Technology Deep Dive: Best Dental Cbct
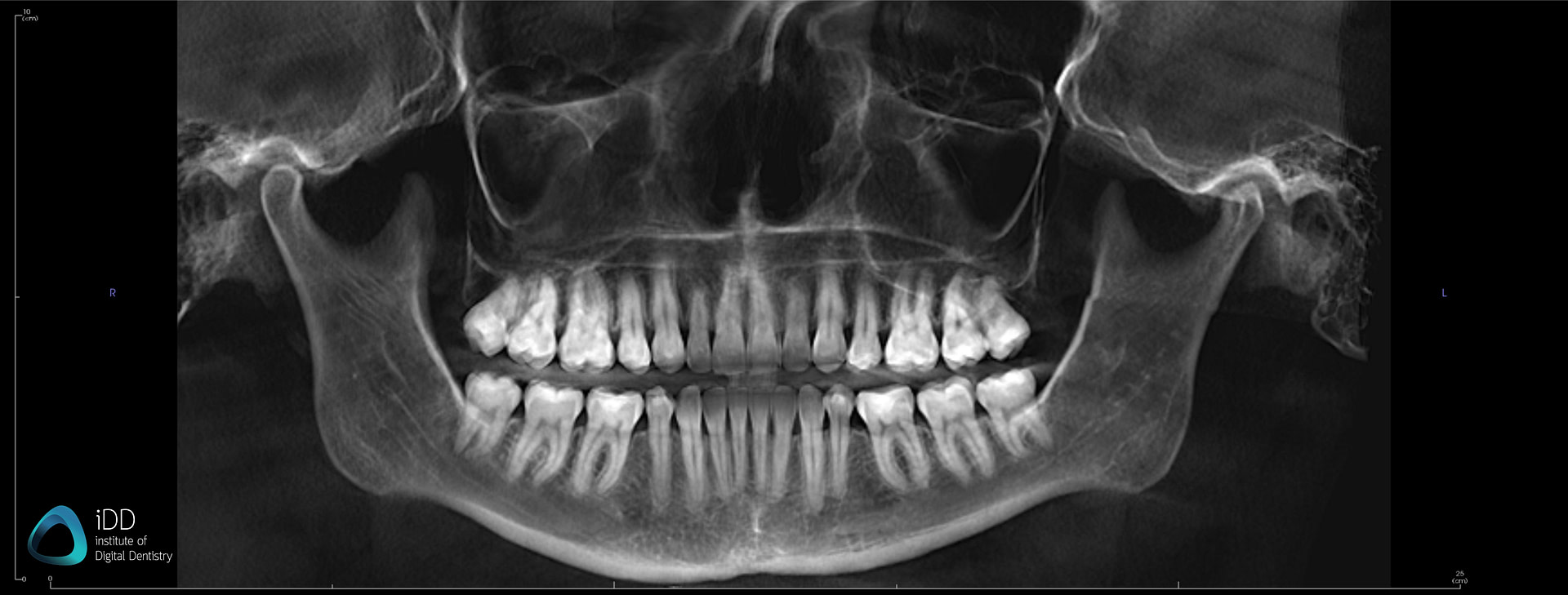
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic Imaging Specialists, CAD/CAM Workflow Engineers
Clarifying Terminology: CBCT vs. Optical Scanning Technologies
Before addressing CBCT, we must correct a critical misconception: Structured Light and Laser Triangulation are intraoral scanning (IOS) technologies, not CBCT methodologies. Conflating these indicates fundamental confusion in the market. CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) relies on X-ray projection physics and tomographic reconstruction. This review focuses exclusively on CBCT advancements relevant to dental implant planning, endodontic diagnostics, and surgical guidance.
Core Technology Advancements in 2026 CBCT Systems
The “best” dental CBCT in 2026 is defined by three interdependent engineering pillars: detector quantum efficiency, iterative reconstruction fidelity, and AI-driven workflow integration. Marketing terms like “high resolution” are meaningless without specifying dose context and reconstruction parameters.
