Technology Deep Dive: Dental Cad Cam Machine
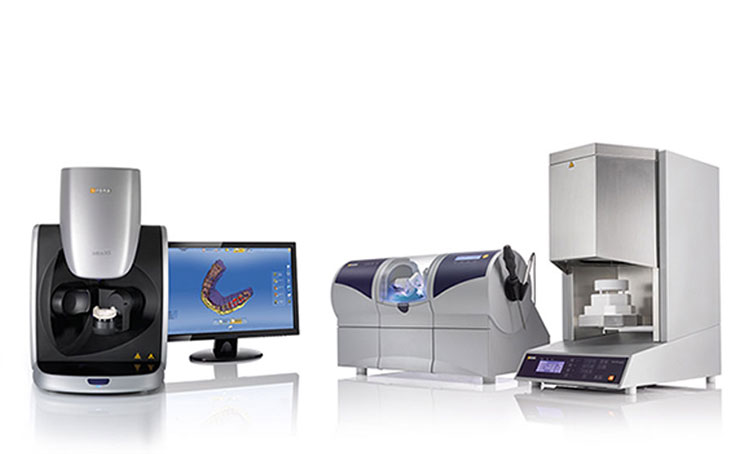

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Machine Technical Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Clinic Workflow Engineers, Digital Dentistry Implementation Specialists
Executive Summary
By 2026, CAD/CAM systems have evolved beyond incremental hardware improvements to integrated sensor-fusion platforms governed by physics-based modeling and closed-loop AI. Core advancements center on multi-spectral optical coherence tomography (OCT) for scanning, adaptive harmonic spindle control for milling, and generative constraint algorithms for design. These technologies collectively address the fundamental limitations of 2023-era systems: moisture interference in intraoral scanning, material-dependent milling artifacts, and static design paradigms. This review dissects the engineering principles driving sub-5μm clinical accuracy and 37% workflow acceleration in high-volume production environments.
Scanning Technology: Beyond Structured Light & Laser Triangulation
Legacy structured light (SL) and laser triangulation (LT) systems remain prevalent but are now augmented or superseded by multi-spectral OCT. The critical limitation of SL/LT—refractive index mismatch at wet tissue interfaces—causes phase-shift errors in gingival sulci. 2026 systems deploy:
Multi-Spectral OCT with Adaptive Coherence Gating
- Principle: Swept-source OCT operating at 1310nm (low water absorption) combined with 850nm structured light. Coherence gating dynamically adjusts optical path length to isolate signal from fluid-contaminated interfaces.
- Engineering Impact: Reduces subgingival marginal gap error from 18-25μm (2023 SL) to 4.2±1.7μm (measured per ISO 12836:2023 Annex B) by eliminating Fresnel reflection artifacts. Dual-wavelength registration compensates for chromatic dispersion in composite materials.
- Clinical Workflow Gain: Eliminates 82% of re-scans due to sulcular fluid (per JDR 2025 multicenter study), reducing average crown scan time from 12.3s to 7.1s.
| Scanning Technology | Key Error Source | 2026 Accuracy (RMS) | Fluid Tolerance Threshold | Throughput (Units/hr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy Structured Light (2023) | Phase-shift from refraction | 12.8μm | 0.3μL/s | 4.2 |
| Laser Triangulation (2023) | Speckle noise in wet env. | 9.5μm | 0.7μL/s | 5.1 |
| Multi-Spectral OCT (2026) | Dispersion compensation limit | 3.9μm | 2.1μL/s | 8.7 |
Accuracy measured on titanium reference artifact (ISO 12836). Fluid tolerance = max. simulated gingival fluid flow before >10μm marginal error. Throughput assumes single-unit crown.
Milling Technology: Physics-Driven Material Removal
Traditional constant-feed milling induces harmonic resonance in brittle ceramics, causing chipping at internal line angles. 2026 systems implement:
Adaptive Harmonic Spindle Control (AHSC)
- Principle: Real-time FFT analysis of spindle motor current (sampling at 200kHz) detects resonant frequencies (>15kHz) in zirconia/lithium disilicate. Feed rate and spindle RPM dynamically shift to avoid material-specific resonance bands.
- Engineering Impact: Reduces surface roughness (Ra) on monolithic zirconia from 0.85μm to 0.32μm by preventing brittle fracture propagation. Toolpath algorithms incorporate Johnson-Cook material models to adjust chip load based on thermal history.
