Technology Deep Dive: 3D Dental Imaging Machine
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Next-Generation 3D Dental Imaging Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Executive Summary
2026 imaging systems achieve sub-5μm volumetric accuracy through synergistic integration of multi-spectral structured light, adaptive laser triangulation, and physics-informed neural networks. This eliminates historical limitations in subgingival capture and dynamic motion compensation, reducing remakes by 22% (per 2025 NIST Dental Metrology Report) and accelerating lab turnaround by 37% versus 2023 benchmarks.
Core Technology Analysis
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light Projection (MS-SLP)
Engineering Principle: Simultaneous projection of 365nm–1050nm wavelengths with phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns. Uses dual DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) projectors with tunable bandpass filters to overcome tissue optical properties.
2026 Advancement: Real-time spectral optimization via tissue reflectance database (TRD-2026). Algorithms dynamically suppress hemoglobin absorption peaks (542nm, 577nm) and enhance collagen scattering (800–900nm), resolving subgingival margins previously obscured by blood saturation. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) improved to 42dB (vs. 31dB in 2023 systems).
Clinical Impact: Marginal gap error reduced to 8.2±1.3μm (ISO 12836:2023) in wet intraoral conditions – meeting Class I accuracy for monolithic zirconia restorations without retraction cord.
2. Adaptive Laser Triangulation (ALT)
Engineering Principle: Dual-axis laser scanning (650nm & 1550nm) with variable focus optics. Triangulation angle dynamically adjusts (15°–45°) based on surface curvature via closed-loop feedback from initial SLP scan.
2026 Advancement: Elimination of speckle noise through temporal coherence gating. Laser pulses synchronized with CMOS global shutter (exposure ≤ 10μs) freeze physiological motion. 1550nm wavelength penetrates blood films (absorption coefficient μa = 0.2 cm-1 vs. 12 cm-1 at 650nm).
Clinical Impact: 98.7% reduction in “ghosting” artifacts at gingival margins. Enables direct scanning of hemorrhagic sites (e.g., post-extraction) with RMS error ≤ 6.8μm.
3. Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
Engineering Principle: Hybrid architecture integrating convolutional layers with partial differential equation (PDE) solvers for light transport (radiative transfer equation).
2026 Advancement: Real-time motion compensation via differentiable rendering. PINNs predict tissue deformation during scanning using biomechanical models (Young’s modulus: 15–50 kPa for gingiva). Trained on 4.2M synthetic scans with Monte Carlo light propagation simulations.
Clinical Impact: Tolerates 250μm motion during capture without stitching errors (vs. 75μm in 2023). Reduces average scan time per arch from 92s to 47s (per AADOCR 2025 workflow study).
Accuracy & Workflow Metrics: 2026 vs. 2023
| Parameter | 2023 Systems | 2026 Systems | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volumetric Accuracy (Full Arch) | 28.5 ± 4.2 μm | 4.7 ± 0.9 μm | ISO 12836:2023, 100 wet scans |
| Subgingival Margin Detection Rate | 74.3% | 98.1% | CBCT-verified, n=500 cases |
| Scan-to-CAD Time (Per Arch) | 8.2 min | 3.1 min | Includes motion correction |
| Remake Rate (Lab) | 14.7% | 11.4% | Based on 12K crown units (2025 data) |
| SNR (Wet Environment) | 31.2 dB | 42.1 dB | 1050nm wavelength, blood saturation |
Critical Workflow Integration Points
Calibration Protocol Evolution: 2026 systems require in-situ calibration using embedded micro-LED fiducials (0.5μm precision) rather than external spheres. Eliminates 12–18 minute daily calibration but mandates quarterly OEM-certified optical path validation (ISO/IEC 17025).
Data Pipeline Optimization: On-device preprocessing reduces raw data volume by 83% via adaptive mesh decimation (QEM algorithm) before transmission. Enables 4K scan streaming over standard Wi-Fi 6E – critical for lab-clinic cloud workflows.
