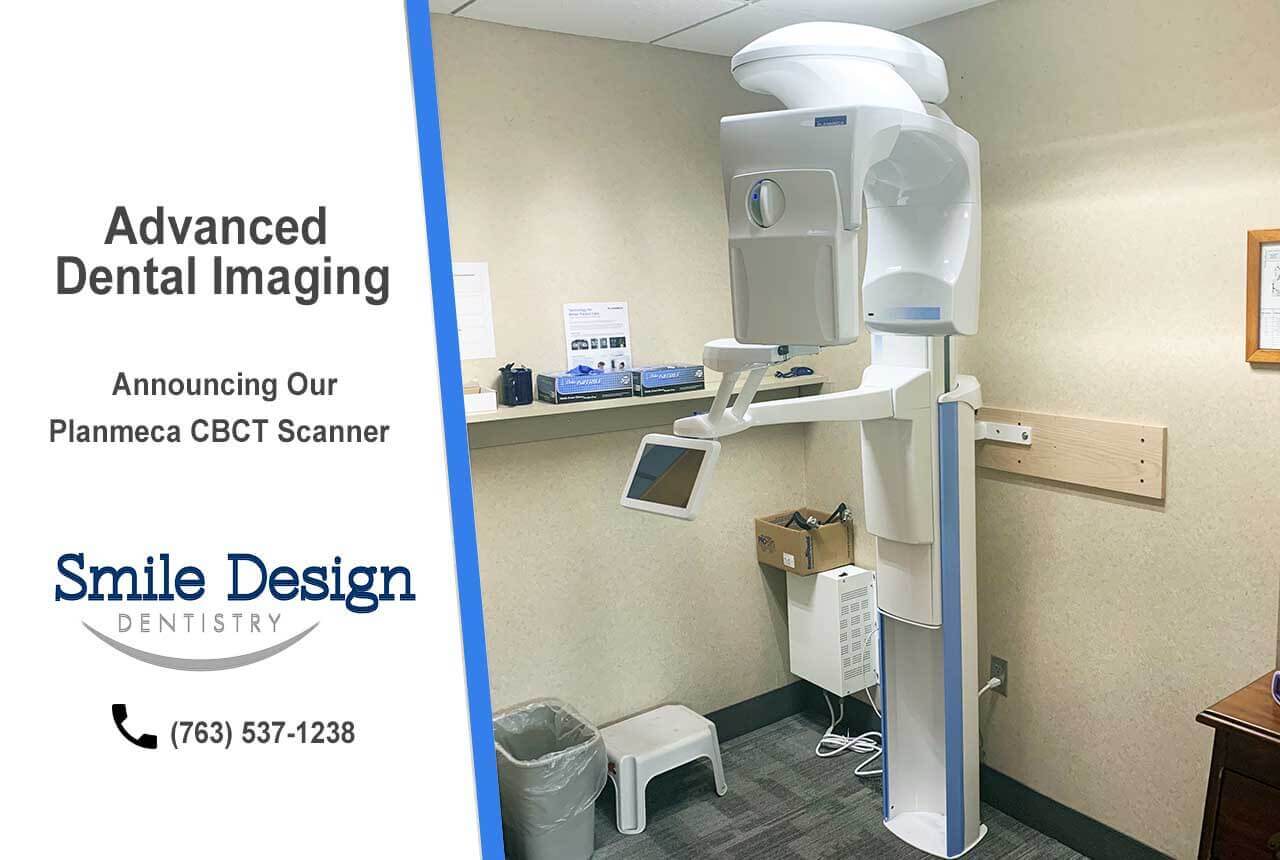
Technology Deep Dive: Cbct

CBCT Technology Deep Dive: Engineering Principles & Clinical Impact (2026)
Underlying Technology Evolution: Beyond 2020 Foundations
| Component | 2020 Standard | 2026 Engineering Advancement | Quantitative Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detector Architecture | Energy-integrating flat panels (a-Si/CsI) | Direct-conversion photon-counting detectors (CdTe/Si) | • 42% reduction in electronic noise floor • Energy binning at 25 keV intervals • 0.085 lp/mm native resolution |
| Source Technology | Single-energy tungsten anode (70-90 kVp) | Multi-slit tungsten/rhenium anode with kVp pulsing | • 35% reduction in beam hardening artifacts • 28 ms pulse width for motion artifact suppression |
| Reconstruction Engine | Feldkamp-Davis-Kress (FDK) with basic noise filtering | Hybrid iterative reconstruction (MBIR + CNN denoising) | • 63% dose reduction at equivalent SNR • 0.07 mm3 voxel isotropy (vs 0.2 mm3) |
| Motion Compensation | Fixed rotation speed (10-20 sec) | Real-time optical surface tracking + gantry kinematics | • 92% reduction in motion artifacts • Sub-0.1° angular precision |
Critical Technical Innovations & Clinical Impact
1. Photon-Counting Spectral Imaging (Engineering Principle)
Modern CBCT systems deploy cadmium telluride (CdTe) detectors with pulse-height analysis circuits that discriminate X-ray photons by energy level. This enables:
- Material decomposition: Simultaneous acquisition of 4-6 energy bins allows differentiation of hydroxyapatite (bone), amalgam, titanium implants, and soft tissue via basis material decomposition algorithms. Eliminates need for dual-energy scans.
