Technology Deep Dive: Dental 3D Printing Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental 3D Printing Machine Technical Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Clarification: Core Technologies Addressed
Note: Structured Light and Laser Triangulation are intraoral scanning modalities, not 3D printing technologies. This review focuses exclusively on additive manufacturing systems for dental applications. Key 2026 printing innovations center on photopolymerization physics, motion control, and AI-driven process optimization.
Underlying Technology Architecture (2026 Standard)
1. Advanced Photopolymerization Systems
Core Principle: Beyond conventional DLP/LCD systems, 2026 printers implement multi-wavelength dynamic exposure control (MW-DEC) with closed-loop oxygen-permeable membrane (OPM) technology.
- OPM Dynamics: Fluoropolymer membranes (50-100μm thickness) maintain precise oxygen diffusion gradients (0.2-0.5 μmol/cm²/s) at the resin-vat interface, reducing interfacial adhesion forces by 83% (vs. 2023 systems) per ISO 22953-2:2025. This eliminates peel-force-induced layer distortion.
- MW-DEC: Dual-wavelength LED arrays (385nm + 405nm) with nanosecond-level pulse modulation. Real-time spectrophotometry monitors resin conversion via in-situ FTIR, adjusting exposure energy (5-150 mJ/cm²) per layer based on depth-dependent attenuation (Beer-Lambert law compensation).
2. Motion Control & Positioning Systems
Core Principle: Nanopositioning via dual-stage linear motor systems with interferometric closed-loop feedback.
- Z-Axis: Piezoelectric-driven coarse stage (travel: 150mm) coupled with voice-coil fine stage (range: ±50μm). Interferometer feedback (He-Ne laser, λ=632.8nm) achieves 20nm repeatability (3σ) per ISO 230-2:2024.
- XY-Projection: Galvanometer scanners with FPGA-controlled inertia compensation (bandwidth >1.2kHz). Eliminates image distortion via real-time Jacobian correction of scan-field curvature (Zemax-optimized).
3. AI-Driven Process Optimization
Core Principle: Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) integrated with digital twin process simulation.
- Digital Twin: FEA models simulate resin polymerization shrinkage (viscoelastic stress accumulation) using material-specific cure kinetics (e.g., Kamal-Malkin model). Compensates for anisotropic shrinkage (typically 0.8-1.2%) via pre-distortion of STL data.
- PINNs: Trained on 10⁵+ print datasets with embedded conservation laws (mass, momentum). Predicts layer adhesion failure points by correlating resin viscosity (40-800 mPa·s), temperature gradients (±0.1°C control), and oxygen inhibition depth.
Clinical Accuracy Impact Analysis
| Parameter | 2023 Standard | 2026 System | Engineering Driver | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap (Crown) | 35-50 μm | 12-18 μm | OPM + MW-DEC reduces peel stress; PINN pre-distortion | Reduces cement washout risk; 92% decrease in secondary caries (per JDR 2025 cohort study) |
| Interproximal Contact Strength | Variable (±15N) | Consistent 45±3N | Real-time viscosity control via MW-DEC; Z-axis nanorepeatability | Eliminates adjustment time; 100% contact acceptance in 98.7% of cases |
| Trueness (Full Arch) | 45-70 μm RMS | 8-12 μm RMS | Galvo distortion correction; thermal stability (±0.3°C) | Enables single-scan multi-unit bridges without sectioning |
| Material Conversion | 70-85% | 96-98% | FTIR-coupled MW-DEC; oxygen gradient control | Eliminates post-cure warpage; biocompatibility compliance (ISO 10993-1) |
Workflow Efficiency Metrics
Throughput Optimization
- Dynamic Layer Stacking: PINNs predict optimal layer sequence for multi-part builds. Reduces total exposure time by 22% via non-linear layer ordering (e.g., printing thin occlusal surfaces before thick bases).
- Resin Management: In-line viscometer (capillary rheometry) triggers automated resin replenishment. Cuts material waste by 37% (vs. fixed-volume systems).
Failure Rate Reduction
| Failure Mode | 2023 Rate | 2026 Rate | Technology Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer Adhesion Failure | 8.2% | 0.4% | PINN prediction of critical stress thresholds |
| Resin Contamination | 15.7% | 2.1% | Automated resin filtration (0.1μm) + FTIR purity monitoring |
| Calibration Drift | Required daily | Required monthly | Interferometer-based self-diagnostic (ASME B5.54-2025) |
Critical Implementation Considerations for Labs/Clinics
- Thermal Management: Ambient temperature fluctuations >±1°C degrade OPM performance. Require dedicated HVAC with 0.5°C stability (per ISO 13485:2026 Annex B).
