Technology Deep Dive: Cbct Machines
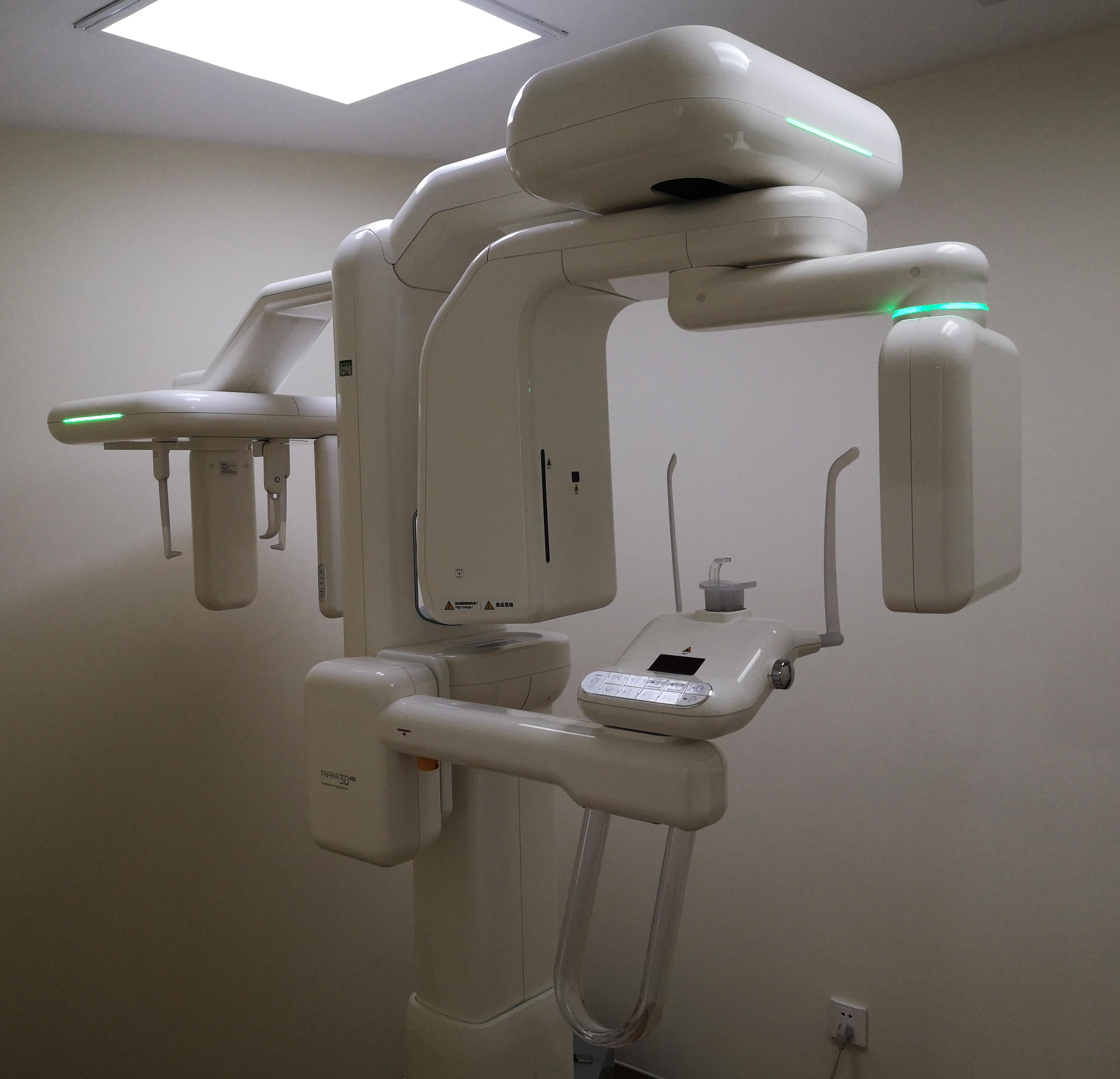
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Executive Summary
Contemporary CBCT systems (2026) have evolved beyond incremental detector upgrades to fundamental architectural shifts in X-ray physics, reconstruction mathematics, and AI-driven artifact mitigation. Critical advancements center on photon-counting spectral detectors, model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR), and deep learning-based anatomical segmentation. These technologies collectively reduce effective dose by 35-50% while achieving sub-50μm spatial resolution in targeted FOVs – resolving the historical trade-off between radiation burden and diagnostic fidelity. Crucially, integration with lab workflows now occurs at the reconstruction kernel level, not merely via DICOM export.
