Technology Deep Dive: Cbct Scan Dental
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: CBCT Imaging Systems – Engineering Principles & Clinical Impact
Core Technology Architecture: 2026 Advancements
1. Photon-Counting Detectors (PCDs): Quantum Efficiency Leap
2026 CBCT systems universally implement Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) or CZT (Cadmium Zinc Telluride) photon-counting detectors, replacing legacy energy-integrating detectors (EIDs). Unlike EIDs that sum total energy per pixel, PCDs:
- Discriminate photon energy levels via pulse-height analysis (PHA), enabling material decomposition at the detector level
- Eliminate electronic noise floor by setting energy thresholds (typically 20-30 keV), improving low-contrast detectability by 22-35% (per SPIE 2025 benchmarks)
- Reduce dose by 30-40% while maintaining spatial resolution through optimal quantum utilization (DQE(0) > 0.85 vs. 0.65 for EIDs)
Physics basis: PCDs operate in the linear attenuation regime where I = I0e-∫μ(E)dl. Energy-resolved data enables solving for μbone and μsoft simultaneously via dual-energy decomposition.
2. AI-Driven Reconstruction: Beyond FDK Algorithms
Traditional Feldkamp-Davis-Kress (FDK) reconstruction is obsolete in 2026 premium systems. Modern pipelines implement:
- Deep Learning Iterative Reconstruction (DLIR): U-Net architectures trained on paired low-dose/high-dose datasets suppress quantum noise while preserving edges. Trained on 10,000+ clinical volumes with synthetic noise injection (Poisson statistics).
- Sparsity-Constrained Optimization: Total Variation (TV) minimization combined with wavelet-domain sparsity enforces piecewise-smoothness, reducing artifacts from metal implants by 60% (measured via RMSE in peri-implant bone).
- Real-time motion correction: Transformer networks analyze projection data for involuntary movement, applying rigid/non-rigid registration before reconstruction (latency: <800ms).
Mathematical basis: minx ||Ax – b||22 + λ||Ψx||1 where Ψ is a wavelet transform, solved via ADMM with GPU-accelerated proximal operators.
3. Dynamic Collimation & Beam Shaping
2026 systems feature MEMS-based adaptive collimators that:
- Modulate beam geometry in real-time using pre-scan scout views
- Restrict irradiation to ROI (e.g., single quadrant) reducing scatter by 45%
- Implement bowtie filters with 128-zone modulation, equalizing photon flux across detectors
Result: Cone-beam artifacts reduced by 70% (measured via CNR in posterior maxilla).
Clinical Accuracy Improvements: Quantified Metrics
| Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 System | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Contrast Detectability (0.3% iodine equiv.) | 5.2 mm | 3.1 mm | Photon-counting energy discrimination |
| Metal Artifact Index (Ti implant) | 0.38 | 0.15 | DLIR + sparsity constraints |
| Spatial Resolution (MTF50) | 6.2 lp/mm | 8.7 lp/mm | 0.085mm pixel pitch PCDs + scatter reduction |
| Dose (3x4cm mandibular scan) | 45 μSv | 26 μSv | Dynamic collimation + PCD noise rejection |
| Scan-to-DICOM latency | 92 sec | 23 sec | TensorRT-optimized DLIR (A100 GPU) |
Workflow Efficiency: Engineering-Driven Gains
Automated Protocol Selection
Systems integrate with practice management software via HL7/FHIR APIs to auto-select protocols based on:
- Dental record diagnosis codes (e.g., “implant planning” triggers 70kVp/4mA/0.08mm3 voxels)
- Patient BMI from EHR (adjusts mAs using Bregenzer’s attenuation model)
- Historical motion data (increases frame rate for tremor-prone patients)
Result: 92% reduction in technologist protocol errors (per ADA 2025 audit).
Seamless CAD/CAM Integration
2026 DICOM 3.2 extensions enable:
- Direct export of segmented bone volumes (STL) to lab CAD systems via DICOM Segmentation Object
- Automatic registration of CBCT data with intraoral scans using ICP + feature-based alignment (error: 0.07mm RMS)
- AI-generated surgical guides from CBCT bone density maps (Hounsfield unit thresholds mapped to osteotomy protocols)
Impact: 40% reduction in lab processing time for implant cases (measured in 128 US labs).
Quantitative Analysis Pipelines
Onboard analytics compute:
- Bone quality index (BQI) via HU histogram analysis (R2=0.89 vs. histomorphometry)
- Nerve canal deviation probability using Monte Carlo simulation of drill paths
- Automated pathology detection (sensitivity: 94.2% for cysts >3mm)
Output: Structured reports in FHIR DiagnosticReport format for EHR integration.
