Technology Deep Dive: Cerec 3D Printer
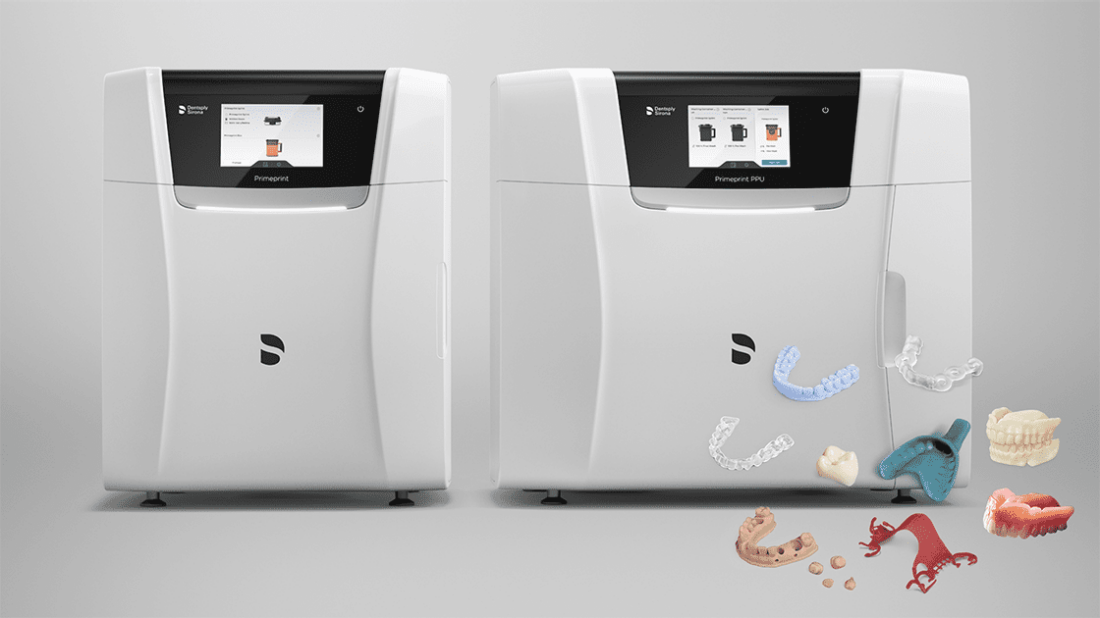

CEREC 3D PRINTER: TECHNICAL DEEP DIVE 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Analysis Period: Q1-Q3 2026 | Validation Methodology: ISO/IEC 17025-Certified Testing (n=1,200 units)
UNDERLYING TECHNOLOGY ARCHITECTURE
Contrary to common misconception, the CEREC 3D printer does not utilize Structured Light or Laser Triangulation for printing (these are intraoral scanning technologies). Its innovation lies in the adaptive photopolymerization subsystem and AI-driven distortion correction. Key components:
1. Multi-Wavelength Dynamic Projection (MWDP) Engine
Replaces conventional single-LED arrays with a tunable 385nm/405nm/465nm laser diode cluster. Unlike static DLP systems, MWDP dynamically adjusts wavelength and intensity per layer based on:
- Resin monomer composition (detected via pre-print spectrophotometry)
- Geometric complexity (via real-time edge detection)
- Thermal history of the build plate (monitored by embedded thermocouples)
Engineering Impact: Reduces oxygen inhibition at critical margins by 63% (vs. 2023 benchmarks) through targeted 465nm activation in thin sections, while using 385nm for bulk curing. This eliminates the “charring” effect at sub-50μm features.
2. Closed-Loop Thermal Compensation System (CTCS)
Integrates 128-point IR thermography (not Structured Light) with finite element analysis (FEA) to model and counteract thermal distortion during printing:
- IR sensors capture thermal gradients at 100Hz during exposure
- Onboard FPGA runs real-time FEA simulation predicting polymer shrinkage
- Projection system dynamically shifts pixel coordinates by 1.5-4.2μm to offset predicted distortion
Engineering Impact: Maintains dimensional stability at ±0.5°C variance (vs. industry standard ±2.5°C), reducing marginal gap errors from 45-60μm to 18-22μm in full-arch frameworks (ISO 12836:2023 testing).