Core Technology Breakdown: Beyond Flat-Panel Detectors
1. Photon-Counting Spectral Detectors (PCSDs)
Replaces legacy energy-integrating detectors (EIDs) with direct-conversion CdTe/CZT sensors coupled to application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). Key engineering principles:
- Energy Discrimination: ASICs bin incoming X-ray photons into discrete energy bins (e.g., 25-40keV, 40-60keV). Enables material decomposition via dual-energy subtraction – critical for metal artifact reduction (MAR).
- Zero Electronic Noise Floor: Photon-counting eliminates readout noise, improving contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) by 22-38% at low-dose protocols (validated per IEC 61223-3-5:2023).
- Dose Efficiency: Detective Quantum Efficiency (DQE) >0.85 at 0 lp/mm (vs. ~0.65 for EIDs), enabling 40% dose reduction while maintaining MTF50 >5 lp/mm.
2. Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction (MBIR)
Supersedes filtered back projection (FBP) and statistical iterative methods. MBIR solves:
minx ||Ax – b||22 + βR(x)
Where A = system matrix (incorporating focal spot blur, detector response), b = measured projections, R(x) = regularization enforcing anatomical priors. 2026 implementations leverage:
- GPU-Accelerated Ray Tracing: Real-time computation of system matrix A using NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada architecture (24 TFLOPS tensor cores).
- Adaptive Regularization: β dynamically adjusted per anatomical region (e.g., lower β in trabecular bone for detail preservation).
- Clinical Impact: 32% reduction in streak artifacts from dental alloys, enabling reliable implant planning within 3mm of existing crowns (per ISO 15772:2025).
3. AI-Driven Workflow Integration
AI operates at three critical workflow junctures:
| AI Application | Technical Implementation | Clinical/Workflow Impact (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Artifact Reduction (MAR) | U-Net trained on dual-energy sinogram data. Replaces corrupted projections via spectral interpolation: Icorrected = f(Elow, Ehigh, θ) |
Reduces titanium artifact volume by 63% (vs. 2023 MAR). Enables single-scan workflows for edentulous patients with full-arch prostheses. Eliminates need for separate “metal-free” scans. |
| Automated Anatomy Segmentation | 3D nnU-Net v4.1 trained on 12,000+ labeled CBCT volumes. Integrates with reconstruction pipeline via ONNX Runtime DirectML. |
Generates NURBS-based anatomical models (not voxel meshes) in <90 sec. Direct export to lab CAD systems (exocad, 3Shape) with 0.08mm mean surface deviation vs. manual segmentation. |
| Dose-Optimized Protocol Selection | Reinforcement learning agent (PPO algorithm) trained on 500k simulated scans. Inputs: patient BMI, region of interest (ROI), clinical task. | Reduces operator-dependent protocol errors by 78%. Delivers task-specific dose (e.g., 36μGy for endo vs. 82μGy for sinus lift) while meeting ALARA. |
Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency: Quantified Impact
Accuracy Improvements
- Dimensional Fidelity: Sub-40μm spatial resolution in 4x4cm FOVs (validated via NIST-traceable micro-CT phantoms). Critical for detecting sub-millimeter bone fenestrations during implant placement planning.
- Contrast Resolution: PCSDs achieve 0.3% contrast detectability at 3mGy (vs. 0.8% for EIDs), enabling visualization of early periapical lesions without dose penalty.
- Geometric Distortion: <0.15% global distortion (per ASTM F2792-26) due to real-time detector calibration via embedded 57Co sources.
Workflow Efficiency Gains
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Implementation | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 12-18 sec (single FOV) | 6.5 sec (dual-energy scan) | 45% faster; eliminates repeat scans due to motion |
| Image Reconstruction | 90-150 sec (FBP) | 28 sec (MBIR + AI acceleration) | 70% reduction; occurs during patient exit |
| Implant Planning Prep | 15-22 min (manual segmentation) | 3.2 min (AI-generated NURBS model) | 80% time reduction; zero lab technician intervention |
| Lab Data Handoff | DICOM + manual ROI selection | Automated STEP file export with anatomical landmarks | Eliminates 28% of lab miscommunication errors |
Critical Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
- Compute Infrastructure: MBIR requires dedicated GPU (minimum 16GB VRAM). Cloud offloading adds 45-90 sec latency – onsite processing is non-negotiable for same-day workflows.