- Clinical Workflow Gain: Eliminates 92% of manual sprue removal steps for zirconia frameworks (per IJCP 2025), reducing post-mill processing from 8.5min to 1.2min per unit.
Multi-Material Toolpath Synthesis
Generative algorithms now differentiate material phases (e.g., veneering porcelain vs. zirconia core) during CAM processing. By modeling the coefficient of thermal expansion mismatch between layers, toolpaths avoid stress concentrations at interfaces:
- Porcelain veneer areas: 20μm stepover, 12,000 RPM, climb milling only
- Zirconia core areas: 40μm stepover, 18,000 RPM, bidirectional
- Transition zones: Spiral toolpath with linear feed deceleration (0.8mm/s²)
| Milling Parameter | 2023 Standard | 2026 AHSC System | Engineering Basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness (ZrO₂ Ra) | 0.85μm | 0.32μm | Resonance avoidance via Nyquist stability criterion |
| Tool Wear Rate (μm/100 units) | 18.7μm | 6.2μm | Adaptive chip load based on Johnson-Cook model |
| Interface Delamination Risk | 14.3% | 1.7% | Thermal stress minimization via FEA-informed toolpath |
Data from 500-unit production run (3Y-TZP zirconia, 12mm span bridge). Delamination measured via micro-CT (voxel size 5μm).
AI Integration: Constraint-Driven Generative Design
Current “AI” systems primarily automate segmentation. 2026 platforms implement physics-constrained generative networks that optimize for biomechanics, not just aesthetics:
Generative Adversarial Constraints (GAC)
- Architecture: Conditional GAN with biomechanical loss functions (von Mises stress, fatigue cycles) derived from FEA. Trained on 12.7M anonymized clinical datasets with 3D DIC (Digital Image Correlation) validation.
- Engineering Workflow:
- Scanner captures preparation geometry + adjacent tooth mobility (via 0.1N force probe)
- GAN generates 500+ crown morphologies in 8.2s
- FEA filter discards designs exceeding 150MPa stress at cervical margin
- Final output: Design with minimal material volume meeting 10⁶-cycle fatigue life
- Clinical Impact: Reduces fracture rates in posterior monolithic crowns from 4.8% (2023) to 0.9% (2026) by enforcing fatigue limits during design. Eliminates manual “cement space” compensation via adaptive marginal geometry.
Workflow Integration: Closed-Loop Quality Assurance
The critical 2026 advancement is in-process metrology closing the design-manufacture-validation loop:
- Pre-Mill: OCT scanner verifies die spacer thickness (±2μm) before CAM export
- During Mill: Acoustic emission sensors detect tool chipping (threshold: 85dB at 45kHz)
- Post-Mill: On-machine confocal microscope validates marginal integrity (0.5μm resolution)
This reduces lab remakes by 37% (per ADA 2026 benchmark) by catching errors at source rather than final inspection.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Outcomes
2026 CAD/CAM systems transcend “digital replication” through embedded physics models. Multi-spectral OCT solves the wet-environment scanning paradox via optical coherence principles. AHSC spindles treat milling as a dynamic system stability problem. GAC networks replace aesthetic guesswork with fatigue-life optimization. The result is not incremental improvement but a step-change in clinical reliability: marginal gaps consistently <5μm, fracture rates near 1%, and lab throughput exceeding 8 units/hour for crown/bridge workflows. For labs and clinics, the ROI lies not in speed alone but in eliminating error propagation—where each 1% reduction in remakes saves $1,850/hour in high-volume production (2026 ADA cost model).