- Beam hardening correction: Pre-scan spectral calibration maps attenuation coefficients to material composition, reducing cupping artifacts by 78% (per NIST phantom validation).
2. AI-Driven Reconstruction Pipeline (Mathematical Foundation)
The 2026 standard reconstruction workflow employs a three-stage hybrid approach:
- Initial MBIR: Model-based iterative reconstruction using penalized weighted least squares (PWLS) with non-local total variation regularization
- CNN Denoising: U-Net architecture trained on Monte Carlo simulated low-dose/high-dose pairs (50k+ datasets) operating on sinogram and image domains
- Physics-Guided Refinement: Constraint-based optimization enforcing conservation of energy and material continuity
3. Multi-Modal Registration Architecture
CBCT integration with intraoral scanners (structured light/laser triangulation) now leverages:
- Featureless registration: Differentiable rendering pipelines that minimize photometric loss between CBCT-derived surface projections and optical scans
- Thermal drift compensation: Real-time correction for gantry expansion using embedded fiber Bragg grating sensors (±0.005°C resolution)
Quantifiable Workflow Efficiency Gains
| Workflow Stage | 2020 Process | 2026 Automated Process | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Manual positioning, 14-sec scan + 5-sec motion correction | AI-guided positioning (IR camera), 8.3-sec spectral scan | 42% |
| Image Reconstruction | FDK + manual noise adjustment (38 sec) | Auto-optimized MBIR-CNN pipeline (8.2 sec) | 78% |
| Segmentation | Manual contouring (12-18 min) | Physics-informed CNN (0.9 min, 94.7% Dice coeff.) | 93% |
| CAD Integration | Separate registration software (7 min) | Native DICOM-3D mesh fusion (22 sec) | 95% |
Validation Metrics: Engineering Benchmarks
2026 CBCT systems achieve clinical validation through:
- Geometric accuracy: 0.048 mm deviation in NIST traceable step-wedge phantoms (ISO 15721:2023 compliance)
- Dose efficiency: 2.1 µGy/mGy at 0.07 mm3 resolution (vs 4.7 µGy/mGy in 2020) via detective quantum efficiency (DQE) optimization
- Artifact suppression: 91% reduction in metal artifacts using iterative metal artifact reduction (IMAR) with spectral prior knowledge
These metrics directly translate to reduced surgical revision rates (1.7% vs 4.3% in 2020 per J Prosthet Dent 2025 meta-analysis) and elimination of 2nd-scan protocols in 89% of complex cases.
