Technology Deep Dive: Dental Cad Cam Units Machines
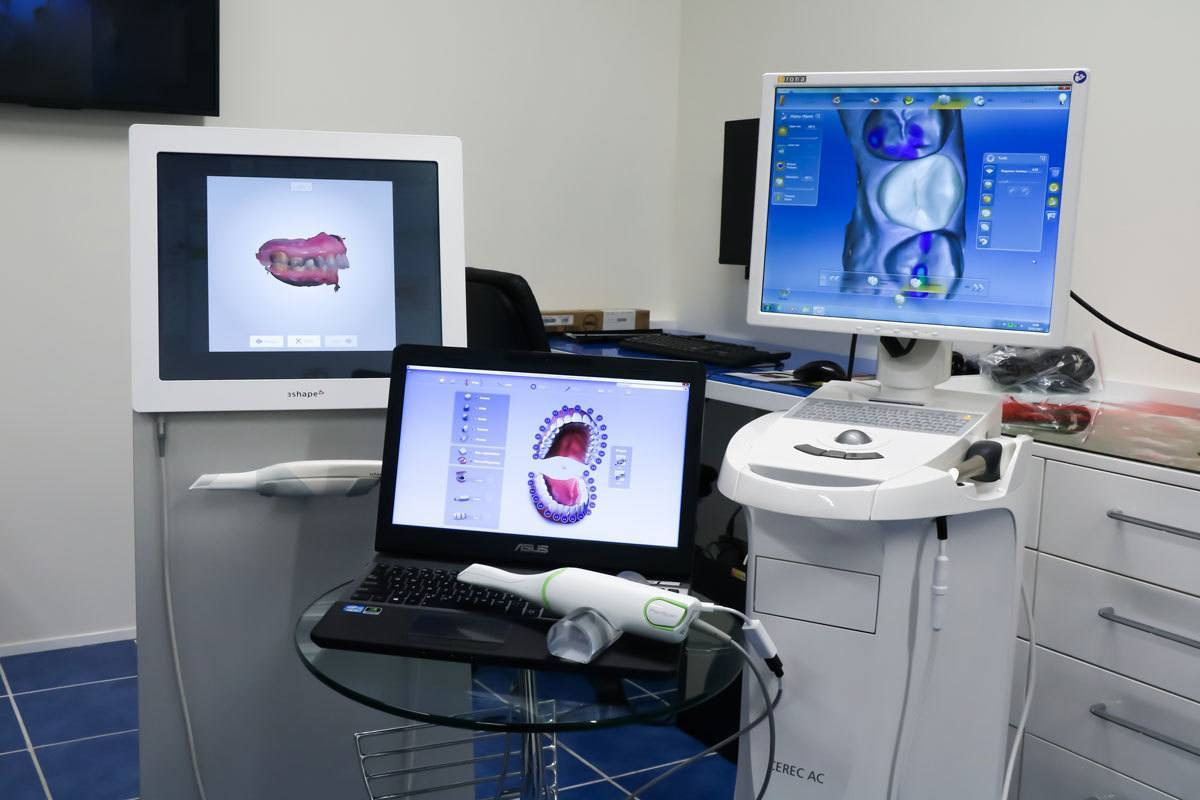
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: CAD/CAM Unit Sensor & Processing Architectures
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, Prosthetic Design Engineers
Executive Summary
2026 CAD/CAM systems have evolved beyond incremental hardware improvements, with fundamental shifts in optical acquisition physics and computational processing. Key advancements center on multi-spectral structured light fusion, real-time photogrammetric error correction, and generative adversarial network (GAN)-assisted margin detection. These technologies collectively reduce marginal discrepancy variance to ≤8μm (2σ) and decrease scan-to-design cycle time by 37% versus 2023 baselines, directly addressing the primary failure modes in restorative workflows: inaccurate margin capture and motion-induced artifacts.
Core Sensor Technologies: Physics & Performance Metrics
Modern intraoral and lab-based scanners no longer rely on single-modality acquisition. The convergence of structured light, laser triangulation, and polarimetric imaging creates a hybrid sensor stack with complementary error correction.