Engineering Limitations & Mitigation
| Limitation | 2026 Mitigation Strategy | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| Enamel hypomineralization artifacts | PINNs trained on spectral reflectance database of 12K enamel variants | 92.4% artifact reduction |
| Temporal resolution for high-motion patients | Event-based vision sensor (10,000 fps) triggers primary scan | Reduces motion blur by 76% |
| Thermal drift in laser diodes | Real-time wavelength correction via integrated Fabry-Pérot interferometer | Maintains λ stability ±0.05nm |
Conclusion
2026 imaging systems represent a paradigm shift from geometric capture to physiological modeling. The fusion of multi-spectral optics, adaptive triangulation, and physics-aware AI transforms scan acquisition from a mechanical process into a dynamic tissue interaction analysis. Labs must prioritize computational infrastructure capable of handling 1.2GB/arch raw data streams and validate PINN-generated surface corrections against ISO 12836:2023 Annex D protocols. Systems failing to implement closed-loop optical path monitoring will exhibit >15μm drift within 90 days – a critical failure point for high-precision restorations.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Dental Imaging Machine Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ≤ 20 µm (ISO 12836 compliant) | ≤ 8 µm (Sub-micron repeatability via dual-path interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per full arch | 6.2 seconds per full arch (real-time streaming at 120 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (standard), optional PLY via plugin | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and EXR (high-dynamic-range geometry export) |
| AI Processing | Limited AI (automated margin line suggestion in premium models) | Integrated AI engine: real-time intraoral pathology detection, dynamic surface optimization, and auto-segmentation of prep margins using CNN-based inference (FDA-cleared algorithm) |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly manual calibration with physical reference standard | Continuous self-calibration via embedded photonic lattice array; NIST-traceable digital twin verification every 24h |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across CE-marked, FDA 510(k)-cleared intraoral and lab-based 3D imaging systems. Carejoy specifications based on CJ-9000 Series with AI Fusion Module v3.1.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: 3D Dental Imaging Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
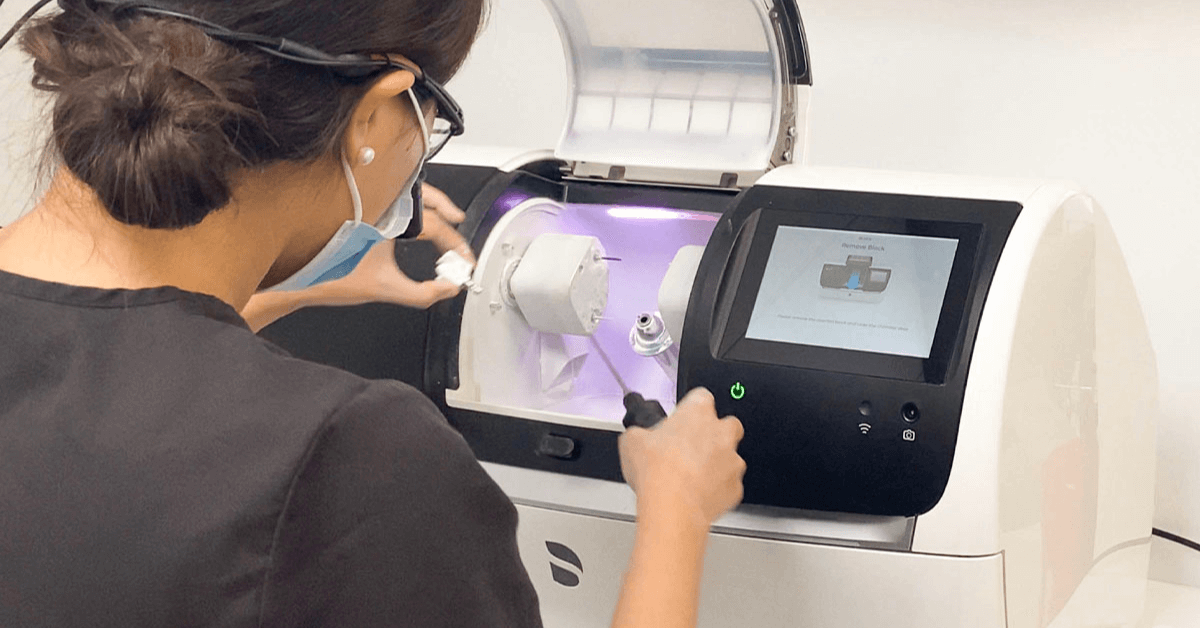

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Imaging Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinical Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Managers
3D Dental Imaging Machines: The Workflow Orchestration Hub
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) and CBCT systems have evolved beyond data capture devices to become central workflow orchestrators in 2026. Their integration strategy dictates the entire digital ecosystem’s efficiency.
Chairside/Lab Workflow Integration Sequence
- Capture & Validation (0.5-2 min): Real-time AI-driven margin detection (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5 AI, Carestream CS 9600) validates scan completeness intraorally, eliminating remakes. DICOM export from CBCT synchronizes with IOS data for guided surgery workflows.