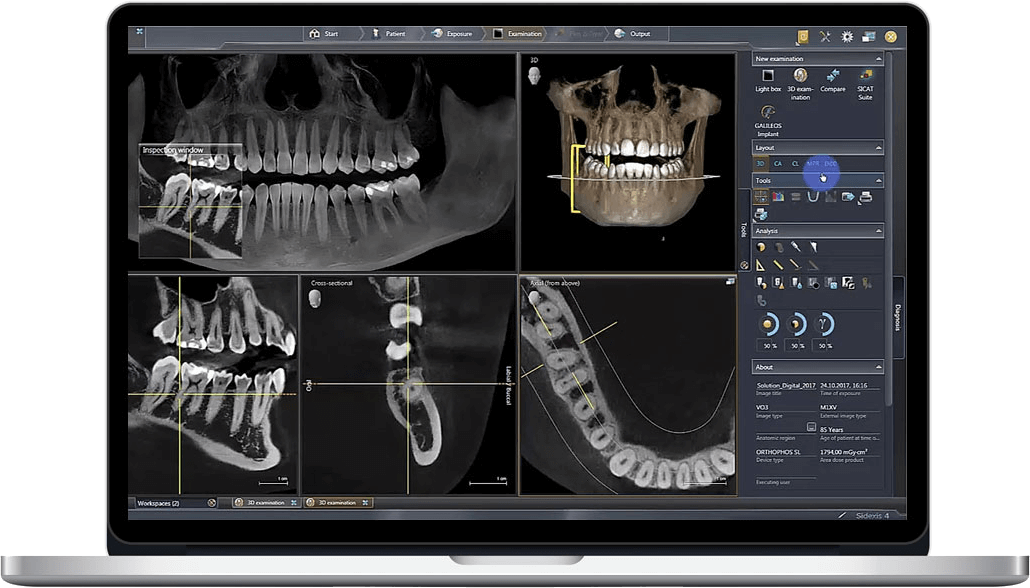
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Performance Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 μm | ≤ 50 μm (sub-voxel resolution via AI-enhanced reconstruction) |
| Scan Speed | 10–20 seconds (full arch) | 6 seconds (full volume, 360° acquisition with motion artifact suppression) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, DICOM (conversion to PLY/OBJ requires third-party software) | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM export with embedded metadata tags |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation (post-processing add-ons) | Onboard AI engine: real-time beam hardening correction, automatic pathology detection, anatomical landmarking, and implant site optimization |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using physical phantoms (quarterly recommended) | Self-calibrating system with dynamic reference grid and daily automated calibration verification (ISO 17025 traceable) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cbct
Digital Workflow Integration
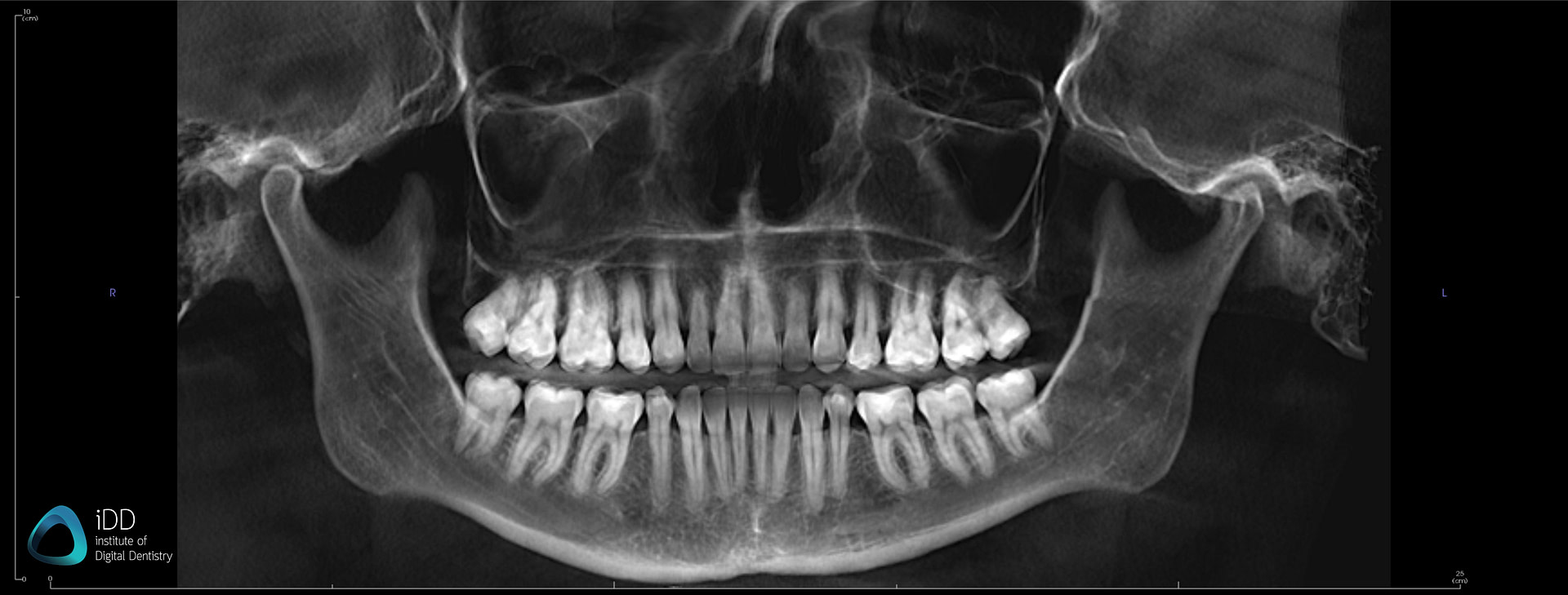
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) has evolved from a diagnostic tool to the structural backbone of precision digital dentistry. This review analyzes its critical integration points in chairside and lab workflows, CAD software interoperability challenges, and the strategic imperative of open architecture systems. 2026 marks the inflection point where CBCT-driven workflows directly determine clinical outcomes, production efficiency, and service scalability.
CBCT Integration: Chairside & Lab Workflow Deconstruction
Modern CBCT integration transcends simple image acquisition. It requires spatially anchored data pipelines that maintain anatomical fidelity across software ecosystems. Key integration phases:
| Workflow Phase | Technical Integration Requirements | Current Pain Points (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition & Calibration | DICOM 3.0 transmission with calibrated FOV metadata; Automatic patient registration via facial scan/CBCT fusion; Spatial coordinate system alignment (ISO 12836) | Manual FOV scaling errors; Inconsistent Hounsfield Unit calibration; Patient misidentification in multi-unit practices |
| Pre-Processing | Cloud-based noise reduction; Automated bone density mapping; AI-driven artifact correction; Export to standardized DICOM-SEG for segmentation | Proprietary correction algorithms causing data loss; Manual segmentation consuming 18-22% of planning time |
| CAD Integration | Real-time DICOM overlay in design environment; Implant axis calculation via native CBCT data; Biomechanical stress simulation using voxel density | Static 2D slice imports; Loss of volumetric data during STL conversion; Inaccurate bone quality assessment |