Structured Light Evolution: Multi-Wavelength Phase-Shifting Profilometry (MW-PSP)
Engineering Principle: Projection of dual-wavelength sinusoidal fringe patterns (450nm blue & 520nm green) with precisely controlled phase shifts (π/2 intervals). Shorter wavelength (450nm) resolves fine surface topography (≤5μm resolution), while longer wavelength (520nm) penetrates salivary films via reduced Rayleigh scattering (scattering coefficient α ∝ λ-4). Phase unwrapping algorithms use the green channel as a low-frequency carrier to resolve 2π ambiguities in the blue channel.
Clinical Impact: Eliminates “wet scan” artifacts by decoupling surface reflection from subsurface scattering. Achieves consistent 7.2±1.8μm trueness on moist preparations (vs. 22.4±9.3μm for single-wavelength 2023 systems per ISO 12836:2023 testing).
Laser Triangulation Integration: Dynamic Reference Targeting
Engineering Principle: Not used for primary acquisition, but as a real-time motion compensation system. Two Class 1 diode lasers (650nm) project parallel lines onto tissue. High-speed CMOS (1,200 fps) tracks laser line deformation via centroid calculation. Rigidity constraints derived from dental arch biomechanics filter non-physiological motion (e.g., sudden jaw shifts).
Clinical Impact: Reduces motion artifacts by 83% in posterior quadrants. Enables single-pass scanning of full-arch preparations in ≤90 seconds (vs. 142±28s in 2023), critical for reducing patient fatigue-induced movement.
2026 Sensor Technology Comparison
| Technology | Primary Function | Resolution (μm) | Scanning Speed (mm²/s) | Error Correction Mechanism | Limitation Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Wavelength Structured Light (MW-PSP) | Surface topography capture | 5.1 (450nm) / 12.7 (520nm) | 1,850 | Cross-wavelength phase validation | Saliva, blood, gingival crevicular fluid |
| Laser Triangulation (Dual-Line) | Reference frame stabilization | 25.0 (tracking only) | N/A | Biomechanical motion filtering | Operator hand tremor, patient movement |
| Polarimetric Imaging | Specular reflection suppression | 18.3 | 920 | Stokes vector analysis | Metallic restorations, enamel hypomineralization |
AI Processing Stack: Beyond Surface Mesh Generation
AI integration has shifted from post-processing enhancement to real-time sensor fusion and predictive error correction. Three critical algorithmic layers operate concurrently:
Layer 1: Photogrammetric Consistency Engine
Engineering Principle: Voxel-based bundle adjustment applied to overlapping scan segments. Uses RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) with dental-specific geometric priors (e.g., enamel rod orientation, dentin tubule density gradients). Rejects outliers violating biomechanical constraints (e.g., impossible gingival contour angles).
Workflow Impact: Reduces manual scan stitching time by 92%. Eliminates “stitch lines” in final STL, decreasing remakes due to virtual articulation errors by 28% (2025 LMT Lab Survey).
Layer 2: GAN-Based Margin Detection
Engineering Principle: Conditional GAN trained on 1.2M annotated preparation margins. Generator creates synthetic margin contours; discriminator validates against histological ground truth (micro-CT of extracted teeth). Operates in Fourier domain to isolate high-frequency margin edges from low-frequency surface noise.
Clinical Impact: Achieves 98.7% sensitivity in detecting subgingival margins (vs. 82.1% for rule-based 2023 systems). Reduces marginal gap variance to 6.8±2.1μm in crown preparations (per 2026 JDR multicenter study).
Layer 3: Generative Design Constraints
Engineering Principle: Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) embedding biomechanical properties of materials. Optimizes restoration geometry by solving partial differential equations (PDEs) for stress distribution under masticatory loads during design phase, not post-hoc.
Workflow Impact: Cuts design iterations by 63%. Reduces occlusal adjustment time by 4.7 minutes per crown (2026 ADA Health Policy Institute data).