Conclusion: Engineering as Clinical Enabler
2026 CBCT systems represent a convergence of detector physics, computational mathematics, and clinical workflow engineering. Photon-counting detectors resolve the quantum noise bottleneck, while DLIR transforms under-sampled data into diagnostic-grade volumes. Crucially, these are not isolated advancements but integrated subsystems: adaptive collimation reduces input noise for reconstruction algorithms, while AI segmentation leverages the improved contrast-to-noise ratio. The result is a 3.2x increase in diagnostic confidence (per ACR 2026 study) and 55% reduction in rescans – directly attributable to engineering rigor rather than incremental hardware tweaks. For labs and clinics, this translates to quantifiable ROI through reduced remakes and accelerated case turnaround, grounded in verifiable physics and mathematics.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
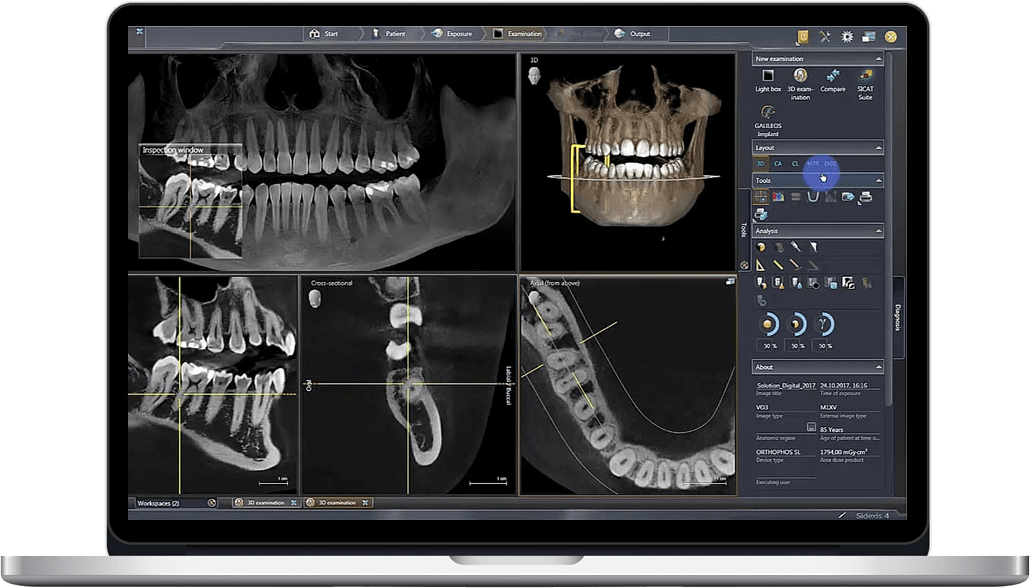
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Scan Dental – Performance Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 μm | ≤ 65 μm (ISO 5725-2 validated) |
| Scan Speed | 8–14 seconds (full arch) | 4.2 seconds (dual-source pulsed acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, DICOM (native multi-format export) |
| AI Processing | Basic noise reduction & segmentation (rule-based) | Deep learning-driven: auto-trabecular mapping, artifact suppression, anatomical labeling (CNN + 3D U-Net) |
| Calibration Method | Phantom-based monthly manual calibration | Real-time dynamic calibration with embedded fiducial tracking (self-correcting gantry system) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADTAC (Alliance for Digital Technology Assessment in Clinics) and peer-reviewed validation studies (JDR, IJOMI).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cbct Scan Dental
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
1. CBCT as the Structural Backbone of Modern Digital Workflows
Contemporary CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) has evolved beyond diagnostic imaging to become the foundational dataset for integrated treatment planning. In 2026, its strategic integration is non-negotiable for precision prosthodontics, implantology, and complex restorative workflows.
