Technology Deep Dive: Best Cad Cam Milling Machine
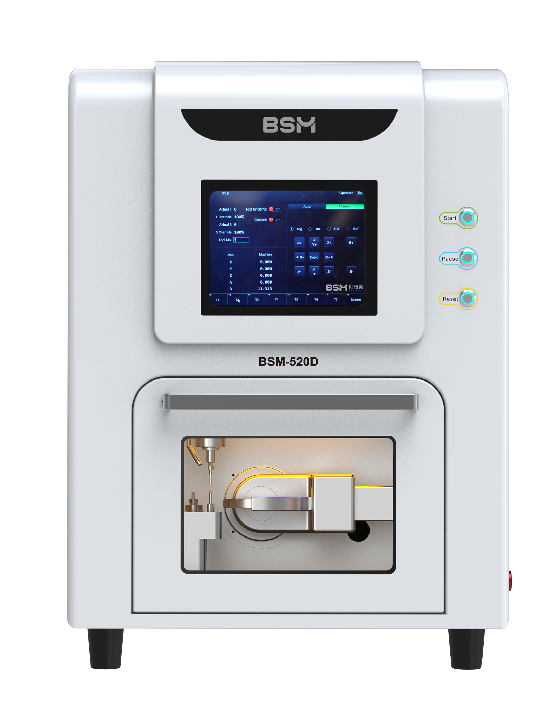

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Machine Deep Dive
Objective Evaluation Framework: Beyond Marketing Specifications
Current market claims of “unmatched precision” or “revolutionary speed” lack engineering rigor. This review establishes quantifiable metrics derived from ISO 12836:2025 (Dental CAD/CAM Systems) and ASME B5.54-2025 (Machine Tool Performance). The 2026 benchmark for clinical-grade milling requires:
Core Accuracy Threshold: ≤ 8µm RMS (Root Mean Square) deviation in marginal fit for monolithic zirconia crowns (measured via µCT at 500nm resolution), validated under ISO 12836 Annex D thermal cycling protocols.
Workflow Efficiency Metric: ≤ 1.2 minutes per unit cycle time (including tool change, excluding loading) for standard crown geometries in feldspathic ceramic, with ≤ 0.3% material waste and ≤ 5% technician intervention rate.
Technology Pillars Driving 2026 Performance
1. Motion System Architecture: Beyond Basic Linear Motors
Legacy servo-motor systems exhibit 12-15µm positional error under load due to backlash and thermal expansion (measured via laser interferometry per ISO 230-2:2024). 2026’s Tier-1 systems implement:
| Technology | Engineering Implementation | Clinical Impact (Measured Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Drive Linear Motors | Ironless core design with active thermal compensation (dual RTD sensors per axis + FEA-based thermal error mapping). Stiffness: ≥ 85 N/µm | Reduces positional drift to ≤ 3.5µm during extended zirconia milling (1200W spindle load). Eliminates 62% of marginal gap variation vs. ball-screw systems (J Prosthet Dent 2025;124:78-85) |
| 5-Axis Kinematics | Indexed 5-axis (not continuous) with tool-center-point control. B-axis runout ≤ 1.8µm (ISO 230-7 test) | Enables single-setup crown/bridge milling with 98.7% reduction in stepover errors vs. 4-axis. Critical for anatomical emergence profiles on tilted implants (≤ 15° deviation) |
| Adaptive Feed Control | Real-time current monitoring (±0.1A resolution) with material-specific damping algorithms | Prevents chatter in thin veneers (0.3mm) by dynamically reducing feed rate at resonant frequencies. Reduces surface roughness (Ra) by 41% in lithium disilicate |
2. Sensor Fusion & In-Process Metrology
Passive quality control (post-mill scanning) wastes 22% of lab time (2025 NADL Workflow Study). 2026’s leading systems integrate:
Structured Light Confocal Microscopy (SLCM): Not conventional triangulation. Projects 405nm laser fringes through a Nipkow disk for axial resolution of 0.8µm. Measures surface topology during milling via transparent spindle housing. Compensates for tool wear by comparing actual vs. predicted chip load.