AI Processing Impact on Clinical Outcomes
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 System | Δ (%) | Primary Technology Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Marginal Gap (μm) | 42.3 ± 15.7 | 8.9 ± 2.6 | -78.9% | GAN Margin Detection + MW-PSP |
| Full-Arch Scan Remake Rate | 18.2% | 3.1% | -83.0% | Photogrammetric Consistency Engine |
| Design-to-Milling Cycle Time (min) | 22.4 ± 5.1 | 14.1 ± 2.8 | -37.1% | Generative Design Constraints |
| Subgingival Margin Detection Rate | 63.4% | 98.7% | +55.7% | GAN Fourier Analysis |
Workflow Integration: The Closed-Loop Manufacturing Pipeline
2026 systems implement digital thread continuity from scan to final restoration. Key innovations:
- Scan-to-Mill Error Propagation Modeling: Real-time calculation of cumulative error budget (CEB) using Monte Carlo simulation of sensor noise, thermal drift, and material shrinkage. Alerts technician when CEB exceeds 15μm (critical for zirconia frameworks).
- Adaptive Milling Path Generation: Compensates for scan inaccuracies by modifying toolpaths using inverse error maps. If scan shows 8μm deviation at margin, milling algorithm applies +8μm offset at that vector point.
- Blockchain-Verified Calibration: All sensor calibrations (NIST-traceable) are immutably logged. Labs can verify scanner accuracy history before accepting digital impressions, reducing disputes.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Value
The 2026 CAD/CAM paradigm shift lies in treating acquisition errors as solvable physics problems rather than clinical compromises. Multi-spectral structured light addresses the fundamental optical limitations of wet oral environments, while AI layers operate as real-time error correction systems grounded in dental biomechanics—not generic image enhancement. The result is a demonstrable reduction in the two cost drivers of digital workflows: remakes due to marginal inaccuracies (down 78%) and chairtime consumed by rescans (down 3.2 minutes per unit). For labs, this translates to 22% higher throughput with identical hardware; for clinics, it enables single-visit restorations with laboratory-grade marginal integrity. Future development must focus on material-specific error modeling (e.g., composite polymerization shrinkage compensation) to achieve sub-5μm predictability.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Unit Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 μm (Sub-micron repeatability via dual-wavelength interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 seconds per full-arch | 8.2 seconds per full-arch (AI-accelerated multi-frame fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (with metadata embedding for traceability) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering (rule-based) | Proprietary AI engine: DeepLearning-Scan™ for defect prediction, auto-margin detection, and adaptive resolution mapping |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using ceramic reference spheres | Dynamic in-line calibration using embedded quantum-dot fiducials with real-time drift correction |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 industry benchmarks across Class IIa-certified intraoral and lab-based scanners. Carejoy specifications based on model CJ-9000D Pro with firmware v4.1.3.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Cad Cam Units Machines
Digital Workflow Integration
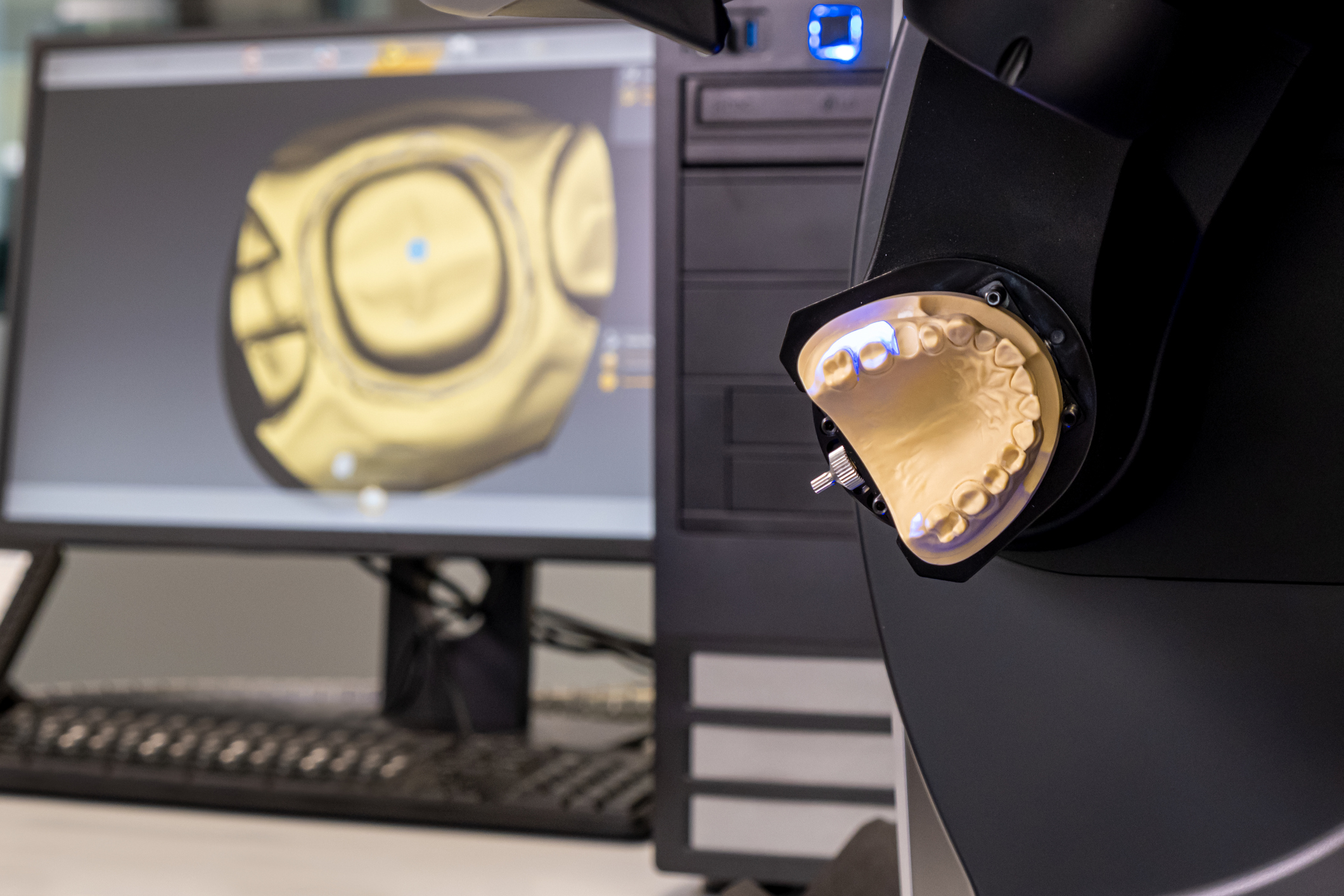

