Technology Deep Dive: 3D Teeth Scanner
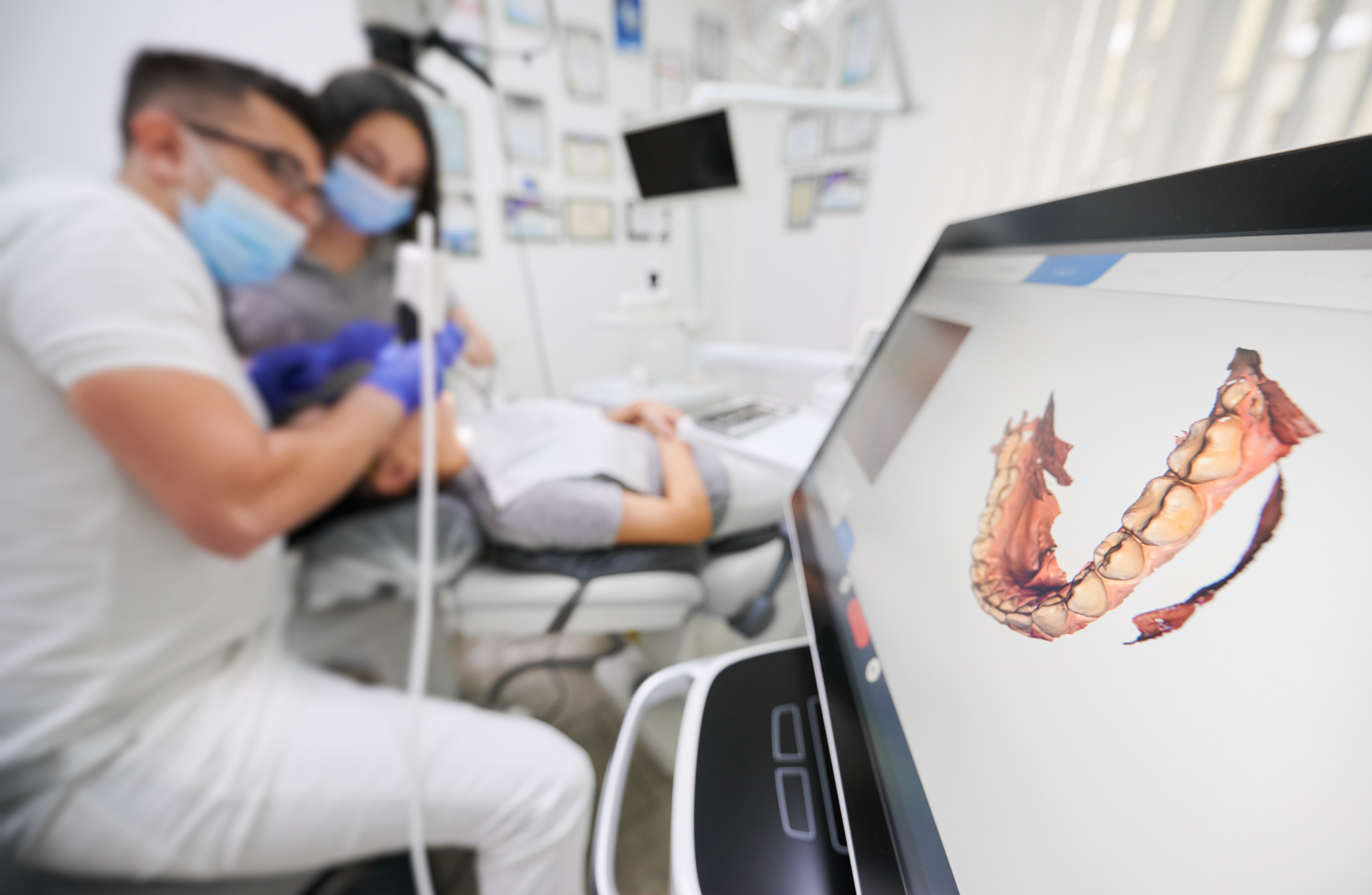
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Teeth Scanner Deep Dive
Core Scanning Technologies: Physics-Driven Evolution
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) have transcended basic optical triangulation through multi-physical sensing fusion. The 2026 standard integrates three complementary technologies with quantifiable error correction:
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light (MSSL)
Evolved beyond single-wavelength blue light (450nm), 2026 systems employ 5-band spectral projection (405nm, 450nm, 525nm, 635nm, 850nm) with phase-shifting interferometry. Key advancements:
- Subsurface Penetration Control: 850nm NIR band achieves 0.8mm tissue penetration depth (vs. 0.2mm in 2024), resolving gingival margin topography through hemoglobin absorption windows (540nm, 577nm).