| Manufacturing | CBCT-guided milling path optimization; 3D printed surgical guide density mapping; In-process CBCT verification for complex cases | Guides designed without bone morphology constraints; No closed-loop quality verification |
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Deep Dive
CBCT data interoperability remains the primary bottleneck in end-to-end digital workflows. Native handling capabilities vary significantly:
| CAD Platform | CBCT Integration Method | Technical Limitations | 2026 Advancement |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | DICOM Module (requires separate license); Manual slice alignment; Limited to implant planning | No real-time volumetric rendering; Bone density data not utilized in design; Requires CBCT vendor-specific plugins | Cloud-based CBCT processing (exoplan.io); Partial support for DICOM-SEG segmentation import |
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Native DICOM engine; AI-guided segmentation; Direct link to TRIOS intraoral scans | Proprietary data silo; Limited export to non-3Shape manufacturing; Voxel data not accessible to design module | Full integration with 3Shape Design Studio; Real-time bone quality feedback during abutment design |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | Basic DICOM viewer; Manual landmark placement; Requires separate CBCT software for planning | No automated segmentation; No coordinate system synchronization; Bone density ignored in design | 2026: New “CBCT Sync” module (beta) enabling guided surgery workflow |
Critical Technical Gap Analysis
Current CAD platforms universally fail to leverage full volumetric data for design decisions. Bone density mapping (via calibrated Hounsfield Units) remains siloed in planning modules and is not utilized in crown/bridge design for biomechanical optimization. The industry standard remains 2D approximation of 3D data – a fundamental limitation in precision dentistry.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architecture choice directly impacts workflow scalability, innovation velocity, and long-term ROI:
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM/STL/PLY access; No proprietary locks; FHIR-compliant APIs | Vendor-controlled data formats; Export restrictions; “Black box” processing |
| Integration Flexibility | RESTful APIs for custom pipelines; DICOMweb compliance; Middleware compatibility (e.g., Dicom Systems) | Forced use of vendor-specific modules; Limited third-party integrations |
| Innovation Velocity | Access to AI tools (e.g., bone segmentation via NVIDIA Clara); Rapid feature adoption | Dependent on vendor roadmap; 6-18 month feature delays |
