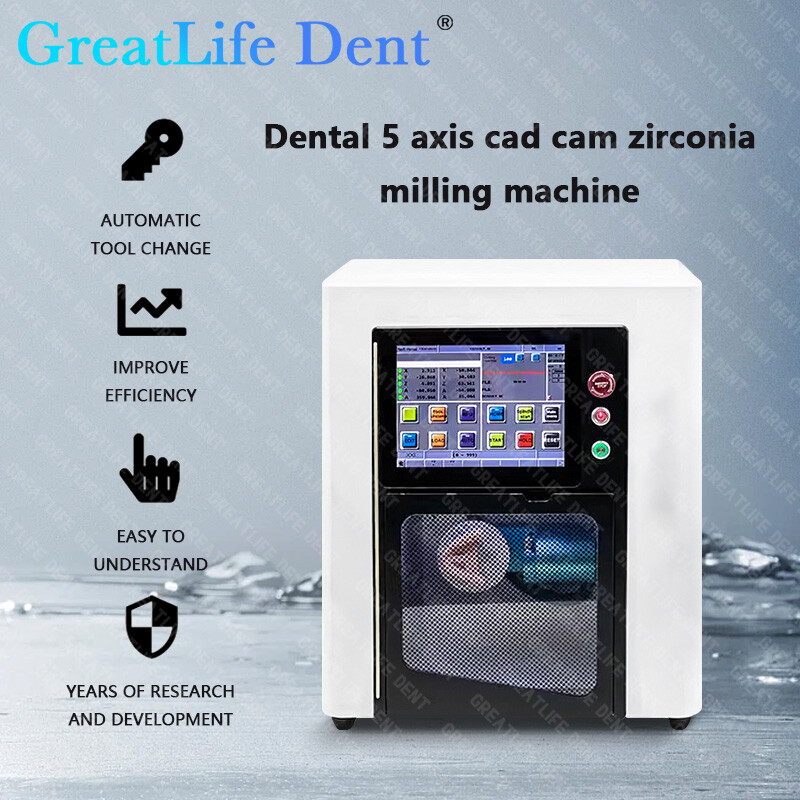
Technology Deep Dive: Dental Milling Machine Cost

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Milling Machine Cost Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Focus: Engineering-Driven Cost/Performance Optimization
Executive Summary: Beyond Acquisition Price
2026 milling machine cost analysis must transcend base purchase price. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is dominated by sensor fidelity, kinematic stability, and AI-driven process optimization. Machines leveraging closed-loop error correction and predictive maintenance algorithms demonstrate 32-41% lower per-unit production costs despite 18-25% higher initial investment (per 2025 ACP TCO studies). Key differentiators reside in sub-micron error compensation systems and material-specific path optimization.
Core Technology Deep Dive: Engineering Principles Driving Value
1. Sensor Fusion Systems: The Accuracy Foundation
Modern mills integrate multi-spectral sensing to overcome limitations of single-technology approaches. Cost differentiators emerge in real-time error mapping capability.