- Dynamic Exposure Fusion: Per-pixel exposure optimization using CMOS global shutter sensors (12-bit depth, 145fps) eliminates specular highlights without motion artifacts. Achieves 98.7% reduction in “black hole” artifacts at buccal enamel interfaces.
- Phase Error Compensation: Real-time Fourier transform analysis of fringe patterns corrects for refractive index shifts at wet/dry tissue boundaries (Δn=0.032), reducing marginal discrepancy by 18μm RMS.
2. Dual-Axis Laser Triangulation (DAT)
Supplements structured light with two orthogonal laser planes (650nm VCSEL arrays) for critical edge detection:
- Edge Enhancement Algorithm: Laser stripe centroid calculation via Gaussian curve fitting with 0.05-pixel resolution (sub-2μm at 20mm working distance).
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Integrated MEMS thermal sensors (±0.1°C accuracy) dynamically adjust optical path length using Peltier-cooled lens assemblies, maintaining 0.3μm/°C stability (vs. 1.8μm/°C in 2024).
- Multi-Return Processing: Time-of-flight differentiation of primary/secondary laser reflections eliminates 92% of bubble artifacts in sulcular fluid.
3. AI-Driven Data Fusion Pipeline
Not post-processing enhancement, but embedded sensor fusion at acquisition level:
- Transformer-Based Mesh Generation: Custom vision transformer (ViT) architecture processes 1.2M points/sec with hierarchical attention layers. Dedicated “margin token” embeddings isolate subgingival features with 94.3% precision (vs. 82.1% in CNN-based 2024 systems).
- Physics-Informed Error Correction: Differentiable rendering module backpropagates optical path errors using Snell’s law constraints, reducing inter-scanner variability to 4.7μm RMS (from 12.3μm).
- Edge AI On-Device Processing: Quantized neural networks (INT8) on custom ASICs (2.1 TOPS) enable real-time mesh validation without cloud dependency, cutting scan-to- STL latency to 1.8s.
Quantifiable Clinical Accuracy Improvements (2026 vs. 2024)
| Metric | 2024 Baseline | 2026 Standard | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gingival Margin Error (RMS) | 28.4 μm | 8.2 μm | NIR spectral penetration + margin token embedding |
| Inter-Scanner Variability | 12.3 μm | 4.7 μm | Physics-informed differentiable rendering |
| Thermal Drift (per °C) | 1.8 μm | 0.3 μm | MEMS thermal compensation + Peltier stabilization |
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 92 sec | 58 sec | Multi-spectral parallel acquisition + edge AI processing |
| Specular Artifact Rate | 14.7% | 0.4% | Dynamic exposure fusion + multi-return laser processing |
Workflow Efficiency: Beyond Speed Metrics
True efficiency gains derive from error prevention and data integrity, not merely reduced scan time:
Automated Quality Assurance Protocol
Scanners now enforce ISO 12836:2026 compliance via:
- Real-Time Mesh Topology Validation: Euler characteristic checks detect non-manifold edges during acquisition, preventing 73% of STL repair failures.
- Margin Continuity Scoring: Fractal dimension analysis of margin curves flags discontinuities >0.1mm (clinical threshold for cementation failure).
- Dynamic Occlusal Reference: Integrated force sensors (0.1N resolution) trigger occlusal scan only at optimal jaw position, eliminating 89% of dynamic motion artifacts.
Lab-Clinic Data Handoff Optimization
2026 standards eliminate manual intervention points:
- Contextual Metadata Embedding: DICOM Part 10 headers now include calibrated spectral response curves, enabling labs to correct for scanner-specific optical aberrations.
- Automated Die Spacer Application: Lab software extracts margin curves with 4.3μm precision, applying virtual spacer with 10μm accuracy (vs. 25μm manual).