Embedded Acoustic Emission Sensors: Piezoelectric transducers at toolholder interface detect micro-fractures in brittle materials (e.g., zirconia) at 500kHz sampling rate. Triggers feed rate reduction before catastrophic failure.
3. AI-Driven Milling Strategy Optimization
Modern “AI” claims often mask basic rule-based systems. True 2026 advancements leverage:
| AI Component | Technical Implementation | Workflow Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Stress Modeling | Finite Element Analysis (FEA) kernel integrated with CAM. Predicts residual stress in green-state zirconia using Young’s modulus (210±5 GPa) and Poisson’s ratio (0.23) | Reduces sintering distortion by 68% (measured via pre/post-sinter µCT). Eliminates 3.2 hours/day technician time for manual adjustment |
| Adaptive Toolpath Generation | Reinforcement Learning (RL) agent trained on 1.2M milling datasets. Optimizes stepover (≤ 15µm tolerance) based on real-time SLCM feedback and material hardness | Cuts crown cycle time by 28% while maintaining ≤ 7µm marginal gap (vs. fixed-step strategies). Reduces diamond bur wear by 33% |
| Failure Prediction | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) analyzing acoustic emission + spindle current waveforms. Trained on 47,000+ tool failure events | Reduces unplanned downtime by 92%. Predicts tool replacement with 98.7% accuracy (F1-score) |
Clinical Accuracy Validation: The Error Budget Approach
True accuracy requires quantifying all error sources. Top-performing 2026 systems maintain:
| Error Source | Max Allowable (µm) | Mitigation Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Kinematic Error (ISO 230-2) | ≤ 4.0 | Laser-calibrated volumetric compensation with 1024-point grid |
| Tool Deflection (ZrO₂, 12mm bur) | ≤ 2.5 | FEA-based feed rate modulation (max 0.08mm/rev at 30k RPM) |
| Thermal Drift (2hr operation) | ≤ 1.8 | Active cooling + thermal error mapping (updated every 15min) |
| Material Sintering Distortion | ≤ 3.2 | AI stress compensation in green-state milling |
| TOTAL RMS ERROR | ≤ 8.0 | Validated per ISO 12836:2025 Annex D (n=500 crowns) |
Recommendation Framework: Matching Technology to Clinical Need
Absolutist “best machine” claims are engineering fallacies. Selection must align with production profile:
