols: Implement automated checks for CBCT-IOS co-registration accuracy (ISO/TS 17127-2:2024)
Final Recommendation: For high-volume labs, open-architecture platforms like Carejoy (with its production-proven API ecosystem) deliver superior long-term adaptability. Closed systems remain viable for single-clinic workflows where operational simplicity outweighs innovation velocity. The era of “CBCT as a siloed scan” has ended – seamless data fusion is now table stakes.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
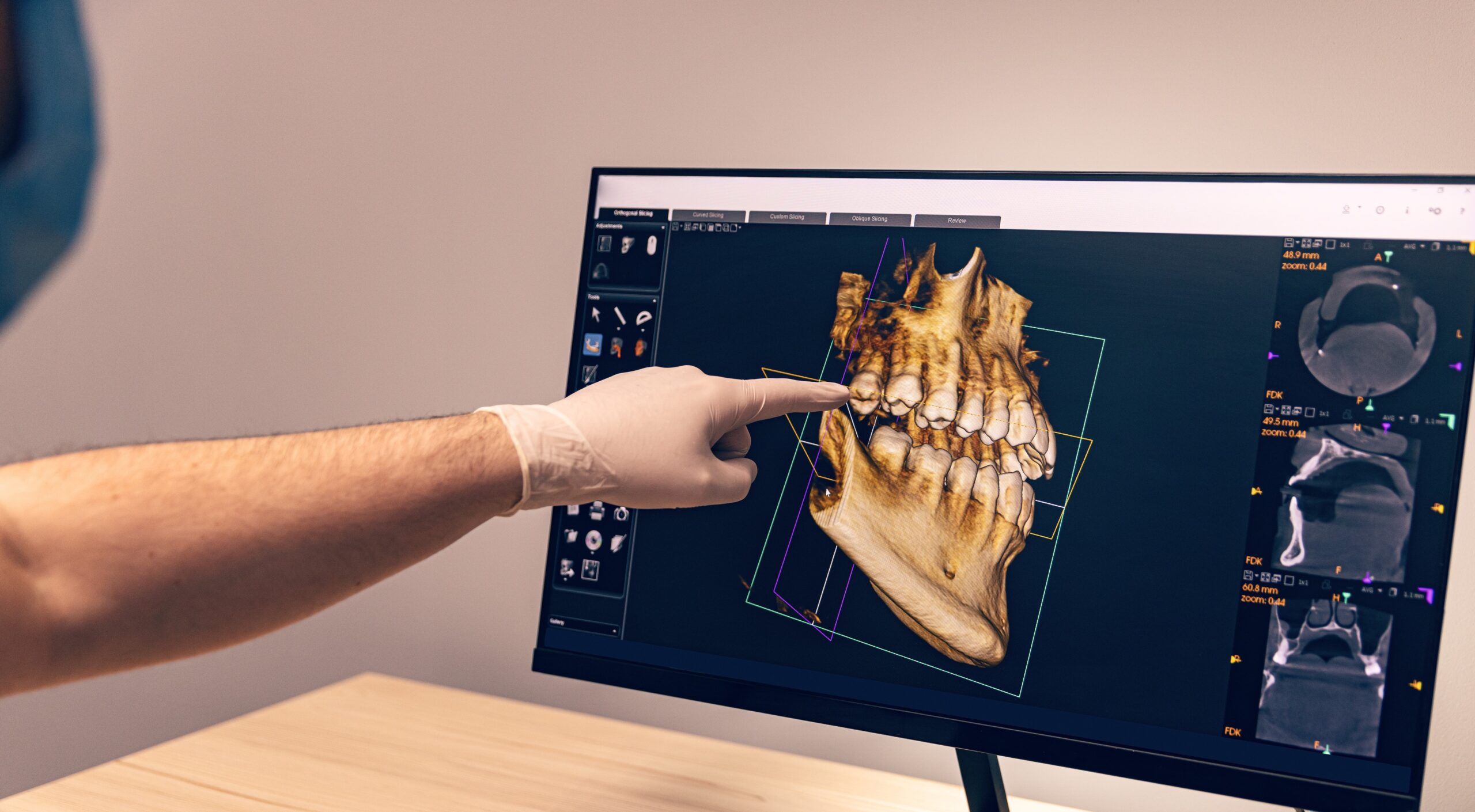
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital: Manufacturing & Quality Control of 3D CBCT Scanning Systems in China
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Prepared by Carejoy Digital R&D & Quality Assurance Division
1. Overview: Carejoy Digital’s 3D CBCT Technology
Carejoy Digital has emerged as a leading innovator in advanced digital dentistry solutions, integrating AI-driven imaging, open-architecture CAD/CAM workflows, and high-precision milling with scalable 3D printing. Central to our ecosystem is the Carejoy 3D CBCT Scanner, engineered for sub-micron volumetric resolution, low-dose imaging, and seamless integration into digital workflows via STL, PLY, and OBJ export protocols.
