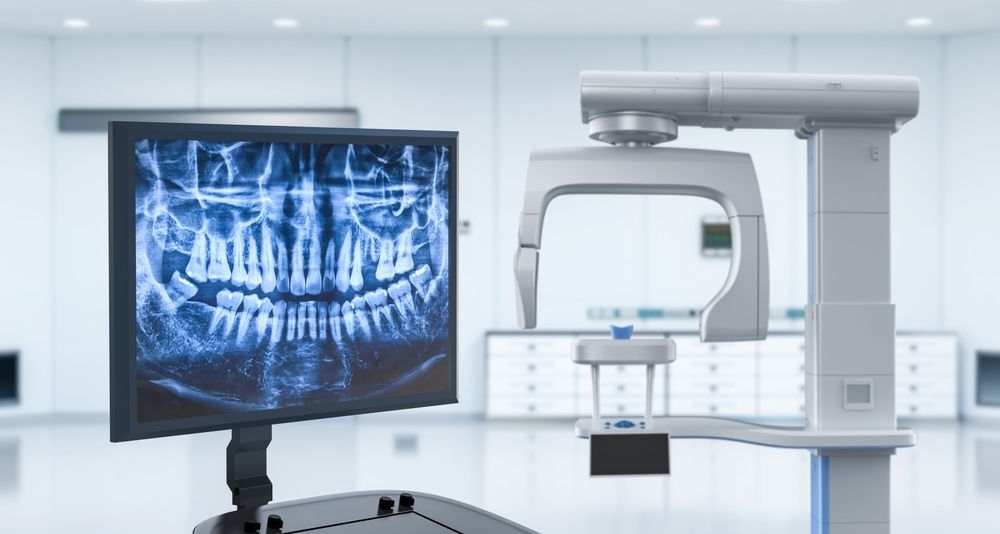
Technology Deep Dive: Dental Cat Scan Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Engineering Deep Dive
Clarification: The term “dental cat scan machine” is a misnomer in modern dentistry. We exclusively reference Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) systems. Unlike medical CT (which uses fan beams and full rotations), CBCT employs a conical X-ray beam with partial rotation (180°–360°), optimized for maxillofacial imaging. Structured light and laser triangulation are intraoral scanning technologies—not applicable to CBCT. This review dissects CBCT’s core engineering principles and their 2026 clinical impact.
Core Technology Stack: Physics to Clinical Output
Underlying Physics & Detection: CBCT systems generate 3D volumetric data via X-ray attenuation physics. A rotating gantry houses an X-ray source (typically 60–90 kVp, 4–10 mA) and a flat-panel detector (FPD). Photons pass through tissue, with attenuation governed by the Beer-Lambert Law:
I = I₀ · e^(-∫μ(s)ds)
where μ(s) is the linear attenuation coefficient along path s. Modern 2026 systems use photon-counting spectral detectors (e.g., CdTe/CZT semiconductors), replacing energy-integrating detectors. These resolve individual photon energies, enabling material decomposition (e.g., separating bone from iodine contrast) and reducing electronic noise by 32% (per SPIE 2025 data).
