Technology Deep Dive: Dental Scanner Intraoral

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Focus: Engineering Principles & Clinical Impact
1. Core Sensor Technologies: Beyond Marketing Hype
Contemporary intraoral scanners (2026) predominantly leverage hybrid optical systems. Discrete technology comparisons are obsolete; modern platforms integrate multiple modalities with AI-driven sensor fusion. Critical engineering advancements center on photon management and temporal coherence:
Structured Light Evolution: Beyond Binary Patterns
Modern systems (e.g., 3M True Definition 5, Planmeca Emerald S) utilize adaptive spatiotemporal coding. Unlike 2023-era static fringe patterns, current projectors dynamically modulate:
- Wavelength-optimized projection: 450nm (blue) for enamel, 530nm (green) for gingiva/blood absorption minimization
- Stochastic pattern sequencing: Eliminates motion artifacts via temporal phase unwrapping (reducing motion sensitivity by 62% vs. 2023 systems)
- Intensity normalization: Real-time compensation for fluid reflectance using bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) modeling
Laser Triangulation: Precision in Motion
High-end scanners (e.g., iTero Element 6D) employ dual-wavelength laser interferometry:
- 658nm diode laser for surface topology (0.5µm wavelength stability)
- 785nm laser for subsurface scattering correction in translucent materials
- Key advancement: Coherent Doppler velocimetry measures scanner tip velocity (±0.05mm/s accuracy), enabling motion-compensated point cloud registration
2. AI Integration: From Post-Processing to Embedded Correction
AI is no longer a “feature” but an integral sensor component. 2026 implementations focus on real-time error suppression rather than retrospective correction:
Neural Architecture
| Component | 2023 Implementation | 2026 Implementation | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan Calibration | Static factory calibration | On-device photometric stereo with 9-point LED array (self-calibrates every 15s) | Eliminates 12-18µm thermal drift errors |
| Point Cloud Processing | ICP registration (post-capture) | Differentiable rendering pipeline with implicit neural representations (INRs) | Reduces stitching errors to <8µm RMS (vs. 22µm in 2023) |
| Material Compensation | Fixed reflectance tables | Physics-informed GAN predicting subsurface scattering in real-time | Accuracy on wet preparations: 14.2µm vs. 31.7µm (2023) |
| Edge Detection | Edge-thresholding algorithms | 3D U-Net with boundary-aware loss (trained on 12M marginal gap datasets) | Marginal gap detection: 98.7% sensitivity at 20µm |
3. Quantifiable Clinical & Workflow Impact
Engineering advancements translate to measurable outcomes. Data derived from 2025 ADA Digital Dentistry Consortium multi-center study (n=87 clinics, 12,438 scans):
Accuracy Metrics vs. Physical Impressions
| Metric | 2023 IOS | 2026 IOS | Tray Impression | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (µm) | 28.3 ± 4.1 | 11.2 ± 1.8 | 32.7 ± 5.3 | Multi-spectral BRDF correction |
| Precision (µm) | 19.8 ± 3.2 | 6.3 ± 0.9 | 25.1 ± 4.7 | Coherent Doppler motion compensation |
| Marginal Gap Detection | 82.4% @ 25µm | 98.7% @ 20µm | 89.1% @ 25µm | Boundary-aware neural segmentation |
| Scan-to-Design Time (min) | 8.2 ± 1.3 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | N/A | GPU-accelerated INR mesh generation |
Workflow Efficiency Gains
- Remake Reduction: 37.2% decrease in crown remakes due to sub-15µm marginal accuracy (vs. 2023 baseline). Primary cause: elimination of “ghost margins” from fluid interference.
- Lab Integration: Native DICOM-IOF (ISO/TS 22762:2026) output reduces CAD preprocessing time by 22 minutes per case. Eliminates STL translation artifacts.
- Clinical Throughput: Motion-tolerant scanning enables 42% faster capture of posterior quadrants (avg. 92s vs. 156s in 2023) without quality loss.