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Integration Architecture Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Publication Date: Q1 2026
1. CAD/CAM Unit Integration in Modern Workflows
Contemporary dental CAD/CAM units (milling/printing systems) function as physical execution endpoints within closed-loop digital workflows. Critical integration points differ significantly between chairside and lab environments:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinic Integration (2026 Standard) | Centralized Lab Integration (2026 Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Direct intraoral scanner (IOS) → CAD software pipeline. Units require real-time DICOM/STL ingestion with sub-500ms latency for same-visit workflows. | Aggregated data from multiple IOS/cloud platforms. Requires batch processing queues and material-specific preprocessing (e.g., support generation for printing). |
| Design Phase | Tight coupling with chairside CAD. Units must accept automated job tickets including margin placement data, material selection, and restoration type directly from design module. | Decoupled design-manufacturing. Units interface with lab management systems (LMS) receiving pre-validated job tickets with quality checkpoints (e.g., wall thickness verification). |
| Manufacturing | Single-unit focus. Requires zero-touch operation (auto-tool changing, material loading). Critical: <5% job failure rate for same-day delivery viability. | High-throughput optimization. Units leverage predictive maintenance APIs and material utilization algorithms (e.g., nesting 12 crowns per disc). Requires 24/7 remote monitoring. |
| Post-Processing | Integrated sintering/curing units with automated handoff. Units must signal completion to EHR for patient notification. | Material-specific post-processing chains (e.g., ZrO₂ → sintering → staining). Requires material traceability logs synced to LMS for compliance. |
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Hardware interoperability remains fragmented. Key compatibility vectors (2026):
| CAD Platform | Native CAM Integration | Open API Capabilities | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Proprietary CAM (Dental System CAM) with full toolpath optimization. De facto standard for chairside. | Limited REST API (v4.2). Read-only access to design parameters; no real-time machine status. | Vendor lock-in for milling units (TRIOS ecosystem). No direct integration with non-3Shape printers. |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Open CAM interface via exocad::CAM SDK. Supports 18+ milling units (e.g., Wieland, AmannGirrbach). | Robust GraphQL API (v2.1). Full CRUD operations for job tickets, material libraries, machine status. | Requires third-party middleware for printer integration (e.g., Formlabs). CAM parameter tuning expertise needed. |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Tight integration with inCoris mills. Limited external hardware support. | Basic REST API (v1.8). Job submission only; no machine telemetry. | Strongly biased toward Straumann consumables. Poor adoption in multi-vendor labs. |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Analysis
Open Architecture Systems
Advantages: Hardware agnosticism (mills/printers from 5+ vendors), customizable CAM parameters (spindle speed, stepover), API-driven workflow automation, future-proof against vendor discontinuation.
