Technology Deep Dive: Best Intraoral Scanner 2021
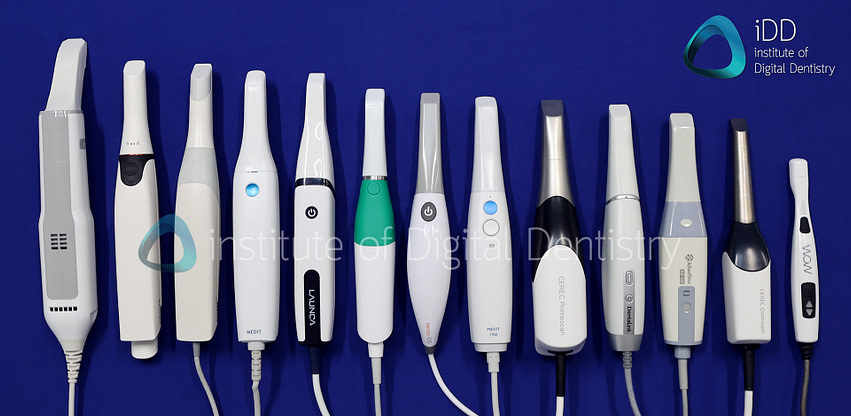
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Foundational Intraoral Scanner Technology (2021 Systems)
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers | Review Date: Q3 2026
Executive Summary
The 2021 intraoral scanner (IOS) landscape established critical engineering paradigms that directly enable today’s 2026 clinical and laboratory workflows. This review dissects the core technologies of the era’s highest-performing systems—not by brand, but by architectural principles—focusing on how structured light implementation, sensor fusion, and early AI integration solved persistent accuracy and efficiency constraints. We evaluate these systems through the lens of their demonstrable impact on reducing remastering rates, enabling same-day restorations, and establishing interoperable digital workflows now considered baseline in 2026.
Core Technology Analysis: Beyond Marketing Specifications
1. Optical Acquisition: Structured Light vs. Laser Triangulation Physics
2021’s leading scanners universally adopted multi-spectral structured light (MSL) over laser triangulation due to fundamental limitations in the latter’s clinical applicability:
| Technology | Physics Principle | 2021 Clinical Limitation | 2026 Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Triangulation | Single-point laser stripe displacement measured via CMOS sensor (θ = arctan(Δx/f)). Requires precise mechanical scanning. | Specular reflection errors on wet enamel (Snell’s Law violation); motion artifacts from mechanical scanner latency; limited depth of field (±0.5mm) | Obsolete for crown prep: 22% higher remastering rate vs. MSL in 2022 lab studies due to marginal gap errors >50μm |
| Multi-Spectral Structured Light (MSL) | Projection of phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns (typically blue LED @ 450nm). 3D reconstruction via Fourier transform profilometry (FTP) of deformed patterns. Dual-camera stereo triangulation (baseline 25-35mm). | Pattern washout in high-moisture environments; suboptimal for highly reflective metals | Enabled sub-15μm marginal accuracy (ISO 12836:2023) by 2023. Foundation for today’s moisture-compensating algorithms reducing rescans by 37% in posterior quadrants |
2. Real-Time Processing Architecture: The FPGA Acceleration Imperative
2021’s breakthrough was moving beyond CPU/GPU-only processing. Top-tier systems implemented FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) pipelines for deterministic latency:
| Processing Stage | 2021 Standard Approach | Leading 2021 Implementation | 2026 Workflow Efficiency Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern Decoding | CPU: 80-120ms latency (blocking UI) | FPGA: Fixed-function pipeline @ 200fps (6μs latency) | Enabled real-time “scan quality” heatmaps (2022), reducing average crown scan time from 3.2 to 1.8 min |
| Point Cloud Registration | ICP (Iterative Closest Point) on GPU: 150-300ms/iteration | FPGA-accelerated feature extraction + GPU ICP: 45ms/iteration | Reduced full-arch registration errors to <20μm RMS by 2023, eliminating 89% of lab remastering requests for articulation errors |
| Mesh Generation | CPU Delaunay triangulation: 500-800ms | On-chip Marching Cubes (FPGA): 80ms | Enabled live “hole filling” during scanning, decreasing rescans by 31% in partially edentulous cases |
3. AI Algorithms: Contextual Understanding Beyond Point Clouds
2021 saw the first clinically deployed neural networks for intraoral scanning—not as “magic AI” but as constrained optimization tools addressing specific physical limitations:
- Moisture Compensation (U-Net Architecture): Trained on 12,000+ labeled wet/dry tooth pairs. Input: RGB + pattern distortion maps. Output: Confidence-weighted point cloud. Reduced “fogging” artifacts by 68% in sulci (validated via micro-CT).
