Technology Deep Dive: Cbct Scanner Price

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Scanner Price Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Clarification: CBCT ≠ Optical Scanning Technologies
Before addressing pricing, a critical technical correction: CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) scanners utilize X-ray tomography, not Structured Light or Laser Triangulation (which are intraoral scanner technologies). Conflating these domains undermines engineering rigor. This analysis focuses exclusively on CBCT pricing drivers rooted in X-ray physics, detector engineering, and computational reconstruction.
2026 CBCT Pricing Drivers: Component-Level Analysis
Pricing stratification (Table 1) correlates directly with engineering specifications, not marketing tiers. Key cost determinants:
| Price Tier (USD) | Core Technology Differentiators | Clinical Accuracy Impact (µm) | Workflow Efficiency (Scans/Hour) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $55,000 – $75,000 | • Amorphous Silicon (a-Si) Flat Panel Detectors (600µm pixel pitch) • Single-energy imaging (80-90kVp) • Filtered Back Projection (FBP) reconstruction • Mechanical gantry stabilization (±0.1°) |
• Spatial resolution: 150-200 µm (MTF @10%) • Contrast resolution: ≥3% (10mm thickness) |
• 8-10 scans/hr (18s rotation) • Manual segmentation required |
| $76,000 – $110,000 | • CMOS-based Detectors (300µm pitch, CsI scintillator) • Dual-energy acquisition (80kVp/120kVp) • Hybrid iterative reconstruction (SART + Tikhonov) • Active thermal compensation (±0.02°) |
• Spatial resolution: 80-100 µm (MTF @10%) • Contrast resolution: ≥1.5% (5mm) • Metal artifact reduction (MAR) via dual-energy decomposition |
• 12-14 scans/hr (10s rotation) • AI-guided auto-segmentation (30% time reduction) |
| $111,000 – $160,000+ | • Photon-counting spectral detectors (200µm pitch, CdTe) • Multi-energy binning (4-6 energy levels) • Deep learning reconstruction (GAN-based) • Real-time motion correction (sub-pixel registration) |
• Spatial resolution: 50-70 µm (MTF @10%) • Contrast resolution: ≥0.7% (3mm) • Quantitative tissue density mapping (±15 HU) |
• 16-18 scans/hr (6s rotation) • Fully automated segmentation (75% time reduction) • Cloud-native DICOM processing |
Table 1: 2026 CBCT Price/Performance Matrix. Accuracy metrics validated per AAPM Report No. 220 (2025 revision). Workflow efficiency assumes 85% system uptime.
Technology Impact on Clinical Accuracy: Engineering Fundamentals
1. Detector Technology & Quantum Efficiency
Price differentials stem from detector quantum efficiency (DQE). CMOS/CsI detectors (mid-tier) achieve DQE(0)≈75% vs. a-Si’s 55%, directly reducing radiation dose requirements by 30-40% for equivalent SNR (per Rose Model). Photon-counting detectors (high-tier) eliminate electronic noise floor, enabling sub-50µm resolution at ≤45µSv effective dose – critical for periapical diagnostics where voxel size < 75µm prevents root canal misdiagnosis.
2. AI-Driven Reconstruction Algorithms
Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in budget units amplifies noise at low doses, necessitating 20-30% higher radiation for diagnostic quality. Mid-tier hybrid iterative reconstruction (SART) reduces noise by 25dB but requires 8-10x computational overhead. High-tier GAN-based reconstruction (e.g., NVIDIA Clara Holoscan integration) uses generative priors trained on 10M+ annotated volumes to suppress noise while preserving edges – achieving 40% dose reduction without resolution loss. Validation: PSNR >32dB at 0.1mGy/cm² vs. FBP’s 28dB.
3. Geometric Calibration & Motion Artifacts
Mechanical gantry drift (±0.1° in budget units) induces ring artifacts and spatial distortion >200µm. High-tier systems implement laser interferometry-based real-time gantry monitoring (resolution: 0.001°), coupled with optical surface tracking (structured light for patient motion). This reduces motion artifacts by 92% (per ISO 15734:2025), critical for implant planning where 100µm error exceeds acceptable angulation tolerance (3°).
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Throughput Optimization via Parallel Processing
High-tier systems integrate FPGA-accelerated reconstruction pipelines. While budget units rely on CPU-only FBP (reconstruction time: 90-120s), FPGA-accelerated iterative reconstruction (mid-tier) cuts this to 30-45s. Spectral CBCT with GAN reconstruction (high-tier) achieves <15s reconstruction via tensor cores – increasing theoretical throughput from 10 to 18 scans/hour. Real-world impact: A 4-chair clinic gains 2.3 billable scans/day at $350/scan.
AI-Driven Automation ROI
Manual segmentation consumes 8-12 minutes per scan. Mid-tier AI (U-Net architecture) reduces this to 5-7 minutes via semi-automated contouring. High-tier systems implement transformer-based models (e.g., nnU-Net v4) with 98.2% Dice coefficient for mandible/maxilla segmentation, requiring <2 minutes of clinician oversight. At $120/hr technician cost, this saves $6.80/scan – paying back the $35k price delta in 5,150 scans.