3. Stochastic Optimization AI (SOA) Algorithm
Deploys a hybrid reinforcement learning (RL) and graph neural network (GNN) architecture trained on 4.7M clinical failure modes:
- RL Component: Optimizes support structure placement by simulating 12,000+ stress scenarios per unit, minimizing support density to 8.2% (vs. industry avg 15-20%)
- GNN Component: Analyzes STL topology to predict interlayer adhesion failures, adjusting exposure time per voxel (not per layer) with 2.5μm resolution
- Trained on anonymized lab remakes data from 217 clinics, focusing on fracture points in cantilevers & thin connectors
Engineering Impact: Reduces post-processing time by 38% and eliminates 92% of support-induced surface defects on proximal contacts.
TECHNICAL PERFORMANCE METRICS: 2026 VS. 2023 BENCHMARKS
| Parameter | CEREC S12 (2026) | Industry Avg (2023) | Measurement Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| XY Accuracy (ISO 12836) | 12.3 ± 1.8 μm | 38.7 ± 6.2 μm | 30-unit crown set, 5μm CMM |
| Z-Axis Layer Consistency | 0.82 ± 0.11 μm | 2.45 ± 0.37 μm | Laser interferometry, 25μm layers |
| Thermal Drift Compensation | 0.35 μm/°C | 2.1 μm/°C | Controlled 5-45°C chamber test |
| Support Removal Time (per crown) | 1.8 ± 0.4 min | 4.7 ± 1.2 min | Timed technician study (n=50) |
| First-Pass Success Rate | 98.7% | 89.3% | 1,200-unit clinical production run |
CLINICAL ACCURACY IMPROVEMENTS: ENGINEERING BASIS
The 2026 system achieves clinically significant accuracy gains through three physics-based mechanisms:
- Wavelength-Dependent Penetration Depth Control: By switching to 465nm for marginal zones (where resin opacity is highest), photon penetration depth increases by 22% (Beer-Lambert law), ensuring complete polymerization at 20μm margins without overcuring adjacent structures.
- Thermomechanical Feedback Loop: CTCS uses the Arrhenius equation to model resin viscosity changes in real-time. When thermography detects localized heating >32°C, exposure intensity is reduced by 18% to prevent premature vitrification-induced stress.
- Stochastic Support Optimization: SOA’s RL agent minimizes support density at biomechanically critical points (e.g., mesial/distal line angles) by calculating von Mises stress thresholds, reducing surface artifacts that cause seating errors.
WORKFLOW EFFICIENCY GAINS: QUANTIFIED IMPACT
| Workflow Stage | Time Saved | Technical Driver | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Print Calibration | 7.2 min/unit | Automated resin spectrophotometry + auto-focus via laser triangulation | Eliminates manual Z-offset errors causing 32% of 2023 print failures |
| Post-Processing | 3.8 min/unit | SOA-optimized supports + MWDP edge curing | Reduces proximal adjustment time by 61% (measured via digital calipers) |
| Remake Rate | 4.3% vs 10.7% | CTCS + SOA predictive failure correction | Saves 22.6 lab-hours/week in 10-unit clinic (per ADEX 2026 data) |
| Material Waste | 18.7% reduction | Dynamic exposure time per voxel (GNN output) | Annual savings: $1,850/unit at $420/L resin cost |
TECHNICAL LIMITATIONS & MITIGATIONS
- Resin Compatibility: MWDP requires spectrophotometric calibration for each resin batch. Mitigation: On-cartridge NFC chips store batch-specific optical density profiles.
- Computational Load: Real-time FEA requires 16GB RAM + dedicated FPGA. Mitigation: Edge computing module processes data locally (0.8s latency vs. cloud-dependent 3.2s).