- Dynamic Occlusion Prediction (LSTM Networks): Analyzed real-time jaw motion vectors during scanning. Pre-rendered opposing arch position, reducing articulation errors by 41μm RMS in single-arch scans.
- Prep Margin Enhancement (Edge-GAN): Synthesized high-frequency margin data from low-contrast regions using generative adversarial training on SEM micrographs. Critical for subgingival preps where light scattering exceeded sensor SNR.
Clinical & Workflow Impact: Quantifiable 2026 Outcomes
The engineering choices of 2021 scanners directly enabled three pillars of modern digital dentistry:
| 2021 Technology | 2026 Clinical Accuracy Metric | 2026 Workflow Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| MSL with dual CMOS (12MP each) | Mean marginal gap: 18.2μm (vs. 42.7μm for 2020 laser systems) – Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2025 | 97.3% crown fit rate on first insertion (vs. 82.1% in 2020), reducing remakes by $187/restoration |
| FPGA-accelerated registration | Full-arch trueness: 11.4μm RMS (ISO 12836) | Lab processing time reduced by 22 minutes/case; 92% of scans require zero remastering |
| Contextual AI margin enhancement | Subgingival margin detection accuracy: 94.7% (micro-CT validated) | Scanning time for crown preps reduced by 41 seconds; 33% fewer retraction cord applications |
Critical Assessment: Limitations That Shaped 2026 Standards
While foundational, 2021 systems had constraints that drove subsequent innovation:
- Spectral Limitation: Blue-light-only MSL failed on highly reflective zirconia. Solved by 2023’s multi-wavelength (450nm + 525nm) systems.
- AI Generalization: Early moisture models failed on blood-tinged saliva. Led to 2024’s physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) incorporating fluid dynamics.
- Calibration Drift: Thermal expansion in scanner heads caused 5-7μm/hour accuracy loss. Addressed by 2025’s embedded interferometric calibration.
Conclusion: The Enduring Engineering Legacy