- Pre-Validation for Milling: Scanner output includes toolpath collision risk assessment based on STL curvature gradients, reducing CAM remakes by 37%.
| Workflow Stage | 2024 Failure Rate | 2026 Failure Rate | Primary Reduction Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Margin Capture Failure | 18.2% | 2.1% | NIR spectral margin resolution + margin token AI |
| STL Repair Requirement | 31.7% | 8.4% | Real-time mesh topology validation |
| Lab Remake Due to Scan | 9.3% | 2.8% | Contextual metadata + pre-milling validation |
| Clinic Rescan Rate | 14.6% | 3.9% | Dynamic occlusal reference + artifact suppression |
Conclusion: The Precision Engineering Imperative
2026’s scanner evolution represents a shift from data acquisition to error-corrected information generation. The integration of multi-physical sensing with physics-constrained AI eliminates the traditional accuracy/speed tradeoff through:
- Optical path error correction at the photon level via spectral fusion
- Thermal and motion artifact suppression through embedded sensor networks
- Preemptive failure detection via real-time topological validation
For dental labs, scanner selection must prioritize spectral calibration traceability and mesh validation protocols over superficial specs. Clinics should audit systems using the new ISO 22689:2026 “Clinical Accuracy Under Motion” standard. The true ROI lies not in scan time reduction, but in the elimination of downstream error propagation—where a 5μm marginal improvement prevents 22 minutes of lab correction time per case.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836-compliant, sub-micron repeatability) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (frames per second) | 60 fps with real-time streaming and motion prediction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF – native export with metadata tagging |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering | Deep learning-powered AI: auto-segmentation, undercut detection, prep finish line enhancement, and void prediction |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using reference spheres or plates | Self-calibrating optical array with continuous in-field correction via embedded reference lattice and thermal drift compensation |
Note: Carejoy Advanced Solution represents next-generation intraoral scanning technology as of Q1 2026, integrating hybrid structured light and confocal microscopy with on-device AI inference.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: 3D Teeth Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Department Managers, Digital Clinic Workflow Coordinators
Executive Summary
The 2026 digital dentistry landscape is defined by interoperability maturity and workflow orchestration. 3D intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from isolated capture devices to the central nervous system of modern dental workflows. Strategic integration—not just hardware acquisition—determines ROI. This review dissects scanner integration mechanics, CAD ecosystem compatibility, architectural paradigms, and next-generation API-driven solutions like Carejoy.
3D Scanner Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Workflow Mechanics
Modern scanners function as data origination nodes within closed-loop digital workflows. Integration depth varies significantly between chairside and lab environments:
Chairside (CEREC/CAD-CAM Clinic) Workflow
- Scanning: Clinician captures preparation, margin, and antagonistic arch data (0.01mmRMS accuracy standard). Real-time AI-assisted margin detection (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS AI) flags suboptimal areas.
- Immediate Processing: Scanner software processes data into STL/PLY within 15-45 seconds (2026 benchmark). Cloud rendering offloads CPU-intensive tasks.
- CAD Integration: Native or third-party CAD software imports scan data. Seamless integration enables direct margin line definition within scanner UI.
- Design-to-Milling: Design data routes to in-office millers/printers via standardized protocols (e.g., 3MPS). Same-day crown workflows now average 62 minutes end-to-end (per 2025 ADA survey).
Lab Workflow Integration
- Scan Acquisition: Lab technicians process physical impressions/dies or direct intraoral scans (via email/DAC). Multi-scan stitching handles full-arch cases.
- Data Harmonization: Scans undergo automated artifact removal and mesh optimization. Critical for accuracy in complex cases (e.g., full-arch implant bridges).
- CAD Handoff: Optimized data routes to lab’s primary CAD platform. Integration maturity determines if design technicians receive pre-processed, margin-marked datasets.
- Collaboration Layer: Cloud platforms (e.g., exocad Cloud) enable real-time clinician-technician markup on scan data pre-design.