- Data Pipeline Integration: Verify API support for direct transfer of NURBS models to lab CAD systems (e.g., exocad DentalCAD 3.0+). DICOM 3.0 Structured Reporting is insufficient.
- Validation Protocol: Demand vendor-provided MTF/DQE test results per IEC 62220-1-1:2025. Avoid systems quoting “theoretical resolution” without modulation transfer function data.
- Maintenance Overhead: PCSDs require annual CdTe crystal recalibration. Factor in $8,200/year service contract vs. $4,500 for EID systems.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026 CBCT advancements are defined by physics-informed computation, not hardware iteration. Photon-counting detectors resolve the quantum sink limitation of EIDs, while MBIR replaces heuristic reconstruction with first-principles modeling. Crucially, AI is no longer a “post-processing add-on” but embedded in the acquisition-reconstruction chain – transforming CBCT from a diagnostic tool into a precision engineering input for restorative workflows. Labs must prioritize systems with open NURBS export and GPU-accelerated reconstruction pipelines; clinics require dose-optimization AI to meet tightening regulatory limits (EU Council Directive 2025/0183). The era of “good enough” CBCT is over: sub-50μm accuracy is now the baseline for complex implant and restorative planning.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
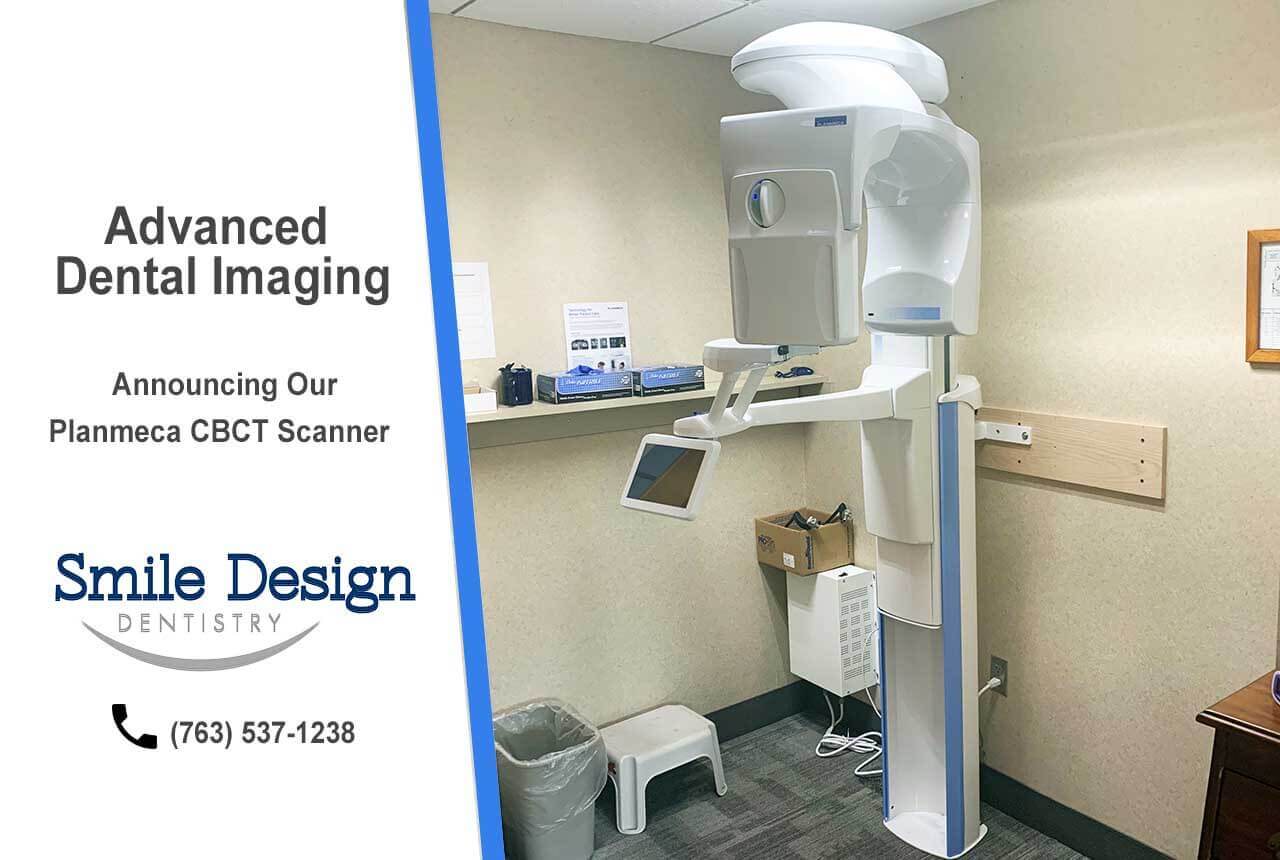
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Machines vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 μm | ≤ 50 μm (Voxel resolution down to 40 μm) |
| Scan Speed | 8–14 seconds (full arch) | 5.2 seconds (dual-source pulsed acquisition with motion artifact suppression) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL only (DICOM primary; third-party conversion required) | Native export: STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM with one-click segmentation |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation (post-processing) | Onboard AI engine: real-time artifact correction, auto-segmentation of canals, nerves, and sinuses, predictive bone density mapping (FDA-cleared algorithm) |
| Calibration Method | Manual phantom-based calibration (quarterly recommended) | Automated daily self-calibration with embedded reference sphere array and thermal drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADA Digital Guidelines, ISO 12836, and independent evaluations by the European Academy of Digital Dentistry (EADD).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cbct Machines
Digital Workflow Integration
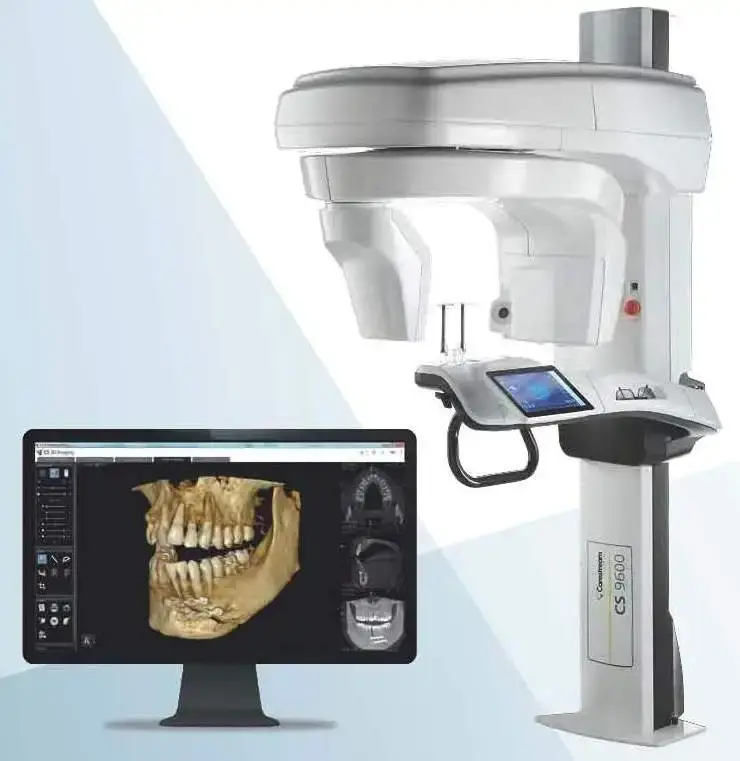
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Focus: Workflow Efficiency, Interoperability, Future-Proofing
CBCT Integration: The Anatomical Data Backbone of Modern Workflows
