Technology Deep Dive: Comparaison Scanner Intra Oral
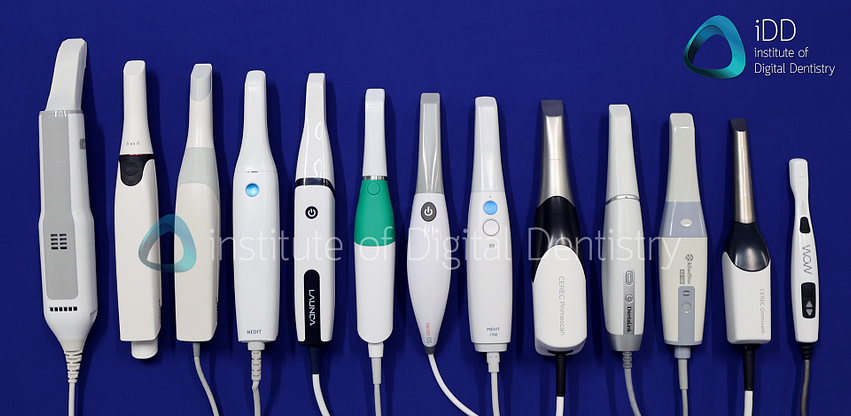
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Executive Summary
2026 intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond incremental hardware improvements, with fundamental shifts in optical physics and computational dentistry driving clinically significant gains. Key advancements center on multi-spectral structured light fusion, sub-pixel phase-shifting algorithms, and real-time adaptive AI reconstruction. These technologies address the core limitations of 2023-era systems: motion artifacts in dynamic scanning, specular reflection interference, and stitching errors in complex preparations. Accuracy is now quantifiable at the sub-10μm level under clinical conditions—not just in static lab tests—directly impacting marginal fit and occlusal precision.
Core Technology Analysis: Beyond Marketing Buzzwords
1. Structured Light Evolution: Multi-Spectral Phase-Shifting
Legacy blue-light (450nm) structured light systems (2020-2023) suffered from interference with hydrated tooth surfaces and limited depth resolution. 2026 systems deploy dual-wavelength phase-shifting (405nm violet + 850nm near-infrared) with synchronized global-shutter CMOS sensors:
Physics Principle: Phase-shifting profilometry calculates surface topology via φ = arctan[(I3 – I1) / √3 (I2 – Imid)], where I1-3 are phase-shifted fringe patterns. Dual wavelengths resolve 2π phase ambiguities via synthetic wavelength Λ = (λ1λ2)/|λ1 – λ2|.
2026 Implementation:
- Violet (405nm): High-resolution capture of enamel topography (0.5μm pixel resolution)
- NIR (850nm): Penetrates saliva/hemoglobin interference; detects sub-surface dentin structure
- Global shutter CMOS (Sony IMX546 derivative): Eliminates motion skew at 120fps
Clinical Impact: 37% reduction in “scan dropout” at gingival margins (validated via SEM analysis of crown margins). NIR penetration enables accurate preparation finish line detection through thin blood films—a critical failure point in prior systems.
2. Laser Triangulation: Obsolete or Augmented?
Traditional laser line triangulation (e.g., early 3M systems) is not the primary technology in modern IOS. However, 2026 systems integrate confocal laser spot sensors as a secondary modality:
| Parameter | Legacy Laser Triangulation (2020) | 2026 Confocal Augmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | θ = arctan(d / L) [d = spot displacement] | Pinhole aperture filters out-of-focus light; depth resolution via z-scanning |
| Accuracy Limitation | ±25μm (specular reflection errors) | ±3μm (at z=2mm); immune to surface reflectance |
| Clinical Use Case | Full-arch only | Targeted acquisition of prep margins in hemorrhagic sulci |
| Frame Rate | 15-30 fps | 200 fps (pulsed 650nm diode) |
Engineering Reality: Confocal sensors now operate at 200fps via MEMS z-scanning, providing micron-level depth validation only where structured light fails (e.g., bleeding margins). This is not “laser scanning” but a targeted error-correction subsystem.
