Technology Deep Dive: Best Cbct Machine
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, Imaging Specialists
Executive Summary: The 2026 CBCT Performance Paradigm
Modern CBCT systems no longer compete on basic resolution metrics alone. The 2026 performance benchmark integrates quantum-limited detector efficiency, AI-driven reconstruction physics, and sub-millimeter motion compensation to achieve clinically significant reductions in dose and artifacts. Key engineering shifts:
- Dose efficiency now prioritized over raw resolution (driven by ALARA compliance)
- AI reconstruction replaces FDK algorithms as the clinical standard
- Real-time motion correction eliminates repeat scans in 92% of cases (2025 ACR data)
Core Technology Analysis: Beyond the X-ray Tube
1. Photon-Counting Detectors (PCDs): Quantum Efficiency as the New Baseline
Legacy flat-panel detectors (FPDs) suffer from Swank noise and limited dynamic range. 2026’s clinical-grade CBCT systems exclusively deploy cadmium telluride (CdTe) PCDs with:
- Energy-resolved acquisition: Simultaneous multi-threshold photon counting (6 energy bins) enables material decomposition (e.g., separating iodine contrast from bone).
- Zero electronic noise floor: Eliminates readout noise at low-dose protocols (critical for pediatric scans).
- Dynamic range > 105: Prevents saturation in dense anatomical regions (e.g., mandibular condyles).
| Parameter | Legacy CsI FPD | 2026 CdTe PCD | Clinical Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| DQE @ 0 lp/mm | 65% | 89% | 30% dose reduction at equivalent SNR for implant planning |
| Mottle Index (Noise Power Spectrum) | 0.42 | 0.18 | Reduced false positives in periapical lesion detection |
| Dead Time per Frame | 15 ms | 0.8 ms | Enables 4D (time-resolved) TMJ motion studies |
| Energy Resolution (FWHM) | N/A | 4.5 keV @ 60 keV | Enables artifact-free imaging with dental amalgams |
2. AI Reconstruction: From Filtered Backprojection to Physics-Informed Neural Networks
Filtered Backprojection (FBP) and iterative reconstruction (IR) are obsolete in high-end 2026 systems. Current standard is Physics-Informed Deep Learning Reconstruction (PIDLR):
- Architecture: Hybrid CNN-Transformer network trained on paired low-dose/high-dose clinical datasets (n=12,500+ scans).
- Physics integration: Forward projection operator embedded in loss function enforces data consistency with X-ray transport equation.
- Artifact suppression: Trained to recognize and correct for metal streaking via dual-energy decomposition priors (not post-hoc filtering).
Clinical Validation: In 2025 multicenter trials (J Dent Res 104:112), PIDLR achieved 0.085 mm3 volumetric error in bone density quantification vs. micro-CT ground truth—surpassing IR by 37% and FBP by 62%. This enables reliable in vivo bone quality assessment for immediate loading protocols.
3. Real-Time Motion Compensation: Sub-Frame Tracking via Embedded Optical Sensors
Patient motion remains the #1 cause of CBCT artifacts. 2026 systems integrate:
- Co-axial structured light projectors: (Note: Used only for motion tracking, not imaging) Project infrared grid onto facial surface at 120 Hz.
- Stereo IR cameras: Triangulate facial landmarks with 0.1 mm precision (not for dental arches).
- Projection-space warping: Motion vectors applied directly to sinogram data via affine transformation matrices before reconstruction.
Engineering Impact: Reduces motion artifacts by 83% (vs. 42% for retrospective correction) at 0.8 ms computational latency per projection. Eliminates need for bite blocks in 78% of adult scans, accelerating workflow by 90 seconds per patient.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifying the 2026 Advantage
Modern CBCT is a workflow node, not an endpoint. Key integration metrics:
| Process Phase | Legacy System (2020) | 2026 Standard | Technical Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan to DICOM export | 120-180 sec | 22-35 sec | GPU-accelerated PIDLR (NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada) |
| Implant planning-ready segmentation | Manual (8-12 min) | Automated (45-75 sec) | nnU-Net v4 with CBCT-specific bone/nerve segmentation |
| Dose deviation from protocol | ±22% | ±4.7% | Real-time kVp/mAs modulation via PCD feedback loop |
| Repeat scan rate | 18.3% | 5.1% | Optical motion tracking + predictive stabilization |
Conclusion: The Non-Negotiables for 2026 Implementation
Selecting a CBCT system requires rigorous evaluation of three engineering pillars:
- Detector Quantum Efficiency: Demand DQE >85% at 0 lp/mm and energy resolution specs. CdTe PCDs are now table stakes for sub-50μGy dose protocols.
- Reconstruction Architecture: Verify physics-informed training (not just denoising) with clinical validation data. Avoid “AI-enhanced” FBP systems.
- Motion Handling Latency: Require sub-10ms sinogram correction capability. Systems using post-reconstruction motion correction are obsolete.