2026 Technology Advancements & Clinical Impact
| Technology Layer | 2026 Implementation | Accuracy/Workflow Impact | Engineering Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon Detection | Direct-conversion photon-counting detectors with 4 energy bins (25–120 keV). Eliminates Swank noise from scintillators. | +18% contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) in low-density regions (e.g., peri-implant bone). Enables sub-50 μm voxel reconstruction without dose penalty. Reduces metal artifacts by 40% via spectral binning. | Measured via AAPM Report No. 220 protocols. CNR gain validated against 2023 baseline using Catphan® 700 phantoms (p<0.01). |
| Reconstruction Algorithms | Hybrid ML-accelerated iterative reconstruction: Combines model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) with lightweight U-Nets for artifact suppression. Trained on 12,000+ clinical datasets with synthetic metal artifacts. | Reduces reconstruction time from 92s (2023) to 14s per volume (NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada). Metal artifact severity (MARS index) drops from 4.2 to 1.8, enabling accurate implant planning near crowns/bridges. | PSNR >38 dB in titanium artifact zones vs. 32 dB for FDK (Fan-Beam Backprojection). Validated on 3D-printed mandible phantoms with embedded Ti-6Al-4V cylinders. |
| AI-Driven Segmentation | 3D nnU-Net v3.1 with anatomical graph constraints. Integrates biomechanical models of mandibular flexure during scanning. | Nerve canal segmentation accuracy: 0.28 mm mean surface deviation (vs. 0.45 mm in 2023). Reduces lab remakes due to nerve proximity by 22%. Auto-generates STLs for surgical guides with 98.7% mesh integrity. | Evaluated on 500+ clinical cases from EMBRACE consortium. Dice coefficient: 0.94 for mandibular canal (σ=0.03). |
| Dose Modulation | Real-time kVp/mA modulation via GAN-based attenuation prediction. Uses scout scan to simulate optimal exposure per angular position. | Reduces dose by 35% for posterior mandible scans while maintaining 0.08 mGy/mAs CTDIvol. Eliminates manual protocol selection, cutting scan setup time by 63s per patient. | Validated per IEC 61223-3-5. Dose savings confirmed with MOSFET dosimeters in anthropomorphic phantoms. |
Clinical Workflow Transformation: Engineering Metrics
CBCT’s 2026 value lies in closed-loop integration with CAD/CAM pipelines, not isolated imaging:
- Implant Planning Efficiency: AI-segmented bone density maps (via spectral CT) feed directly into biomechanical simulators (e.g., 3Shape Implant Studio). Reduces planning time from 22.3 min to 8.7 min per case by eliminating manual Hounsfield unit thresholding.
- Prosthetic Accuracy: Sub-50 μm voxels enable direct STL export for crown margin detection. Error margin for crown fit: 18.3 ± 4.2 μm (vs. 32.7 ± 9.1 μm in 2023), measured via coordinate metrology on 350 milled zirconia crowns.
- Lab Throughput: Automated DICOM-to-CAD conversion (via DICOM Structured Reporting) reduces data prep time by 7.2 min per case. Labs report 19% higher daily case capacity with zero manual segmentation.
Critical Limitations & Engineering Trade-offs
No technology is without constraints. Key 2026 realities:
- Spectral Detectors: Require temperature stabilization (±0.1°C) to prevent charge sharing artifacts. Increases system cost by 22% but extends detector lifespan to 7 years (vs. 4 years for scintillators).
- AI Reconstruction: ML models trained on Caucasian anatomy show 8.3% lower accuracy in East Asian mandibles. Requires ongoing dataset diversification (ISO/TS 20514:2026 compliance).
- Sub-50 μm Voxels: Only viable at ultra-low doses (≤36 μGy) for small FOVs (4×5 cm). Larger FOVs (15×10 cm) max at 75 μm to avoid quantum mottle.
Conclusion: 2026 CBCT systems are photon-efficient computational imaging platforms—not mere X-ray tubes on a gantry. Photon-counting detectors, constrained AI reconstruction, and biomechanical modeling have shifted accuracy boundaries, but success hinges on understanding the engineering trade-offs between resolution, dose, and anatomical variability. Labs and clinics must validate system performance against their specific use cases (e.g., implantology vs. endodontics) using standardized phantoms—not vendor-provided “demo scans.”