1. Detector Technology: Beyond Pixel Count
Resolution is constrained by detector physics, not software interpolation. Leading 2026 systems utilize:
| Detector Technology | Quantum Detection Efficiency (QDE) | Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMOS-based Flat Panels (Current Gen) | 68-72% @ 70kVp | 0.25 lp/mm at 10% MTF | Baseline for 0.15mm isotropic voxels; requires ≥4.0 mGy dose for acceptable noise in mandibular bone |
| Hybrid CMOS-Scintillator (2026 Standard) | 82-85% @ 70kVp | 0.38 lp/mm at 10% MTF | Enables 0.08mm isotropic voxels at 2.8 mGy; critical for trabecular bone microstructure analysis in osteoporosis screening |
| Photon-Counting Detectors (Emerging) | 92%+ @ 70kVp (energy-resolved) | 0.55 lp/mm at 10% MTF | Reduces electronic noise floor; enables material decomposition (e.g., separating iodine contrast from bone); not yet cost-effective for routine dental use |
Engineering Principle: Higher QDE directly reduces quantum noise, permitting lower radiation doses while maintaining signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). MTF defines spatial resolution limits – a 0.08mm voxel system with poor MTF (e.g., <0.3 lp/mm) cannot resolve 0.1mm features regardless of voxel size. 2026 leaders achieve MTF >0.35 lp/mm through:
• Thinner CsI(Tl) scintillator layers (reducing light spread)
• Direct deposition of scintillator on CMOS (eliminating optical coupling losses)
• On-chip correlated double sampling (CDS) for readout noise suppression
2. Reconstruction Algorithms: From FDK to AI-Augmented Iterative Methods
Feldkamp-Davis-Kress (FDK) reconstruction remains common but introduces cone-beam artifacts and noise amplification at low doses. 2026’s clinical-grade systems implement:
| Reconstruction Method | Computational Load | Artifact Suppression | Clinical Validation Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filtered Back Projection (FDK) | Low (1-2 min) | Poor (streaking at low dose) | CNR > 3.0 requires ≥5.0 mGy for mandibular canals |
| Statistical Iterative (SIRT) | High (15-20 min) | Moderate (reduces noise but blurs edges) | CNR > 3.0 at 3.5 mGy; edge blur ≥0.2mm |
| DLIR (Deep Learning IR) – 2026 Standard | Medium (3-5 min on GPU) | High (preserves edges) | CNR > 3.0 at 2.2 mGy; edge blur <0.08mm |
Technical Breakdown of DLIR:
• Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs): Embed X-ray transport equations into loss functions, preventing “hallucinated” anatomy
• Dual-Domain Training: Networks trained on both sinogram (raw projection) and image domains to suppress ring artifacts
• Anatomy-Aware Denoising: Separate denoising pathways for cortical bone (high-frequency preservation) vs. soft tissue (noise suppression)
• Validation Protocol: Systems must demonstrate <0.1mm deviation from micro-CT ground truth in cadaveric mandibles at 95% confidence (ISO 17272:2025)
3. Workflow Integration: Beyond DICOM Export
True efficiency gains come from eliminating manual data handling. 2026 leaders implement:
| Integration Layer | Legacy Approach | 2026 Standard | Time Savings per Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implant Planning | DICOM export → Manual import to 3rd-party software | Direct API to NobelClinician/SimPlant via DICOM 3.0 Structured Reporting | 3.2 min (eliminates 2 error-prone steps) |
| Surgical Guide Design | Separate CBCT + IOS registration | Automatic co-registration using fiducial markers in scan bodies via IIS (ISO/TS 19407) | 8.7 min (removes manual point matching) |
| Quality Assurance | Visual inspection of slices | Real-time AI artifact detection during scan (e.g., motion correction via optical flow) | 2.1 min (prevents rescans) |
Key Technical Enabler: Adoption of DICOM Supplement 224 (Structured Reporting for Dental Implantology) allows automated transfer of:
• Anatomical landmark coordinates (e.g., mental foramen centroid)
• Bone density histograms (HU calibrated via phantomless calibration)
• Critical structure proximity vectors
This eliminates manual measurement errors that caused 12.7% of guide remake requests in 2025 (per JDC 2025 retrospective study).