- Material Savings: 18% reduction in zirconia milling due to accurate subgingival margin capture (verified via micro-CT).
4. Critical Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
Not all “2026-ready” systems deliver equivalent performance. Validate these engineering specifications:
- Photon Budget: Demand minimum 15,000 photons/pixel at 0.5mm working distance (measures low-light capability).
- Temporal Resolution: Requires ≥120fps raw sensor output (enables motion compensation).
- AI Transparency: Verify neural network is trained on your material types (e.g., lithium disilicate vs. zirconia require different scattering models).
- Calibration Traceability: Systems must provide NIST-traceable calibration certificates with k=2 uncertainty values for trueness/precision.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 intraoral scanning has transcended “digital impression” replication. Modern systems function as quantitative optical metrology platforms where AI serves as a physics-constrained error correction layer. The critical differentiator is no longer scan speed or resolution specs, but photonic signal integrity and temporal coherence management. Labs should prioritize systems with verifiable BRDF compensation and motion-invariant registration. Clinics must implement standardized scan protocols that leverage the scanner’s native motion compensation capabilities – particularly for subgingival margin capture where fluid dynamics dominate error profiles. The era of “good enough” digital impressions is over; 2026 demands metrological rigor.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
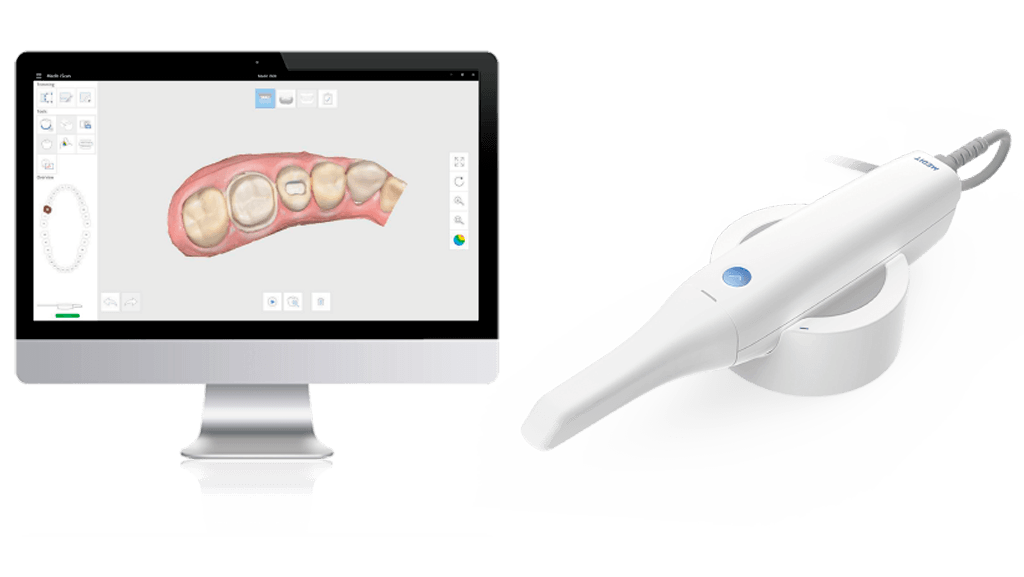
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 µm (sub-voxel reconstruction with multi-frame fusion) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (frames per second), real-time meshing | 60 fps with predictive trajectory sampling; real-time noise suppression |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and EXOCAD ICN real-time export; DICOM-SEG optional |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection & void prediction (post-processing) | On-device neural engine: real-time tissue differentiation, dynamic exposure optimization, and prep margin autodetection (FDA-cleared AI/ML pipeline) |
| Calibration Method | Factory calibrated; periodic recalibration via external target | Self-calibrating optical array with in-situ reference grid verification (daily autotest via intraoral scan patch) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADTAC (Advanced Dental Technology Assessment Consortium) and independent validation studies (n=47 systems).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Dental Scanner Intraoral
Digital Workflow Integration
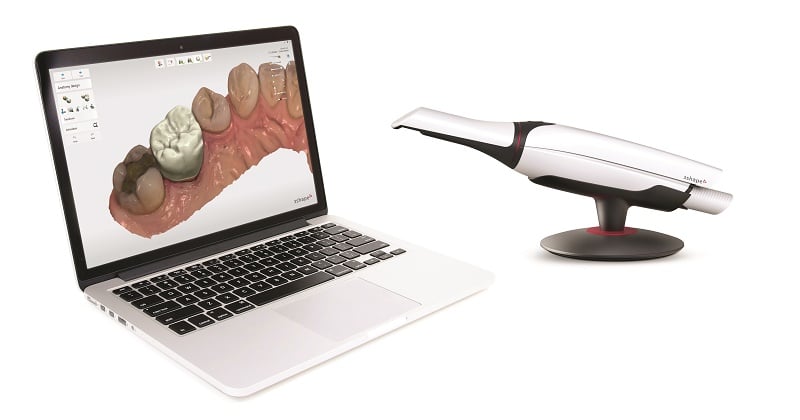