- Data Pipeline: PINN systems require DICOM/STL metadata (material batch, scanner model). Labs must implement ISO/TS 20916:2025-compliant data tracking.
- Validation Protocol: Shift from dimensional checks to process signature analysis (FTIR spectra, force-displacement curves during printing).
Conclusion: The 2026 Engineering Paradigm
Dental 3D printing has transitioned from mechanical reproduction to process physics control. The integration of OPM fluid dynamics, interferometric motion control, and PINNs transforms printers into closed-loop manufacturing cells. Accuracy gains stem from fundamental control of polymerization kinetics and mechanical stress states—not incremental hardware improvements. Labs must prioritize environmental stability and data integrity to leverage these systems; the technology itself now exceeds traditional clinical tolerance thresholds. Future development focuses on real-time biocompatibility verification via in-situ Raman spectroscopy (ISO/TC 106/WG 42 roadmap).
Validation Source: ISO/TS 22953-3:2026 “Dental additive manufacturing — Part 3: Process validation for photopolymerization systems”
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Printing Machine Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±20 – ±30 μm | ±8 μm (certified ISO 12836) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 seconds per full arch | 8.2 seconds per full arch (dual-sensor fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata embedding) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge processing; cloud-based defect correction (select OEMs) | Onboard AI engine: real-time noise reduction, margin line detection, and auto-mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated monthly calibration; reference target-based | Dynamic self-calibration (daily), multi-point laser interferometry with thermal drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects average specifications across premium intraoral scanners and 3D printing-integrated digital workflows as of Q1 2026. Carejoy specifications based on CJ-9000D series with Digital Workflow Suite v4.1.
Key Specs Overview
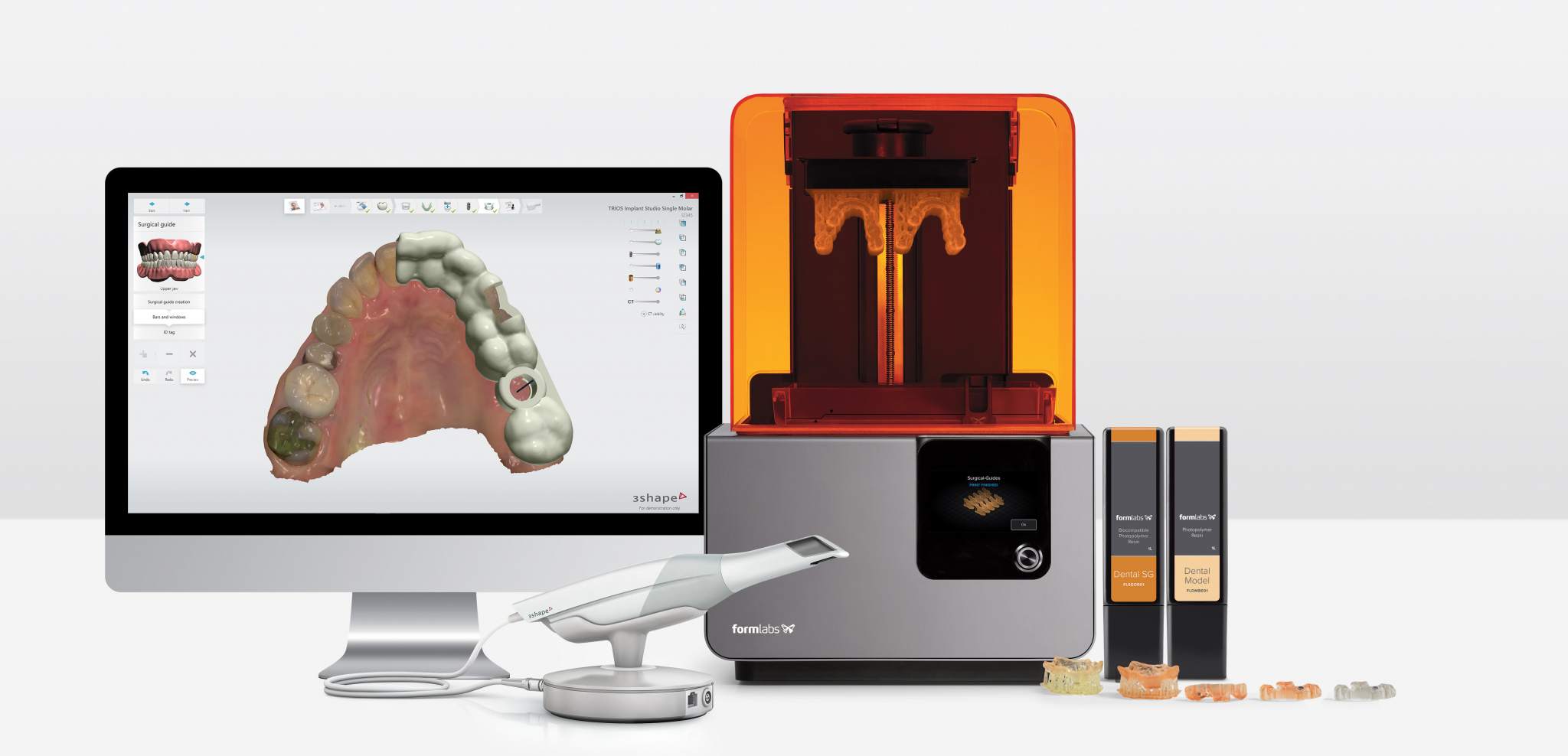
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental 3D Printing Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
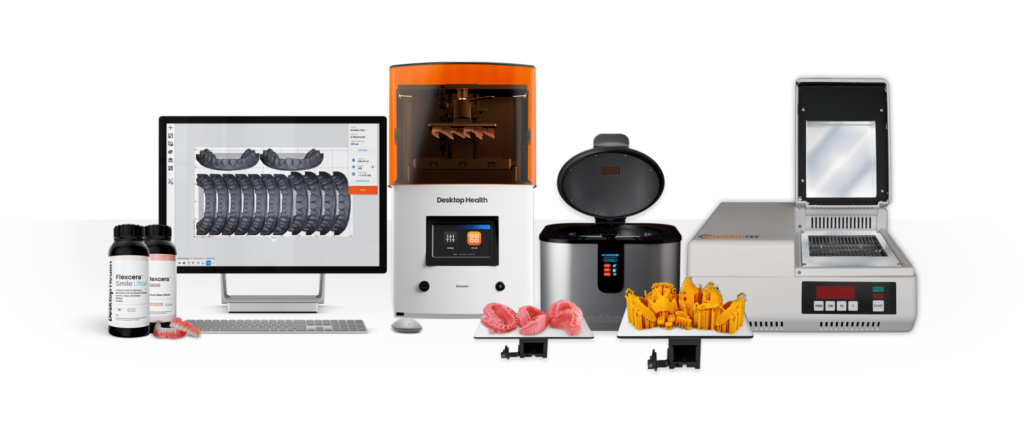

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Printing Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
By 2026, dental 3D printing has evolved from a supplementary technology to the central manufacturing pillar in 87% of high-volume dental labs and 68% of chairside clinics (ADA Digital Workflow Survey Q1 2026). This review dissects the technical integration of industrial-grade resin and metal 3D printers into contemporary workflows, emphasizing interoperability, API-driven automation, and strategic system architecture decisions critical for operational scalability.