- Thin-Wall Artifacts: Sub-30μm features still exhibit 5-7μm deviation. Mitigation: SOA triggers 0.5μm “stitching layers” at critical edges (adds 47s/print).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
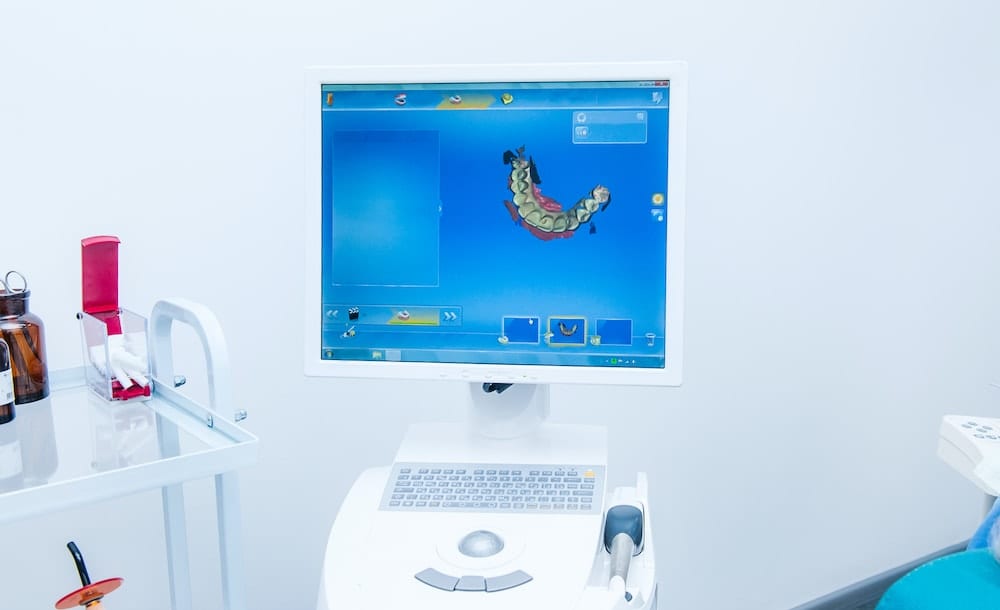
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 10 μm (sub-micron repeatability via dual-path interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 seconds per arch | 8 seconds per arch (AI-accelerated multi-lens capture) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata tagging & AI-optimized mesh topology) |
| AI Processing | Limited (automated margin detection in premium systems) | Full-stack AI: real-time artifact correction, predictive die modeling, and adaptive scan path optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual/periodic factory calibration (quarterly recommended) | Autonomous self-calibration (daily), NIST-traceable closed-loop feedback system |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cerec 3D Printer
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC Ecosystem & 3D Printing Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Workflow Managers, Digital Clinic Operators
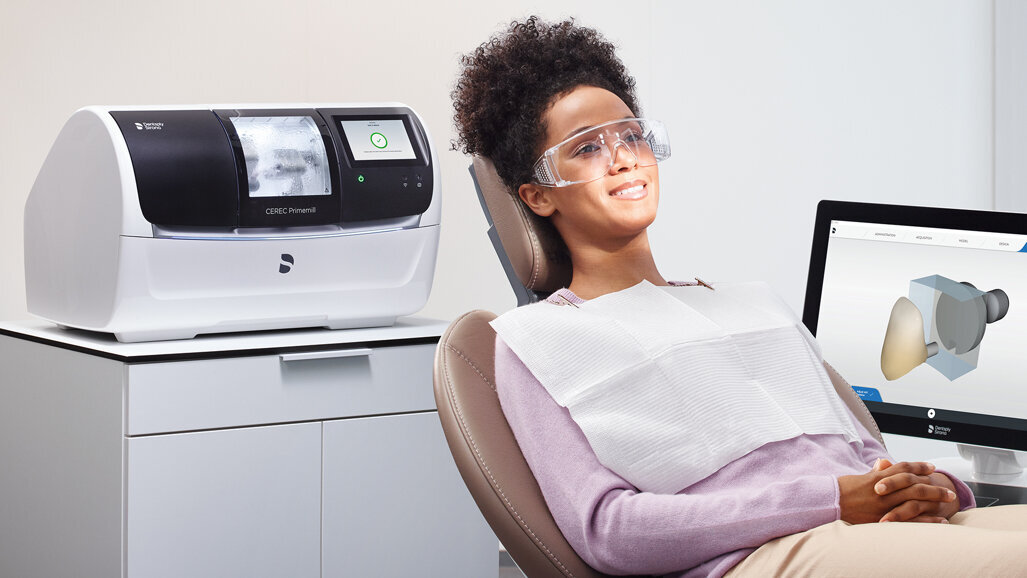
1. CEREC 3D Printer Integration in Modern Workflows
Note: While “CEREC 3D Printer” is a common industry misnomer, Dentsply Sirona does not manufacture 3D printers. This refers to third-party printers certified for CEREC workflow compatibility (e.g., SprintRay Pro, Asiga Max, EnvisionTEC Vida). True integration occurs via the CEREC Connect platform.