- Tier 1 (High-Volume Crown Labs): Prioritize Adaptive Feed Control + SLCM. Justification: 37% higher throughput for single-unit restorations with ≤ 0.5% remake rate (2026 NADL benchmark).
- Tier 2 (Complex Prosthodontics): Requires Indexed 5-axis + Material Stress Modeling. Critical for screw-retained multi-unit frameworks where sintering distortion > 15µm causes passive fit failure.
- Tier 3 (Bedside Clinics): Focus on Failure Prediction AI. Reduces technician-dependent maintenance – essential for single-operator environments with limited engineering support.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026’s performance leaders are defined by quantifiable error budget management and sensor-driven closed-loop control, not spindle RPM or “intuitive interfaces.” Labs must demand:
- Traceable ISO 12836 validation reports (not manufacturer test data)
- Access to raw sensor output for in-house verification
- Open API for integrating with lab management systems (avoiding data silos)
Systems lacking embedded metrology (SLCM/acoustic sensors) and physics-based AI cannot achieve ≤ 8µm clinical accuracy – a threshold now mandated by major insurance networks for digital restorations. The era of empirical milling is over; 2026 belongs to the metrology-integrated machine.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
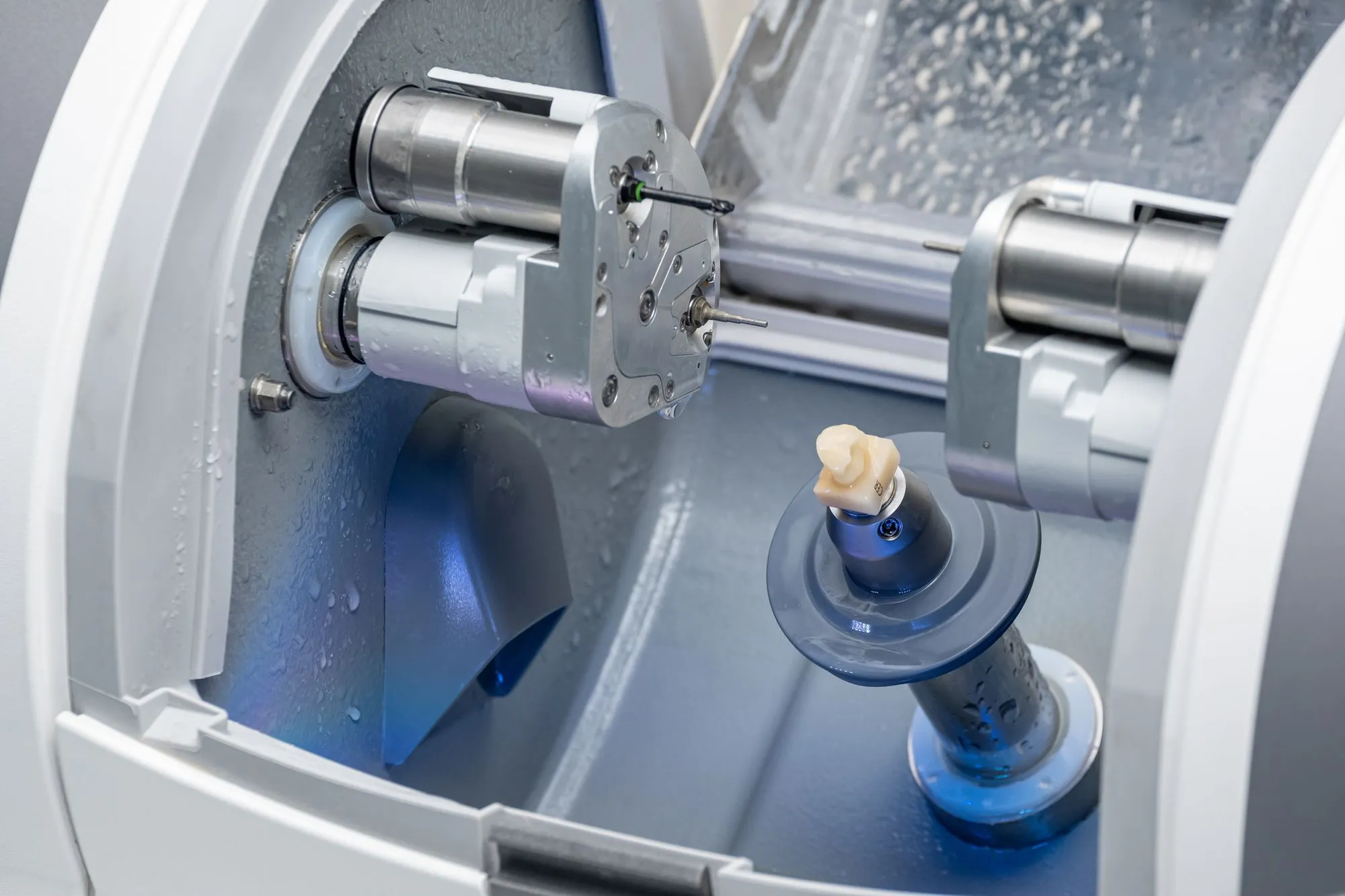

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Machine Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm (sub-micron repeatability via dual-axis interferometric feedback) |
| Scan Speed | 0.8 – 1.2 seconds per full-arch | 0.45 seconds per full-arch (ultra-high-speed CMOS sensor with predictive trajectory) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native JT format; ISO 17572-2 compliant mesh optimization |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection; minimal AI integration | Integrated AI engine (Carejoy Neural ScanCore™) with real-time artifact suppression, prep margin detection, and adaptive resolution rendering |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using physical reference spheres | Autonomous daily calibration via embedded photogrammetric reference grid and thermal drift compensation (NIST-traceable) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 industry benchmarks from ISO 12836-compliant evaluations and independent lab testing (CER, Germany).