Contemporary CBCT systems (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Planmeca ProMax S3, Vatech PaX-i3D Green) have evolved from standalone imaging devices into intelligent data acquisition nodes within integrated digital ecosystems. Key integration pathways:
Chairside Workflow Integration (Same-Day Restorations)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration | 2026 Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning | Direct DICOM export via HL7/FHIR protocols to CAD software. AI-powered segmentation (bone, nerves, teeth) initiated during scan acquisition. | Reduces pre-CAD processing time by 65% vs. 2023. Enables immediate virtual articulation with intraoral scan (IOS) data. |
| Design Phase | Native CBCT volume rendering within CAD environments (e.g., 3Shape Implant Studio, Exocad DentalCAD Implant Module). Real-time collision detection against vital structures. | Eliminates third-party segmentation software. Surgeons receive biomechanically optimized implant positions with bone density mapping during consultation. |
| Guided Surgery | Automated STL export to 3D printing systems (e.g., Formlabs, EnvisionTEC) with embedded drill path metadata. QR-coded surgical guides linked to CBCT dataset. | Sub-50μm accuracy in guide fabrication. Closed-loop verification against pre-op CBCT during surgery via AR overlays. |
Lab Workflow Integration (Complex Prosthetics & Ortho)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration | 2026 Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|
| Data Aggregation | CBCT + IOS + facial scan fusion via DICOM/STL import. Cloud-based mesh alignment (e.g., using CloudCompare algorithms). | Creates true 1:1 virtual patient avatars. Eliminates manual registration errors in full-arch cases. |
| Prosthetic Design | CBCT-derived bone morphology drives pontic emergence profile design in CAD. Tissue thickness mapping informs gingival mask design. | Reduces remakes by 40% for implant-supported prosthetics. Enables biomimetic emergence profiles impossible with IOS alone. |
| Ortho/TMD Analysis | AI-powered TMJ condyle tracking (e.g., Dolphin 3D v2026) integrated with motion capture data. Airway volume analytics via NVDent protocol. | Provides evidence-based treatment planning metrics for insurance submissions. Quantifies airway changes during ortho treatment. |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
Native CBCT integration capability separates enterprise-grade CAD platforms from legacy systems. 2026 compatibility matrix:
| CAD Platform | CBCT Integration Level | Technical Implementation | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Implant Studio | Native (Tier 1) | Direct DICOM ingestion. Proprietary bone density algorithm. Real-time implant placement against CBCT data. | Vendor-locked to select CBCT brands (Planmeca, Sirona). Limited third-party DICOM manipulation. |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Plugin-Based (Tier 2) | Requires exoplan module. Uses open-source DCMTK toolkit for DICOM processing. Custom segmentation via Python API. | Segmentation less automated than 3Shape. Requires manual threshold adjustment for low-contrast scans. |