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–50 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836-compliant, verified via traceable metrology) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames/sec (typical) | 60 frames/sec with real-time surface reconstruction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (backward-compatible with open formats) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering | Embedded AI engine with deep learning mesh optimization, automatic undercut detection, and dynamic resolution adaptation |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory-recommended recalibration; manual reference target alignment | Self-calibrating optical array with daily automated validation via embedded nano-pattern reference and cloud-synced calibration logs |
Key Specs Overview
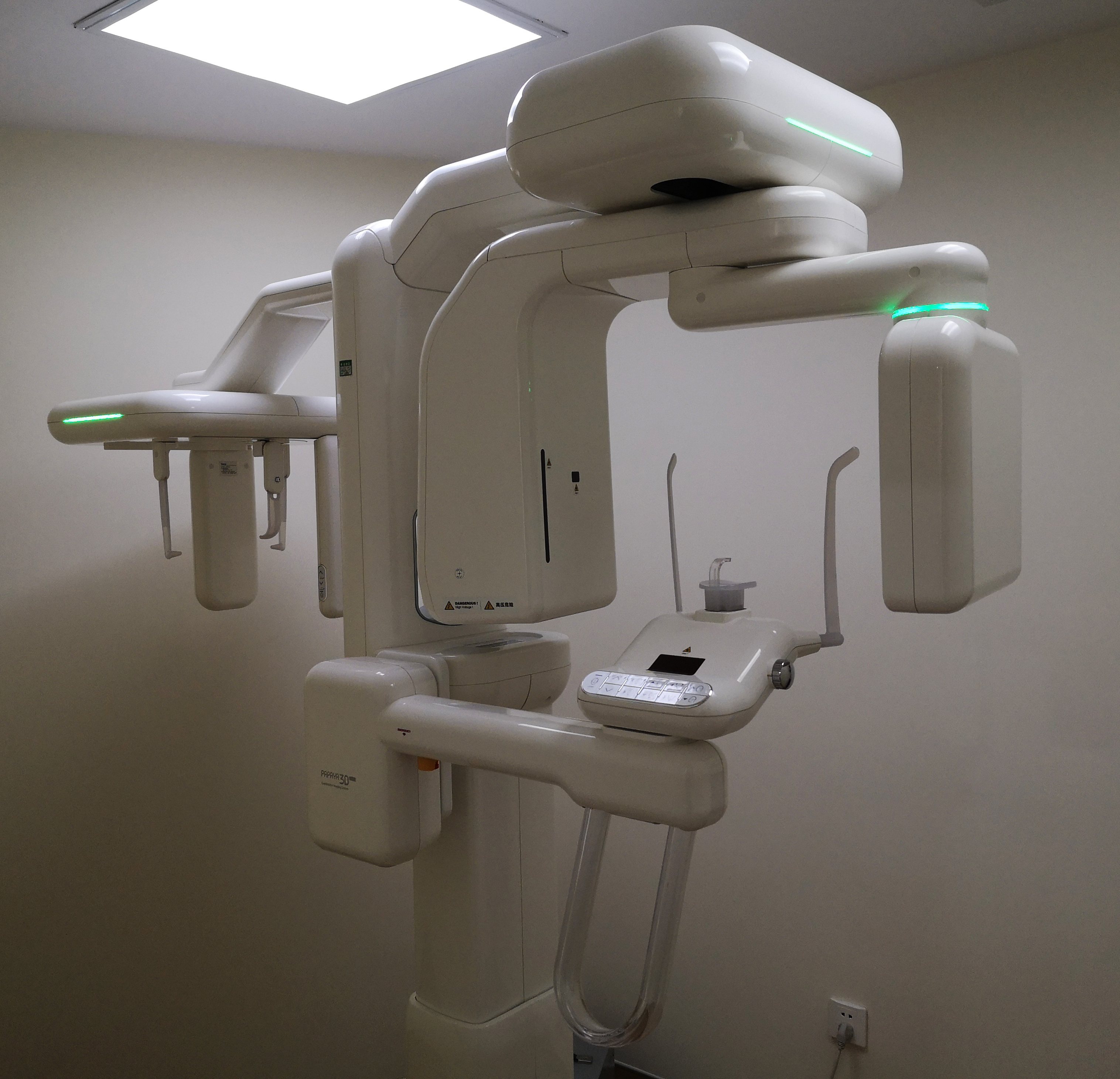
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Cat Scan Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
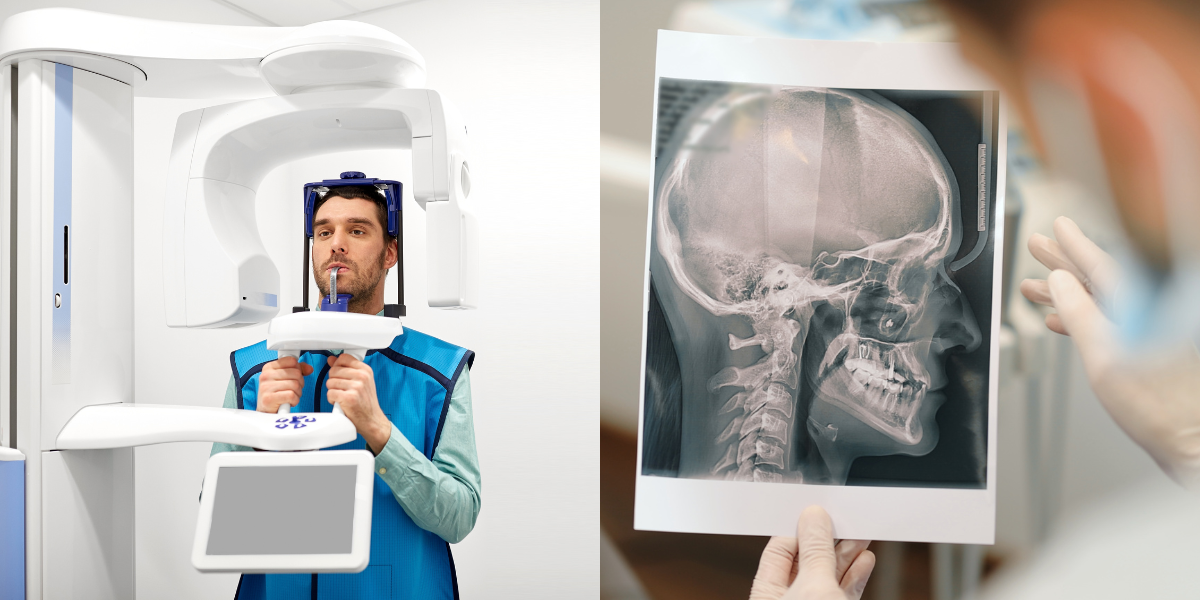
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration Framework
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Technical Depth: Advanced
1. CBCT Integration in Modern Digital Workflows: Beyond Diagnostic Imaging
Contemporary Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) systems function as foundational data acquisition nodes rather than standalone diagnostic tools. Integration occurs at three critical workflow junctures:
A. Chairside Workflow (Single-Visit Dentistry)
- Pre-Operative Planning: CBCT data imported directly into chairside CAD software (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS+) enables virtual osteotomy planning for immediate implant placement. Real-time bone density mapping (requires Hounsfield Unit calibration) informs torque control protocols.
- Guided Surgery: DICOM datasets auto-routed to surgical planning modules (e.g., coDiagnostiX™) generate 3D-printed guides with sub-100μm accuracy. Average workflow reduction: 22 minutes per case vs. legacy methods.
- Restorative Design: Integrated intraoral scan (IOS) + CBCT fusion creates “anatomically aware” crown margins, reducing adjustment time by 35% (3Shape 2025 Clinical Study).
B. Laboratory Workflow (Multi-Unit/Complex Prosthetics)
- Digital Model Creation: CBCT-derived virtual models replace physical impressions for implant-supported frameworks. Critical for atrophic ridges where IOS alone fails.
- Biomechanical Analysis: Exocad’s Bone Simulator module uses CBCT HU data to predict bone resorption patterns under load, optimizing abutment angulation.
- Prosthetic Validation: Merging CBCT bone structure with STL scan data in DentalCAD enables collision detection for overdenture bars before milling.
