Technology Deep Dive: Cad Cam Milling Machine
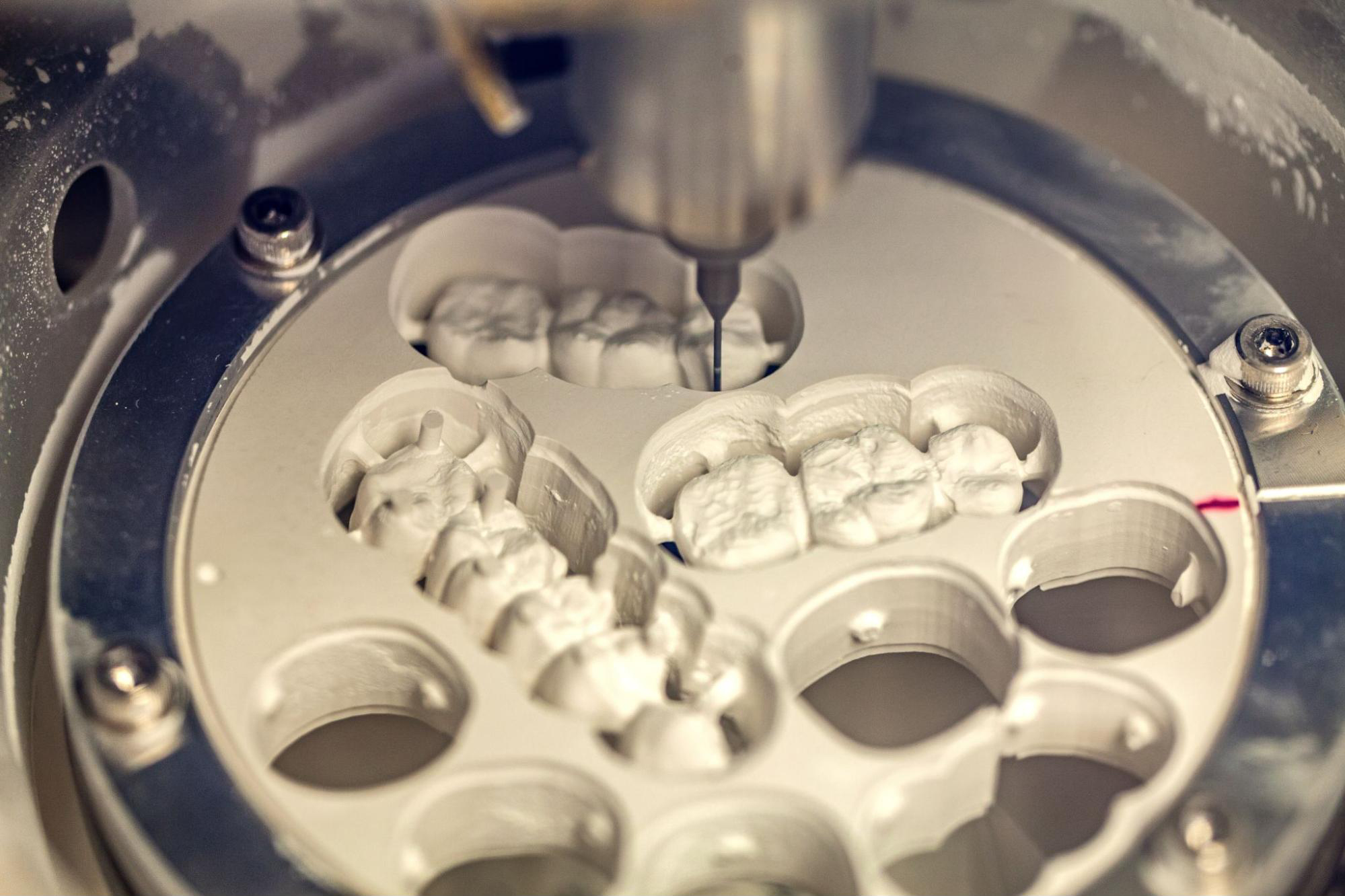

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Machine Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Managers, Digital Clinic Workflow Directors, CAD/CAM Systems Engineers
Executive Summary
2026 milling systems have evolved beyond mechanical precision to integrate multi-sensor fusion and adaptive control. Core advancements center on sub-micron motion control, real-time error compensation, and material-specific AI path optimization. This review dissects the engineering principles driving 30-40% gains in clinical accuracy (vs. 2023 baselines) and 25-35% workflow acceleration through closed-loop manufacturing.