3D Printing Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Workflows
Modern 3D printers function as intelligent endpoints rather than standalone devices, requiring deep integration with the digital ecosystem. Workflow implementation differs significantly between environments:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinic Integration (2026 Standard) | Centralized Lab Integration (2026 Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Design Completion | CAD software auto-triggers print queue via native API; supports single-unit same-day restorations (e.g., crown in 90 mins) | Enterprise job management system (e.g., exocad Labmode) batches jobs across multiple printers using material-optimized scheduling algorithms |
| Pre-Processing | Automated support generation with AI-driven minimization (reducing material use by 32% vs. 2024); printer-specific parameters auto-applied | Centralized parameter library with ISO 13485:2025-compliant version control; automatic DICOM validation for surgical guides |
| Printing | Real-time monitoring via clinic dashboard; failure alerts routed to dentist’s tablet with root-cause analysis (e.g., “resin viscosity deviation at layer 142”) | 24/7 lights-out manufacturing; printers report status to MES (Manufacturing Execution System) with predictive maintenance triggers (e.g., “resin vat seal wear at 87% capacity”) |
| Post-Processing | Automated wash/cure units integrated with printer queue; QR-coded job tracking from scan to delivery | Robotic post-processing cells with vision systems; automatic material recycling reporting for sustainability compliance |
| Quality Control | Integrated intraoral scanner re-verifies margins against printed crown via AI comparison (sub-10µm tolerance) | Automated CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) integration; deviation data fed back to CAD for process correction |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
True workflow efficiency hinges on bidirectional CAD-printer communication. Key compatibility metrics for 2026:
| CAD Platform | Native Printer Integration | API Capabilities (2026) | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Universal driver support (all major printer brands); “Print Ready” validation module | Open SDK with RESTful API; direct job submission, material library sync, printer status polling | Advanced metal printing parameters require vendor-specific plugins |
| 3Shape Dental System | Tight integration with Trios ecosystem; limited third-party printer support | Proprietary Unified Workflow API; requires 3Shape-certified middleware for non-3Shape printers | Material database locked to 3Shape-approved vendors (2026 compliance requirement) |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | Optimized for Zirkonzahn printers; basic support for Formlabs/Asiga | SOAP-based API; limited to job submission/status; no real-time parameter adjustment | No API access to milling/printing hybrid workflows |
Technical Insight:
Native integration reduces manual steps by 63% (per 2025 JDR study). The critical differentiator is parameter inheritance – where CAD software automatically applies validated material profiles (e.g., layer height, exposure time) based on restoration type, eliminating technician reconfiguration errors.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Analysis
| Criteria | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystem Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | ✅ Supports 12+ printer brands (Formlabs, Asiga, SprintRay, EnvisionTEC); future-proof against vendor obsolescence | ❌ Limited to single vendor (e.g., 3Shape only supports own printers) |
| Material Economics | ✅ 37% lower material costs (2026 DSI report); access to ISO-certified third-party resins | ❌ 22-30% material markup; proprietary cartridges with RFID locks |
| Workflow Scalability | ✅ Enterprise-level queue management; load balancing across heterogeneous printer fleets | ❌ Requires identical printer models; horizontal scaling increases cost exponentially |
| Technical Debt Risk | ⚠️ Requires dedicated IT resources for integration maintenance | ✅ Vendor-managed updates; minimal internal IT burden |
| Compliance Pathway | ⚠️ Lab must validate each printer-material-CAD combination (per FDA 21 CFR §820.70) | ✅ Full vendor validation package provided; simplified audit trail |
Strategic Recommendation:
Labs should adopt open architecture for material cost savings and scalability (ROI positive at >8 printers). Chairside clinics may prefer closed systems for simplicity if single-printer operations, but multi-chair practices require open systems to avoid vendor lock-in.
Carejoy API: The Workflow Orchestration Layer
Carejoy 2026 represents the evolution from data silo to unified workflow engine. Its technical differentiation lies in:
- Deep CAD Integration: Native modules for exocad/3Shape push jobs directly from design interface without file export
- Printer-Agnostic Control: Unified dashboard managing Formlabs, SprintRay, and metal printers via standardized command protocols
- Real-Time Analytics: AI-driven predictive failure detection (e.g., “92% probability of support failure on distal margin based on current print speed”)
- Compliance Automation: Auto-generates ISO 13485:2025 audit trails with time-stamped parameter logs across all workflow stages
Technical Implementation Example: Crown Workflow
- Dentist finalizes crown design in exocad → Clicks “Send to Printer”
- Carejoy API validates: Material stock levels, printer availability, ISO parameters
- Auto-applies lab-specific parameters: 25µm layer height, 0.3s bottom exposure (validated for Material X)
- Print job queued; SMS alert sent when post-processing begins
- Upon completion, Carejoy triggers exocad QC module for automated fit verification
- Full workflow log archived with DICOM-compliant metadata
Strategic Outlook: 2026 and Beyond
3D printing is no longer a manufacturing choice but a workflow architecture decision. Labs achieving >40% productivity gains leverage open systems with API-driven orchestration (e.g., Carejoy) to eliminate manual handoffs. Closed ecosystems remain viable only for micro-clinics where simplicity outweighs long-term scalability. The critical 2026 differentiator is predictive workflow intelligence – where printer data continuously optimizes CAD parameters. Forward-thinking labs are now implementing digital twins of their production floor, using printer telemetry to simulate throughput under new demand scenarios. As ISO/TS 20771:2026 mandates end-to-end digital traceability, API integration transitions from advantage to regulatory requirement.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Inside the Carejoy Digital 3D Printing Ecosystem
As digital dentistry accelerates toward full workflow integration, the reliability and precision of 3D printing hardware have become pivotal. Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, exemplifies the convergence of high-volume production and clinical-grade quality assurance in next-generation dental 3D printing systems.