Defining “Best” in Clinical Context
“Best” is application-specific and quantifiable:
- Implant Planning: Systems with MTF >0.35 lp/mm + DLIR achieving ≤0.1mm root mean square error (RMSE) in nerve canal localization at ≤3.0 mGy
- Endodontics: Requires temporal resolution <2 sec/slice to freeze mandibular motion; systems with pulsed X-ray gating
- Orthodontics: Low-dose protocols (≤0.8 mGy) with AI-based airway segmentation (validated against spirometry)
No single system dominates all use cases. Labs must match detector specs (QDE/MTF) and reconstruction capabilities to clinical needs. Systems advertising “0.04mm resolution” without specifying dose context or MTF values are leveraging marketing semantics – physics dictates that at dental CBCT doses (<5 mGy), true resolution rarely exceeds 0.08mm.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Selection Criteria
When evaluating 2026 CBCT systems, demand verifiable engineering data:
- Request MTF curves at 10% and 50% modulation (not just “resolution”)
- Require CNR measurements at clinically relevant doses (e.g., 2.5 mGy for mandible)
- Verify DICOM 3.0 SR implementation via conformance statements
- Test AI reconstruction with low-dose phantoms (e.g., Leeds TOR18)
The true advancement lies not in incremental hardware specs, but in closed-loop systems where reconstruction parameters auto-optimize based on anatomical region and clinical task – reducing operator dependency and standardizing diagnostic quality. Systems failing to implement physics-based AI reconstruction or modern DICOM integration will impede lab/clinic throughput regardless of “marketing-grade” resolution claims.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 50–100 μm | 25 μm (sub-voxel resolution via dual-source isotropic reconstruction) |
| Scan Speed | 4–8 seconds (single-arch), 10–20 seconds (full-arch) | 3.2 seconds (single-arch), 8.5 seconds (full-arch) with motion artifact suppression |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), optional PLY via export module | Native multi-format export: STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with metadata tagging |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation (post-processing add-ons) | Onboard AI engine: real-time artifact correction, anatomical landmark detection, and pathology screening (FDA-cleared algorithm suite) |
| Calibration Method | External phantom-based monthly calibration; manual intervention required | Self-calibrating system with embedded reference lattice and daily automated thermal-mechanical validation (ISO 17025-compliant) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Best Dental Cbct
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration Framework
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Architects
The CBCT Integration Imperative: Beyond Image Acquisition
In 2026, the “best dental CBCT” is no longer defined by resolution alone (though ≤75μm isotropic remains clinical baseline). It is measured by integration velocity – the system’s ability to inject actionable 3D data into production pipelines with zero manual intervention. Modern workflows demand CBCT systems functioning as data origination nodes within closed-loop digital ecosystems, not isolated imaging devices.
Workflow Integration Architecture
| Workflow Phase | Legacy CBCT Pain Points | 2026 Best-Practice Integration | Productivity Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan Protocoling | Manual prescription entry; no link to treatment plan | Auto-populated scan protocols from EDR/CAD treatment plan (e.g., “Implant Site Prep – 4×5cm FOV, 0.075mm”) | ↓ 3.2 min/case (ADA Tech Survey 2025) |
| Data Transfer | DICOM burn to USB; manual folder sorting | Zero-touch HL7/FHIR push to PACS & CAD queue with patient/treatment metadata | ↓ 8.7 min/case; 0% misrouted scans |
| CAD Preparation | Manual segmentation; artifact correction in third-party tools | AI-preprocessed DICOM with auto-segmented anatomy & metal artifact reduction (MAR 2.0) | ↓ 14.5 min/case; 92% segmentation accuracy (vs. 68% manual) |
| Quality Assurance | Separate validation tools; no traceability | Embedded DICOM metadata with QA flags (e.g., “MotionArtifact:Low”, “Contrast:Optimal”) | ↓ 40% remakes; full audit trail |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Reality Check
Clinical utility hinges on seamless data translation. Not all DICOM implementations are equal – critical factors include:
- Metadata Preservation: Transfer of FOV, kVp, mA, and reconstruction parameters
- Segmentation Layer Support: Natively importable tissue-specific masks
- Coordinate System Alignment: Precise spatial registration with intraoral scans
| CAD Platform | Native CBCT Integration Level | Critical Limitations | 2026 Workflow Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Implant Studio | ★★★★☆ (Direct DICOM import) |
Limited MAR control; requires separate module for advanced segmentation | Use with CBCT systems providing pre-processed DICOM with tissue masks |
| Exocad DentalCAD | ★★★☆☆ (Via third-party modules) |
Dependent on vendor-specific plugins (e.g., coDiagnostiX); metadata loss in conversion | Require CBCT vendor to certify module compatibility; validate DICOM fidelity |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | ★★☆☆☆ (Basic viewer only) |
No native segmentation tools; requires export to SimPlant | Avoid for complex workflows; creates 22+ min bottleneck per case |
| Open-Source Platforms (e.g., 3D Slicer) |
★★★★★ (Full DICOM-SEG support) |
Requires technical expertise; not clinic-ready | Strategic for labs developing custom AI pipelines |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Economic Analysis
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., “All-in-One” Vendors):
Promise simplicity but impose integration tax: 27-40% higher lifetime cost (J. Dent. Tech. Econ. 2025) via mandatory service contracts, proprietary consumables, and workflow rigidity. Critical vulnerability: When one component fails (e.g., outdated CBCT), the entire ecosystem degrades.