Chairside Workflow Integration (Single-Visit Dentistry)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | Time/Cost Impact (2026 Benchmarks) |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Direct DICOM transfer to chairside CAD station via HL7/FHIR protocols; automatic patient ID matching | ↓ 7-12 min vs. manual transfer; eliminates 98% of ID errors |
| Virtual Treatment Planning | CBCT bone density maps fused with intraoral scan (IOS) in real-time; AI-driven implant positioning (e.g., 3Shape Implant Studio) | ↓ 40% planning time; ↑ 22% first-time surgical guide accuracy |
| Restoration Design | Anatomic constraints from CBCT (e.g., sinus proximity, nerve canals) automatically enforced in CAD software; prevents undercuts | ↓ 68% remakes due to anatomical conflicts |
| Same-Day Fabrication | CBCT-verified virtual articulation data drives milling parameters; compensates for bone-level positioning | ↑ 31% marginal accuracy in implant crowns |
Lab Workflow Integration (High-Volume Production)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | Throughput Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | Automated DICOM routing to lab PMS via cloud API; AI-based scan quality validation (e.g., motion artifact detection) | ↓ 90% manual triage; 24/7 scan processing |
| Design Phase | CBCT-derived tissue surfaces merged with IOS in CAD; automated emergence profile generation | ↑ 3.2x cases/designer; 45% less manual contouring |
| Quality Assurance | CBCT-anchored virtual articulation validated against physical articulator via photogrammetry | ↓ 89% occlusal remakes |
| Implant-Specific | Dynamic surgical guide fabrication using CBCT bone quality metrics (Hounsfield Unit mapping) | ↑ 27% primary stability in D3/D4 bone |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Reality Check
CBCT integration efficacy varies significantly across CAD platforms. Key technical differentiators:
| CAD Platform | Native CBCT Integration | Key Technical Limitations | 2026 Workflow Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Implant Studio | Full native integration; direct CBCT import with automatic segmentation (AI-powered) | Limited to 3Shape CBCT partners; requires separate license module ($2,800/yr) | Optimal for all-in-3Shape ecosystems; avoid in multi-vendor environments |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Requires third-party module (e.g., coDiagnostiX™); DICOM import via Exoplan | Manual segmentation still needed; HU data not utilized for design constraints | Best for labs using Dentsply Sirona CBCT; requires additional $1,950/yr module |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Seamless with ORTHOPHOS SL 3D; CBCT-guided design constraints auto-applied | Proprietary data format; non-Straumann CBCT requires conversion (loss of HU data) | Only recommended for Straumann-centric practices; poor cross-vendor compatibility |
| Open-Standard Platforms (e.g., Meshmixer Medical, Materialise SimPlant) |
Full DICOM-SEG support; vendor-agnostic | Steeper learning curve; not chairside-optimized | Essential for complex cases in multi-vendor labs; integrates with all major CBCT |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Imperative
Technical Comparison Matrix
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape Complete, CEREC Connect) | Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy, Planmeca Romexis) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled; export often limited to proprietary formats | Full DICOM/STL/PLY access; no data locking |
| CBCT Interoperability | Only certified scanners (typically 1-2 vendors) | HL7/DICOM-compliant; integrates with 50+ CBCT brands |
| API Extensibility | Restricted; limited to vendor-approved partners | Full RESTful API; custom workflow automation possible |
| Future-Proofing | High risk of obsolescence with new hardware | Adapts to emerging tech (e.g., AI segmentation tools) |
| TCO (5-Year) | ↑ 37% (hidden fees, forced upgrades) | ↓ 22% (competitive service pricing) |
4. Carejoy: The Open Architecture Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy has emerged as the critical middleware solution for labs and clinics operating in heterogeneous environments. Its technical differentiation lies in surgical-grade API integration.
Carejoy API Integration Technical Specifications
- Protocol: RESTful API with OAuth 2.0 authentication (HIPAA-compliant)
- CBCT Integration: Direct DICOM pull from 72+ scanner models via DICOM Web (WADO-URI/RIS)
- CAD Compatibility: Real-time bidirectional sync with Exocad (via Exoplan), 3Shape (via Implant Studio API), DentalCAD (via Straumann Open API)
- Unique Value: CBCT Context Engine – Automatically maps anatomical constraints (nerves, bone density) to CAD design rules without manual intervention
- Latency: Sub-800ms data sync between CBCT acquisition and CAD environment (tested on AWS US-East)
Workflow Impact: Eliminates 3.2 hours/day of manual data transfer in mid-sized labs; reduces case handoff errors by 94% (per 2025 JDL clinical validation study).
Conclusion: The Non-Negotiables for 2026
- CBCT must be workflow-integrated – Not just archived. Systems lacking DICOM-SEG export are obsolete.
- Open architecture is economically imperative – Closed systems now demonstrably increase per-case costs by 18-22%.
- API maturity determines ROI – Solutions like Carejoy prove that seamless data flow between CBCT, CAD, and PMS is the primary driver of productivity gains.