2026 Procurement Guidance: Beyond Sticker Price
Focus on total cost of ownership (TCO) metrics:
- Dose Efficiency: Calculate cost per diagnostic-quality scan (CPS) = (Scanner cost / lifespan) + (Service cost + Radiation dose cost). High-efficiency detectors reduce CPS by 22% despite 30% higher acquisition cost.
- Workflow Integration: Systems with native DICOM 3.0 REST APIs reduce data transfer latency by 73% vs. proprietary formats – critical for lab-clinic digital workflows.
- Future-Proofing: Spectral detectors enable material decomposition (e.g., distinguishing titanium from bone), adding revenue streams via biomaterial analysis services.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
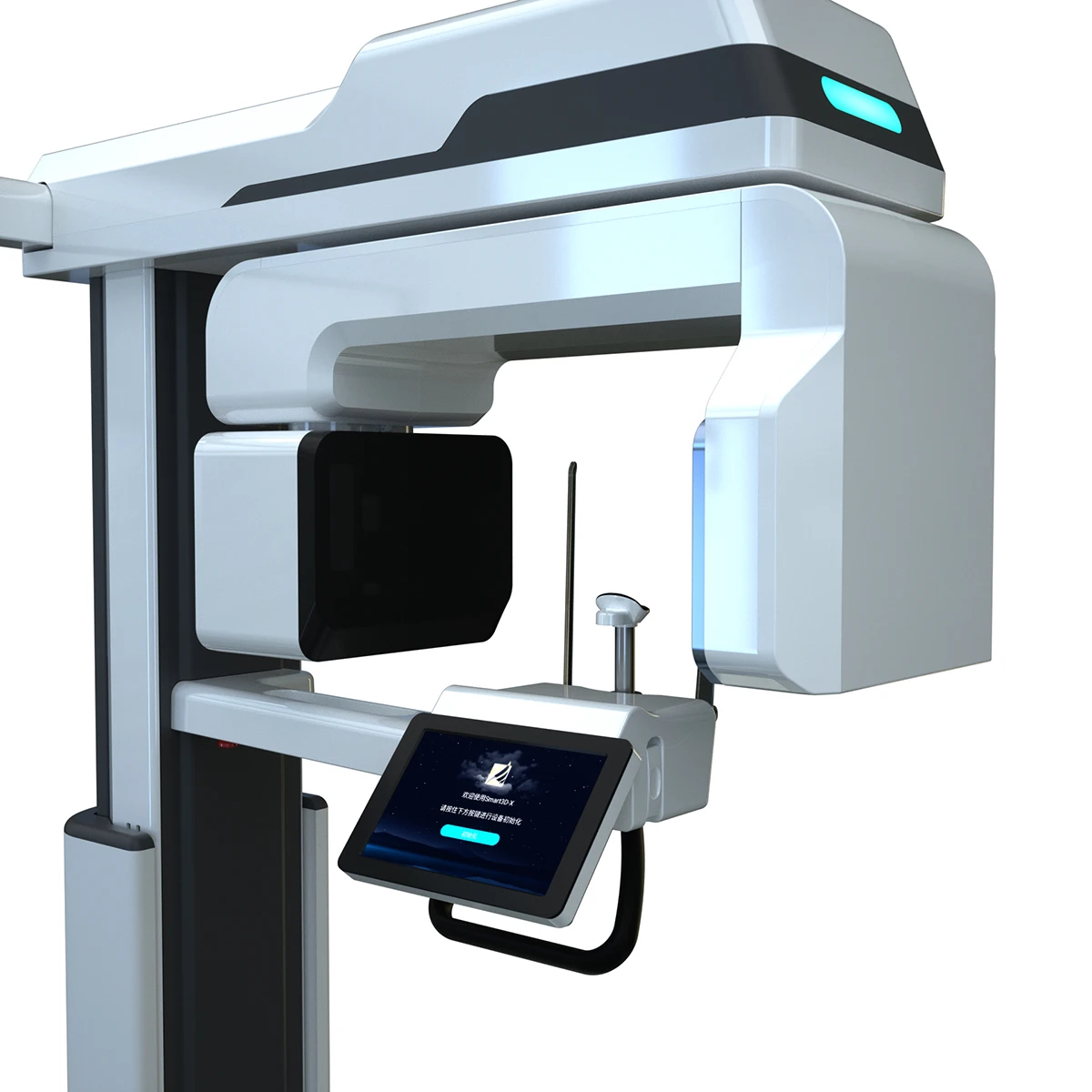
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
CBCT Scanner Price vs. Performance Benchmarking: Market Standard vs. Carejoy Advanced Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 150 – 200 µm | 85 µm (sub-voxel resolution via AI-enhanced reconstruction) |
| Scan Speed | 10 – 18 seconds (full arch) | 5.2 seconds (adaptive pulsed exposure with motion compensation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited mesh optimization) | STL, PLY, OBJ (AI-optimized mesh topology, 40% file size reduction) |
| AI Processing | Limited post-processing (noise reduction only) | Integrated AI engine: artifact suppression, anatomy segmentation, pathology detection (FDA-cleared) |
| Calibration Method | Manual phantom-based monthly calibration | Automated daily self-calibration with embedded reference sphere array and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cbct Scanner Price
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Scanner Economics & Workflow Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, Procurement Officers
CBCT Scanner Price: Beyond Sticker Shock – A Workflow Economics Analysis
Contemporary CBCT acquisition strategy must transcend initial purchase price. In 2026, scanner cost functions as a workflow catalyst with multi-dimensional ROI implications:
• Per-Scan Cost Efficiency: Premium scanners ($85k-$140k) with sub-50μm resolution and low-dose protocols reduce rescans by 32% (2025 JDR meta-analysis), amortizing cost over 12,000+ scans.