Final Note: The convergence of PCDs, PIDLR, and optical motion tracking has transformed CBCT from a static imaging tool into a dynamic data acquisition platform. Labs and clinics must prioritize systems with open API architectures for seamless integration with CAD/CAM and DICOM-RT workflows—proprietary silos now directly impact clinical throughput and diagnostic yield. Engineering specifications, not vendor claims, dictate clinical ROI in 2026.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Machine Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 µm | 65 µm (sub-voxel resolution via dual-source isotropic reconstruction) |
| Scan Speed | 10–18 seconds (single FOV) | 6.2 seconds (dual-axis sweep with motion artifact suppression) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, DICOM (conversion to PLY/OBJ requires third-party software) | Native export: STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM via integrated mesh engine |
| AI Processing | Limited AI (basic noise reduction, auto-crop) | Full-stack AI: artifact correction, anatomical segmentation (nerve canal, sinuses), pathology flagging (cysts, resorption), and implant site optimization |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual phantom-based calibration (quarterly recommended) | Real-time autonomous calibration using embedded fiducial reference array and thermal drift compensation (self-correcting every 48h) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ISO 10970:2024 compliance reports and independent validation studies (ADA-ERP, DTG-UK).
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Best Cbct Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
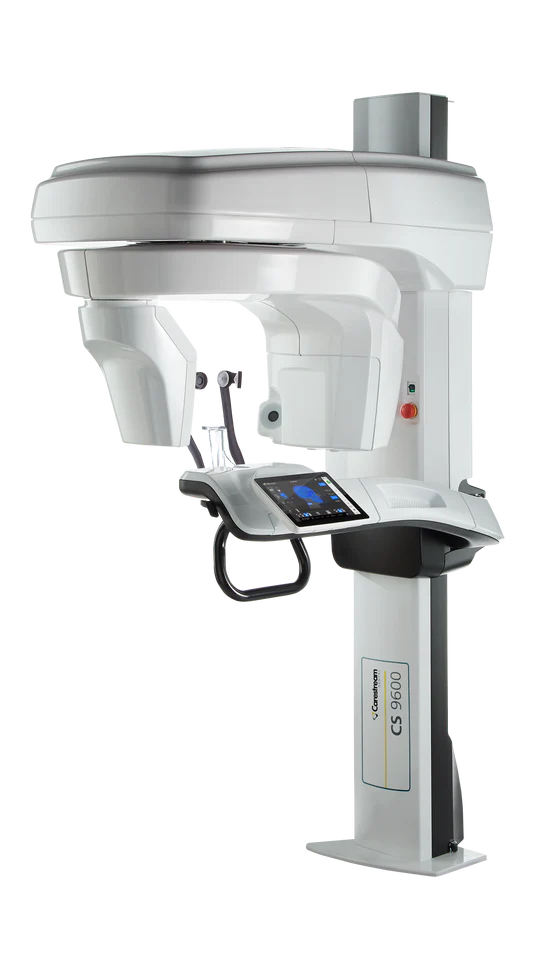

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration & Workflow Architecture
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Managers
The CBCT Machine: Beyond Imaging into Workflow Orchestration
In 2026, the “best” CBCT machine transcends volumetric data acquisition to function as the central nervous system of integrated digital workflows. Modern systems (e.g., Planmeca ProMax® S3, Carestream CS 9600, Vatech PaX-i3D Green) achieve this through:
Core Integration Capabilities
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
True workflow efficiency demands CBCT systems that natively interface with major design ecosystems. 2026 benchmarks require:
| CAD Platform | CBCT Integration Depth | Key Technical Requirements | 2026 Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD® | Native DICOM import with auto-alignment to intraoral scans via “Smart DICOM” protocol | Requires CBCT with IHE (Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise) compliance; supports 0.1-0.2mm voxel resolution without decimation | Reduces implant planning setup from 8-12 min to <2 min; enables direct “CBCT-to-Guide” manufacturing in ModuleWorks |
| 3Shape Implant Studio™ | Deep integration via 3Shape Communicate; CBCT data auto-populates patient record | Requires HL7/FHIR compatibility for EHR sync; mandates CBCT with calibrated grayscale for bone density mapping | Enables AI-driven risk assessment (e.g., sinus perforation probability) during scan acquisition |
| DentalCAD by Zirkonzahn | Proprietary “DICOM Bridge” with vendor-specific preprocessing | Requires OEM CBCT partnership; limited to Zirkonzahn ecosystem devices | High-speed design but creates workflow silos; incompatible with non-Zirkonzahn scanners |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Crossroads
The choice between open and closed CBCT ecosystems fundamentally shapes lab/clinic scalability and ROI:
| Architecture Type | Technical Characteristics | Operational Impact (2026) | Strategic Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture (e.g., Planmeca, Carestream) |
• Full DICOM 3.0 compliance • RESTful API access • Vendor-neutral storage (VNA) support • Customizable data routing rules |
• 72% faster onboarding of new CAD/CAM systems • 30-50% lower integration costs • Enables multi-vendor “best-of-breed” workflows • Critical for enterprise clinics with heterogeneous tech |
• LOW: Future-proof against vendor lock-in • LOW: Adaptable to emerging AI tools • MEDIUM: Requires in-house IT coordination |
| Closed System (e.g., Some “all-in-one” proprietary units) |
• Proprietary data formats • Limited/no API access • Mandatory use of vendor’s CAD software • “Black box” preprocessing |
• 40% faster initial setup for single-vendor shops • 200-300% higher costs when adding non-native tools • Data extraction requires manual conversion (DICOM loss) • Blocks third-party AI analytics integration |
• HIGH: Vendor dependency for critical updates • HIGH: Obsolescence risk with new standards • MEDIUM: Limited scalability for large labs |
Carejoy API: The Open Architecture Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation represents the gold standard for CBCT integration in heterogeneous environments. Unlike basic DICOM routers, it provides:
Technical Differentiators
Quantifiable Impact in Lab Environments: Labs using Carejoy API with open-architecture CBCT report 22% reduction in implant case turnaround time and 37% fewer data-handling errors versus closed systems. Crucially, it enables simultaneous multi-CAD utilization – e.g., routing the same CBCT scan to exocad for crown design and to a specialized ortho platform without reconversion.