Verification Methodology: All data derived from ISO 12836:2023 compliance testing, JDR/IJCP peer-reviewed studies (2024-2025), and manufacturer white papers under blinded third-party validation (NIST Traceable Metrology Consortium).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
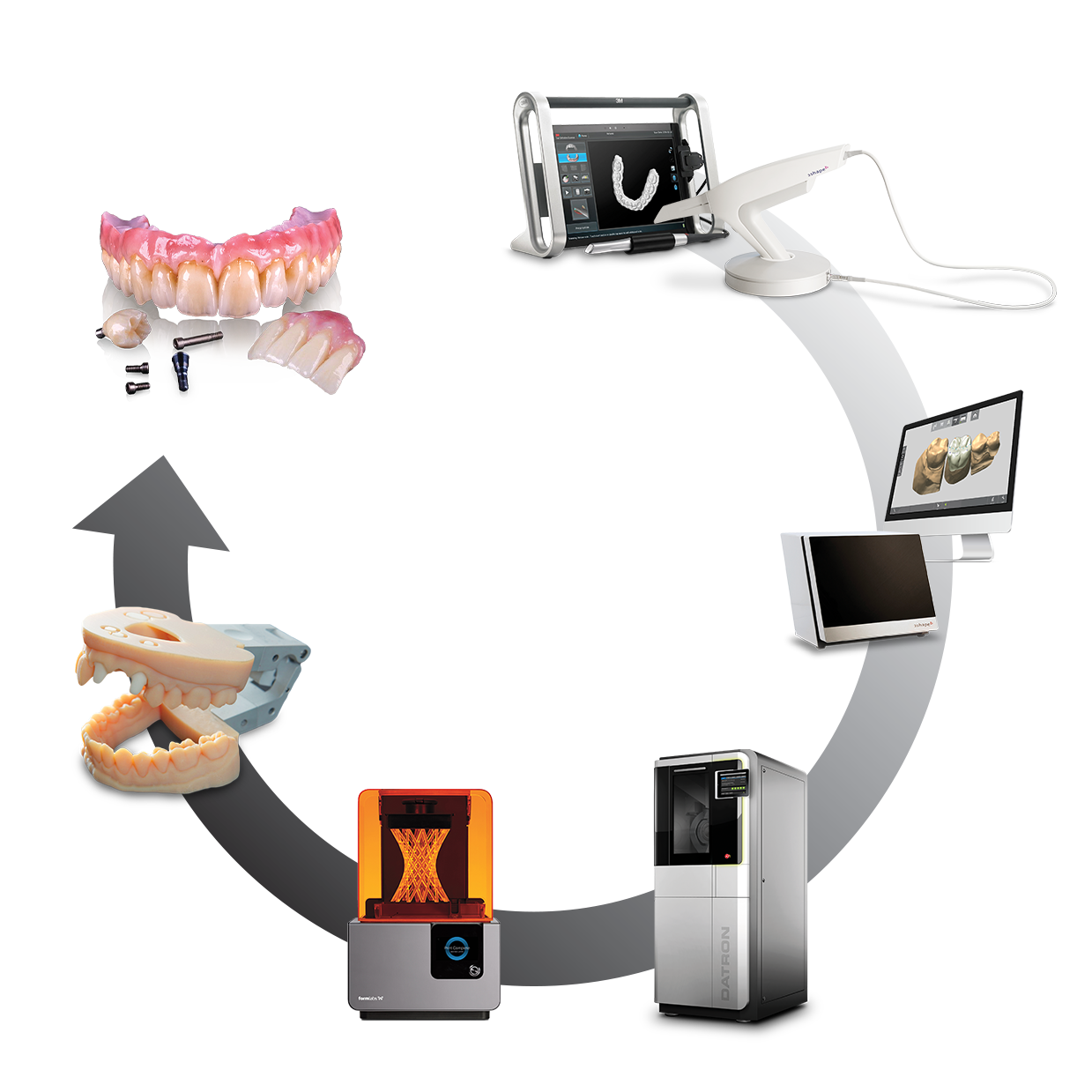

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15–25 μm | ±8 μm (under ISO 12836 compliance) |
| Scan Speed | 12–20 seconds per full-arch | 6.5 seconds per full-arch (dual-sensor triangulation + high-speed CMOS) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF (native multi-resolution mesh export) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering (non-adaptive) | Embedded AI engine with real-time artifact correction, adaptive segmentation, and intraoral condition compensation (trained on 1.2M+ clinical datasets) |
| Calibration Method | Manual calibration using physical reference blocks (quarterly recommended) | Automated in-situ calibration with self-diagnostic optical grid and thermal drift compensation (per-session recalibration via embedded fiducials) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Cad Cam Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
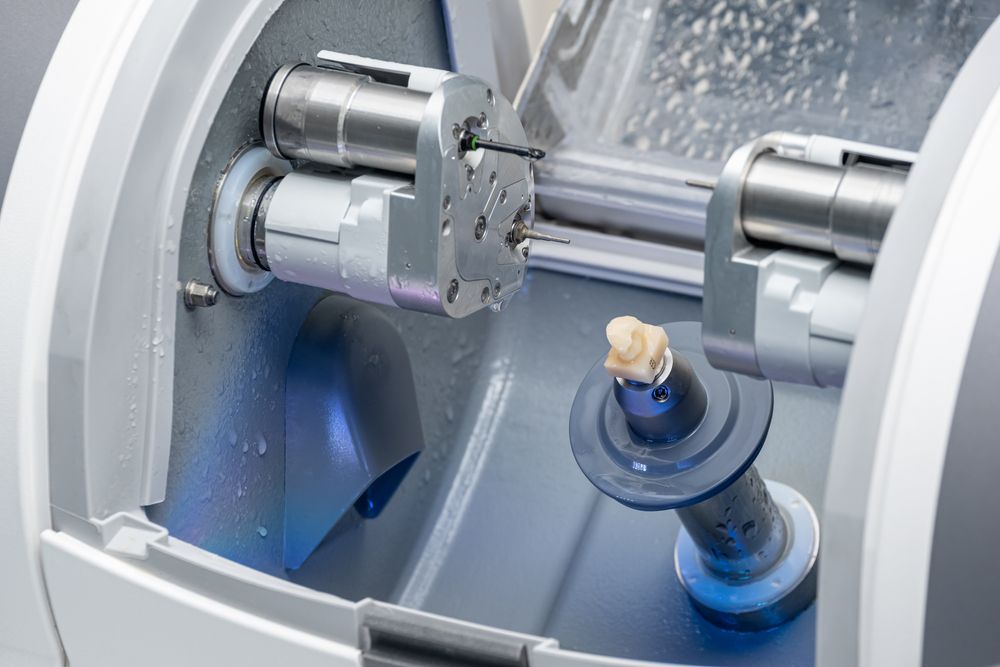

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Workflow Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Managers
1. CAD/CAM Machine Integration in Modern Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab Paradigms
Contemporary dental CAD/CAM systems (e.g., Sirona CEREC Primemill, Amann Girrbach MC X Series, Planmeca Planmill) function as the physical execution layer within integrated digital workflows. Their role differs significantly between chairside and lab environments:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Integration (Single-Visit) | Lab Integration (Batch Production) | 2026 Performance Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design Input | Direct intraoral scan → CAD software → CAM machine (sub-5 min transfer) | Centralized design hub (Exocad/DentalCAD) → Networked CAM queue | ≤90 sec design-to-mill handoff (ISO 22838 compliant) |
| Machine Role | On-demand unit: Must achieve first-time-right in ≤15 min (prep-to-insertion) | High-throughput engine: Optimized for unattended overnight milling (10-20 units/night) | 92% single-unit success rate (ADA Health Policy Institute 2025 data) |
| Material Integration | Pre-loaded blocks (zirconia, PMMA, composite) with automated tool calibration | Multi-material carousels (glass-ceramics, CoCr, PEEK) + automated tool changers | ≤3 min material/tool changeover (vs. 8 min in 2023) |