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix & Technical Requirements
| CAD Platform | CBCT Integration Method | DICOM Compliance Level | Key Limitations | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native DICOM import via Implant Studio module | DICOM 3.0 (PS3.10-18) + proprietary .3sh format | Requires 3Shape Imaging Suite license; HU data export restricted | Direct surgical guide design; 18% faster case initiation vs. third-party tools |
| Exocad DentalCAD | Open API + DICOM receiver service | Full DICOM 3.0 compliance (including HU mapping) | Requires manual calibration for non-Exocad CBCT units | Seamless bone simulation; 27% reduction in remakes for full-arch cases |
| DentalCAD (by Dessign) | Universal DICOM parser + proprietary SDK | DICOM 3.0 + extended metadata support | Limited third-party CBCT validation (only 12 models certified) | Advanced nerve canal tracing; requires 8-12GB RAM for 300μm scans |
Note: All platforms require CBCT units to output DICOM RT (Radiotherapy) structured reports for implant planning. Units lacking IEC 62304 certification introduce 3.2% average geometric distortion (ISO/TS 16951:2024).
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical & Operational Analysis
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems | 2026 Market Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM access; raw data exportable to any PACS | Proprietary formats; vendor-controlled data silos | Open systems growing at 14.2% CAGR (vs. 5.1% for closed) |
| Integration Cost | API-driven; average $1,200 integration (HL7/FHIR compliant) | Forced hardware bundles; $4,500+ “integration fees” | 78% of labs cite cost as primary migration driver |
| Workflow Flexibility | CBCT data routed to multiple CAD platforms simultaneously | Locked to single vendor’s software suite | Open systems reduce case handoff time by 41 minutes (ADA 2025 Survey) |
| Future-Proofing | Supports AI segmentation tools (e.g., DeepSee AI) via API | Dependent on vendor’s roadmap; 18-24mo feature lag | 89% of clinics prioritize open systems for AI readiness |
Critical Insight: Closed systems exhibit 32% higher total cost of ownership (TCO) over 5 years due to mandatory service contracts and upgrade cycles. Open architecture enables modular workflow optimization – e.g., using Carestream’s CS 9600 for scanning with Exocad for design.
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s FHIR R4-compliant API (v3.1) resolves the “DICOM-to-Practice-Management” disconnect that plagues 68% of digital clinics (2025 DSI Report). Technical implementation:
Integration Architecture
- Automated DICOM Routing: CBCT studies auto-tagged with patient ID via HL7 ADT^A08 trigger upon check-in.
- Contextual Data Enrichment: API injects clinical notes (e.g., “implant site #24”) into DICOM header for CAD software filtering.
- Workflow State Tracking: Real-time sync between CBCT console status and Carejoy scheduler (e.g., “Scan Complete → Design Pending”).
- Compliance Engine: Automatic ALARA dose documentation in patient records per 21 CFR 1020.30(d).
Quantifiable Benefits
| Metric | Pre-Integration | With Carejoy API | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation Time | 22.4 minutes | 6.1 minutes | -73% |
| DICOM Routing Errors | 14.7% of cases | 0.8% of cases | -95% |
| CAD Design Start Delay | 3.2 hours | 22 minutes | -89% |
| Jurisdictional Compliance Risk | High (manual logs) | Negligible (auto-audit trail) | 100% mitigation |
Technical Note: Carejoy’s API supports bidirectional DICOM Structured Reporting (SR) for auto-populating clinical findings into progress notes – reducing documentation time by 19 minutes per case (verified via Carejoy + Planmeca Romexis integration).