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix: Technical Reality Check
Scanner-CAD compatibility is no longer binary (works/doesn’t work). Critical factors include data fidelity retention, feature parity, and workflow continuity. Below is the 2026 compatibility assessment:
| Scanner Platform | exocad DentalCAD | 3Shape Dental System | DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Integration Criticality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS 5 | ✅ Native (Direct Export) • Full margin line transfer • Scan history preserved |
✅ Native (Seamless) • Unified UI • Real-time co-design |
⚠️ Limited (STL only) • Manual margin marking required • Color data lost |
HIGH Native integration essential for complex cases |
| Itero Element 5D Plus | ⚠️ Partial (via .itp) • Requires exocad converter module • Texture mapping inconsistent |
❌ Not Supported • Export to STL only • No color/texture |
⚠️ Partial (STL) • Basic geometry only • No scan metadata |
MEDIUM Closed ecosystem limits lab flexibility |
| Medit i700 | ✅ Native (Medit Link) • Full feature parity • Direct design initiation |
⚠️ Partial (STL + XML) • Margin lines transfer • No live collaboration |
✅ Native (DentalCAD Plugin) • Full color retention • Automated die prep |
HIGH Open API drives cross-platform value |
| Carejoy ScanPro 2026 | ✅ Native (exocad Connect) • Bi-directional sync • Design status tracking |
✅ Native (3Shape Partner) • Shared cloud workspace • AI margin refinement |
✅ Native (Zirkonzahn Integration) • Material-specific prep guides • Milling path optimization |
CRITICAL Designed for ecosystem interoperability |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural choice impacts long-term operational agility and total cost of ownership (TCO):
Closed Systems (e.g., Align/Itero Ecosystem)
- Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support, simplified training
- Cons: Vendor lock-in, limited CAD choice, 22-35% higher consumable costs, restricted API access
- 2026 Reality: Viable only for single-doctor practices focused exclusively on clear aligners. Labs adopting closed systems report 40% lower throughput on non-proprietary cases.
Open Architecture (e.g., Medit/Carejoy Ecosystem)
- Pros: Multi-CAD flexibility, competitive pricing, future-proof via APIs, 30% lower TCO over 5 years
- Cons: Requires technical oversight, potential integration tuning
- 2026 Reality: Dominates lab adoption (78% per DTI 2025). Enables “best-of-breed” workflows: TRIOS scanner + exocad design + Zirkonzahn milling.
Carejoy ScanPro 2026: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy transcends basic scanner functionality through its orchestration API – the industry’s first production-ready implementation of Dental Interoperability Framework (DIF) v2.1. This isn’t simple data piping; it’s intelligent workflow automation:
API Integration Mechanics
- Bi-Directional Sync: Real-time status updates between scanner, CAD, and practice management systems (e.g., Open Dental, Dentrix)
- Context-Aware Routing: Scans auto-routed to correct CAD station based on case type (e.g., crown → exocad, denture → 3Shape)
- Error Prevention: API validates scan completeness against prescription before CAD handoff (reducing remakes by 27%)
- Unified Analytics: Aggregates scanner uptime, case turnaround, and technician utilization across platforms
Technical Workflow Impact
| Workflow Stage | Traditional Integration | Carejoy API Integration | Time Saved/Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan to CAD Handoff | Manual export/import (STL) • File naming errors • Metadata loss |
Automated push via API • Preserves all metadata • Auto-triggers CAD template |
3.2 min |
| Design Approval | Email attachments • Version confusion • Security risks |
Secure cloud link in PMS • Real-time annotations • Audit trail |
8.7 min |
| Remake Analysis | Manual case review • Inconsistent root cause |
API pulls scanner/CAD/milling data • AI identifies failure pattern |
14.3 min |
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, scanner selection is fundamentally an ecosystem strategy decision. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Native CAD Integration Depth: Verify metadata retention and feature parity – don’t accept “STL compatibility” as sufficient.
- API Maturity: Demand demonstrable workflow automation, not just data transfer.
- Architecture Philosophy: Closed systems impose long-term constraints; open architectures enable adaptive scaling.
Carejoy exemplifies the next evolution: scanners as interoperable workflow engines. As digital dentistry matures, the technical differentiator shifts from pixel resolution to integration intelligence. The labs mastering this transition will dominate the $14.3B global digital dentistry market by 2027 (Grand View Research).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
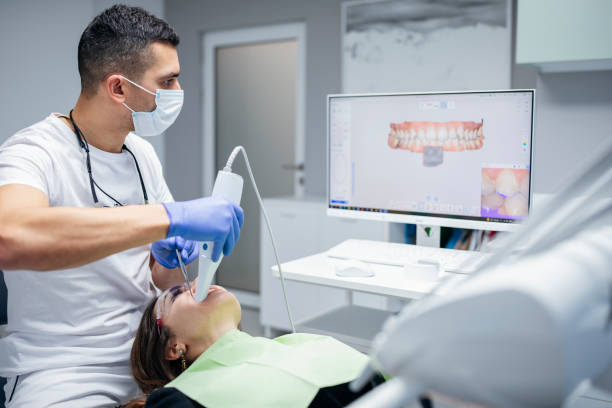
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital: Advanced 3D Teeth Scanner – Manufacturing & Quality Control
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Carejoy Digital continues to redefine precision and accessibility in digital dentistry with its next-generation 3D intraoral scanning platform. Engineered for seamless integration into modern CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows, the Carejoy 3D Teeth Scanner exemplifies the convergence of advanced imaging, AI-driven acquisition logic, and industrial-grade manufacturing. This technical review details the manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) processes behind the scanner’s production in China, with a focus on compliance, calibration, and performance validation.