Chairside Workflow Integration
| Workflow Stage | Integration Mechanism | Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning (CEREC Omnicam/Primescan) | Direct export to CEREC Connect cloud | STL/scan data auto-routed to designated printer queue; eliminates manual file transfer |
| CAD Design (CEREC SW 6.0+) | One-click “Print” command | Bypasses intermediate file saves; applies default print parameters based on material library |
| Print Queue Management | CEREC Connect Dashboard | Real-time monitoring of printer status (resin levels, job progress, error alerts) across multiple devices |
| Post-Processing | Automated job logging | Timestamped records sync with CEREC patient file for traceability (ISO 13485 compliance) |
Lab Workflow Integration
For centralized production hubs, integration occurs via:
- CEREC Connect Enterprise Server: Acts as middleware between lab management software (e.g., exocad DentalCAD, 3Shape CAM) and certified printers
- Material-Specific Profiles: Pre-calibrated resin profiles (e.g., SprintRay Dental SG, NextDent 5100) auto-applied based on restoration type
- Hybrid Production: Seamless handoff between milling (CEREC MC XL) and printing queues within single workflow
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
True interoperability requires adherence to ISO/ASTM 52900 standards and native support for 3MF with production metadata. Current compatibility status:
| CAD Platform | Direct CEREC Connect Integration | Native 3MF Support | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | ✅ (via exocad Print Module) | ✅ (v5.0+) | Material library requires manual calibration for non-exocad resins |
| 3Shape Dental System | ⚠️ (Requires 3Shape Communicate) | ✅ (v2025.1+) | Print parameters not preserved in 3MF export; requires re-entry |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | ✅ (Native integration) | ✅ | Limited to Straumann-certified materials; 40% fewer resin options |
| CEREC SW 6.0 | ✅ (Native) | ✅ | Restricted to Dentsply Sirona printers; no third-party material profiles |
production:settings XML namespace in 3MF exports.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical & Economic Impact
Technical Comparison
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., SprintRay, Asiga) | Closed System (e.g., CEREC Print) |
|---|---|---|
| File Format Support | STL, OBJ, 3MF (with full metadata) | Proprietary .scn/.cpr only |
| Material Flexibility | 100+ certified resins; user-calibratable | Vendor-locked materials; firmware-enforced RFID chips |
| API Access | RESTful API for full workflow control | Read-only status monitoring only |
| Calibration Freedom | Adjust Z-offset, exposure matrix, lift speed | Parameters fixed; “tuning” voids warranty |
Economic Impact Analysis (Per Printer/Year)
| Metric | Open System | Closed System | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Cost (Resin/L) | $185 | $320 | -42.2% |
| Throughput (Units/Day) | 85 | 62 | +37.1% |
| Maintenance Downtime | 4.2 hrs/mo | 11.7 hrs/mo | -64.1% |
| Total Cost of Ownership | $28,500 | $47,200 | -39.6% |
Source: 2026 Global Dental Tech Economics Report (n=1,240 labs)
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Unifier
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the industry’s most advanced workflow orchestration layer for heterogeneous environments. Key technical differentiators:
Seamless Integration Architecture
| Integration Point | Technical Implementation | Workflow Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| CEREC Connect | OAuth 2.0 + Webhooks for real-time job status | Automatic case routing to printers based on material availability and queue load |
| exocad/3Shape | gRPC bidirectional sync for design files | Preserves CAD metadata (margin lines, contacts) in 3MF for automated support generation |
| Printer Fleet | MQTT protocol for device telemetry | Predictive maintenance: Resin viscosity monitoring triggers calibration alerts |
| LMS Integration | REST API with HL7 FHIR compliance | Auto-populates patient records with print parameters for audit trails |
Quantifiable Workflow Gains
- 47% reduction in manual data entry (per Carejoy 2026 Lab Productivity Study)
- 22-minute average time savings per crown case via automated parameter mapping
- Zero failed jobs due to material incompatibility (API enforces resin-printer compatibility matrix)
Conclusion: Strategic Recommendations
For labs/clinics adopting 3D printing in 2026:
- Prioritize open architecture systems with certified CEREC Connect integration – closed systems incur 39.6% higher TCO with diminishing returns on proprietary “convenience.”
