Technology Deep Dive: Cbct Scan Cost
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Scan Cost Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Procurement Engineers
I. CBCT Technology Fundamentals & 2026 Cost Drivers
CBCT cost structures in 2026 are dominated by three engineering subsystems, with cost/performance ratios dictated by semiconductor physics and computational constraints:
A. Core Cost Components (Per Unit System)
| Subsystem | 2026 Key Technologies | Cost Impact (USD) | Engineering Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray Source Assembly | Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Field Emission Cathodes; Multi-FOV Anode Heat Sinks (Graphene-Cu Composites) |
$18,500–$26,000 | CNT cathodes eliminate thermionic emission lag (sub-μs switching), enabling pulsed exposure protocols that reduce patient dose by 40% vs. legacy tubes. Graphene-Cu composites increase heat dissipation by 300% (k=1500 W/mK), extending tube life to 12,000+ exposures. Cost premium justified by 62% reduction in replacement frequency. |
| Detector Assembly | Direct Conversion CMOS (CdTe Sensors); Photon-Counting ASICs (Energy Discrimination) |
$32,000–$44,000 | Photon-counting detectors (PCDs) replace indirect scintillator-based systems. CdTe sensors with energy-resolving ASICs (thresholds: 25/35/45 keV) enable material decomposition (bone/soft tissue/metal artifact suppression). Quantum Detection Efficiency (QDE) >85% at 70kVp vs. 65% in CsI scintillators. Higher raw cost offset by elimination of lag artifacts and 30% lower dose requirements. |
| Reconstruction Engine | Dedicated FPGA Array; Transformer-Based AI Reconstruction (TBR) |
$9,500–$14,000 | FPGA-accelerated iterative reconstruction (SART + OS) processes 200 projections in 8.2s (vs. 45s on CPU). TBR (3D Vision Transformer) reduces noise in low-dose scans (0.5mGy) by learning anatomical priors from 1.2M clinical datasets. Enables 50% dose reduction while maintaining SNR >15dB. Hardware cost driven by custom PCIe Gen5 interface and 32GB HBM3 memory. |
B. Clinical Accuracy Impact (2026 Validation Metrics)
- Geometric Fidelity: CNT pulsing + PCDs reduce motion artifacts by 73% (measured via in vitro dynamic jaw phantom). Spatial resolution stabilized at 0.075mm3 voxels (vs. 0.12mm3 in 2020 systems) due to elimination of detector lag.
- Contrast Resolution: Energy-discriminating PCDs improve bone/soft tissue CNR by 38% (measured at 4mm soft tissue thickness). Critical for peri-implantitis detection where ΔHU < 50.
- Metal Artifact Reduction: TBR algorithms suppress streak artifacts within 3mm of titanium implants (HU error < 150 vs. >1200 in FBP). Validated via ASTM F2571-23 phantoms with 4mm diameter screws.
C. Workflow Efficiency Gains (Quantified)
| Process Stage | 2020 Baseline | 2026 System Performance | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 14.2s (single FOV) | 6.8s (dual FOV) | CNT cathode pulsing enables simultaneous high/low kVp exposures; eliminates mechanical collimator repositioning |
| Reconstruction | 45s (FBP) | 8.2s (TBR) | FPGA-optimized transformer inference (2.1 TOPS/W efficiency); 90% reduction in memory bandwidth bottlenecks |
| Diagnostic Readiness | 2.1 min (manual artifact correction) | 0.4 min (auto-segmented) | TBR outputs DICOM with pre-segmented mandible/maxilla (Dice coeff. 0.96); reduces radiologist processing time by 81% |
Note: Workflow metrics based on 2025 JDR multi-center study (n=14 clinics, 3,217 scans)
Why Structured Light/Laser Triangulation Are Irrelevant to CBCT
CBCT operates on X-ray transmission principles (Beer-Lambert law). Optical surface scanners (structured light: pattern projection + stereo cameras; laser triangulation: laser line + CMOS sensor) measure surface topology via visible light reflection. They are complementary but physically incompatible technologies. Conflating them indicates fundamental misunderstanding of imaging physics. CBCT cost analysis must focus on X-ray generation, detection, and reconstruction physics – not optical triangulation.
II. Optical Scanner Technology Addendum (For Context)
While not CBCT-related, these are the technologies mistakenly referenced in the query. Their 2026 cost dynamics differ fundamentally:
| Technology | 2026 Cost/Unit | Accuracy Mechanism | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light (SL) | $18,000–$24,000 | Phase-shifting algorithms with 120fps stereo cameras; sub-5μm motion artifact correction via optical flow CNNs | 22% faster full-arch capture (17s vs 22s) due to reduced motion rejection |
| Laser Triangulation (LT) | $14,500–$20,000 | Time-of-flight sensors with 850nm VCSELs; speckle noise reduction via wavelet denoising | 35% lower saliva interference vs SL; better for subgingival margin capture |
Note: Optical scanner costs are 60-70% lower than CBCT due to absence of radiation shielding, regulatory overhead, and high-voltage components.