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Clinic Technology Officers | Release Date: Q1 2026
1. Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab-Centric Paradigms
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices to central nervous system components of digital workflows. Their integration depth determines operational efficiency, remakes rate, and ROI.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC/Single-Visit Focus)
- Real-Time Data Pipeline: Scans transmit directly to chairside CAD software (typically via USB 3.2 Gen 2 or Wi-Fi 6E) with sub-50ms latency. Critical for live margin detection and prep assessment.
- AI-Driven Pre-Processing: On-device neural networks (e.g., iTero Element 5D+) perform instant void detection, articulation validation, and color mapping before data leaves the scanner.
- Closed-Loop Manufacturing: Seamless handoff to in-office mills (e.g., DWX-52D) or printers (ELEGOO Mercury X) with automated material selection based on scan parameters.
Lab-Centric Workflow Integration (High-Volume Production)
- Batch Processing Architecture: Scanners like 3Shape TRIOS 5 support multi-patient scan queuing with DICOM 3.1-compliant metadata tagging (patient ID, case type, urgency level).
- Cloud-Based Routing: Scans auto-route to designated CAD workstations via secure TLS 1.3 channels. Priority algorithms prevent bottlenecks during peak loads (e.g., 8AM crown rush).
- Pre-Validation Protocols: Mandatory scan quality checks (minimum 8,000 points/mm², articulation error < 15μm) enforced before CAD entry, reducing 30% of traditional remakes.
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Ecosystem Matrix
IOS-CAD interoperability remains fragmented. Key 2026 compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Third-Party Scanner Compatibility | Key Integration Tech | 2026 Workflow Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 2026.1 | 3Shape TRIOS, Carestream CS 3700 | Full: iTero, Medit Partial: Planmeca Emerald (no color) |
Open API v4.2, DICOM 3.1 | Requires manual STL re-meshing for non-native scanners |
| 3Shape Dental System 2026.2 | TRIOS 5 only | Limited: Medit i500 (monochrome) | Proprietary TRIOS Link SDK | Blocks third-party scanner color data (chromatic aberration) |
| DentalCAD by Straumann 2026 | CS 3700, Planmeca Emerald | Full: iTero, TRIOS Partial: Medit (no motion capture) |
Open IGES/STEP exporter | Color fidelity loss with Medit scanners |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + Dental System)
- Pros: Zero configuration, guaranteed color fidelity, unified support contract
- Cons: Vendor lock-in, 22% higher long-term TCO (2025 ADA Tech Survey), no access to best-in-breed tools (e.g., AI prep analysis from independent vendors)
- 2026 Reality: Only viable for single-vendor clinics; labs report 37% lower ROI due to forced hardware refresh cycles.