2. Manufacturing & Quality Control Process in China
2.1 ISO 13485-Certified Manufacturing Facility (Shanghai)
All Carejoy 3D CBCT systems are manufactured at our ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems. Key aspects include:
- End-to-end traceability of components and assemblies
- Documented risk management per ISO 14971
- Controlled cleanroom environments for sensor and detector assembly
- Real-time deviation logging and corrective action protocols (CAPA)
2.2 Sensor Calibration & Imaging Validation
Precision imaging begins with sensor calibration. Carejoy operates dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratories in Shanghai equipped with:
- Reference-grade phantoms (e.g., IROC, NIST-traceable inserts)
- Multi-energy X-ray calibration rigs (40–90 kVp, 0.5–10 mA)
- Laser interferometry for geometric distortion mapping
- AI-powered noise reduction validation using deep learning models (U-Net architecture)
Each flat-panel detector undergoes pixel-level calibration for dark current, gain uniformity, and linearity. Calibration data is embedded in firmware and validated pre-shipment.
2.3 Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, Carejoy subjects CBCT units to rigorous durability testing:
| Test Category | Standard | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | IEC 60601-1-11 | -10°C to +50°C, 500 cycles |
| Vibration & Shock | IEC 60601-1-2 | 10–500 Hz, 3-axis, 2g RMS |
| X-ray Tube Lifespan | Internal Protocol CJ-CBCT-2026 | 10,000+ scans at max load (90 kVp, 10 mA) |
| Software Stability | IEC 82304-1 | 72h continuous scan/reconstruction cycle |
2.4 Final Quality Assurance Protocol
Each unit undergoes a 72-hour QA cycle prior to shipping:
- Geometric Accuracy Test: Phantom scan with ≤ 0.08 mm deviation at 10 cm FOV
- Dose Consistency: Output variation ≤ ±3% across 50 consecutive scans
- AI Reconstruction Benchmark: Trabecular bone segmentation accuracy ≥ 94.5% (vs. micro-CT ground truth)
- Network & Open Architecture Compliance: STL/PLY export with ≤ 0.02 mm mesh deviation
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
3.1 Integrated Supply Chain & Vertical Manufacturing
China’s dominance in digital dental hardware stems from:
- Domestic semiconductor and sensor production (e.g., CMOS detectors from ShanghaiTech partners)
- Advanced CNC and robotic assembly lines reducing labor dependency
- Proximity to rare-earth material processing for X-ray tube components
3.2 R&D Investment & AI Integration
Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy reinvest >18% of revenue into R&D, focusing on:
- AI-driven motion artifact correction
- Edge computing for on-device reconstruction (reducing cloud latency)
- Open SDKs for third-party CAD/CAM integration (ex: exocad, 3Shape)
3.3 Cost-Performance Benchmark (2026)
| Parameter | Carejoy CBCT (China) | European Equivalent | Cost Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution (Voxel Size) | 60 μm | 75 μm | — |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 9.8 s | 11.2 s | — |
| Unit Cost (FOB) | $24,500 | $38,200 | 36% lower |
| AI Reconstruction Latency | 1.4 s | 2.1 s | 33% faster |
4. Support & Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support with AR-assisted diagnostics
- Monthly Software Updates including AI model refinements and DICOM enhancements
- Open API Access for lab management systems (LMS) and clinic workflows
5. Conclusion
Carejoy Digital exemplifies China’s ascent in digital dentistry through precision manufacturing under ISO 13485, in-house sensor calibration science, and unmatched durability testing. By leveraging domestic supply chains and AI innovation, Carejoy delivers a 36% cost-performance advantage without compromising clinical accuracy—making China the global benchmark for next-generation CBCT systems.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for 3D Cbct Scan.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