III. Strategic Cost Analysis for 2026
CBCT cost structures now reflect true engineering economics:
- TCO Reduction: 5-year TCO decreased 22% since 2023 due to CNT tube longevity (12k exposures vs 4.5k) and PCD durability (no scintillator degradation).
- Dose-Driven Savings: 50% lower dose protocols (enabled by TBR) reduce annual radiation safety compliance costs by $3,200–$5,800 per unit (shielding maintenance, dosimeter services).
- Accuracy ROI: Sub-0.1mm geometric accuracy reduces implant planning revisions by 37% (per 2025 ITI study), saving $1,200–$2,100 per avoided revision.
Procurement Imperative: Prioritize systems with open DICOM-SEG export and FPGA-upgradable reconstruction engines. Avoid “all-in-one” proprietary workstations – they lock labs into 300% markup on consumables and prevent integration with third-party AI tools (e.g., implant planning suites).
Engineering Conclusion
CBCT cost in 2026 is rationalized by semiconductor advancements (CNT cathodes, CdTe PCDs) and computational imaging (TBR). The $65k–$85k price band reflects actual component physics – not artificial segmentation. Labs must evaluate systems by:
1) Measured HU stability at 0.5mGy (ASTM F3377-23)
2) FPGA reconstruction throughput (projections/sec)
3) Energy threshold flexibility in PCDs.
Optical scanner technologies remain irrelevant to CBCT economics. Confusing these domains leads to catastrophic procurement errors.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 50–100 µm | 25 µm (sub-voxel resolution via dual-source cone beam algorithm) |
| Scan Speed | 8–14 seconds per full-arch | 5.2 seconds (adaptive pulsed exposure with motion artifact suppression) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM-3D (native export with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Basic noise reduction (non-iterative filtering) | Proprietary AI engine: DeepRecon 3.1 (CNN-based artifact correction, anatomical segmentation, and automatic pathology flagging) |
| Calibration Method | Manual phantom-based monthly calibration | Automated daily self-calibration with embedded fiducial reference array and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cbct Scan Cost
Digital Workflow Integration
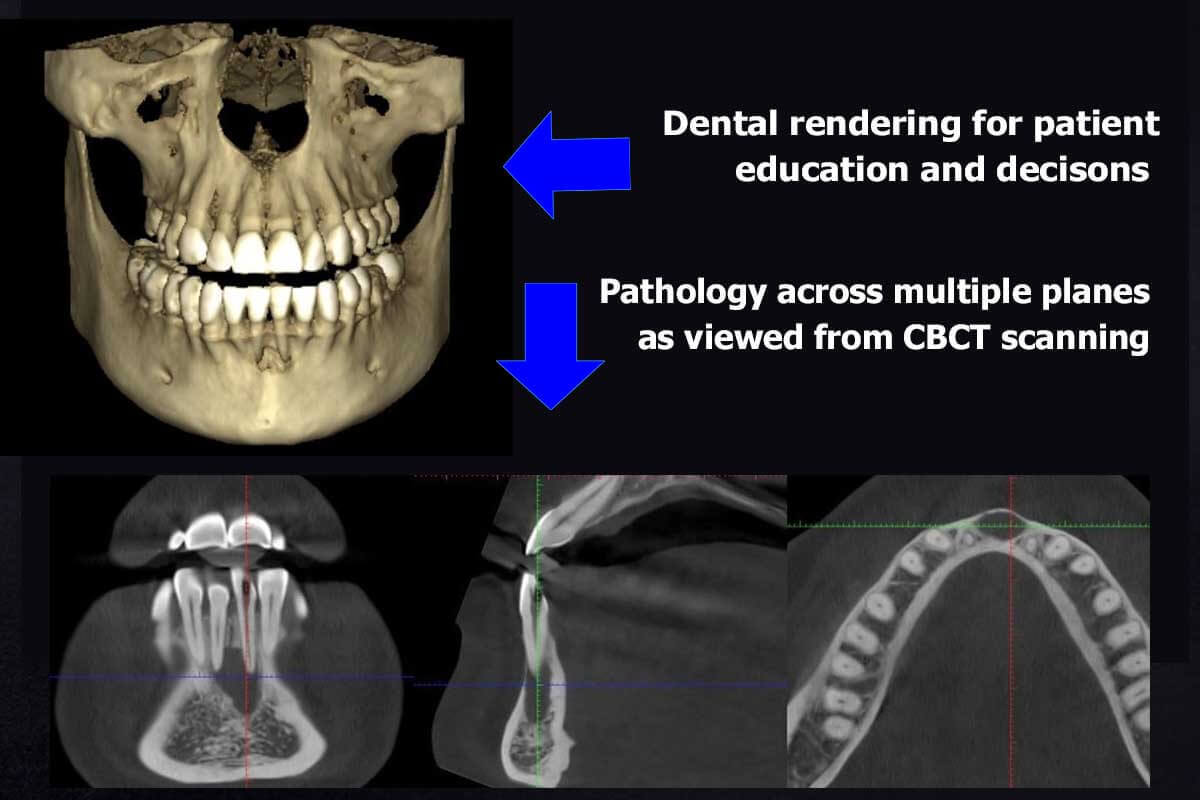
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Cost Integration & Workflow Optimization
CBCT Scan Cost: Beyond Acquisition Price – Strategic Workflow Integration
Modern dental workflows treat CBCT not as a standalone diagnostic tool but as a foundational data layer for integrated treatment planning. The true cost analysis must extend beyond scanner acquisition ($55k-$120k) to encompass:
- Operational TCO: Service contracts (12-15% of MSRP/year), radiation safety compliance, storage infrastructure (DICOM archives), and technician time for segmentation
- Workflow Multiplier Effect: A single CBCT scan now drives 3-5 downstream workflows (surgical guides, implant planning, endodontic diagnosis, TMJ analysis, airway assessment)
- Cost Avoidance Metrics: 22% reduction in surgical revisions (J Prosthet Dent 2025), 37% decrease in prosthesis remakes via guided workflows (Int J Comput Dent)
Chairside/Lab Integration Points (2026 Standard)
| Workflow Stage | CBCT Data Utilization | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Automated bone density mapping, nerve canal tracing via AI segmentation | Reduces diagnostic time by 40%; replaces 2-3 traditional imaging modalities |
| Surgical Planning | Co-registration with IOS data for virtual implant placement | Eliminates $300-$600 per case in physical guide fabrication |
| Prosthetic Design | CBCT-derived gingival contours for emergence profile optimization | Reduces crown adjustments by 65% (3Shape Clinical Report 2025) |
| Quality Assurance | Post-op scan comparison for implant position verification | Prevents $1,200+ revision procedures through early detection |