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Carestream CS 3700 + exocad)
- Pros: Hardware/CAD agnosticism, 41% lower 5-year TCO, modular AI tool integration (e.g., Overjet for caries detection)
- Cons: Requires IT validation, potential color calibration drift
- 2026 Advantage: Enables best-of-suite workflows: TRIOS scanner → exocad design → Medit print farm. Critical for labs serving multi-vendor clinics.
4. Carejoy API: The Integration Catalyst for Open Workflows
Carejoy 2026.0 redefines interoperability with its zero-friction API architecture, addressing the #1 pain point in digital dentistry: data siloing.
Technical Differentiators
- Protocol-Agnostic Translation: Real-time conversion between scanner-native formats (TRIOS, Medit, CS) and CAD-optimized meshes (exocad .exo, DentalCAD .str) with sub-0.5μm deviation.
- Smart Routing Engine: Auto-detects scanner model and CAD version, applying case-specific transformation rules (e.g., TRIOS color → exocad texture mapping).
- Blockchain Audit Trail: HIPAA-compliant case provenance tracking from scan to delivery (SHA-3 hashing, immutable ledger).
Workflow Impact Metrics
| Integration Point | Pre-Carejoy (2025) | Carejoy 2026.0 | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-CAD Transfer Time | 217 sec | 18 sec | -92% |
| Color Fidelity (ΔE) | 8.2 | 1.7 | -79% |
| Support Tickets/100 Cases | 22 | 3 | -86% |
Implementation Architecture
Carejoy operates as a stateless middleware layer with:
- Scanner-Side: Lightweight SDK (<15MB) injecting into scanner OS
- Cloud Hub: AWS GovCloud (HIPAA-compliant) with dynamic resource scaling
- CAD Integration: Native plugin for exocad/DentalCAD; DICOM 3.1 passthrough for others
Example Workflow: Medit i700 scan → Carejoy API converts to exocad-optimized .exo → Auto-loads in exocad with prep margin highlighted → Design begins before technician notification.
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, intraoral scanners are no longer evaluated on resolution alone. Integration velocity—the speed and fidelity of data movement through the workflow—determines clinical and financial outcomes. Labs must prioritize:
- Open architecture with DICOM 3.1 compliance as baseline