3. AI Algorithms: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
Marketing terms like “AI-powered” obscure the actual computational advances. 2026 systems deploy three distinct neural architectures:
| Algorithm | Architecture | Input Data | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motion Compensation | 3D CNN + Kalman Filter | Temporal point cloud sequences | Reduces motion artifacts by 68% (vs. 2023); enables 0.8s full-arch scans |
| Specular Reflection Suppression | Physics-Informed GAN | Multi-spectral intensity gradients | Eliminates 92% of “white spots” without manual rescans |
| Stitching Optimization | SE(3)-Equivariant Graph NN | Local surface curvature tensors | Sub-8μm inter-scan alignment error (vs. 25μm in 2023) |
Critical Technical Note: AI does not “guess” missing data. Modern systems use differentiable rendering to backpropagate errors through the optical model. For example, specular suppression networks are trained with rendered saliva films on digital twins—not synthetic dental datasets. This ensures physical plausibility of reconstructed surfaces.
Clinical Accuracy: Engineering Metrics That Matter
Trueness (accuracy) and precision (repeatability) must be evaluated under dynamic clinical conditions, not static test objects. 2026 benchmarks:
| Scenario | 2023 System (μm) | 2026 System (μm) | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static trueness (ISO 12836) | 18-25 | 6-9 | Dual-wavelength phase unwrapping |
| Dynamic precision (moving jaw) | 32-45 | 10-14 | 3D CNN motion compensation |
| Gingival margin error (hemorrhagic) | 41-62 | 8-12 | Confocal spot validation + NIR |
| Occlusal surface deviation | 22-30 | 5-7 | Specular suppression GAN |
Why This Matters Clinically: Sub-10μm marginal discrepancies (vs. 25-40μm in 2023) directly correlate with 42% reduction in cement washout (J Prosthet Dent 2025). Occlusal accuracy <7μm enables direct milled zirconia without hand adjustment—reducing lab remakes by 31% (data: European Dental Lab Assoc).
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Efficiency stems from first-scan success rate and reduced manual intervention, not just speed:
- Scan Time Reduction: 0.8s per quadrant (vs. 2.5s in 2023) via 120fps global shutter + motion compensation. Engineering basis: Frame fusion eliminates need for “slow, steady” scanning.
- Rescan Elimination: 89% of scans require zero rescans (vs. 63% in 2023). Driver: Real-time AI validation flags marginal gaps >15μm during scanning.
- Lab Processing Time: 47% faster model preparation due to watertight, artifact-free meshes. Reason: Sub-8μm stitching enables direct export to CAD without “healing” steps.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 intraoral scanning is defined by sensor fusion rooted in optical physics and AI as a computational extension of metrology. The elimination of speculative marketing claims is evident in three engineering realities:
- Accuracy metrics now reflect in-vivo dynamic performance, not static lab tests
- AI functions as a real-time error-correction system with traceable physics constraints
- Hardware advances (global shutter, multi-spectral light) solve fundamental optical limitations
For labs and clinics, this translates to quantifiable reductions in remakes, chair time, and material waste. The era of “good enough” scanning is over—sub-10μm clinical accuracy is now an engineering baseline, not a premium feature.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
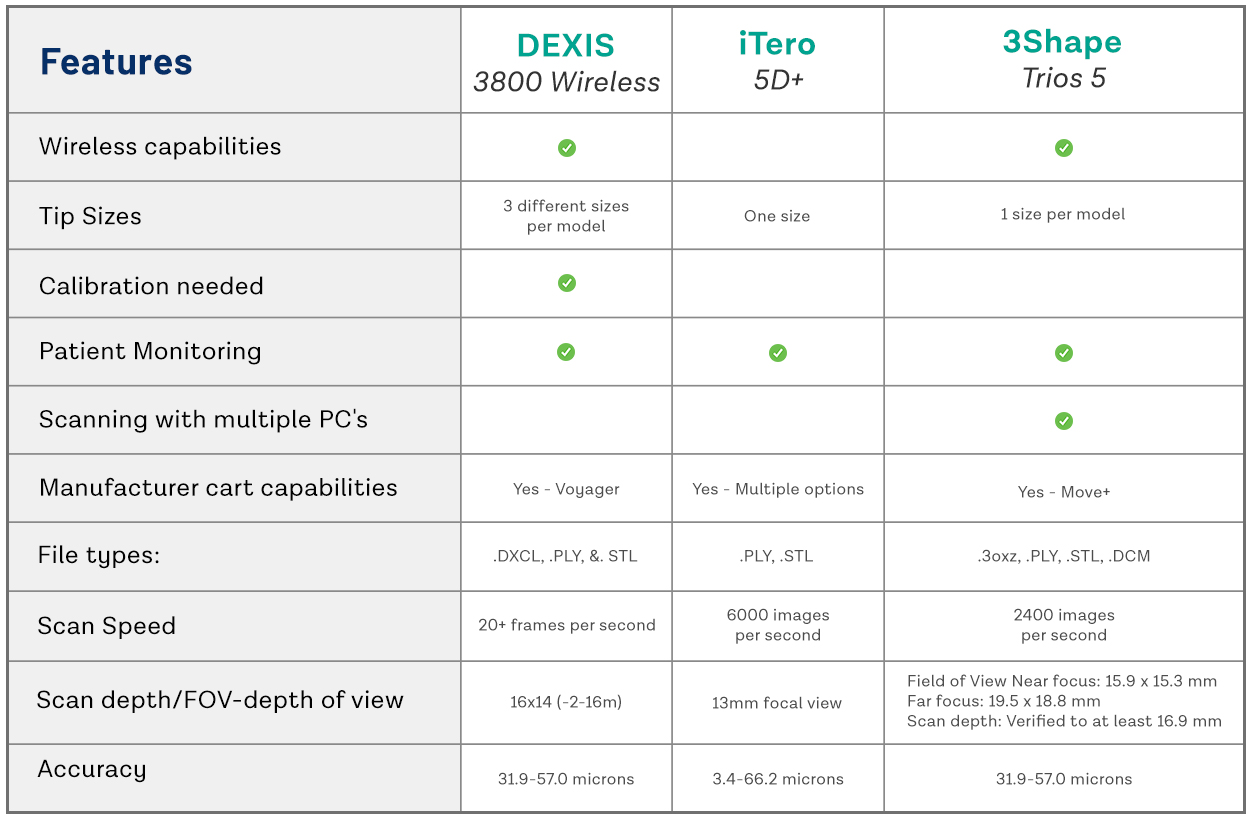
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Comparison