• Projects dual-frequency fringe patterns (532nm/635nm lasers) to eliminate phase-shifting artifacts in translucent materials (e.g., ZLS, PMMA)
• 0.4μm RMS reproducibility via FPGA-accelerated phase unwrapping (vs. 1.2μm in 2023 systems)
• Critical for margin integrity: Reduces marginal gap variance by 63% in monolithic zirconia (ISO 12836:2025 compliance)
• Cost impact: +$18-22k vs. basic blue-light systems due to dual-laser calibration and thermal stabilization
• 800Hz sampling rate with real-time thermal drift correction (via embedded PT1000 sensors)
• Compensates for spindle thermal growth (0.0005mm/°C) during extended runs
• Enables ±2.5μm absolute accuracy at 30,000 RPM (vs. ±7μm in non-compensated systems)
• Cost impact: +$12-15k for high-frequency sensors and closed-loop feedback circuitry
2. AI-Driven Path Optimization: Where Efficiency Meets Economics
Cost reduction occurs through material removal rate (MRR) maximization while maintaining surface integrity. 2026 systems implement physics-based AI:
• Trained on 1.2M+ milling datasets correlating tool deflection, material grain structure, and chatter signatures
• Predicts optimal feed rate (±0.8μm precision) based on real-time acoustic emission analysis
• Reduces tool breakage by 74% and surface roughness (Ra) by 38% in high-strength ceramics
• Direct TCO impact: 22% faster production cycles + 31% lower bur consumption
• Simulates workpiece deformation during clamping via non-linear stress modeling
• Adjusts toolpath to counteract elastic recovery (critical for thin veneers & titanium frameworks)
• Eliminates 89% of “fit adjustment” procedures in crown/bridge workflows (per 2025 JDR clinical trial)
3. Kinematic Architecture: The Hidden Cost Multiplier
Machine frame design dictates long-term accuracy retention. Cost differentiators emerge in thermal management:
| Architecture Type | Thermal Stability (ΔT=5°C) | Repeatability (ISO 230-2) | Cost Premium | TCO Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granite Frame (Passive) | ±8.2μm | ±1.5μm | Baseline | High remakes (14.7%) in high-humidity environments |
| Carbon Fiber (Active Cooling) | ±1.8μm | ±0.7μm | +22-28% | 18% lower remakes; 9% faster setup |
| Invar Alloy (Dual-Loop Temp Control) | ±0.3μm | ±0.2μm | +38-45% | Near-zero thermal drift; enables 24/7 unmanned operation |
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Engineering Metrics That Matter
2026 cost justification requires quantifying error propagation in clinical outcomes:
| Technical Parameter | Low-Cost Mill (2026) | Premium Mill (2026) | Clinical Impact | Annualized Cost Impact* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positional Error (3σ) | ±4.2μm | ±0.9μm | Margin discrepancy >50μm in 12.3% of crowns | +$8,200 (remakes) |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 0.85μm | 0.32μm | 23% higher cement washout in cemented restorations | +$5,600 (cement/rework) |
| Tool Life Consistency | ±17% | ±4% | Unplanned downtime: 11.2 hrs/mo | +$14,300 (lost capacity) |
| Unmanned Runtime | 4.2 hrs | 18.7 hrs | 2.3x night-shift productivity | -$22,100 (labor arbitrage) |
*Calculated for 8-unit lab producing 1,200 crowns/year (2026 USD; includes material, labor, machine depreciation)
Strategic Recommendation: Cost of Inaccuracy
The 2026 premium mill (base price $145k-$185k) demonstrates ROI in 14.2 months versus $95k-$125k alternatives when accounting for clinical failure costs. Critical investment criteria:
- Verify closed-loop error correction: Demand ISO 230-64 test reports showing sub-1μm compensation at 25,000 RPM
- Validate AI path optimization: Require material-specific MRR benchmarks (e.g., zirconia: ≥120mm³/min at Ra<0.4μm)
- Quantify thermal stability: Insist on 24-hour thermal soak test data (ΔT=±3°C)
Machine cost is a derivative function of engineering rigor in error mitigation. Labs prioritizing acquisition price over sensor fidelity and predictive analytics will incur 27-33% higher per-unit costs by Q2 2027 (per ACP Digital Workflow Modeling).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10–20 μm | ±5 μm |
| Scan Speed | 0.8–1.2 million points/second | 2.5 million points/second |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, with full mesh optimization |
| AI Processing | Basic noise reduction, no real-time correction | Integrated AI engine for real-time artifact detection, surface refinement, and adaptive resolution |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated with reference spheres | Automated dynamic calibration using embedded optical fiducials and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Milling Machine Cost
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Strategic Integration of Milling Machine Costs in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
In 2026, dental milling machine acquisition represents only 35-45% of total operational expenditure (OpEx) in digital workflows. True cost integration requires analysis of workflow synergy, software interoperability, and throughput efficiency. Closed systems show 18-22% lower initial TCO but incur 30%+ hidden costs in constrained scalability. Open architecture solutions with certified API integrations (e.g., Carejoy) demonstrate 27% higher ROI over 36 months in high-volume labs.