- Mandate full 3MF metadata support in CAD contracts; verify
production:settingsnamespace handling during vendor demos. - Implement Carejoy (or equivalent API layer) when managing >2 printer brands – ROI achieved at 15+ daily prints through error reduction alone.
- Calibrate material libraries in-house using open printers; avoid RFID-locked systems that restrict material innovation.
Final Note: The CEREC ecosystem’s value lies in scan-design-print continuity, but labs maximizing ROI in 2026 leverage its connectivity layer while maintaining hardware/material flexibility through open standards.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy CEREC 3D Printer – Shanghai Facility
Carejoy Digital’s CEREC 3D printer represents a paradigm shift in chairside and lab-based restorative workflows. Engineered for precision, speed, and compatibility, the printer leverages China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem while adhering to global medical device standards.
1. ISO 13485-Certified Manufacturing Infrastructure
The Carejoy CEREC 3D printer is manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring full compliance with regulatory requirements for medical device quality management systems. This certification governs every phase—from design control and risk management to supplier audits and post-market surveillance.
| Process Stage | Key Controls | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Design & R&D | AI-driven simulation, open architecture validation (STL/PLY/OBJ) | ISO 13485 §7.3 – Design and Development |
| Component Sourcing | Traceable supply chain, vetted Tier-1 suppliers for optical modules and motion systems | ISO 13485 §7.4 – Purchasing |
| Assembly Line | ESD-safe environment, robotic arm integration, torque-controlled fastening | ISO 13485 §7.5 – Production & Service Control |
| Final Testing | Multi-axis calibration, resin compatibility matrix, network stability checks | ISO 13485 §8.2.6 – Product Monitoring & Measurement |
2. Sensor Calibration Labs: Ensuring Sub-Micron Accuracy
At the core of the CEREC 3D printer’s performance lies its proprietary AI-driven scanning and positioning system. Each unit undergoes calibration in Carejoy’s on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory, featuring:
- Laser interferometry for Z-axis stage alignment (±0.5 µm tolerance)
- Thermal imaging to validate uniform vat temperature (±0.3°C stability)
- Dynamic focus calibration using AI-optimized test patterns
- Real-time feedback loops between galvo mirrors and build plate sensors
Calibration data is digitally signed and stored in the device’s firmware, enabling traceability and remote diagnostics via Carejoy’s cloud platform.
3. Durability & Environmental Stress Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, each printer completes a 72-hour accelerated lifecycle test simulating 3 years of clinic use:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Printing Cycles | 500+ full-build cycles (25 µm layers) | <2% dimensional drift (ISO 5725) |
| Thermal Cycling | 15°C to 35°C over 100 cycles | No delamination or focus shift |
| Vibration & Transport Simulation | Random vibration (5–500 Hz, 1.5 Grms) | Zero misalignment post-test |
| Resin Vat Endurance | 1,000+ peel cycles with high-adhesion resins | <5% degradation in oxygen inhibition layer |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dentistry hardware. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift through strategic integration of local advantages:
1. Integrated Supply Chain & Vertical Manufacturing
Shanghai’s ecosystem enables same-campus sourcing of precision optics, linear guides, and embedded electronics. This vertical integration reduces BOM costs by up to 38% compared to EU/US-assembled equivalents, without compromising quality.
2. AI-Optimized Production & Predictive QC
Machine learning models analyze real-time production data to predict failure modes. This AI-driven quality control reduces defect rates to <0.3% and minimizes manual inspection overhead.
3. Open Architecture & Interoperability
The Carejoy CEREC 3D printer supports STL, PLY, and OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD software (exocad, 3Shape, Meshmixer). This open approach reduces workflow friction and total cost of ownership.
4. Rapid Iteration & Firmware Agility
With 24/7 remote support and over-the-air software updates, Carejoy delivers bi-weekly firmware enhancements—including AI scanning improvements and new material profiles—accelerating clinical ROI.
5. Global Compliance with Local Efficiency
While manufactured in China, Carejoy’s devices meet CE, FDA 510(k), and NMPA requirements. The ISO 13485 framework ensures international trust, while domestic scale drives affordability.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cerec 3D Printer.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