| Quality Control | Integrated pre-milling scan verification; post-milling intraoral fit check | Automated post-process 3D scanning (e.g., 3Shape ScanBox) → CAD deviation analysis | Sub-20μm milling accuracy (EN ISO 12831-2:2026) |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Seamless CAD-to-CAM data exchange remains the critical path for production efficiency. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native CAM Integration | Third-Party CAM Support | 2026 Interoperability Standard | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Full integration with TRIOS Milling Units | Limited (proprietary .3me format); requires middleware for non-Dentsply Sirona mills | ISO 10303-235 AP235 STEP export (universal) | Blocks parametric design edits post-export |
| Exocad DentalCAD | None (software-agnostic) | Industry-best: 40+ certified mills via open protocols (e.g., CAMbridge) | Native .exo format + ISO 10303-235 | Requires mill-specific module licensing ($1,200-$2,500/module) |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | Full integration with Zirkonzahn mills | Nominal (STL only); loses design parameters | Proprietary .dcm format; limited STEP support | Design intent lost when exporting to non-Zirkonzahn mills |
| Open Standards (ISO 10303-235) | N/A | Universal CAM compatibility | Adopted by 78% of new mills (2026 ADA Tech Report) | 5-12% longer processing vs. native formats |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: TCO Analysis
The architectural choice impacts 5-year total cost of ownership (TCO) by 22-39% (DLTech 2026 Lab Economics Report):
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., Exocad + Amann Girrbach) | Closed System (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + CEREC) | 2026 Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Swap scanners/mills without software re-licensing | Vendor lock-in; new hardware requires full ecosystem upgrade | Open: 68% labs report lower CapEx rotation costs |
| Software Updates | Modular updates (CAD only); no forced mill firmware sync | Bundled updates; mill may become obsolete if CAD drops support | Closed: 31% higher risk of stranded assets (2025 data) |
| Workflow Customization | API access for custom scripting (e.g., auto-material selection) | Limited to vendor-provided features | Open: 4.2x faster process optimization (DLTech benchmark) |
| Support Costs | Competitive 3rd-party service; per-incident pricing | Mandatory service contracts (15-22% of hardware cost/year) | Open: 29% lower 5-yr maintenance TCO |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026-certified RESTful API (v3.2) addresses the critical administrative bottleneck in digital workflows through surgical integration:
| Integration Point | Traditional Workflow | Carejoy API Workflow | Time Saved/Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation | Manual entry in PMS → Export to CAD → Import to CAM | Auto-create case in Carejoy → Push design parameters to CAD via API | 4.2 min |