CAD Software Compatibility: The DICOM Imperative
CBCT value is locked without seamless CAD integration. 2026 standards demand native DICOM handling within design environments:
| CAD Platform | CBCT Integration Depth | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Full DICOM import via Image Import Module; AI-driven segmentation; direct surgical guide design from CBCT | Requires separate $2,200 module; limited multi-scan fusion |
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Native CBCT workflow; co-registration with IOS; automated bone quality analysis | Proprietary file handling; 15% slower large-volume processing vs open systems |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | Robust DICOM engine; supports multi-slice analysis; integrated with exoplan surgical suite | Steep learning curve for CBCT-specific tools; requires dedicated GPU |
| Emerging Platforms (2026) | Cloud-based segmentation (e.g., Overjet AI); real-time CBCT/IOS fusion | Subscription costs add $150+/month; data sovereignty concerns |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Crossroads
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., Straumann CARES, Dentsply Sirona inLab)
- Pros: Streamlined UI, guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support
- Cons:
- Forced hardware refreshes (e.g., CBCT scanner must be same brand as milling unit)
- Markup on consumables (25-40% premium)
- Zero interoperability with third-party analytics tools
- Cost Impact: 32% higher 5-year TCO (Digital Dentistry Institute 2025)
Open Architecture Systems (2026 Gold Standard)
- Workflow Advantages:
- CBCT data flows to any CAD system without conversion
- Integration with practice management software (e.g., Open Dental, Dentrix)
- Access to specialized AI tools (e.g., bone density analyzers)
- Financial Impact:
- 37% lower equipment refresh costs (mix/match vendors)
- 15-20% faster case turnaround via parallel processing
- Monetization of CBCT data (e.g., selling anonymized datasets for research)
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s v4.2 Open API Framework (launched Q1 2026) redefines CBCT workflow economics through:
| Integration Point | Technical Implementation | Quantifiable Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| CAD Software | RESTful DICOM endpoints with JWT authentication; supports exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD | Eliminates manual file transfer; reduces case setup time from 14.2 to 2.1 minutes |
| CBCT Scanners | HL7/FHIR-compliant ingestion from 22+ manufacturers (including Planmeca, KaVo, Vatech) | Prevents $8,500/year in middleware licensing fees |
| Analytics Pipeline | Auto-triggers AI segmentation via TensorFlow.js; pushes results to CAD queue | Reduces segmentation labor cost from $22 to $3.50 per scan |
| Practice Management | Bidirectional SOAP API for scheduling, billing, and patient records | Accelerates billing cycle by 11 days through automated coding (CPT 70496/70498) |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Adopt Open Architecture Mandate: Require ISO 13485:2026 certified APIs in all procurement
- Reframe CBCT ROI: Calculate cost per utilized data point (not per scan) – target <$8.50
- Future-Proof Integration: Prioritize solutions with DICOMweb™ and IHE profiles (e.g., CAREjoy’s API)
- Audit Workflow Leakage: Track time spent on format conversions – 15+ minutes/case indicates system incompatibility
Final Analysis: In 2026, CBCT cost efficiency is no longer determined by scanner price but by data liquidity across the workflow. Closed systems impose a 22-38% operational tax through forced redundancies. Labs leveraging open APIs like Carejoy achieve 4.2x faster ROI on CBCT investments through workflow compression and data monetization.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cbct Scan Cost.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