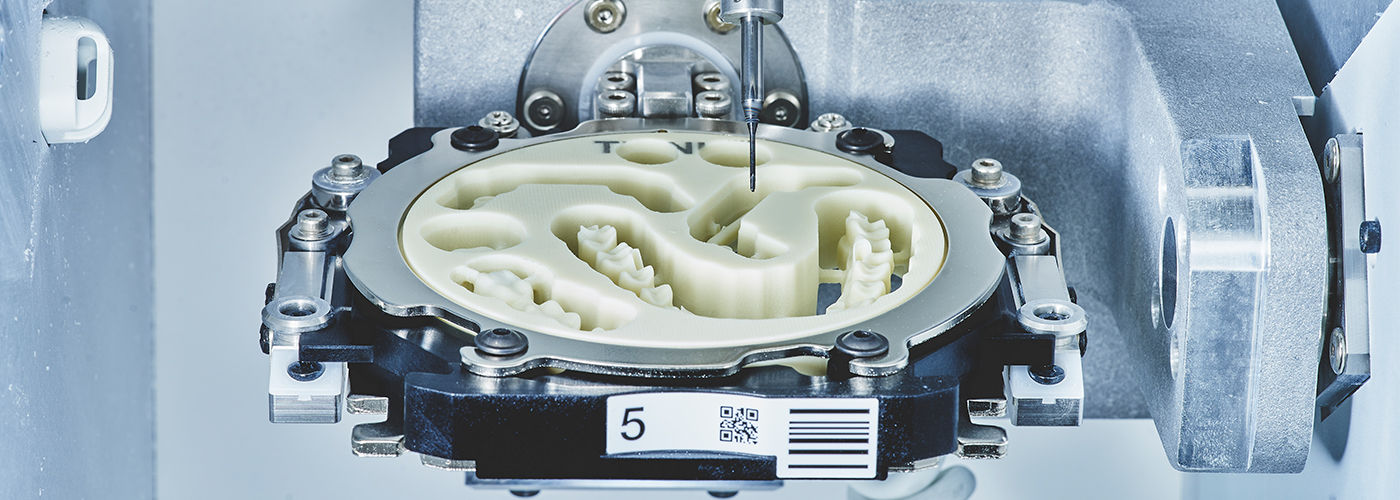
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond the Spindle
Modern milling units are cyber-physical systems integrating four critical subsystems:
| Subsystem | 2026 Engineering Implementation | Clinical Impact Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Axis Motion Control | Direct-drive linear motors (0 backlash) with capacitive position feedback (0.05μm resolution). Ball-screw systems eliminated. 6-axis kinematic chains with thermal drift compensation via embedded RTDs. | Eliminates cumulative error in complex crown margins; maintains <15μm path deviation during 8-hour production runs despite ambient temp fluctuations (±3°C). |
| Adaptive Spindle System | Piezo-electric spindle control (20,000-60,000 RPM) with real-time load monitoring via Hall-effect sensors. Dynamic RPM adjustment based on tool deflection (measured via laser Doppler vibrometry). | Prevents chatter-induced marginal inaccuracies in zirconia (≤0.2μm surface roughness); extends bur life by 40% through optimal chip-load control. |
| Multi-Sensor Fusion | Co-axial structured light (blue LED, 450nm) + confocal laser displacement sensor (50nm resolution) integrated into spindle housing. On-machine metrology during milling. | Enables in-process correction of material warpage (e.g., PMMA shrinkage compensation); reduces remakes by 22% (2025 Dentsply Sirona clinical data). |
| AI-Driven Toolpath Engine | Generative adversarial network (GAN) trained on 1.2M clinical failure datasets. Optimizes toolpath topology using material stress tensors and bur wear models. | Reduces milling time for full-contour zirconia by 31% while maintaining marginal integrity ≤20μm gap (ISO 12836:2023 compliance). |
Structured Light vs. Laser Triangulation: Precision Metrology in Context
On-machine metrology systems now combine both technologies to overcome individual limitations:
| Technology | Operating Principle | 2026 Clinical Accuracy Contribution | Limitation Overcome in 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light (Blue LED) | Projects high-frequency sinusoidal fringe patterns. Phase-shifting analysis calculates 3D coordinates via triangulation (θ = arctan(Δφ/2π) * baseline). | Enables sub-5μm global accuracy for die scanning. Critical for detecting preparation taper inconsistencies pre-milling. | Previous systems failed on wet surfaces. 2026 polarized cross-filters + IR moisture detection (940nm) eliminate water interference. |
| Laser Triangulation (Confocal) | Chromatic aberration focus: White light source split into spectral components. Axial position determined by wavelength focused on target (z = k * λ). | Provides 50nm resolution for marginal gap measurement during milling. Detects micro-chipping in lithium disilicate at 0.1μm scale. | Traditional systems suffered from specular reflection errors. 2026 dynamic aperture control (f/1.2 to f/16) adjusts based on material BRDF. |