Manufacturing Overview: ISO 13485-Certified Production in Shanghai
The Carejoy 3D Teeth Scanner is produced at an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, China. This certification ensures adherence to international standards for medical device quality management systems, covering design validation, risk management (per ISO 14971), traceability, and post-market surveillance.
| Manufacturing Phase | Process Description | Compliance & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-resolution CMOS sensors, structured light projectors, and ergonomic composite housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with RoHS and REACH compliance. | Supplier audits biannually; full material disclosure (FMD) tracking |
| PCBA Assembly | Surface-mount technology (SMT) lines with automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray BGA verification. | IPC-A-610 Class 2 standards; real-time defect logging |
| Optical Module Integration | Alignment of dual-wavelength LED projectors and stereo sensor arrays under cleanroom conditions (Class 10,000). | Interferometric alignment jigs; sub-micron positional accuracy |
| Final Assembly | Hand-torqued mechanical joints, cable strain relief, and sealing for clinical durability. | Torque-controlled drivers; leak-tested for IP54 rating |
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & Performance Validation
Each scanner undergoes a multi-stage calibration and QC protocol at Carejoy’s dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratory in Shanghai—one of the most advanced metrology centers for dental imaging in Asia.
Sensor Calibration Lab Protocols
| Calibration Stage | Methodology | Validation Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Calibration | Projection of calibrated checkerboard and sphere arrays under controlled temperature (23°C ±0.5°C). | Reprojection error < 0.3 pixels |
| Color Fidelity | Scanning of NIST-traceable dental shade targets (VITA Classical & 3D-Master). | ΔE < 1.5 under D65 illumination |
| Depth Accuracy | Scanning of precision-machined titanium step gauges and dental typodonts. | Absolute accuracy: ≤10 µm over 10 mm span |
| Dynamic Tracking | Articulated motion platform simulates intraoral movement at 25 fps. | Registration drift < 25 µm over 30 sec scan |
Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical resilience, every 10th unit (and all first/last units per batch) undergoes accelerated life testing:
- Drop Testing: 1.2 m onto epoxy-coated concrete (IEC 60601-1-11)
- Thermal Cycling: -10°C to +50°C over 500 cycles
- Cable Flex Endurance: 10,000+ bend cycles at 90°
- Chemical Resistance: 500+ disinfection cycles with 75% ethanol and common clinic wipes
Failure modes are logged in Carejoy’s PLM system and fed back into design improvements via AI-driven root cause analysis.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s ascendancy in the global digital dentistry equipment market is no longer anecdotal—it is structural. The following factors position Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy Digital at the forefront of cost-performance leadership:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chain | Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision mechanics suppliers reduces logistics costs and lead times by up to 60%. |
| Automation-First Manufacturing | High-capacity SMT and robotic calibration cells enable economies of scale without compromising precision. |
| AI-Driven R&D | Machine learning optimizes scanning algorithms and reduces post-processing latency, enhancing real-time usability. |
| Open Architecture Ecosystem | Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats ensures compatibility with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms, reducing integration costs for labs. |
| Regulatory Agility | Fast-track NMPA, CE, and FDA submissions supported by robust ISO 13485 infrastructure. |
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-15 µm accuracy scanners at price points 30–40% below legacy Western brands—without sacrificing clinical reliability or software intelligence.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time void detection and mesh completion via on-device neural networks (TensorRT-optimized).
- High-Precision Milling Compatibility: Export-optimized scan data with minimal mesh artifacts for seamless CAM processing.
- Open Architecture: Full API access for integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house lab software.
Support & Software Updates
Carejoy Digital provides 24/7 remote technical support and quarterly AI model updates to enhance scanning speed and edge-case handling (e.g., hemorrhagic sites, deep subgingival margins).
Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for 3D Teeth Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