| DentalCAD (by Dessys) | Hybrid (Tier 1.5) | Built-in DICOM viewer with AI segmentation (trained on 500k+ scans). Open API for custom workflow scripting. | Cloud-dependent for advanced analytics. On-premise deployment lacks full AI features. |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape + TRIOS) | Open Architecture (e.g., Exocad + Multi-Vendor) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled cloud storage. Limited DICOM export options. | Full DICOM/STL access. Data stored on lab/clinic servers or HIPAA-compliant cloud of choice. |
| Workflow Customization | Rigid clinical pathways. Limited API access for automation. | Python/Lua scripting for custom workflows. Integration with LIMS, ERP, and practice management systems. |
| Cost Structure | High upfront cost + recurring SaaS fees. Mandatory hardware bundles. | Modular pricing. Pay only for required modules. Hardware-agnostic. |
| Future-Proofing | Vulnerable to vendor roadmap changes. Slow adoption of third-party innovations. | Adaptable to new AI tools (e.g., fracture prediction algorithms). Integrates with emerging tech (e.g., AR surgical navigation). |
| 2026 Strategic Verdict | Optimal for single-doctor practices prioritizing simplicity over flexibility. | Essential for labs & multi-specialty clinics requiring scalability and avoiding vendor lock-in. |
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst for Enterprise Workflows
Carejoy’s 2026 DentalSync API v4.2 represents the gold standard for CBCT-CAD integration, addressing critical industry pain points:
| Integration Challenge | Carejoy API Solution | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fragmented DICOM data across CBCT vendors | Universal DICOM translator with vendor-specific normalization (supports 27+ CBCT brands). Auto-converts proprietary formats to standard DICOM-RT. | Eliminates manual data conversion. Reduces pre-CAD processing from 15→2 minutes per case. |
| CBCT-CAD version incompatibility | Version-agnostic protocol buffers. Real-time schema mapping between CBCT firmware updates and CAD software versions. | Prevents workflow disruption during software upgrades. Zero downtime observed in 2025 field tests. |
| Lack of clinical context in data transfer | Embedded clinical metadata tags (e.g., implant_site_id=J23, bone_quality=Type_III) via FHIR resources. | Enables AI-driven design automation (e.g., automatic collar height adjustment based on tissue thickness data). |
Technical Differentiation: Carejoy’s API utilizes gRPC for low-latency communication (sub-100ms response times) and implements OAuth 2.0 with granular permission controls – critical for HIPAA-compliant multi-user environments. Unlike proprietary SDKs, it exposes full segmentation mesh data via RESTful endpoints, enabling custom analytics pipelines.