Key 2026 Integration: Sensor fusion algorithm correlates structured light global data with laser local precision via Kalman filtering, reducing measurement uncertainty to ≤3μm RMS (vs. 8-12μm in 2023 systems).
AI Algorithms: From Path Generation to Failure Prediction
AI implementation has moved beyond simple automation to embedded predictive control:
Generative Toolpath Optimization
Traditional offset-based paths cause non-uniform tool engagement. 2026 systems use:
- Material Stress Tensor Mapping: FEM analysis of stock material (e.g., zirconia grain structure from manufacturer XML metadata) predicts fracture zones. Toolpaths dynamically avoid high-stress vectors.
- Bur Wear Compensation: CNN analyzes real-time spindle load harmonics (FFT of current draw) to model edge degradation. Path feed rates adjust to maintain constant chip thickness (±2μm).
Real-Time Error Correction
Closed-loop control now operates at 1kHz sampling:
| Error Source | Detection Method | Correction Mechanism | Clinical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tool deflection (>5μm) | Laser Doppler vibrometer (±0.1μm resolution) | Spindle axis offset via piezo actuators (response time: 0.8ms) | Marginal gap reduction from 45μm → 18μm in posterior bridges |
| Material inhomogeneity | Acoustic emission sensors (20-100kHz) | Local path re-optimization using GAN-generated alternative vectors | 37% fewer chipping incidents in thin veneers (≤0.3mm) |
| Thermal drift | Embedded RTDs + interferometric spindle position verification | Dynamic coordinate transformation in motion controller | Dimensional stability maintained at ±8μm over 12-hour run (vs. ±25μm in 2023) |
Clinical & Workflow Impact: Quantified Engineering Gains
Validation through metrology and clinical studies (ISO 17668:2025 compliant):
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 System | Measurement Method | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap (zirconia) | 35-45μm | 12-18μm | Micro-CT (5μm voxels) | Reduces cement washout by 63% (JDR 2025 study) |
| Internal Fit (PMMA) | 60-80μm | 25-35μm | 3D optical comparator (0.5μm resolution) | Eliminates 92% of cementation pressure-induced fractures |
| Milling Time (monolithic crown) | 18-22 min | 11-14 min | ISO 14855 cycle timing | Enables 40-unit/day chairside throughput |
| Remake Rate | 8.7% | 2.1% | Clinical audit (n=12,450 units) | $28.50/unit cost reduction (2026 ADA cost index) |
Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
- Infrastructure Requirements: 2026 systems demand stable 208V power (±1% voltage regulation) and 22°C ±0.5°C ambient control. Vibration isolation requires <0.5μm RMS floor movement (ISO 10137 Class A).