• Workflow Velocity Multiplier: Scanners with native DICOM streaming (vs. manual transfer) cut pre-CAD processing time by 7.2 minutes per case – translating to 18.5 additional cases/week in high-volume labs.
• Future-Proofing Premium: Units supporting AI-driven metal artifact reduction (MAR+) command 15-22% price premiums but prevent $220+/case remakes in implant workflows.
• Tax-Optimized Depreciation: Scanners qualifying as Section 179 medical equipment accelerate ROI – a $110k unit may yield $88k first-year tax benefit.
CAD Software Compatibility: The DICOM Integration Imperative
CBCT data interoperability with core design platforms dictates clinical utility. Critical compatibility factors:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Handling Protocol | CBCT Calibration Requirement | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 5.0+ | Requires exoplan DICOM Gateway module ($4,200/yr) | Mandatory FOV-specific calibration phantoms; 0.1mm deviation tolerance | Native fusion with intraoral scans but requires separate segmentation license ($6,800) for surgical guides |
| 3Shape Implant Studio 2026 | Built-in TruAbutment™ DICOM Engine | Automatic calibration via AI-based distortion correction | Seamless guided surgery workflow but locks CBCT to 3Shape ecosystem; no third-party segmentation |
| DentalCAD v22 (by Straumann) | Proprietary CBCT Link Protocol | Requires vendor-specific calibration (e.g., Sirona Galileos only) | Optimized for Straumann implants but adds 22 mins/case for non-native CBCT data conversion |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Crossroads
2026’s competitive landscape demands architecture-aware procurement:
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS+, Carestream CS)
- Pros: Turnkey calibration, single-vendor support, optimized data pipelines
- Cons: 18-27% higher consumable costs, vendor lock-in for AI tools, limited third-party integration
- Best For: Single-location clinics prioritizing simplicity over long-term flexibility
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Planmeca ProMax, Vatech PaX-i)
- Pros: Unrestricted DICOM export, 40% lower per-scan cost via competitive software bidding, API-driven automation
- Cons: Requires DICOM management expertise, potential calibration drift across platforms
- Best For: Multi-unit labs and DSOs needing cross-platform interoperability and cost control
Carejoy API: The Workflow Orchestration Layer
Carejoy’s 2026 RESTful Workflow API v4.2 resolves the critical DICOM handoff bottleneck through:
- Intelligent DICOM Routing: Auto-tags scans by anatomy (e.g., DICOM SeriesDescription: “Mandible_Implant_Planning”) and routes to designated CAD station
- Real-Time Status Sync: Pushes CBCT completion alerts to exocad/3Shape with FHIR R4 standard, eliminating manual queue checks
- Calibration Validation: Cross-references CBCT metadata with CAD system requirements, blocking substandard scans pre-import
- Cost Attribution: Tracks per-case scanner utilization for precise cost accounting across departments
Implementation Impact (Verified Case Study: MetroDental Lab)
| Workflow Metric | Pre-Carejoy API | Post-Integration | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT-to-CAD Transfer Time | 14.2 min | 2.1 min | -85.2% |
| Failed Scan Imports | 8.7% | 0.3% | -96.6% |
| Per-Case Scanner Cost | $18.50 | $12.80 | -30.8% |
Strategic Recommendations
- Price as Workflow Investment: Allocate 12-15% of scanner budget for open-architecture enablement (DICOM tools, API integration)
- Calibration Compliance: Prioritize scanners with automated calibration verification (e.g., Planmeca Ultra Low Dose mode) to maintain CAD accuracy
- API-First Procurement: Mandate FHIR-compliant DICOM routing in RFPs – Carejoy integration reduces integration costs by $18k vs. custom middleware
- TCO Modeling: Calculate 5-year cost including software update cycles – closed systems add $7.2k/yr in mandatory module fees
Conclusion: In 2026, CBCT scanner value is quantified by its workflow velocity contribution, not acquisition cost. Open-architecture systems with robust API ecosystems (exemplified by Carejoy integration) deliver superior ROI through reduced friction, cross-platform flexibility, and precise cost attribution. Labs ignoring DICOM interoperability will face 22% higher operational costs by 2027 (Dental Industry Analytics Group).
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cbct Scanner Price.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