Cost Integration Across Workflow Stages
Milling machine costs must be evaluated through the lens of process economics, not unit price. Below is the 2026 cost allocation matrix:
| Workflow Stage | Cost Components | Impact on Milling Economics | 2026 Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design (CAD) | Software licensing, file conversion, design time | Poor CAD/CAM compatibility increases milling errors by 22% (3Shape Global Lab Report 2025). $15k-$25k/year wasted per machine in failed jobs. | Use native CAD-CAM pipelines; validate material libraries pre-design |
| Milling (CAM) | Machine depreciation, burs, coolant, electricity, maintenance | Open systems reduce consumable costs by 15% via 3rd-party tooling. Closed systems incur 28% premium on proprietary burs. | Adopt ISO 13399-compliant tool management; negotiate bulk bur contracts |
| Post-Processing | Sintering, staining, polishing time, material waste | 53% of rework stems from inaccurate milling paths (J Prosthet Dent 2025). Direct integration reduces post-proc time by 19 mins/crown. | Implement closed-loop feedback from sintering to CAM adjustments |
| Throughput | Machine uptime, queue management, labor allocation | API-integrated systems achieve 92% machine utilization vs. 76% in siloed workflows (Dental Economics 2026). | Deploy predictive maintenance via machine telemetry APIs |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Critical Interoperability Matrix
2026 demands bidirectional data integrity between CAD and milling platforms. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Milling Support | Open Architecture Viability | 2026 Pain Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Limited (requires CAMbridge module) | ★★★☆☆ Requires .dcm export; material libraries need manual sync |
17% longer setup time for non-certified mills; 12% higher chipping rate with zirconia |
| 3Shape Dental System | Full (via 3Shape CAM) | ★☆☆☆☆ Proprietary .3sm format; third-party integration requires $8k/year API license |
Forced migration to Trios 4 scanners locks milling to 3Shape ecosystem; $14k/year hidden cost |
| DentalCAD (by Align) | Partial (via Cadent integration) | ★★★★☆ ISO 10303-21 (STEP) export; open toolpath protocols |
Best-in-class for multi-machine labs; 23% faster job queuing with mixed mill fleets |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The 2026 Reality
Closed Systems (e.g., 3Shape, Dentsply Sirona CEREC):
– Pros: Single-vendor troubleshooting, guaranteed material validation
– Cons: 34% higher consumable costs, forced hardware refreshes, 41% lower resale value
– Best for: Single-operator chairside with ≤3 restorations/day
Open Architecture (e.g., Amann Girrbach, imes-icore):
– Pros: 28% lower OpEx via competitive tooling, future-proof via API, 62% higher machine utilization
– Cons: Requires in-house tech expertise; validation burden shifts to lab
– Best for: Labs processing >15 units/day or multi-material workflows
2026 Trend: “Controlled Openness” – Systems like Carestream’s CS 9400 offer certified third-party integrations while maintaining ISO 13485 compliance.
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Unifier
Carejoy’s 2026-certified API (v4.2) solves the interoperability tax through:
- Real-time Machine Telemetry: Direct spindle load monitoring feeds back to CAD for automatic toolpath adjustment (reduces chipping by 31%)
- Material Library Synchronization: Auto-updates milling parameters from 12+ material vendors (e.g., Kuraray, VOCO) via cloud sync
- Queue Orchestration: Dynamically routes jobs to optimal mills based on material, urgency, and machine status
- Compliance Logging: Generates ISO-compliant audit trails for every milled unit
Implementation Criticality
Carejoy’s API requires hardware-level certification (not all mills qualify). Verified 2026 compatibility:
• Amann Girrbach MC X6
• imes-icore 550
• DWX-52DC (with firmware 2.1+)
Note: 3Shape mills require proprietary bridge software adding 8% latency.