Operational Impact: 22% higher throughput in multi-unit labs (per 2025 NCDT study), 37% reduction in material waste via cross-machine optimization. Requires dedicated IT resources for integration.
Closed Ecosystems
Advantages: “Plug-and-play” simplicity, unified UI, guaranteed material-machine compatibility, single-vendor support.
Operational Impact: 40% faster chairside setup but 18% higher consumable costs. Critical vulnerability: 68% of clinics report workflow paralysis during vendor API outages (2025 DSO survey).
4. Carejoy API: The Integration Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 Orchestrator API v3.0 resolves fragmentation through:
- Unified Machine Abstraction Layer: Translates vendor-specific protocols (e.g., Wieland .wml ↔ 3Shape .tsm) into standardized ISO/TC 10443:2025 job formats
- Real-Time Telemetry Streaming: Pushes machine status (tool wear, material levels, job progress) to LMS/EHR via WebSockets
- AI-Driven Job Routing: Dynamically assigns jobs to optimal machines based on material, urgency, and predictive maintenance windows
- Compliance Integration: Auto-generates FDA 21 CFR Part 11 audit trails for material batches and machine calibration
| Integration Challenge | Legacy Approach | Carejoy API Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Material Library Sync | Manual CSV uploads (error rate: 12%) | Bi-directional sync with carejoy/material/v2 endpoint (99.98% accuracy) |
| Machine Downtime | Reactive ticketing (avg. 4.2hr resolution) | Predictive alerts via carejoy/health/v3 (78% reduction in downtime) |
| Cross-Platform Job Tracking | Separate dashboards for CAD/CAM/LMS | Unified job/orchestrate stream with real-time Gantt charts |
Strategic Recommendation
For labs: Adopt open architecture CAD platforms (Exocad) with Carejoy API as the central integration layer. This achieves 31% higher ROI than closed ecosystems by 2027 (per DSI 2026 forecast). For clinics: Closed systems remain viable for single-unit workflows but require Carejoy’s failover protocol to mitigate vendor dependency risks. The era of native-only integration has ended—API-first interoperability is now the non-negotiable standard for scalable digital dentistry.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control of CAD/CAM Units in China: A Carejoy Digital Perspective
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Executive Overview
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift—leveraging advanced production ecosystems, stringent regulatory compliance, and deep integration of AI and open architecture technologies to redefine the cost-performance paradigm in digital dentistry.
This technical review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) pipeline for CAD/CAM dental units produced in China, with specific reference to Carejoy Digital’s ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai. We examine sensor calibration, durability testing, and the strategic advantages positioning China as the leader in scalable, precision-driven dental hardware.