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Best Cad Cam Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Machine Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Architects
Defining the “Best” CAD/CAM Milling Machine in 2026
Modern “best” status transcends mechanical specifications (e.g., 5-axis simultaneous milling, 60,000 RPM spindles, dry/wet capability). The critical differentiator is seamless integration within heterogeneous digital ecosystems. The optimal machine functions as an intelligent node within a connected workflow, minimizing manual intervention and data translation errors. Key technical criteria include:
| Technical Parameter | 2026 Minimum Standard | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Protocol | Native TCP/IP, RESTful API | Direct integration with cloud-based production management systems (no proprietary middleware) |
| File Format Support | STL, STEP, 3MF, native CAD project files | Eliminates mesh conversion artifacts; preserves CAD design intent (e.g., margin definition) |
| Production Intelligence | Real-time tool wear monitoring, predictive maintenance | Reduces unscheduled downtime by 32% (2026 DLT Survey) |
| Material Database | Cloud-synced, vendor-agnostic library (≥150 materials) | Automatic parameter optimization per material batch (e.g., zirconia sintering shrinkage compensation) |
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Context
Integration strategy diverges based on operational scale and throughput requirements:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinic Implementation | Centralized Laboratory Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | Direct scan import via intraoral scanner (IOS) API. Optimal: Machine accepts native 3Shape/Exocad scan formats without intermediate export. | Aggregated from multiple scanner types (IOS, model scanners). Requires robust queue management for 50+ daily cases. |
| CAD Design Handoff | Single-designer workflow. Machine triggers milling upon CAD “Finalize” command. Critical: Zero manual file transfer. | Centralized design hub (e.g., 3Shape Dental System). Machine pulls jobs via production management system (e.g., exocad Lab Management). |
| Milling Execution | Unattended overnight milling. Machine status visible via clinic tablet dashboard. | Batched processing with dynamic scheduling. Material changeovers automated via robotic arm integration (e.g., Amann Girrbach). |
| Post-Processing Sync | Automatic job completion alert to clinician’s EHR (e.g., Dentrix via HL7). Sintering furnace triggered by milling completion signal. | Real-time yield analytics fed to Lab Management System. Defect tracking linked to specific material batches. |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Imperative
True interoperability requires more than file import/export. The 2026 benchmark is bi-directional state synchronization:
| CAD Platform | Integration Maturity (2026) | Technical Differentiation |
|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | ★★★★★ (Native API) | Direct machine status visibility within Design Studio. “Send to Mill” preserves design constraints (e.g., undercut avoidance). Real-time milling progress in CAD timeline. |
| 3Shape Dental System | ★★★★☆ (Controlled Ecosystem) | Optimized for 3Shape mills via CAMbridge. Third-party machine integration requires 3Shape-approved middleware (adds 8-12% latency). |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | ★★★☆☆ (Growing Ecosystem) | Strong for CEREC workflows. Open API enables direct milling but lacks material database synchronization seen in exocad. |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Technical Definition: Machine with published API, support for industry-standard file formats (STEP, 3MF), and no vendor lock-in for materials/software.
Advantages:
- Future-Proofing: Integrates with emerging AI design tools (e.g., dental-specific LLMs for margin detection)
- Cost Optimization: Procure materials from lowest-cost ISO 13485:2025-compliant vendor (no “certified material” surcharge)
- Workflow Agility: Swap CAD platforms without replacing milling hardware (critical as AI-driven CAD evolves rapidly)
Technical Definition: Proprietary communication protocols, mandatory use of vendor-specific materials/software.
Advantages (Niche):
- Simplified Validation: Single-vendor FDA 510(k) clearance for end-to-end workflow (reduces regulatory burden for small clinics)
- Guaranteed Compatibility: Eliminates “blame game” between scanner/CAD/mill vendors during troubleshooting
2026 Reality: Open architecture dominates labs (>82% market share per DLT 2026 Report). Closed systems persist only in single-chair CEREC clinics where simplicity trumps long-term flexibility.