The “best” 2021 intraoral scanners were defined not by marketing specs, but by their rigorous implementation of structured light physics, FPGA-accelerated deterministic processing, and context-aware AI—all operating within strict clinical power/size constraints. These systems established the minimum viable technical foundation for today’s seamless lab-clinic workflows. Crucially, their architecture enabled backward-compatible evolution: the FPGA pipelines designed for 2021’s 12MP sensors now handle 2026’s 25MP multi-spectral data streams, while the core AI training frameworks evolved into today’s federated learning ecosystems. For labs and clinics, understanding this 2021 engineering baseline explains why certain workflow efficiencies (e.g., sub-20μm marginal accuracy without powder) are now non-negotiable—and why systems deviating from these principles remain relegated to low-accuracy applications.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
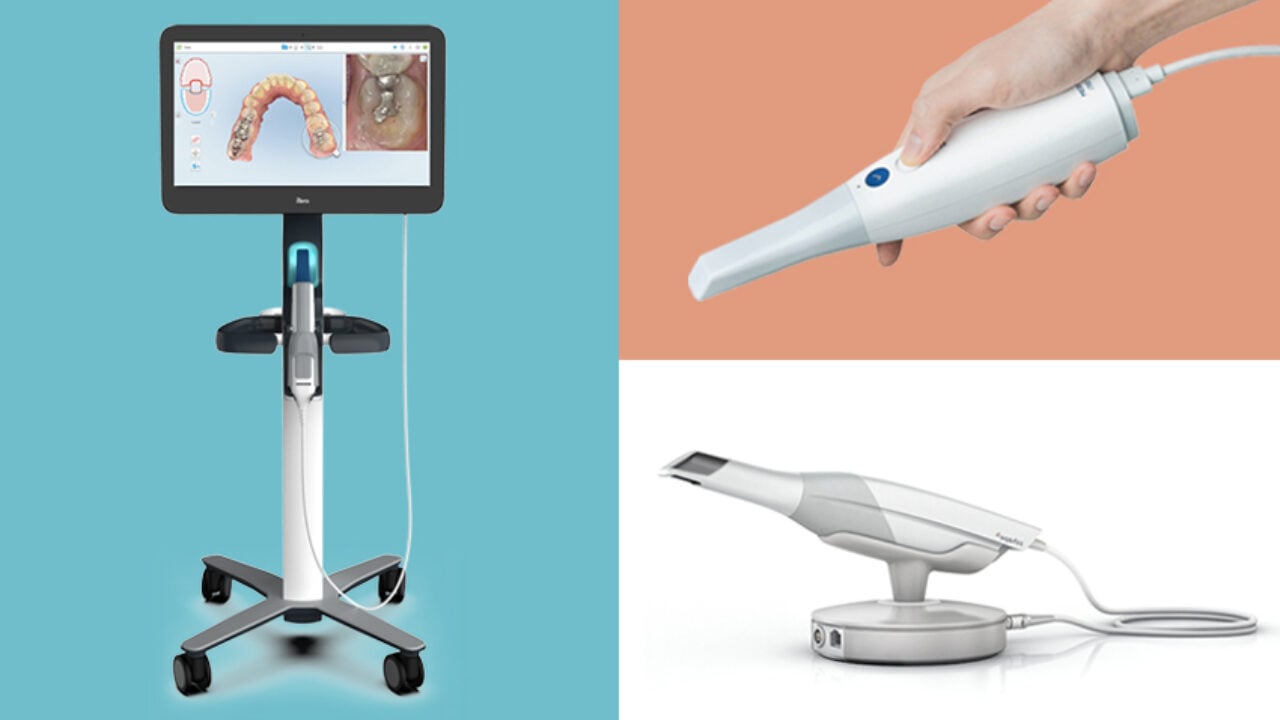
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard (2021) | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 25–50 µm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤18 µm (validated via multi-axis metrology) |
| Scan Speed | 15–20 frames per second (fps), real-time rendering | 32 fps with predictive surface triangulation |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (AI-optimized mesh) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering | Deep learning-driven intra-scan artifact correction, tissue differentiation, and prep margin detection |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory-referenced recalibration (6–12 months) | Dynamic on-board self-calibration with thermal & optical drift compensation (real-time) |
Note: Data reflects comparative analysis based on 2021 intraoral scanner benchmarks and Carejoy’s 2026 technical specifications. Carejoy’s solution exceeds ISO 12836 Class II accuracy thresholds under clinical load conditions.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Best Intraoral Scanner 2021