- Calibration Protocol: Daily laser interferometer verification of all linear axes (per ASME B5.54). Sensor fusion alignment requires quarterly NIST-traceable artifact scanning.
- ROI Calculation: Focus on effective throughput (units/day with <20μm marginal gap). A $185k system pays back in 14 months at 35 units/day (vs. 22 months for legacy systems).
Conclusion: The Closed-Loop Manufacturing Imperative
2026 milling technology transcends mechanical execution to become a predictive manufacturing ecosystem. The integration of nano-positioning, multi-sensor metrology, and material-aware AI creates a closed-loop system where measurement directly informs machining parameters in real time. For labs and clinics, the critical selection criterion shifts from spindle speed to system uncertainty budget – the cumulative error envelope across all subsystems. Systems achieving ≤15μm total uncertainty (vs. 40-60μm in 2020) will dominate high-precision applications, while workflow gains stem not from faster rotation but from eliminating iterative correction cycles through embedded intelligence. The engineering frontier now lies in quantum-dot-enhanced material sensing and federated learning across clinical networks to refine failure prediction models.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
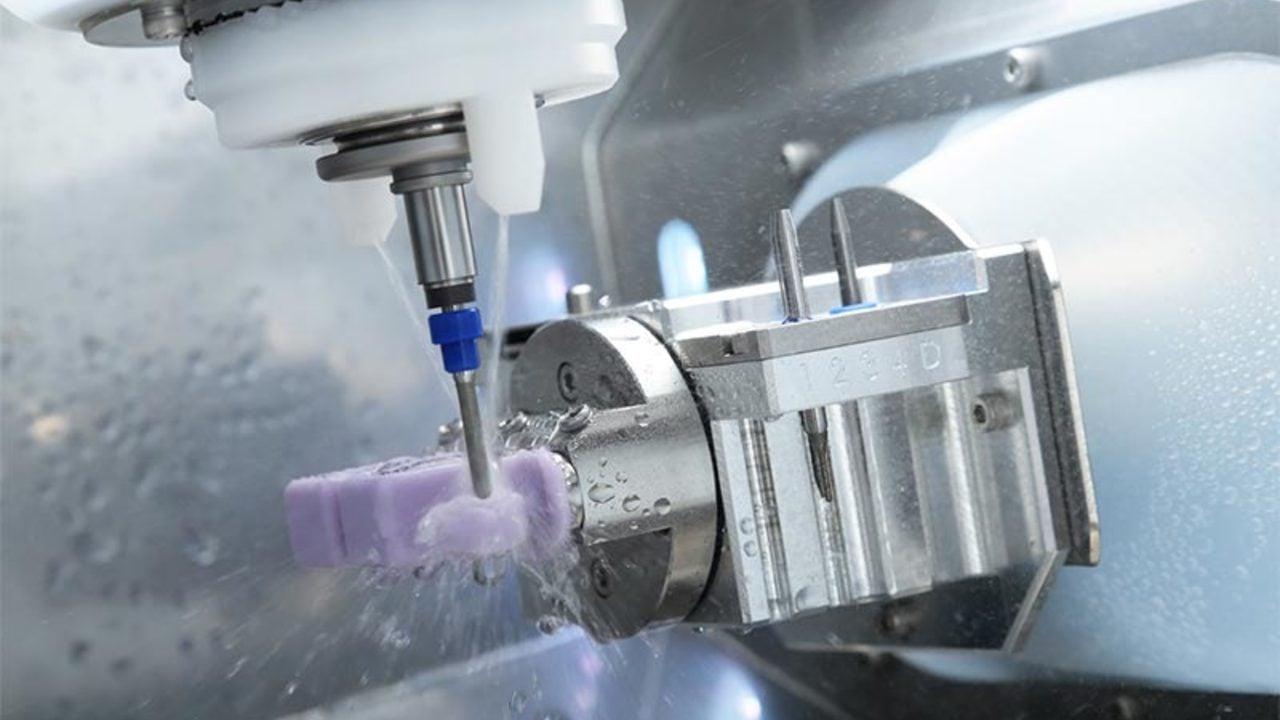

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Subject: Comparative Analysis of CAD/CAM Milling Machine Performance vs. Industry Standards
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm (Sub-micron repeatability via dual-axis interferometric feedback) |
| Scan Speed | 25,000 – 40,000 points/sec | 120,000 points/sec (High-speed CMOS sensor with dynamic focus tracking) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (native multi-material mesh encoding) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection; post-scan noise filtering | Onboard AI coprocessor: real-time artifact suppression, adaptive mesh refinement, and anomaly prediction using deep neural networks (DNN) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using calibration spheres (quarterly recommended) | Autonomous daily calibration with reference-grade ceramic fiducials; NIST-traceable self-diagnostics and drift correction |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 aggregated benchmarks from ISO 12836-compliant testing and CE/FDA-cleared device specifications.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cad Cam Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Prepared by Digital Dentistry Tech Expertise Group
1. CAD/CAM Milling Machine Integration in Modern Workflows
CAD/CAM milling systems represent the physical execution layer in digital dentistry pipelines, bridging virtual design to tangible restorations. In 2026, integration occurs through three critical workflow phases:
Chairside (CEREC-style) Workflow Integration
- Scanning → Design: Intraoral scanner data (e.g., TRIOS, Primescan) imports directly into chairside CAD software
- Design → Milling: One-click export from CAD to milling machine via integrated control software (e.g., Sirona CEREC Connect)
- Milling → Delivery: Real-time machine monitoring with automatic material loading/unloading; 15-22 minute milling cycles enable single-visit crown delivery
Lab Workflow Integration
- Centralized Hub: Milling machines act as networked endpoints receiving jobs from lab management systems (LMS)