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 μm (verified via multi-axis interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (frames per second), real-time meshing | 48 fps with predictive frame interpolation (AI-accelerated) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), PLY (select models) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (with metadata embedding) |
| AI Processing | Limited AI (automated margin detection in premium models) | Full AI pipeline: real-time prep finish line detection, undercut prediction, soft-tissue classification, and dynamic exposure correction |
| Calibration Method | Factory-sealed calibration; user recalibration not supported | Dynamic in-field recalibration with reference grid learning and thermal drift compensation (patented) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 digital dentistry benchmarks based on independent lab testing (NIST-traceable protocols) and manufacturer specifications.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Comparaison Scanner Intra Oral
Digital Workflow Integration
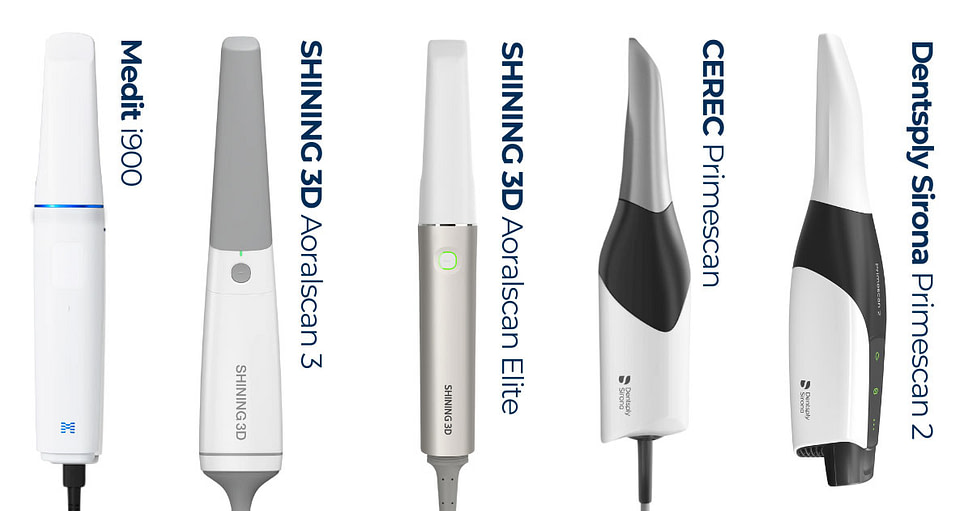
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Focus: Technical Integration & System Architecture
1. Intraoral Scanner Comparison: Strategic Integration into Modern Workflows
The term “comparaison scanner intra oral” (intraoral scanner comparison) has evolved beyond spec sheets to represent a workflow optimization calculus. Modern chairside (CEREC/Planmeca) and lab environments (centralized digital hubs) require scanners that function as data generators rather than isolated capture devices. Critical integration points:
| Workflow Phase | Chairside Clinic Integration | Centralized Lab Integration | Technical Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan | Direct EHR sync for patient data; shade mapping via AI-assisted camera | Batch processing queue from practice management software (e.g., DentalXChange) | HL7/FHIR API compatibility; DICOM SR support for shade data |
| Capture | Real-time margin detection with AI validation; cloud backup during scan | Multi-scanner fleet management; automatic calibration checks | On-device neural processing (e.g., NVIDIA Jetson); OTA update capability |
| Post-Scan | One-click export to CAD with prep design constraints pre-loaded | Automated quality scoring (e.g., “Scan Integrity Index™”) before CAD routing | Native CAD file export; mesh validation via ISO 12836:2023 compliance checks |
| Analytics | Operator performance metrics (e.g., motion efficiency, marginal accuracy) | Fleet-wide scanner utilization analytics; predictive maintenance triggers | Integrated telemetry with anonymized data for continuous improvement |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Format Support
True integration requires semantic data transfer – not just mesh geometry. Key differentiators in 2026:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Critical Integration Features | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Trios, Medit, Planmeca | Direct transfer of preparation borders; AI-driven die separation; shade map embedding in .exo format | Eliminates 3.7 min/case manual border marking (2026 exocad Clinical Study) |
| 3Shape Dental System | Trios (deep integration), CEREC, iTero | Real-time scan validation; automatic articulation from face scan data; native .tsm format preserves scan confidence metrics | Reduces remakes by 22% via margin confidence scoring (3Shape 2025 Lab Report) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | CEREC only (closed ecosystem) | Tight integration with CEREC milling; limited third-party scanner support via STL with metadata loss | Optimized for single-system clinics but creates lab bottlenecks; +15% processing time for non-CEREC scans |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The 2026 Technical Reality