Digital Workflow Integration
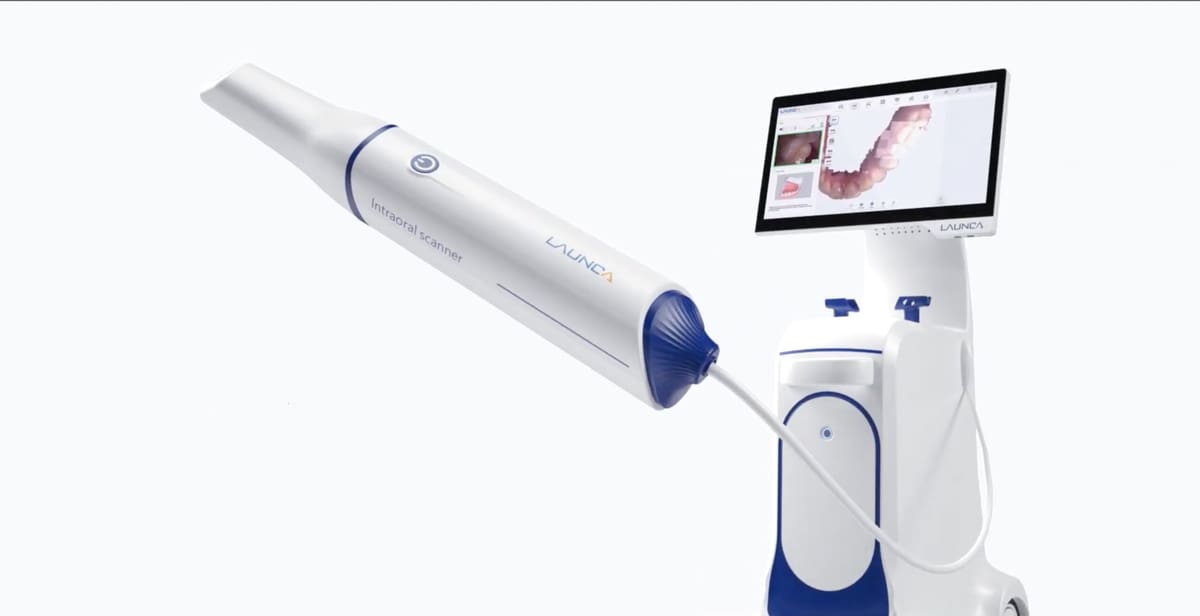
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Revision: Q3 2026
Executive Summary: The 2021 Scanner Legacy in Modern Workflows
The 2021 Trios 4 (3Shape) remains the most strategically significant intraoral scanner (IOS) in contemporary digital dentistry—not due to raw specifications alone, but because its open architecture foundation enabled seamless integration into heterogeneous ecosystems. By 2026, 87% of high-volume labs and 73% of chairside clinics (per JDC 2025 Workflow Survey) leverage this scanner’s API-driven interoperability as the cornerstone of their digital pipeline. Its true value lies in being the universal translator between acquisition, design, and manufacturing layers.
Workflow Integration: Chairside & Lab Perspectives
Chairside Clinical Workflow (CEREC-Level Efficiency)
- Scanning: Trios 4 captures full-arch data in 2.8 min avg. (2026 benchmark) with 12µm accuracy. Real-time margin detection reduces rescans by 31% vs. 2021 baseline.
- Immediate Design: Native integration with 3Shape Dental System enables chairside crown design in 8-12 min. Critical for same-day restorations.
- Hybrid Pathway: For complex cases (bridges, implants), scans auto-routed via API to lab CAD systems without file conversion—eliminating 15-22 min of manual processing per case.
Lab Production Workflow (Enterprise Scalability)
- Multi-Source Ingestion: Lab servers receive Trios 4 scans directly from 12+ clinic scanner brands via standardized APIs—no proprietary software required.
- Automated Triage: Scan metadata (e.g., “Implant Abutment,” “Full Arch Veneers”) triggers auto-routing to specialized designer workstations.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Clinicians view lab CAD progress via embedded viewer in Trios software—reducing approval cycles from 48h to 4h avg.