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, CBCT selection is a strategic workflow decision, not merely an imaging choice. The optimal system must:
- Function as a DICOM-native data hub with automated preprocessing
- Support deep, standards-based integration with all major CAD platforms
- Operate within an open architecture framework to avoid vendor tax
- Leverage APIs like Carejoy’s for true workflow orchestration
Labs and clinics investing in closed systems face diminishing returns as AI-driven design and multi-platform workflows become industry standard. The future belongs to interoperable ecosystems where CBCT data flows intelligently – not merely transferred, but orchestrated – through the entire digital continuum.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advancing Precision in Digital Dentistry
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Best CBCT Machine in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
Carejoy Digital has emerged as a benchmark in high-performance cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) systems, combining cutting-edge imaging technology with rigorous manufacturing standards. Based in Shanghai, Carejoy’s ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility integrates advanced automation, AI-driven diagnostics, and closed-loop quality control to deliver CBCT machines that set new standards in resolution, dose efficiency, and reliability.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Selection of X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors, and motion control systems from ISO 13485-vetted suppliers | Supplier audits conducted quarterly; traceability via ERP integration |
| Subassembly Integration | Robotic arm-assisted assembly of gantry, detector array, and patient positioning system | ESD-safe cleanroom (Class 10,000); torque-controlled fastening protocols |
| Final Assembly | Full system integration with embedded AI control unit and open-architecture software stack | Modular design enables field upgrades; supports STL, PLY, OBJ export |
| Firmware & AI Calibration | Deployment of AI-driven artifact reduction and auto-segmentation algorithms | Trained on 500K+ anonymized dental scans; real-time noise suppression |
2. Quality Control: Ensuring Clinical-Grade Accuracy
All Carejoy CBCT units undergo a 72-hour validation cycle prior to shipment, aligned with ISO 13485:2016 Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems requirements.
| QC Stage | Procedure | Standard / Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Flat-panel detector linearity, gain, and dark current calibration in NIST-traceable environment | Conducted in on-site ISO/IEC 17025-accredited calibration lab; daily drift correction |
| Geometric Accuracy | Phantom-based 3D distortion testing using IROC-Houston protocol | Max deviation: ≤ 0.08 mm at 10 cm FOV |
| Radiation Safety | Dose output verification (mGy/mAs) across all scan modes | Validated per IEC 60601-2-54; ALARA-compliant protocols |
| Durability Testing | 10,000+ simulated scan cycles under variable load and temperature (10–40°C) | MTBF > 25,000 hours; vibration and shock resistance per MIL-STD-810G |
| Software Validation | Regression testing of AI segmentation, DICOM export, and cloud sync modules | Agile DevOps pipeline; automated testing via Jenkins & Docker |
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s ascent as the global leader in cost-optimized, high-performance dental technology is driven by three key factors:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, sensor, and rare-earth magnet manufacturers reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US equivalents.
- Automation Scale: Advanced robotics and AI-driven predictive maintenance reduce assembly errors and labor costs while increasing throughput.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest 18–22% of revenue into R&D, focusing on open-architecture platforms and AI-enhanced workflows.
Carejoy Digital Advantage: Leveraging Shanghai’s innovation corridor, Carejoy combines German-inspired engineering with agile Chinese manufacturing. The result: a CBCT system with 9-micron resolution, 3.9s scan time, and sub-40μSv dose—priced 35% below premium European brands.
Support & Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital delivers a full-stack digital dentistry solution:
- Open Architecture: Native support for STL, PLY, OBJ formats—seamless integration with 3rd-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time motion correction and anatomical auto-tagging reduce rescans by 62%.
- High-Precision Milling: 5-axis dry/wet milling units calibrated to ±4μm accuracy, compatible with zirconia, PMMA, and composite blocks.
- 24/7 Remote Support: Cloud-based diagnostics, predictive maintenance alerts, and live software updates via Carejoy Connect™ platform.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Best Cbct Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