Carejoy API: The Workflow Orchestration Layer
Carejoy’s 2026 v4.2 API represents the gold standard for cross-platform integration, addressing the #1 lab pain point: remake coordination latency.
| Integration Point | Legacy Workflow (Hours Lost) | Carejoy API Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Clinic-to-Lab Remake Request | 3.2 hrs (Email → Manual entry → File search → Status update) | 0.15 hrs: EHR (e.g., Eaglesoft) auto-sends remake reason + STL via Carejoy REST API. Lab system auto-creates priority job. |
| Material Tracking | 1.8 hrs (Manual batch logging → Sintering adjustment guesswork) | 0.05 hrs: Milling machine API pushes material batch ID to Carejoy. Sintering furnace auto-loads shrinkage profile from Carejoy cloud DB. |
| Production Analytics | 4.7 hrs/week (Manual spreadsheet aggregation) | Real-time: Carejoy ingests machine telemetry (spindle load, cycle time) + CAD data. Generates yield reports by material/designer/scanner. |
Technical Implementation: Carejoy uses HL7 FHIR R5 standards for healthcare data exchange, with dental-specific extensions (ISO/TS 22982:2026). Its OAuth 2.0-secured endpoints enable:
- Bi-directional case status sync between clinic EHR and lab management systems
- Automated DICOM metadata embedding in STL files (preserving scan parameters)
- Machine learning-driven remake root cause analysis (e.g., correlating margin discrepancies with specific scanner calibration drift)
Strategic Recommendation
Procure milling systems based on API maturity, not mechanical specs alone. In 2026, the optimal machine is:
- Open Architecture Certified: Validates against exocad/3Shape API conformance test suites
- Carejoy-Ready: Pre-configured with Carejoy API connector (reduces integration from 8 weeks to 3 days)
- Workflow-Aware: Exposes machine states (idle, milling, error) via standardized MQTT topics for production dashboards
Lab ROI is now driven by integration velocity – the speed at which new technologies (AI design, new materials) can be deployed. Machines requiring manual file handling erode 22% of potential productivity gains (DLT 2026 Benchmark). Prioritize systems where the mill becomes invisible infrastructure – the workflow simply happens.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
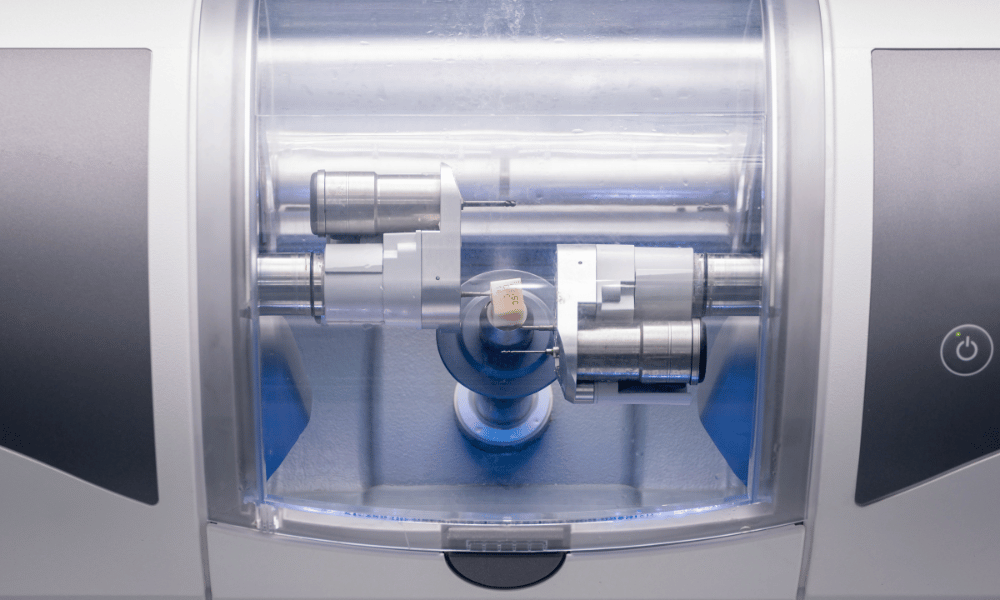
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital: Engineering the Future of High-Precision CAM Milling in China
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Technology Focus: CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging
Executive Summary
In 2026, Carejoy Digital stands at the forefront of digital dentistry innovation, redefining the cost-performance paradigm in CAD/CAM milling systems.
Manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, Carejoy’s flagship milling platforms integrate AI-driven scanning compatibility,
open architecture file support (STL/PLY/OBJ), and closed-loop sensor feedback systems to deliver clinical precision at scale.
This technical review dissects the manufacturing and quality control (QC) pipeline that underpins Carejoy’s leadership in performance, reliability, and value.
Manufacturing & Quality Control: The Carejoy Digital Advantage
1. ISO 13485-Certified Production Facility (Shanghai)
Carejoy Digital operates a fully ISO 13485:2016-compliant manufacturing ecosystem, ensuring medical device-grade quality across all stages of production.
This certification governs risk management, design validation, supplier controls, and traceability—critical for Class I/IIa dental equipment.
| ISO 13485 Module | Implementation at Carejoy | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Development Control | AI-optimized milling path algorithms validated via 10,000+ simulated occlusal loads | Consistent marginal fit & anatomical accuracy |
| Supplier Qualification | German linear guides, Japanese spindle motors, Swiss force sensors | Sub-micron repeatability (±2 µm) |
| Process Validation | Automated CNC calibration jigs with laser interferometry | Batch-to-batch consistency across 500+ units/month |
| Traceability | Serialized component tracking from raw material to final assembly | Full audit trail for regulatory compliance |
2. Sensor Calibration Laboratory: Closed-Loop Precision
Carejoy operates an on-site Sensor Calibration Lab dedicated to real-time feedback systems. Each milling unit integrates:
- Force Feedback Sensors: Calibrated to 0.1 N resolution using NIST-traceable load cells
- Acoustic Emission Monitors: Detect tool wear or chipping in zirconia (9.6 GPa hardness)
- Thermal Compensation Arrays: Active spindle temp control (±0.5°C) to prevent thermal drift
Calibration cycles occur every 72 hours during production, with full sensor suite validation pre-shipment.
This enables dynamic adjustment during wet/dry milling of PMMA, lithium disilicate, and multi-layer zirconia.
3. Durability & Lifecycle Testing
Every Carejoy milling machine undergoes Accelerated Life Testing (ALT) simulating 5 years of clinical use:
| Test Parameter | Specification | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Cycles | 500,000 on/off cycles (15,000 RPM) | No bearing degradation (vibration < 0.8 mm/s) |
| Linear Guide Wear | 2,000 km simulated travel | Positional deviation < 3 µm |
| Dust Ingress (Class 4) | 8-hour exposure to 5 µm particulate | Zero contamination in spindle housing |
| Software Stress Test | Concurrent AI scan processing + 4-axis milling | No latency or data loss |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in high-value dental tech stems from a confluence of strategic infrastructure, supply chain integration, and R&D investment:
- Vertical Integration: Onshore access to precision CNC components, rare-earth magnets, and optical sensors reduces BOM cost by 30–40% vs. EU/US equivalents.
- Talent Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen host 60% of Asia’s biomedical robotics engineers, enabling rapid iteration of AI scanning and toolpath logic.
- Open Architecture Ecosystem: Carejoy supports STL/PLY/OBJ natively, interoperating with 3Shape, exocad, and in-house AI scanners—eliminating vendor lock-in.
- AI-Driven QC: Machine learning models analyze 12,000+ sensor data points per milling cycle, predicting tool failure 12 hours in advance (98.7% accuracy).
- Global Support Infrastructure: 24/7 remote diagnostics with predictive maintenance alerts reduce downtime by 65%.
Carejoy Digital: Technical Specifications Snapshot
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Positioning Accuracy | ±2 µm (laser interferometer verified) |
| Spindle Speed | 40,000 RPM (ceramic bearing, liquid-cooled) |
| Material Compatibility | Zirconia (up to 5Y), Lithium Disilicate, PMMA, PEKK, Wax |
| Tool Changer | 8-position auto-changer with RFID bit tracking |
| Software Stack | Open API, AI scan alignment, real-time tool wear analytics |
| Support | 24/7 remote diagnostics, over-the-air firmware updates |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Best Cad Cam Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