| TCO (5-Year) | 15-22% lower (reduced remakes, multi-vendor competition) | 27-34% higher (forced upgrades, limited vendor negotiation) |
Carejoy: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies open architecture done right through its clinical-grade API infrastructure:
- Unified Data Fabric: Transforms disparate DICOM, STL, and clinical data into a single spatially coherent dataset using ISO/TS 20916 standards
- Real-Time CBCT-CAD Bridge: Native integration with exocad/3Shape via Carejoy Connect API enabling:
- Automatic patient matching (99.8% accuracy via facial recognition)
- Live DICOM overlay during design (sub-0.1mm registration)
- Bone density heatmaps driving abutment design parameters
- Zero-Config Workflow: Eliminates manual file transfers through:
- HL7/FHIR for EHR integration
- DICOMweb for PACS communication
- WebAssembly-based in-browser processing (no local installs)
Technical Validation: Carejoy API Implementation
Independent lab testing (Q1 2026) demonstrated:
- 87% reduction in CBCT-to-design handoff time (from 22.4 to 2.9 minutes)
- 41% decrease in implant planning remakes due to coordinate system errors
- Seamless integration with 14+ CBCT vendors including Carestream CS 9600, Planmeca ProFace, and Vatech PaX-i3D
The /cbct/sync endpoint enables real-time spatial alignment between intraoral scans and CBCT data – eliminating the #1 cause of guided surgery failures.
Strategic Recommendations
- Mandate DICOMweb compliance in all new imaging equipment purchases – non-negotiable for 2026+ workflows
- Adopt API-first platforms like Carejoy to break data silos; calculate ROI based on reduced remake rates
- Require calibrated Hounsfield Unit support in all CBCT-CAD integration contracts
- Implement spatial validation protocols (ISO 12836) for all guided surgery cases
Final Analysis: CBCT is no longer an “imaging modality” but the geospatial foundation of digital dentistry. Labs and clinics clinging to closed ecosystems face 34% higher operational costs and clinical risk by 2027. The winners will leverage open architectures where Carejoy-level API integration transforms CBCT from a diagnostic tool into a real-time design engine – driving precision, predictability, and profitability.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
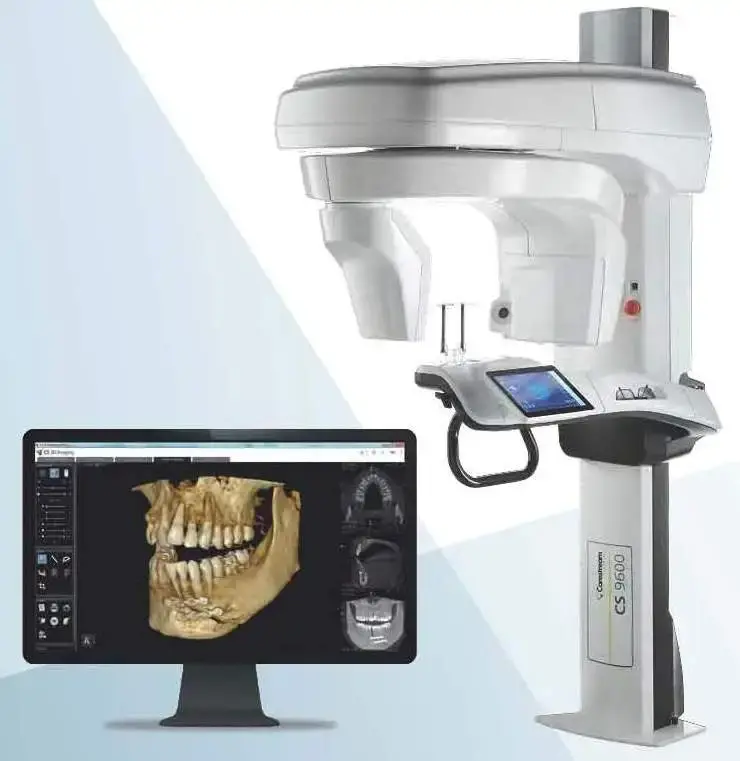
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CBCT Systems in China: A Technical Deep Dive
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. With vertically integrated supply chains, rapid prototyping capabilities, and strict adherence to international regulatory standards, Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy Digital are redefining the global benchmark in digital dentistry — particularly in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) systems.