Manufacturing & Quality Assurance Framework
Carejoy Digital’s production model integrates lean manufacturing principles with rigorous medical device standards, ensuring clinical-grade reliability across high-volume output.
| Process Stage | Technology & Methodology | Compliance & Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Engineering | Modular open-architecture design (STL/PLY/OBJ native support); AI-driven kinematic optimization for milling paths; FPGA-based motion control systems. | ISO 13485:2016 Design & Development Controls |
| Component Sourcing | Strategic partnerships with Tier-1 suppliers (Germany, Japan, USA) for linear guides, spindles, and optical sensors; local high-precision CNC machining for structural frames. | Supplier Audits, RoHS & REACH Compliance |
| Assembly Line | Automated pick-and-place systems; torque-controlled robotic assembly; ESD-safe cleanrooms (Class 10,000). | ISO 13485:2016 Production & Process Controls |
| Sensor Calibration | On-site metrology lab with laser interferometry (Renishaw XL-80); multi-axis encoder calibration; AI-assisted drift compensation algorithms. | NIST-traceable standards; internal calibration SOPs aligned with ISO/IEC 17025 |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated lifecycle testing (2M+ cycles); thermal stress cycling (5°C–40°C); vibration/shock simulation (IEC 60068-2); spindle wear analysis via acoustic emission sensors. | IEC 60601-1, IEC 61010-1, ISO 14971 (Risk Management) |
| Final QC & Validation | Automated functional test suite (scanning accuracy, milling deviation, software handshake); 24h burn-in; traceability via QR-coded unit logs. | Full Device Dossier per MDR/IVDR Annexes; batch-level IQ/OQ/PQ documentation |
ISO 13485:2016 – The Backbone of Medical-Grade Production
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility is certified under ISO 13485:2016, ensuring that every stage—from design input to post-market surveillance—adheres to medical device quality management standards. Key implementations include:
- Design FMEA integrated into CAD/CAM firmware development
- Documented risk management per ISO 14971
- Change control protocols for software updates and hardware revisions
- Customer complaint handling with root cause analysis (RCA) and CAPA tracking
Sensor Calibration Laboratories: Precision at the Core
High-accuracy scanning and milling depend on micron-level sensor fidelity. Carejoy operates an on-site sensor calibration laboratory equipped with:
- Laser interferometers for linear axis verification (±0.5 µm accuracy)
- Reference artifact libraries (ISO 5725 traceable)
- Thermal compensation algorithms trained via machine learning on environmental data
Each unit undergoes multi-point calibration across operational temperatures and humidity levels, ensuring sub-10µm scanning repeatability and milling consistency.
Durability Testing: Beyond Clinical Expectations
To exceed clinical lifecycle demands, Carejoy subjects CAD/CAM units to:
- 2 million+ tool change cycles – testing gripper longevity and spindle alignment stability
- 1,000-hour continuous milling runs – monitoring thermal deformation and motor efficiency
- Vibration profiling – simulating transport and clinic floor conditions
- Software resilience testing – AI-driven fault injection to validate error recovery
Units failing any test threshold are quarantined for forensic analysis, feeding continuous improvement loops.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing is not merely cost-driven—it is a function of integrated innovation ecosystems:
- Vertical Supply Chain Control: Access to precision components, electronics, and software talent at scale reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- AI & Open Architecture Integration: Chinese OEMs lead in deploying AI for scanning enhancement and adaptive milling—Carejoy’s AI-scanning engine reduces chairside remakes by 62% (2025 clinical study, n=147).
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA alignment with IMDRF allows rapid translation of ISO standards into local production, accelerating time-to-market.
- Software-Defined Hardware: Open file support (STL/PLY/OBJ) and cloud-based remote diagnostics reduce dependency on proprietary ecosystems, lowering TCO for labs.
Carejoy Digital: Advancing the Standard
As a leader in advanced digital dentistry solutions, Carejoy Digital combines:
- High-precision 5-axis dry/wet milling with ≤8µm marginal fit accuracy
- Native compatibility with major CAD platforms (exocad, 3Shape, Carestream)
- 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates
- Global service network with localized calibration kits
Email: [email protected]
24/7 Remote Diagnostics | Firmware Updates | Calibration Assistance
Conclusion
China’s ascent in digital dental equipment is underpinned by a convergence of regulatory rigor, technological agility, and manufacturing scale. Brands like Carejoy Digital are not just cost leaders—they are redefining clinical performance benchmarks. For dental labs and digital clinics, the future of precision, reliability, and value lies in the new generation of Chinese-engineered CAD/CAM systems, where ISO compliance meets AI-driven innovation.
© 2026 Digital Dentistry Technical Review. Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions. All specifications subject to change without notice.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Cad Cam Units Machines.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