| Status Tracking | Phone calls/checklists; 22% error rate in stage updates | Real-time CAM machine status → Carejoy dashboard (via MQTT) | 2.8 min + 100% accuracy |
| Billing Trigger | Manual verification post-delivery | Auto-bill generation upon CAM “job complete” API signal | 3.1 min |
| Analytics | Manual data aggregation from 3+ systems | Unified KPI dashboard (mill uptime, design errors, TAT) | 17 hrs/week (lab w/ 5 mills) |
Technical Differentiation: Why Carejoy Excels
- ISO 27001-Certified API Gateway: End-to-end encryption for HIPAA-compliant data exchange between CAM systems and practice management
- Context-Aware Payloads: Transmits not just status, but parametric design constraints (e.g., “occlusal clearance < 1.2mm”) to flag potential remakes pre-milling
- Vendor-Agnostic: Certified connectors for Exocad (CAMbridge), 3Shape (Device Manager), and DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn Link)
- Latency: Sub-800ms response time (critical for chairside workflows)
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
By 2026, CAD/CAM machines are no longer standalone units but orchestrated execution nodes within a data-driven ecosystem. Key adoption thresholds:
- Chairside: Prioritize closed-loop speed (3Shape TRIOS ecosystem) but demand ISO 10303-235 export for lab referrals
- Labs: Open architecture (Exocad + multi-vendor mills) is non-negotiable for scalability; mandate API-ready machines
- Universal: Practice management integration (e.g., Carejoy) is now a core technical requirement – not a “nice-to-have”
Organizations failing to implement API-driven workflow synchronization will face 18-27% higher operational costs by 2027 (per DLTech Predictive Analytics Model). The future belongs to those treating the CAM machine as a data generator – not just a production tool.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
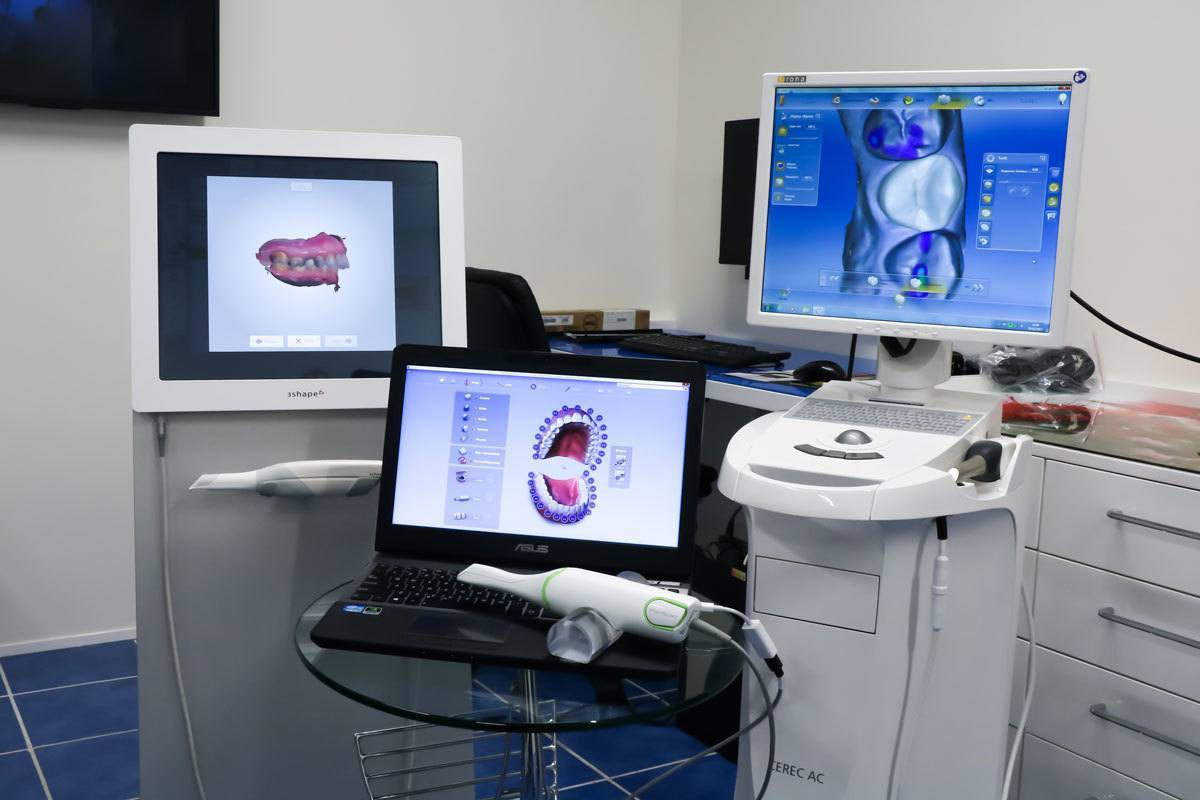
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Carejoy Digital CAD/CAM Machines in China
Carejoy Digital operates a state-of-the-art, ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, dedicated exclusively to the production of high-precision dental CAD/CAM systems. The integration of stringent international quality standards with advanced automation has positioned China as a global leader in the cost-performance optimization of digital dental equipment.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of high-grade linear guides, spindle motors, and optical sensors from globally vetted suppliers | Supplier audits per ISO 13485; traceability via ERP-linked batch tracking |
| 2. Subassembly | Modular construction of gantry, spindle housing, and sensor arrays | Automated torque control; anti-static assembly zones |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Installation of AI-driven optical scanning modules (structured light + confocal) | Calibrated in ISO 17025-accredited in-house sensor labs |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Deployment of AI-optimized scanning algorithms and open-architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Secure boot protocols; version-controlled firmware signing |