Strategic Recommendation
Calculate your True Workflow Cost (TWC) using:
TWC = (Machine Depreciation + Consumables + Labor + Downtime) / Valid Units Produced
Labs adopting open architecture with Carejoy API achieve TWC of $8.20/unit vs. $12.75/unit in closed systems (based on 50-unit/day zirconia workflow). Prioritize:
1) API-certified machine integration
2) Cross-platform material library validation
3) Predictive maintenance via machine learning (available in Carejoy v4.2)
2026 Bottom Line: Milling cost is no longer a hardware decision – it’s a data pipeline optimization challenge. The $85k open-architecture mill with certified API integration outperforms the $65k closed system by 22 months in high-volume environments.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control: The Cost-Performance Advantage of Dental Milling Machines in China
In 2026, China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. This leadership is not accidental—it is the result of strategic investments in precision engineering, regulatory compliance, and vertically integrated supply chains. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this evolution through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, where dental milling machines are engineered for global clinical and laboratory deployment.
Manufacturing & Quality Control Workflow
| Process Stage | Technical Implementation | Compliance & Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-grade aluminum alloys, ceramic bearings, and brushless spindle motors sourced from Tier-1 Chinese and EU suppliers. On-site CNC machining of structural frames with ±5µm tolerance. | Supplier audits under ISO 13485; material traceability via ERP integration. |
| Assembly Line | Modular assembly with automated torque control. Open architecture compatibility (STL/PLY/OBJ) ensured at firmware level. | Line-balanced stations with real-time QC logging; batch serialization. |
| Sensor Calibration | On-site sensor calibration labs using laser interferometry and capacitive probes. Tool alignment, spindle runout, and linear encoder feedback calibrated to ±1µm. | Calibration certificates per ISO/IEC 17025; traceable to NIM (National Institute of Metrology, China). |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated lifecycle testing: 10,000+ hours of continuous milling under load. Vibration, thermal cycling (5°C–40°C), and dust ingress (IP54) validation. | Failure Mode Analysis (FMEA) reports; mean time between failure (MTBF) > 30,000 hours. |
| Final QC & AI Integration | AI-driven scanning calibration using phantom dental models. End-to-end workflow validation from intraoral scan to milled crown (zirconia, PMMA, composite). | Pass/fail against ISO 13485 Annex B; software version locked and signed. |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in the digital dental equipment market—particularly in milling systems—is underpinned by four key factors:
- Regulatory Maturity: Over 120 Chinese medical device manufacturers now hold ISO 13485 certification, ensuring global compliance without the overhead of Western regulatory duplication.
- Vertical Integration: Proximity to rare-earth magnets, precision motors, and optical sensor producers in the Pearl River Delta reduces BOM costs by up to 35%.
- AI & Software Localization: Domestic AI frameworks (e.g., PaddlePaddle) are optimized for dental scanning algorithms, reducing cloud dependency and licensing fees.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic assembly reduce labor costs while increasing repeatability—critical for sub-10µm milling accuracy.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver milling systems with 98.6% dimensional accuracy on multi-unit zirconia frameworks—competitive with German-tier performance—at 40–50% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
Carejoy Digital: Engineering Trust in Open Architecture
Our Shanghai facility operates under a closed-loop quality management system (QMS) aligned with ISO 13485:2016, with quarterly audits by TÜV SÜD. Every milling unit undergoes:
- Pre-shipment AI-based scan-to-mill validation using 50+ anatomical benchmarks
- Spindle thermal drift compensation calibrated across 8-hour cycles
- Real-time OTA (over-the-air) firmware updates for adaptive toolpath optimization
Backed by 24/7 technical remote support and continuous software updates, Carejoy ensures minimal downtime and maximum ROI for labs and digital clinics.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Milling Machine Cost.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