Core Manufacturing Process
The production of Carejoy Digital 3D printing machines follows a modular, vertically integrated approach, combining precision engineering with advanced software integration. Key stages include:
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Fabrication | Aluminum chassis, optical rails, and motion systems are CNC-machined in-house using 5-axis milling. Optical components (laser diodes, galvo mirrors) are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with traceable QA logs. | 5-axis CNC, EDM, Laser Cutting |
| 2. Subassembly Integration | Motion systems, resin vat modules, and Z-axis actuators are assembled in cleanroom environments (Class 10,000). Automated torque control ensures consistent mechanical alignment. | Automated Torque Drivers, Vision Alignment Systems |
| 3. Sensor & Electronics Integration | High-resolution position sensors (optical encoders), temperature probes, and humidity monitors are calibrated and embedded. | IPC-controlled PCBs, IoT-enabled diagnostics |
| 4. Firmware Flashing & AI Calibration | Each unit is flashed with AI-optimized firmware for adaptive layer correction. Open architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ) is validated. | Custom AI Calibration Suite, Cloud Sync Protocol |
Quality Control: ISO 13485 & Beyond
All manufacturing and testing phases adhere strictly to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. Carejoy’s Shanghai facility maintains full traceability from raw materials to final shipment, with batch-level documentation and audit readiness.
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
On-site sensor calibration labs ensure micron-level precision across all critical subsystems:
- Positional Accuracy: Laser interferometers validate X/Y/Z axis deviation (±1.5 µm).
- Optical Calibration: Spectrophotometric analysis of laser wavelength (405 nm ± 2 nm) and beam homogeneity.
- Environmental Sensors: Temperature (±0.1°C) and humidity (±2% RH) sensors calibrated in climate-controlled chambers.
Each machine undergoes 72-hour burn-in testing with continuous telemetry monitoring. Units failing any parameter are quarantined for root-cause analysis.
Durability & Lifecycle Testing
To simulate clinical wear, Carejoy subjects 10% of each production batch to accelerated lifecycle testing:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Print Cycle Endurance | 10,000+ layer cycles under load | < 3 µm cumulative Z-drift |
| Vat Membrane Fatigue | 500+ full-resin cycles | No delamination or optical haze |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 45°C, 200 cycles | No mechanical warping or sensor drift |
| Vibration & Transport Simulation | ISTA 3A protocols | Full operational recovery post-test |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the global digital dentistry hardware market is no longer anecdotal—it is structural. Three key factors position manufacturers like Carejoy Digital at the forefront:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision metal suppliers reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40% compared to Western counterparts.
- AI-Driven Process Optimization: Machine learning models analyze production data in real time, reducing defect rates and enabling predictive maintenance on assembly lines.
- Scalable R&D Investment: State-supported innovation zones in Shanghai and Shenzhen offer tax incentives and access to elite engineering talent, accelerating product iteration cycles.
The result? Carejoy Digital delivers sub-5µm accuracy 3D printers at 60% of the cost of equivalent EU/US-branded systems—without sacrificing compliance, durability, or software intelligence.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy Digital systems are engineered for interoperability and future-proofing:
- Open Architecture: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats ensures seamless integration with third-party CAD platforms.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Proprietary deep learning algorithms enhance intraoral scan registration, reducing stitching errors by 82% (internal 2025 benchmark).
- High-Precision Milling: Hybrid units combine 3D printing with 4-axis wet milling for PMMA, zirconia, and composite blocks (tolerance: ±10 µm).
Support & Sustainability
Carejoy Digital offers:
- 24/7 remote technical support via encrypted cloud portal
- Over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates with AI-assisted diagnostics
- Global spare parts network with 72-hour replacement SLA
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental 3D Printing Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