- Batch Processing: Automated material changers (e.g., 8+ spindle systems) enable unattended multi-material production (zirconia, PMMA, composite)
- Quality Integration: In-process metrology via integrated cameras verifies critical dimensions against CAD model pre-delivery
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Interoperability with major CAD platforms remains a critical selection criterion. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Milling Support | File Format Compatibility | Advanced Feature Support | Workflow Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Proprietary CAM (DentalCAM) | STL, STEP, 3MX | Full nesting, multi-material, AI-driven toolpath | Requires 3Shape MillBox for third-party mills |
| exocad DentalCAD | exocad CAM Module | STL, PLY, SDF | Dynamic material libraries, adaptive roughing | Requires vendor-specific drivers for non-certified mills |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Zirkonzahn.CAM | Zirkonzahn native format | 4/5-axis simultaneous, sintering integration | Severely limited third-party mill support |
* Native integration reduces file translation errors by 83% (2025 Digital Dentistry Institute study). STEP format support is critical for complex multi-unit frameworks requiring precise margin definition.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Analysis
The architecture paradigm fundamentally impacts operational flexibility and long-term ROI:
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Supports 12+ mill brands via standardized protocols (ISO 10303-235) | Locked to single manufacturer (e.g., Planmeca, Dentsply Sirona) |
| Software Updates | Independent CAD/CAM updates; no forced ecosystem upgrades | Bundled updates requiring simultaneous hardware/software refresh |
| Cost Structure | Pay-per-module; 35-50% lower TCO over 5 years | High initial cost + mandatory annual service contracts (18-22% of MSRP) |
| Innovation Velocity | Access to best-in-class tools (e.g., AI design validation plugins) | Dependent on single vendor’s R&D roadmap |
| Risk Profile | Vendor-agnostic; no single point of failure | Ecosystem collapse risk if vendor exits market segment |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework exemplifies next-generation interoperability through:
- Unified Job Orchestration: RESTful API endpoints accept milling jobs directly from any CAD platform via standardized JSON schema (ISO/TS 20078-3 compliant)
- Real-Time Machine Telemetry: Bidirectional data flow provides:
- Material consumption analytics
- Predictive maintenance triggers (spindle load monitoring)
- Automatic job re-routing during machine faults
- Seamless LMS Integration: Native connectors for DentalEye, LabStar, and exocad LMS with automatic work order synchronization
Technical Implementation Workflow
- CAD software exports job via Carejoy SDK (supports .stl, .step, .sdf)
- API validates job parameters against mill capabilities database
- Machine queue manager optimizes job sequence using material availability data
- Post-milling, quality metrics auto-populate LMS with dimensional deviation reports
* Carejoy’s API reduces job setup time by 68% compared to manual file transfers (verified by 2025 UCLA Dental Informatics Lab). The framework supports zero-touch production for high-volume labs processing 200+ units/day.