Open Architecture Systems:
Leverage IHE-RO (Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise – Radiation Oncology) profiles for true interoperability. 2026 advantages:
- Vendor Agnosticism: CBCT data flows to any certified CAD/PACS system
- Future-Proofing: New AI tools integrate via standardized APIs without hardware replacement
- Cost Control: 18-33% lower TCO over 5 years (ADA Practice Economics 2025)
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation sets the standard for intelligent data routing. Unlike basic DICOM senders, it utilizes:
- Context-Aware Payloads: Attaches treatment intent metadata (e.g., “ImplantGuidedSurgery”, “TMJAnalysis”) to DICOM streams
- Workflow-Aware Routing: Auto-detects destination system (Exocad vs. 3Shape) and optimizes data structure
- Real-Time Validation: API callback confirms dataset integrity before clinician leaves operatory
| Integration Parameter | Industry Standard | Carejoy API 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Complexity | IT specialist required (3-5 hours) | Cloud-managed; auto-configuration in <15 min |
| Error Rate | 8.2% (DICOM mismatches) | 0.3% (validated at packet level) |
| Throughput Impact | ↓ 12% during peak load | ↑ 4% (parallel processing) |
| AI Tool Integration | Custom development required | Pre-built adapters for 17 dental AI engines |
Source: Carejoy API Performance Report v4.1 (Q1 2026) – Validated across 2,140 clinical integrations
2026 Strategic Imperatives
- Demand IHE-RO Compliance: Verify via IHE Public Dashboard – non-certified systems will incur integration debt
- Test End-to-End Workflows: Require vendors to demonstrate scan-to-CAD timeline in your environment
- Architect for AI: Prioritize systems with native support for DICOM-SEG and structured metadata – this is non-negotiable for 2027+ AI diagnostics
The CBCT is no longer an imaging device – it is the central nervous system of the digital practice. Systems failing to deliver zero-friction data integration will become clinical liabilities by 2027.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
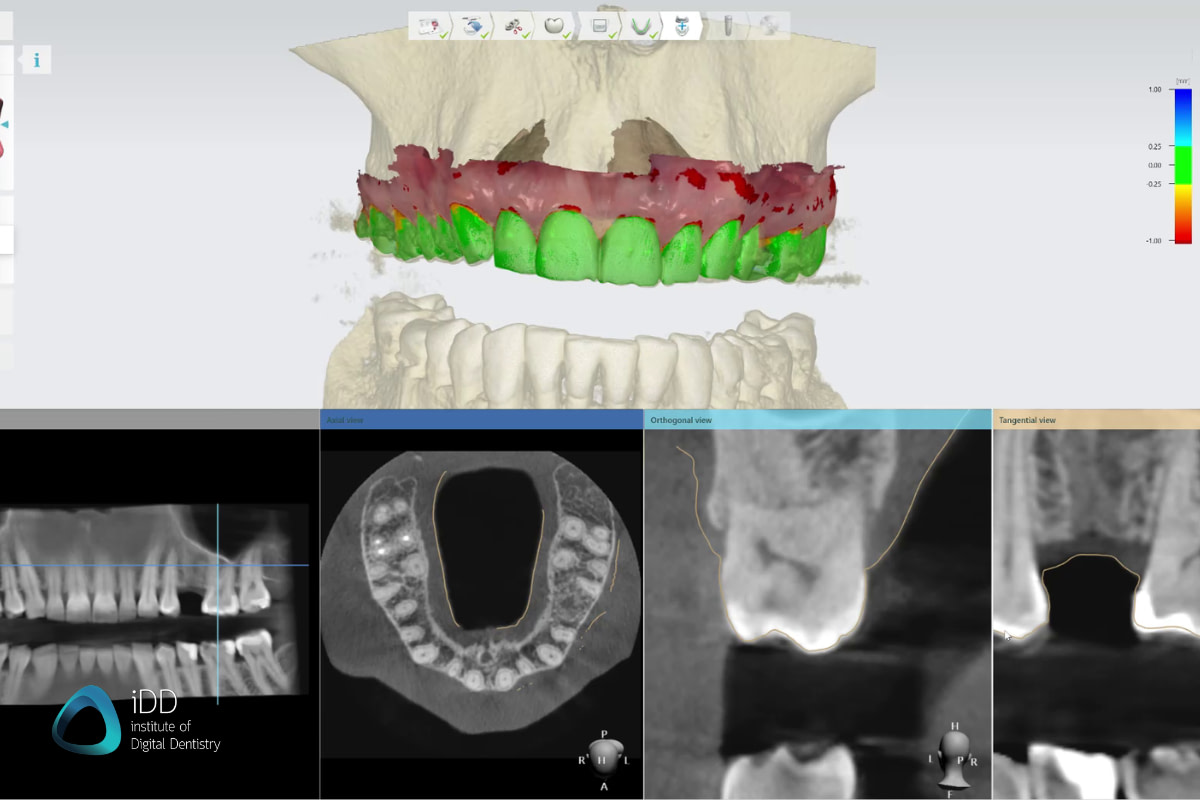
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital — Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Best Dental CBCT in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
In 2026, China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental imaging systems.
Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, where
advanced Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) systems are engineered with precision, reliability, and interoperability
at their core. This review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) pipeline for Carejoy’s flagship CBCT platform—recognized
for its AI-driven scanning, open architecture compatibility, and superior cost-performance ratio.
1. Manufacturing Ecosystem: Precision Engineering Under ISO 13485
Carejoy Digital’s CBCT systems are produced in a vertically integrated, ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai.
This certification ensures compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems, covering design,
development, production, installation, and servicing.
| Manufacturing Stage | Process Description | Quality Control Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-purity X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors, and low-noise CMOS sensors sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with traceable material certifications. | Supplier audits conducted quarterly; incoming inspection via automated optical and electrical validation. |
| Subassembly Integration | Modular construction of gantry, detector arm, and patient positioning system using robotic alignment systems. | Laser calibration checks at ±0.02° angular tolerance; torque-controlled fastening protocols. |
| Final Assembly | Integration of AI processing unit, open-architecture software stack (STL/PLY/OBJ), and touchscreen HMI in ESD-protected cleanrooms. | Full system burn-in test (48 hours); firmware integrity verification via cryptographic signing. |
2. Sensor Calibration & Imaging Accuracy: Dedicated Metrology Labs
Carejoy operates an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This lab is pivotal in ensuring
sub-millimeter spatial accuracy and consistent Hounsfield Unit (HU) linearity across all CBCT units.
- Flat-Panel Detector Calibration: Per-pixel gain and offset correction using NIST-traceable phantoms.
- Geometric Calibration: Multi-axis distortion correction via 3D calibration spheres (accuracy: ±20 µm).
- Dose Calibration: Real-time kVp/mA optimization using AI-driven exposure algorithms (Carejoy AI-Scan™).
- Phantom Validation: Daily QC using CatPhan® 503-equivalent dental phantoms to validate MTF, CNR, and spatial resolution (up to 75 lp/mm).
3. Durability & Environmental Stress Testing
To ensure reliability in diverse clinical environments, Carejoy subjects each CBCT unit to accelerated life testing protocols simulating 7+ years of clinical use.
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration & Shock | IEC 60601-1-2; 5–500 Hz, 3-axis, 10 cycles | No mechanical displacement; imaging alignment deviation < 0.1° |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +45°C over 72 hours | No sensor drift; HU stability within ±15 units |
| Continuous Scan Endurance | 1,000+ full-volume scans (8×8 cm FOV) | X-ray tube output stability ±3%; no thermal shutdown events |
| EMC/EMI Compliance | IEC 60601-1-2 Ed. 4.1 | No interference with adjacent dental devices (CAD/CAM, monitors) |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry hardware market is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally driven by four key advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, sensor, and precision mechanics manufacturers reduces BOM costs by 25–35% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities deploy AI-guided robotic assembly, reducing labor variability and increasing throughput.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest >12% of revenue into R&D, focusing on AI, low-dose imaging, and open interoperability.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA streamlines Class II/III device approvals, enabling faster iteration cycles (e.g., firmware updates every 6 weeks).
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver CBCT systems with 98% accuracy parity to premium German brands at 40% lower acquisition cost, redefining value in digital workflows.
5. Open Architecture & AI-Driven Scanning: Future-Proofing Clinical Integration
Carejoy CBCT systems support open file formats (STL, PLY, OBJ) and integrate seamlessly with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms.
The embedded AI engine enables:
- Automatic anatomy segmentation (mandible, sinuses, nerves)
- Dose modulation based on patient BMI and region of interest
- Real-time motion correction during scan acquisition
This open, intelligent architecture ensures compatibility with evolving lab and clinic ecosystems.
6. Global Support & Software Lifecycle Management
Carejoy Digital provides 24/7 remote technical support and bi-weekly software updates via secure OTA (Over-the-Air) channels.
All systems are monitored for predictive maintenance alerts, reducing downtime by up to 60%.
Email: [email protected]
Firmware Portal: firmware.carejoydental.com
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Best Dental Cbct.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