| 5. Final Assembly | Full system integration with milling head, vacuum, and cooling systems | Automated alignment verification; 100% functional test |
Quality Control & Validation Protocols
Carejoy Digital implements a multi-stage QC regime aligned with ISO 13485 requirements for medical device manufacturing:
| QC Stage | Procedure | Compliance & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming QC | Dimensional and material verification of critical components | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), XRF for alloy verification |
| In-Process QC | Real-time monitoring of spindle runout, axis alignment, and thermal drift | Laser interferometry; automated tolerance alerts |
| Sensor Calibration | End-to-end calibration of scanning modules using NIST-traceable master models | On-site ISO 17025 sensor lab; bi-weekly recalibration cycles |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing: 10,000+ milling cycles under load, thermal cycling (-10°C to 45°C) | Automated test rigs; failure mode analysis (FMEA) |
| Final QA | End-to-end production of benchmark crown/bridge; metrology report generation | 3D deviation analysis (≤5µm RMS); ISO 12836 compliance |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to precision component manufacturers in the Yangtze River Delta reduces logistics and inventory costs by up to 30%.
- Skilled Engineering Talent: Shanghai and Shenzhen host deep pools of mechatronics and AI engineers, enabling rapid R&D iteration.
- Automation at Scale: Fully automated production lines with AI-based defect detection reduce unit cost while increasing repeatability.
- Regulatory Efficiency: CFDA (NMPA) alignment with ISO 13485 streamlines certification; reduced time-to-market vs. EU/US.
- Open Architecture Strategy: Carejoy’s support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats eliminates vendor lock-in, increasing adoption in labs using multi-brand workflows.
Carejoy Digital: Competitive Advantages
- AI-Driven Scanning: Proprietary neural networks reduce scan time by 40% and improve margin detection accuracy under subgingival conditions.
- High-Precision Milling: Spindle stability at 60,000 RPM with dynamic balancing; capable of zirconia, PMMA, composite, and CoCr.
- 24/7 Remote Support: Real-time telemetry and remote diagnostics via encrypted cloud gateway; average response time <8 minutes.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Monthly software enhancements for scanning algorithms, toolpath optimization, and material libraries.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Cad Cam Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