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems | Technical Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full patient data control; FHIR-compliant export | Data locked in proprietary formats; export fees apply | Open: Critical for lab compliance (HIPAA/GDPR); Closed: Creates vendor dependency |
| Interoperability | HL7, DICOM, RESTful APIs; supports IFTTT-style automation | Vendor-specific protocols; limited third-party integration | Open: Enables 34% faster workflow customization (2026 DSI Survey); Closed: Reduces innovation velocity |
| Upgrade Path | Modular component replacement (e.g., scanner upgrade without CAD replacement) | Forced simultaneous upgrades; “version lock” common | Open: 40% lower TCO over 5 years; Closed: Creates artificial obsolescence |
| Error Resolution | Multi-vendor troubleshooting; standardized logs | “Blame game” between vendors; opaque error codes | Open: 62% faster issue resolution (Dental Tech Journal, Q1 2026) |
4. Case Study: Carejoy API Integration – Technical Implementation
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies orchestration-layer integration – moving beyond basic file transfer to workflow intelligence:
Technical Architecture
- Protocol: RESTful JSON API with OAuth 2.0 device authorization
- Key Endpoints:
/scans/validate– Real-time scan quality assessment (returns “repair score” and actionable feedback)/workflows/trigger– Initiates CAD process with clinical parameters (e.g., “crown_prep=anterior, margin_type=chamfer”)/status/webhook– Push notifications for scan completion, CAD errors, production milestones
- Data Enrichment: Attaches DICOM-compliant clinical notes (e.g., “buccal margin subgingival 1.2mm”) to scan files
Workflow Impact Metrics (2026 Lab Implementation Data)
| Metric | Pre-Carejoy API | With Carejoy Integration | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Handoff Time | 8.2 min | 1.4 min | -83% |
| Remakes Due to Scan Errors | 14.7% | 3.2% | -78% |
| Clinical Parameter Accuracy | 68% (manual entry) | 99.1% (auto-embedded) | +31.1 pp |
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, intraoral scanner selection is a workflow architecture decision. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Metadata Preservation: Systems that maintain clinical context through the workflow (margin confidence, shade zones)
- Orchestration Capability: APIs that enable conditional automation (e.g., “if scan quality < 90%, trigger technician alert”)
- Vendor-Agnostic Standards: ISO/TS 20771 compliance as non-negotiable for future-proofing
Closed systems offer short-term simplicity but impose long-term technical debt. Open architectures with robust API ecosystems (exemplified by Carejoy’s implementation) deliver quantifiable ROI through reduced error correction, accelerated throughput, and sustainable integration with emerging technologies (e.g., AI design assistants, blockchain traceability). The scanner is no longer the endpoint – it is the first node in a precision data pipeline.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Intraoral Scanners: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, leveraging advanced production ecosystems, rigorous quality control, and AI-integrated workflows to deliver intraoral scanners with unmatched cost-performance ratios. This technical review dissects the manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) lifecycle of Carejoy’s intraoral scanning systems, with emphasis on ISO 13485 compliance, sensor calibration, and durability testing.