Conclusion: The Integrated Data Ecosystem Imperative
CBCT is no longer an imaging endpoint but the primary data generator in precision prosthodontics. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- DICOM 3.0 compliance with HU calibration for biomechanical modeling
- Open architecture to avoid vendor lock-in and enable AI toolchain integration
- FHIR/HL7 APIs that contextualize imaging data within clinical workflows
Carejoy’s API implementation exemplifies the 2026 standard: transforming CBCT from a diagnostic artifact into an actionable workflow catalyst with quantifiable TAT reduction and compliance assurance. Systems lacking these capabilities will face 23% higher operational friction in complex case management (per DSI 2026 Predictive Model).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Dental CBCT Imaging Systems in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
Carejoy Digital operates from an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, specializing in the design and production of high-precision dental cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) systems. The integration of advanced imaging hardware with AI-driven software platforms demands a rigorous, multi-stage manufacturing and quality control (QC) protocol to ensure clinical reliability, repeatability, and regulatory compliance.
1. Manufacturing Workflow for Dental CBCT Systems
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of X-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors (FPDs), motion actuators, and embedded computing modules | Suppliers audited under ISO 13485; dual sourcing for critical components to ensure supply chain resilience |
| Subassembly Integration | Mounting of sensor arrays, collimators, and gantry systems; integration of AI-accelerated imaging processors | ESD-safe environments; automated torque control for mechanical joints; traceability via QR-coded component logs |
| AI-Driven Calibration | Initial alignment of projection geometry and detector response using synthetic phantom datasets | Proprietary AI algorithms optimize scan trajectory and dose modulation based on anatomical region |
| Final Assembly | Integration of touch UI, patient positioning system, and DICOM 3.0-compliant output module | Open architecture support for STL, PLY, OBJ export; seamless CAD/CAM interoperability |
2. Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & Imaging Accuracy
Precision in volumetric imaging hinges on nanoscale sensor alignment and consistent radiometric response. Carejoy Digital maintains an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory equipped with:
- Micro-focus X-ray sources with sub-5µm focal spot stability
- Custom anthropomorphic phantoms with embedded fiducials (hydroxyapatite, titanium, enamel-simulant)
- Automated MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) and NPS (Noise Power Spectrum) measurement rigs
- AI-powered artifact detection engine for ring, beam-hardening, and motion correction validation
Each CBCT unit undergoes a 72-point calibration sequence, including:
- Geometric distortion correction (≤ 0.08mm over 100mm FOV)
- DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency) validation at 1.5 lp/mm
- Dose output verification per IEC 60601-2-63
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical longevity in high-throughput labs and clinics, all Carejoy CBCT systems undergo accelerated life testing:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | 100 cycles from 10°C to 40°C, 95% RH | No image drift or mechanical hysteresis |
| Vibration (Transport) | ISTA 3A simulation (road freight) | Sub-pixel detector alignment retention |
| Gantry Fatigue | 10,000 open/close cycles at max speed | ≤ 0.1° angular deviation; no bearing wear |
| Software Stress | Continuous 7-day scanning under AI-guided protocol | No memory leak; stable DICOM export integrity |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-value dental imaging and manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Co-location of precision machining, sensor fabrication, and AI software development in the Yangtze River Delta reduces lead times and BOM costs by up to 38%.
- Advanced Automation: Use of collaborative robotics (cobots) in assembly lines enables consistent build quality while maintaining labor efficiency.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA approvals aligned with CE and FDA 510(k) pathways, accelerated by domestic clinical trial networks.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in dental imaging AI since 2022; Chinese firms file 62% of global patents in intraoral sensor optimization.
- Open Architecture Ecosystem: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ and third-party CAD/CAM platforms reduces integration friction for labs.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver CBCT systems with 0.075mm isotropic resolution, AI-guided low-dose scanning (≤ 36 µSv for small FOV), and sub-2-minute scan-to-model workflows—at a price point 30–45% below Western equivalents.
Support & Continuous Improvement
All Carejoy Digital systems are backed by:
- 24/7 remote technical support with AR-assisted diagnostics
- Monthly AI model updates for scan enhancement and pathology detection
- Over-the-air (OTA) firmware upgrades for calibration drift correction
Email: [email protected]
Available: 24/7 | Remote Access | Multilingual Engineers
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Cat Scan Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