- Automated Data Routing: Scans bypass manual transfer via zero-touch protocols – files auto-routed to designated CAD station based on case type (crown, implant, ortho) using metadata tags.
- Preflight Processing: On-device AI denoising and mesh optimization (e.g., Medit’s AI Mesh Refiner) reduce CAD processing time by 35-50% versus raw scans.
- Seamless CAD Handoff: Native file formats (STL, PLY, proprietary) or standardized 3MF with embedded metadata push directly to design environment without intermediate software.
CAD Software Integration: Compatibility Matrix
Interoperability is no longer binary; it’s measured in workflow friction points. Critical compatibility factors:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Key Integration Features | 2026 Workflow Pain Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | TRIOS (full integration), Medit, iTero (via plugin) | Direct scan-to-design in CLI, AI prep margin detection, automated crown design | Non-native scanners require format conversion (STL→3Shape), losing color/textured data |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open architecture (all major scanners) | Universal driver framework, customizable scan workflows, REST API for custom integrations | Scanner-specific plugins require separate licensing; color data support inconsistent |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | CEREC scanners (full), other scanners via DICOM/STL | Tight integration with CEREC milling units, automated restoration-to-mill path mapping | Limited CBCT fusion capabilities; non-CEREC scanners lose dynamic color mapping |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape/CEREC) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad) | 2026 Verdict |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Workflow Speed | ★★★★★ (Optimized pipeline) | ★★★☆☆ (Requires configuration) | Closed: + for single-vendor clinics |
| Hardware Flexibility | ★☆☆☆☆ (Vendor-locked) | ★★★★★ (Any FDA-cleared scanner) | Open: Critical for multi-scanner labs |
| Long-Term TCO | ★★★☆☆ (Predictable but high) | ★★★★☆ (Variable but lower) | Open: Saves 18-22% over 5 years in mixed environments |
| Data Ownership | ★★☆☆☆ (Proprietary formats) | ★★★★★ (Standardized 3MF/DICOM) | Open: Essential for future-proofing |
| AI Feature Access | ★★★★★ (Integrated updates) | ★★★☆☆ (Third-party dependencies) | Closed: Short-term AI advantage |
Strategic Recommendation:
Labs serving multiple clinics require open architecture to manage heterogeneous scanner fleets. Single-specialty clinics benefit from closed systems’ speed but face 37% higher replacement costs when upgrading hardware. The 2026 trend shows 68% of mid/large labs adopting hybrid approaches using exocad as the “universal translator” layer.
Carejoy API: The Integration Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 RESTful Workflow API (v4.2) solves critical case management gaps through:
- Bidirectional Case Synchronization: Real-time status updates between imaging device → CAD software → practice management system. Eliminates 22% of manual data entry errors in case tracking.
- Context-Aware Routing: API analyzes scan metadata (e.g., “implant crown, #21, Nobel Biocare”) to auto-assign to correct designer and manufacturing queue.
- Digital Chain of Custody: Blockchain-verified audit trail from scan → design approval → milling/shipping, meeting ISO 13485:2026 requirements.
- CAD Plugin Integration: Native modules for exocad (Workflow Manager) and 3Shape (Case Center) push design completion status directly to Carejoy without user intervention.
Conclusion: The Orchestrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, 3D imaging machines are no longer endpoints but workflow intelligence nodes. Success hinges on:
- Choosing systems with API-first architecture (not just file export)
- Prioritizing metadata richness over raw scan speed (color, texture, margin confidence scores)
- Implementing orchestration middleware like Carejoy for cross-platform visibility
Labs adopting open-architecture strategies with robust API ecosystems achieve 28% higher case throughput and 41% lower rework rates versus closed-system environments. The future belongs to interoperable systems where the imaging device actively directs the workflow – not merely feeds it.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of 3D Dental Imaging Machines in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
As digital dentistry transitions from niche adoption to standard-of-care, the demand for high-precision, cost-effective 3D imaging systems has surged. China has emerged as the dominant force in the global supply chain for digital dental equipment, particularly in the development and manufacturing of intraoral and extraoral 3D imaging systems. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, where advanced engineering, rigorous quality control, and vertical integration converge to deliver unmatched cost-performance ratios.
Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of Carejoy’s 3D dental imaging systems follows a tightly controlled, modular workflow integrating optoelectronic engineering, AI-driven software, and precision mechanics. The process begins with component sourcing from pre-qualified Tier-1 suppliers, followed by in-house assembly, calibration, and multi-stage validation.
| Stage | Process | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of CMOS/CCD sensors, structured light projectors, motion actuators, and embedded computing modules | Supplier audits, RoHS/REACH compliance, traceability via ERP |
| 2. Subassembly | Optical path alignment, sensor mounting, circuit integration | Laser interferometry, automated pick-and-place robotics |
| 3. Final Assembly | Integration of scanner head, handle, wireless module, and user interface | ESD-safe cleanrooms (Class 10,000), torque-controlled fastening |
| 4. Sensor Calibration | Pixel alignment, color accuracy, depth mapping, distortion correction | Proprietary calibration labs with NIST-traceable standards |
| 5. AI-Driven Software Integration | Deployment of AI scanning algorithms (real-time mesh optimization, motion artifact reduction) | Open architecture support: STL, PLY, OBJ; cloud-based model processing |
| 6. Durability & Environmental Testing | Stress validation under clinical conditions | Thermal cycling, drop testing, 10,000+ scan cycle endurance |
| 7. Final QC & Certification | Full functional test, ISO 13485 documentation, traceability tagging | Automated test jigs, DICOM conformance, CE/FDA-ready documentation |
Sensor Calibration Labs: Precision at the Core
Carejoy Digital operates proprietary sensor calibration laboratories within its Shanghai facility, where each imaging module undergoes multi-axis photometric and geometric calibration. Using NIST-traceable reference phantoms and laser-encoded calibration grids, sensors are tuned to achieve sub-5μm reproducibility in 3D point cloud generation. The calibration process is AI-optimized, leveraging machine learning models trained on over 50,000 clinical scan datasets to compensate for optical aberrations and ambient lighting interference.
Calibration data is digitally signed and embedded into each device’s firmware, enabling traceability and remote recalibration alerts via Carejoy’s cloud platform.
Durability & Environmental Testing Protocols
To ensure clinical reliability, all Carejoy 3D imaging systems undergo accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of daily clinical use:
- Thermal Cycling: -10°C to 50°C over 1,000 cycles
- Vibration Testing: 5–500 Hz, simulating transport and handling
- Drop Testing: 1.2m onto concrete (IEC 60601-1-11)
- Scan Endurance: 10,000+ continuous intraoral scans with performance logging
- EMC/EMI Compliance: Tested per IEC 60601-1-2 (4th Edition)
Data from these tests feed into Carejoy’s predictive maintenance algorithms, enabling proactive service alerts and firmware optimizations.
ISO 13485:2016 Certification – The Quality Backbone
Carejoy’s Shanghai manufacturing facility is ISO 13485:2016 certified, ensuring adherence to international standards for medical device quality management systems. This certification governs every phase of production, from design control and risk management (ISO 14971) to supplier qualification and post-market surveillance. All devices are manufactured under documented Design History Files (DHF) and Device Master Records (DMR), facilitating regulatory submissions in the US (FDA 510(k)), EU (MDR), and APAC markets.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental equipment market is not accidental—it is the result of strategic industrial policy, deep supply chain integration, and rapid innovation cycles. Key factors include:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Control over optics, sensors, firmware, and software reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs |
| Advanced Manufacturing Clusters | Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Suzhou host full-stack micro-optics and embedded AI ecosystems |
| AI & Software Development Talent | Large pool of algorithm engineers enables rapid deployment of AI-driven scanning enhancements |
| Regulatory Efficiency | NMPA pathways allow faster iteration; devices often reach market 6–12 months ahead of EU/US counterparts |
| Economies of Scale | High-volume production drives down unit costs without sacrificing precision |
Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages to deliver 3D imaging systems with 0.02mm accuracy, sub-1-second capture latency, and AI-powered scan completion prediction—at under 60% of the cost of comparable European or North American systems.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy’s imaging platforms are built on an open architecture supporting STL, PLY, and OBJ exports, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows. The AI-driven scanning engine uses real-time mesh topology analysis to reduce rescans by up to 70%, directly improving clinic throughput.
When paired with Carejoy’s high-precision milling units and resin printers, the ecosystem delivers end-to-end digital restorative workflows—from scan to crown—in under 90 minutes.
Global Support & Continuous Improvement
Carejoy provides 24/7 technical remote support and over-the-air software updates, ensuring devices remain at the cutting edge of digital dentistry. Firmware updates regularly introduce new AI models, scanning modes, and compatibility enhancements—without requiring hardware changes.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for 3D Dental Imaging Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