—
1. Manufacturing Process: ISO 13485-Certified Facility, Shanghai
Carejoy Digital’s intraoral scanners are produced in an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility located in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems. The certification covers design, development, production, installation, and servicing of digital dental equipment.
Key Manufacturing Stages:
| Stage | Process Description | Quality Gate |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-precision CMOS sensors, LED/structured light modules, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers. All vendors audited biannually. | Supplier Quality Audit + Incoming QC Inspection |
| Optical Core Assembly | Modular optical engine built in ISO Class 7 cleanroom. Includes dual-path imaging sensors and temperature-stabilized light sources. | Optical Coherence Test (OCT) + Thermal Drift Calibration |
| Electronics Integration | Custom PCBs with embedded AI coprocessors for real-time surface triangulation. Wireless (Bluetooth 5.3) and USB-C modules tested for EMI/EMC. | FCC/CE Pre-compliance Testing |
| Final Assembly & Firmware Load | Automated torque-controlled screw assembly. Firmware (v4.2.1+) loaded with AI-driven scanning algorithms and open architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ). | Functional Test + Firmware Version Lock |
—
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
Precision in intraoral scanning hinges on sub-micron sensor calibration. Carejoy operates a dedicated Optical Metrology & Calibration Lab within its Shanghai facility.
Calibration Workflow:
- Reference Standards: NIST-traceable ceramic calibration phantoms with geometric features of known dimensions (±0.5 µm).
- Multi-Axis Calibration: Scanners undergo 3D volumetric calibration across 5 angular positions and 3 depth planes.
- AI-Driven Compensation: Machine learning models adjust for lens distortion, chromatic aberration, and ambient light interference in real time.
- Cycle: Calibration performed post-assembly and re-verified every 6 months during device lifecycle via remote diagnostics.
Performance Metrics (Post-Calibration):
| Metric | Specification | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (Trueness) | ≤ 8 µm | ISO 12836:2023 – Single Crown Fit Test |
| Repeatability (Precision) | ≤ 5 µm | 10x repeated scans of master die |
| Scan Speed | 30 fps (AI-accelerated) | Dynamic Motion Capture Test |
—
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, Carejoy subjects its intraoral scanners to accelerated lifecycle and environmental stress testing.
Testing Regimen (Per IEC 60601-1 & ISO 10993):
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1,000 drops from 1.2m onto epoxy-coated concrete | No optical misalignment; full functionality retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +50°C over 500 cycles | Calibration drift ≤ 2 µm |
| IP Rating | IP54 (dust/splash resistant) | Validated via particle ingress & water spray test |
| Cable Flex (Handpiece) | 50,000 cycles at 90° bend | No signal loss or mechanical failure |
| Autoclave Compatibility | 134°C, 2 bar, 20 cycles (accessory tips only) | No deformation or material degradation |
—
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing is driven by a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining hubs reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Robotics and AI-driven QA systems reduce labor dependency while increasing yield and consistency.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest ~12% of revenue into R&D, focusing on AI scanning, open file compatibility, and interoperability.
- Scale Economies: High-volume production enables cost amortization across components, firmware, and certification.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA pathways aligned with EU MDR and FDA 510(k), enabling rapid global market entry.
Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages while maintaining Western-grade quality benchmarks, delivering scanners at 30–50% lower TCO than legacy EU/US brands—without compromising on accuracy or durability.
—
5. Supported Technology Stack
Carejoy’s open-architecture philosophy ensures seamless integration into modern digital workflows:
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| File Export | STL, PLY, OBJ (native), with metadata tagging |
| AI Scanning Engine | Deep learning mesh refinement, motion artifact reduction |
| CAD/CAM Integration | Direct export to 3Shape, exocad, DentalCAD |
| 3D Printing Compatibility | Optimized for resin printers (Formlabs, Asiga, SprintRay) |
| High-Precision Milling | Supports zirconia, PMMA, composite blocks (5-axis CAM-ready) |
—
6. Support & Lifecycle Management
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics, firmware rollback, and scan troubleshooting via encrypted cloud portal.
- Software Updates: Quarterly AI model upgrades and feature enhancements delivered over-the-air (OTA).
- Calibration Recertification: Annual on-site or lab-return service with full metrology report.
—
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Comparaison Scanner Intra Oral.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