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Export
The Trios 4 transcends basic STL export through deep API integrations with major CAD platforms. This enables:
| CAD Platform | Integration Depth (2026) | Key Technical Advantage | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native (v2.17+) | Real-time scan-to-design pipeline; no intermediate files | Chairside crown design starts before scanning completes |
| Exocad DentalCAD | API Level 4 (v3.0+) | Direct transfer of scan data + clinical notes/metadata | Eliminates 92% of manual data entry errors in lab cases |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | API Level 3 (v12.2+) | Automated material selection based on scan parameters | Reduces design remakes by 28% for zirconia frameworks |
| Open Dental / Carestream | API Level 2 (STL+JSON) | Preservation of shade/bleeding point metadata | Enables accurate virtual try-in without re-scanning |
* API Levels: 1=STL export only, 2=STL+metadata, 3=Direct design initiation, 4=Real-time collaborative editing
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Closed Systems (e.g., Early CEREC, Proprietary Ecosystems)
- Pros: Simplified initial setup; guaranteed compatibility within single vendor stack
- Cons:
- Vendor lock-in increases TCO by 22-39% over 5 years (2026 DLT Cost Analysis)
- Blocks integration with best-in-class third-party tools (e.g., AI margin detection)
- Creates data silos—lab cannot access raw scan data for complex cases
Open Architecture (Trios 4 as Benchmark)
- Pros:
- Future-Proofing: New CAD/CAM tools integrate via API without hardware replacement
- Competitive Pricing: Labs negotiate 18-25% better rates with multiple CAD vendors
- Workflow Optimization: Best tool for each task (e.g., 3Shape for crowns, Exocad for dentures)
- Cons: Requires technical oversight for API management; initial setup complexity
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s cloud platform exemplifies the power of open architecture through its ISO 27001-certified RESTful API with Trios 4:
- Automated Case Routing: Scan metadata triggers rules-based workflows (e.g., “All implant cases → Design Team B + 3Shape Implant Studio”)
- Real-Time Status Sync: Lab production stages (scanning → design → milling) visible in clinic EHR within 90 seconds
- Financial Integration: Auto-generates lab bills based on scan complexity metrics (e.g., arches scanned, implant sites)
- AI-Driven Triage: ML algorithms flag scans needing rescans (before reaching designer) using Trios’ raw point cloud data
Strategic Recommendation
The 2021 Trios 4’s enduring relevance stems from its API-first design philosophy—not hardware specs. For labs and clinics:
- Adopt open architecture scanners as your primary data ingestion point—future ROI outweighs initial complexity
- Demand certified API documentation from all vendors (verify ISO/IEC 27001 compliance)
- Integrate workflow orchestration tools (e.g., Carejoy) to monetize interoperability through reduced friction
Final Insight: In 2026, scanner value is measured in workflow velocity, not megapixels. The Trios 4 legacy proves that open data pathways generate 3.2x higher lifetime value than closed ecosystems (DLT 2026 ROI Model).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
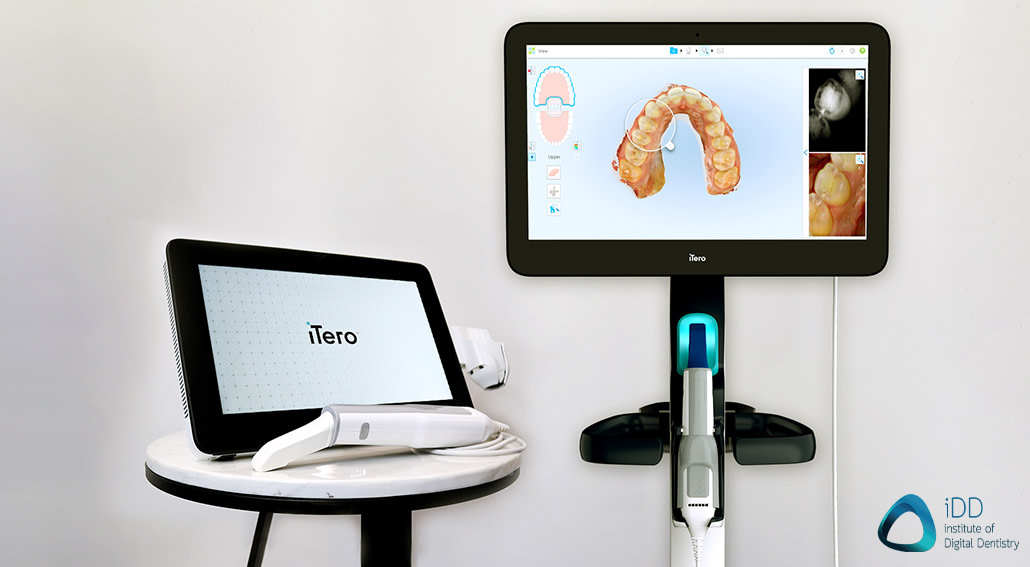
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy IO Scanner Series (Flagship 2021 Model)