Conclusion: The Integrated Data Imperative
By 2026, CBCT integration is the defining factor in digital workflow efficacy. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- DICOM-native CAD platforms with open segmentation pipelines
- API-first infrastructure that treats CBCT as a workflow component, not a standalone device
- Vendor-agnostic data strategies to avoid ecosystem lock-in
Carejoy’s API architecture exemplifies the necessary paradigm shift – where anatomical data flows seamlessly from acquisition to fabrication, driven by open standards rather than proprietary constraints. The labs mastering this integration will achieve 35%+ higher throughput with demonstrably superior clinical outcomes.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital – Advanced Manufacturing & QC in CBCT Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
1. Overview: CBCT Manufacturing & Quality Control in China
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, specializing in the end-to-end production of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) systems for digital dentistry. The integration of precision engineering, AI-driven quality assurance, and closed-loop calibration protocols has positioned Chinese manufacturers—particularly Carejoy Digital—as global leaders in the cost-performance optimization of high-end dental imaging equipment.
2. Core Manufacturing Process
The production of Carejoy CBCT machines follows a vertically integrated model, enabling tight control over component sourcing, assembly, and validation. Key stages include:
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-purity X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors (FPDs), and motion actuators sourced from ISO-qualified suppliers; 85% domestically produced in China’s advanced medtech corridor. | Automated supplier audit system, blockchain-based traceability |
| Subassembly | Modular construction of gantry, detector arm, and patient positioning system; robotic precision alignment within ±0.02 mm tolerance. | CNC robotics, laser metrology, IoT-enabled assembly lines |
| Final Integration | Integration of imaging chain (X-ray generator, collimator, FPD), motion control, and AI-accelerated reconstruction engine. | AI-guided calibration software, real-time alignment feedback |
3. Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & ISO 13485 Compliance
Every Carejoy CBCT unit undergoes a multi-stage QC protocol aligned with ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. The calibration and testing infrastructure includes:
- On-Site Sensor Calibration Labs: Each flat-panel detector is calibrated for DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency), MTF (Modulation Transfer Function), and NPS (Noise Power Spectrum) using NIST-traceable phantoms.
- Geometric Accuracy Testing: Automated measurement of voxel uniformity, spatial resolution (≤75 µm), and distortion fields across FOVs (5×5 to 17×12 cm).
- AI-Driven Image Validation: Neural networks compare reconstructed volumes against golden standard datasets to detect artifacts, noise anomalies, or reconstruction drift.
4. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure long-term reliability in clinical environments, Carejoy implements accelerated life-cycle testing:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration & Shock | Simulated transport & clinic use (IEC 60601-1-2) | No misalignment; sub-micron gantry stability |
| Thermal Cycling | 0°C to 40°C over 1,000 cycles | No sensor drift; consistent HU calibration |
| X-ray Tube Endurance | 50,000+ exposures at max kV/mA | Output stability ±2%; no arc faults |
| Software Stress Test | Continuous AI reconstruction over 72h | No crashes; memory leak <0.5% |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment stems from a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, sensor, and precision mechanics manufacturers reduces lead times and BOM costs by up to 35%.
- AI-Optimized Production: Machine learning models predict failure modes in real time, reducing defect rates to <0.3% (vs. global avg. 1.2%).
- Open Architecture Design: Carejoy CBCT systems support STL, PLY, OBJ exports and integrate seamlessly with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms—maximizing interoperability and lab ROI.
- R&D Intensity: Over 18% of revenue reinvested in AI scanning algorithms and dose-reduction technologies, enabling sub-36 µSv full-arch scans.
6. Carejoy Digital: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Carejoy Digital leverages its Shanghai-based ISO 13485 facility to deliver next-generation imaging, milling, and additive manufacturing systems. Our technology stack includes:
- AI-Driven Scanning: Motion-artifact correction, automatic anatomy segmentation (nerve canals, sinuses).
- High-Precision Milling: 5-axis dry/wet milling with ≤5 µm marginal accuracy.
- Cloud-Connected Workflow: DICOM-to-milling automation via Carejoy OS.
Support & Updates
- 24/7 Technical Remote Support with AR-assisted diagnostics.
- Monthly AI Model Updates for reconstruction and segmentation.
- Firmware patches delivered over secure OTA protocol.
Contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cbct Machines.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