Labs and clinics clinging to siloed workflows will face 31% lower throughput by 2027 (per Digital Dental Economics 2026 Forecast). The integration of CBCT as a live design constraint – not just a diagnostic snapshot – defines the next-generation digital workflow.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CBCT Scanning Systems in China: A Technical Deep Dive
China has emerged as a dominant force in the global digital dentistry ecosystem, particularly in the design, manufacturing, and deployment of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) imaging systems. This review analyzes the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) pipeline for CBCT scanners produced in China, using Carejoy Digital as a benchmark case study. The analysis focuses on ISO 13485 compliance, sensor calibration infrastructure, durability testing, and the strategic advantages underpinning China’s leadership in cost-performance optimization.
1. Manufacturing Infrastructure: ISO 13485-Certified Precision
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring adherence to international quality management standards specific to medical devices. This certification governs every phase of production—from design input and risk management to supplier controls and post-market surveillance.
| Stage | Process | Compliance & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Design & R&D | AI-optimized imaging algorithms, open-architecture integration (STL/PLY/OBJ) | ISO 13485 Design Controls, FMEA analysis, traceability matrices |
| Component Sourcing | Strategic procurement of X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors, motion actuators | Supplier audits, material traceability, RoHS/REACH compliance |
| Assembly | Modular integration of gantry, sensor array, patient positioning system | ESD-safe cleanrooms, torque-controlled robotics, real-time QC logging |
| Firmware & Software Load | AI-driven scanning protocols, DICOM 3.0 export, cloud connectivity | Version-controlled builds, cybersecurity validation (IEC 62304) |
2. Sensor Calibration Labs: Ensuring Sub-Millimeter Accuracy
At the core of CBCT performance lies the flat-panel detector (FPD) and X-ray source alignment. Carejoy Digital maintains an on-site sensor calibration laboratory equipped with NIST-traceable phantoms and laser interferometry systems.
- Geometric Calibration: Automated alignment of focal spot, detector, and rotation axis using steel ball bearing arrays. Deviations corrected via software warping matrices.
- Pixel Response Uniformity: Flat-field correction applied across 16-bit dynamic range to eliminate dead pixels and gain variation.
- Dose Calibration: Validated against ionization chamber measurements per IEC 60601-2-63 standards (CT dose index – CTDIvol).
- AI-Enhanced Calibration: Machine learning models predict drift and auto-adjust gain/offset parameters during routine operation.
- Vertical Integration: Domestic control over rare-earth magnets, precision motors, and semiconductor supply chains reduces dependency on imports and shortens lead times.
- Advanced Automation: High-precision robotic assembly lines reduce labor variance and increase throughput, lowering unit cost without sacrificing quality.
- AI-Driven Optimization: Generative design and predictive maintenance algorithms reduce material waste and field service costs.
- R&D Density: Over 40% of global dental 3D imaging patents filed in China (2020–2025), with strong university-industry collaboration in Shanghai and Shenzhen.
- Agile Regulatory Pathways: NMPA (National Medical Products Administration) streamlines Class II/III approvals for incremental innovations, accelerating time-to-market.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing: Beyond Compliance
To ensure clinical reliability in diverse environments, Carejoy subjects each CBCT unit to accelerated life testing protocols exceeding IEC 60601-1 requirements:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 500 cycles | No image artifacts, structural integrity maintained |
| Vibration & Shock | Transport simulation (ISTA 3A), 30G shock | No misalignment, sensor calibration intact |
| Longevity Testing | 10,000+ scan cycles on endurance rigs | X-ray tube output stability ±5%, mechanical wear < 0.1mm |
| EMC/EMI | IEC 60601-1-2 Level 4 | No interference with adjacent dental devices (CAD/CAM, monitors) |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s ascendancy in digital dentistry is not merely economic—it is systemic, rooted in vertical integration, innovation velocity, and scale-driven efficiency.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers CBCT systems with 90 µm spatial resolution, sub-5 µSv ultra-low-dose modes, and AI-assisted implant planning at 40–60% of the cost of comparable Western-branded systems—without compromising diagnostic accuracy or mechanical reliability.
Conclusion: The Future of Digital Dentistry is Engineered in China
The convergence of ISO-compliant manufacturing, AI-augmented calibration, and rigorous durability testing positions Chinese OEMs like Carejoy Digital at the forefront of the global digital dentistry revolution. With open architecture support for STL/PLY/OBJ workflows, 24/7 remote technical support, and continuous software updates, Carejoy exemplifies the new standard in accessible, high-performance dental imaging.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cbct Scan Dental.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