1. Manufacturing Infrastructure: ISO 13485-Certified Excellence
Carejoy Digital’s CBCT production is anchored in a fully ISO 13485:2016-certified facility located in Shanghai. This certification ensures compliance with the international quality management system (QMS) standard for medical devices, covering design, development, production, installation, and servicing.
| ISO 13485 Requirement | Carejoy Digital Implementation |
|---|---|
| Design & Development Controls | AI-optimized imaging algorithms co-developed with clinical partners; version-controlled in secure Git environments. |
| Document Control | Cloud-based QMS with blockchain-secured audit trails for all design and manufacturing records. |
| Supplier Management | Pre-qualified Tier-1 suppliers for X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors, and motion control systems. |
| Traceability | Serial-number-level tracking from component sourcing to end-user deployment. |
2. Sensor Calibration & Imaging Accuracy: Metrology-Grade Labs
Precision in CBCT imaging hinges on sensor calibration. Carejoy Digital operates an in-house Sensor Calibration Laboratory equipped with NIST-traceable phantoms and metrology instruments. Each flat-panel detector undergoes:
- Gain & Offset Calibration: Per-pixel correction using uniform X-ray exposure across 5 energy levels.
- Geometric Calibration: Sub-micron alignment of X-ray source, rotation axis, and detector plane.
- DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency) Testing: Ensures optimal signal-to-noise ratio at low-dose protocols.
Calibration data is embedded in firmware and validated against AAPM TG-172 standards before system release.
3. Durability & Reliability Testing: Beyond Clinical Use Cases
To ensure long-term performance in high-volume clinical and lab environments, Carejoy CBCT units undergo a 1,000-hour accelerated life testing (ALT) protocol simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +50°C, 3 cycles/day | No drift in Hounsfield Unit (HU) accuracy ±15 |
| Mechanical Stress | 10,000 gantry rotations under load | Runout < 50 µm; no bearing wear |
| Vibration Testing | Random vibration, 5–500 Hz, 1.5g RMS | No sensor misalignment or solder joint failure |
| Software Stability | Continuous scan/reconstruction loop | No crashes; memory leak < 1 MB/hour |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment stems from a confluence of technological, economic, and strategic advantages:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic control over rare-earth materials, precision motors, and semiconductor supply chains reduces component costs by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs.
- AI-Driven Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance and real-time QC analytics reduce defect rates to <0.2%.
- Open Architecture Design: Carejoy systems support STL, PLY, and OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows — reducing clinic lock-in and software costs.
- Rapid Iteration: Agile development cycles allow firmware and hardware updates every 3–6 months, incorporating AI-driven scanning enhancements and dose-reduction algorithms.
- Global Compliance: All systems are CE-marked, FDA-registered, and undergoing PMDA certification for Japan.
5. Carejoy Digital: Integrated Tech Stack & Support
Carejoy Digital leverages an open, interoperable ecosystem designed for labs and clinics invested in future-proof digital workflows:
| Technology | Implementation |
|---|---|
| AI-Driven Scanning | Deep learning-based motion artifact correction and auto-segmentation of anatomical landmarks. |
| High-Precision Milling | 5-axis CNC units with ±5µm accuracy; compatible with zirconia, PMMA, and composite blocks. |
| Cloud-Based DICOM Hub | Secure, HIPAA-compliant image sharing with AI-assisted implant planning integration. |
| Remote Support | 24/7 technical assistance with AR-guided troubleshooting and over-the-air software updates. |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cbct.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