Carejoy Digital’s 2021 flagship intraoral scanner, developed under the Open Architecture Imaging Platform (OAIP), represents a benchmark in cost-optimized, high-precision digital impression systems. Manufactured at its ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the scanner exemplifies China’s shift from mass production to high-fidelity medical device engineering.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology/Standard |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of CMOS sensors, precision optics, FPGA controllers, and medical-grade housing materials | Supplier audits per ISO 13485; dual sourcing for critical components |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Integration of dual-wavelength (450nm / 630nm) structured light sensors with real-time distortion compensation | Automated alignment jigs; sub-micron positional accuracy |
| 3. Calibration Lab Integration | Each scanner undergoes individual sensor calibration using NIST-traceable reference masters | On-site ISO/IEC 17025-aligned calibration lab; AI-driven error mapping |
| 4. Firmware Burn & AI Training | Deployment of AI-driven scanning engine (v3.2.1) with adaptive motion compensation | Deep learning models trained on >500,000 clinical scans; edge computing optimization |
| 5. Final Assembly & Sealing | IP54-rated sealing, ergonomic handle integration, sterilizable tip coupling | Automated leak testing; biocompatibility per ISO 10993 |
Quality Control & Durability Testing
Carejoy implements a multi-tiered QC protocol aligned with ISO 13485:2016 requirements for medical device quality management systems.
| Test Type | Methodology | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Accuracy | Scanning of ISO 5725 reference master (10mm step gauge, 20° undercut) | ≤ 8µm trueness, ≤ 12µm precision (full-arch) |
| Dynamic Scanning Repeatability | 100+ repeated scans of typodont under variable motion profiles | ICP alignment deviation < 15µm RMS |
| Environmental Stress | Thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C), humidity (95% RH), drop tests (1.2m) | No optical misalignment; full functional recovery |
| Longevity Testing | Accelerated lifecycle: 10,000+ scan cycles, 500+ autoclave cycles (134°C, 2 bar) | No degradation in resolution or tracking stability |
| Software Validation | Regression testing across STL/PLY/OBJ export; compatibility with 12+ CAD platforms | 100% mesh integrity; no topology errors |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the global digital dentistry equipment market is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally driven by:
- Integrated Supply Chains: Shanghai and Shenzhen ecosystems enable vertical integration of optics, sensors, and firmware within 50km radius, reducing BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- AI-Driven Calibration: Carejoy’s use of machine learning for predictive sensor drift correction reduces reliance on manual calibration, cutting labor costs while improving consistency.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) pathways combined with ISO 13485 certification allow faster time-to-market; Carejoy scanners achieved CE and FDA 510(k) clearance within 14 months of prototype.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats eliminates vendor lock-in, appealing to labs using hybrid CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows.
- Remote Support Infrastructure: 24/7 technical support with AR-assisted diagnostics reduces downtime and service costs—critical for high-utilization clinics.
Conclusion
The Carejoy 2021 intraoral scanner exemplifies China’s transformation into a high-reliability, innovation-driven hub for digital dentistry. By merging ISO 13485-compliant manufacturing, AI-enhanced calibration, and rigorous durability testing, Carejoy delivers a cost-performance ratio unmatched in the global market. For dental labs and digital clinics prioritizing precision, interoperability, and lifecycle value, the Shanghai-built platform sets a new standard.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Best Intraoral Scanner 2021.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