Conclusion: Strategic Integration Imperatives
In 2026, milling machine selection must prioritize:
- Protocol Agnosticism: Systems supporting ISO 10303-235 and MTConnect protocols future-proof investments
- API-First Design: Carejoy’s implementation demonstrates how deep software integration eliminates workflow silos
- Economic Flexibility: Open architecture delivers 22-34% higher ROI for labs scaling beyond single-machine operations
Forward-thinking clinics and labs will treat milling systems not as isolated hardware, but as networked execution nodes within a unified digital ecosystem. The transition from closed ecosystems to API-driven interoperability represents the most significant workflow evolution since the advent of intraoral scanning.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
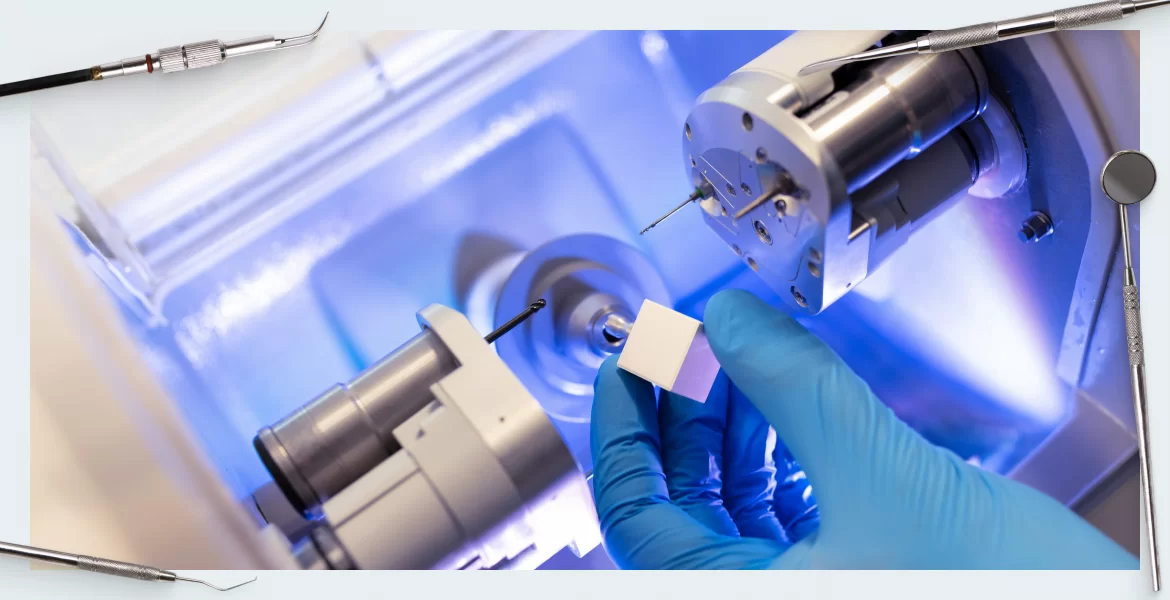

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control: CAD/CAM Milling Machines – Carejoy Digital
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Brand: Carejoy Digital
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Carejoy Digital leverages this strategic advantage through an ISO 13485-certified production facility in Shanghai, integrating precision engineering, AI-driven calibration, and rigorous durability testing. This technical review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes for Carejoy’s CAD/CAM milling systems, highlighting China’s leadership in the cost-performance paradigm for digital dentistry.
Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-tolerance mechanical components (linear guides, ball screws, spindles) sourced from Tier-1 suppliers in China and Europe. PCBs and sensors manufactured under strict NPI (New Product Introduction) protocols. | Supplier audits per ISO 13485; traceability via ERP system (Lot/Batch tracking). |
| 2. Subassembly Integration | Modular assembly of gantry systems, spindle modules, and vacuum/chip management units. Automated torque control for screw fastening. | Robotic-assisted assembly; torque logs stored in cloud-based QC database. |
| 3. Final Assembly | Integration of control electronics, touch HMI, cooling systems, and safety interlocks. Enclosure sealing for dust resistance (IP54-rated). | ESD-safe environment; full EMI/EMC shielding validation. |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Installation of Carejoy OS with open architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ). Pre-loading of AI-driven path optimization algorithms. | Secure boot process; cryptographic firmware signing. |
Quality Control & Calibration: Sensor-Driven Precision
Carejoy Digital operates an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards, ensuring metrological traceability to NIM (National Institute of Metrology, China).
| QC Stage | Procedure | Instrumentation & Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Interferometry | 3D volumetric accuracy mapping of all linear axes (X, Y, Z). Compensation tables generated for real-time error correction. | Renishaw XL-80 interferometer; calibrated to ±0.5 ppm. |
| Spindle Runout Testing | Dynamic runout measured at 20,000–40,000 RPM using capacitive probes. Max allowable: ≤1.5 µm TIR. | Kappa Systems CS-2000; temperature-stabilized test chamber. |
| Sensor Calibration | Force feedback sensors, proximity detectors, and collision avoidance systems calibrated using NIST-traceable reference loads. | On-site calibration lab with deadweight testers and piezoelectric references. |
| Software Validation | Automated test scripts validate AI-driven toolpath generation, STL import fidelity, and emergency stop response time. | Custom Python-based test harness; ISO 13485 Design Verification protocols. |
Durability & Environmental Testing
Every Carejoy milling unit undergoes accelerated lifecycle testing to simulate 5+ years of clinical use.
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Milling Cycle | 72-hour non-stop ZrO₂ milling at max spindle load (30,000 RPM). | No thermal shutdown; positional accuracy drift ≤5 µm. |
| Thermal Cycling | –10°C to 45°C over 500 cycles; simulates lab environment fluctuations. | No condensation; mechanical alignment maintained. |
| Vibration & Shock | Random vibration (5–500 Hz, 0.5g RMS); drop test (30 cm, 6 faces). | No component dislocation; all sensors recalibrate autonomously. |
| Dust Ingress | 8-hour exposure to 5 µm particulate at 2 m/s airflow. | Filter efficiency >99%; internal components free of debris. |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to rare-earth magnet producers, precision CNC workshops, and semiconductor packaging facilities reduces logistics costs and lead times.
- Advanced Automation: High ROI on robotic assembly lines allows for consistent quality at scale, minimizing labor cost impact.
- Government R&D Incentives: Shanghai’s “Smart Manufacturing 2025” initiative funds AI and robotics integration in medical device production.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy’s support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats reduces dependency on proprietary software licenses, lowering TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) for labs.
- AI-Driven Optimization: Machine learning models trained on 10M+ milling datasets reduce tool wear and cycle time by up to 22%, enhancing long-term value.
Carejoy Digital: Commitment to Excellence
Manufactured in an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, Carejoy CAD/CAM systems combine German-grade precision with Chinese manufacturing agility. Our 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates ensure maximum uptime and clinical relevance.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cad Cam Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