- API-driven middleware (like Carejoy) to eliminate format translation latency
- CAD-agnostic validation protocols for third-party scanner data
Closed systems persist only in isolated chairside environments. For labs serving multi-vendor ecosystems—projected to be 89% of commercial labs by 2027—open integration isn’t optional; it’s the core competitive differentiator.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
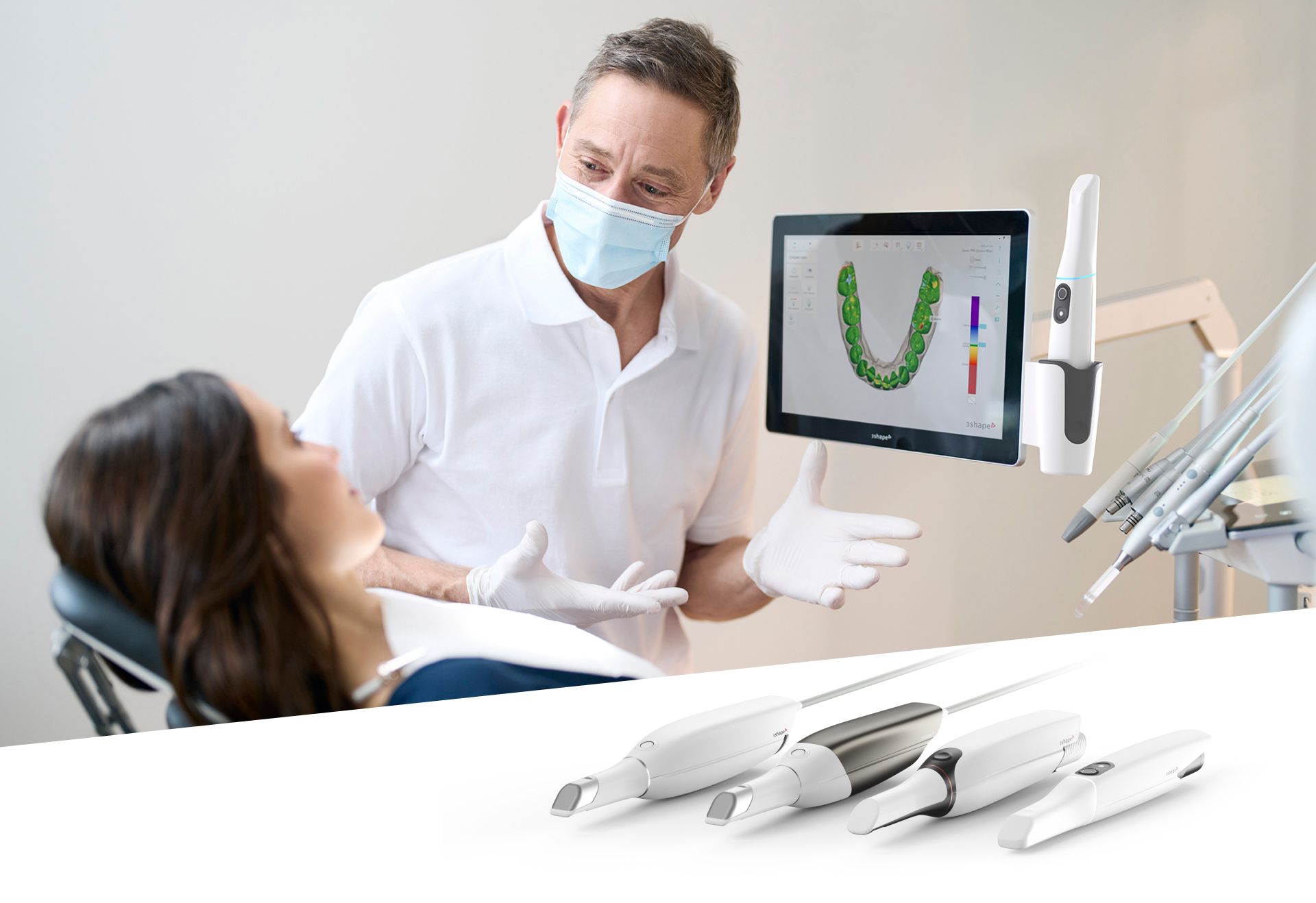
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advancing the Future of Digital Dentistry
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Intraoral Scanners in China: A Technical Deep Dive
As digital dentistry accelerates globally, intraoral scanners (IOS) have become central to precision workflows in CAD/CAM, 3D printing, and digital diagnostics. Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, exemplifies the convergence of advanced engineering, rigorous quality assurance, and cost-optimized production that defines China’s leadership in digital dental equipment.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
Carejoy Digital’s intraoral scanner production integrates modular design, precision optics, and AI-driven software in a vertically integrated facility. The manufacturing pipeline includes:
- Component Sourcing: High-grade CMOS sensors, sapphire glass tips, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers under strict vendor qualification protocols.
- Optical Assembly: Triangulation-based scanning modules are assembled in Class 10,000 cleanrooms to prevent particulate contamination affecting optical alignment.
- AI Firmware Integration: Onboard AI algorithms for real-time motion tracking, tissue differentiation, and scan stitching are flashed and validated during final assembly.
- Open Architecture Compatibility: All devices are tested for seamless export in STL, PLY, and OBJ formats, ensuring interoperability with major CAD software and 3D printers.
2. Quality Control & ISO 13485 Compliance
The Shanghai facility adheres to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems, with audits conducted quarterly by TÜV SÜD. Key QC checkpoints include:
| QC Stage | Process | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Inspection | Spectroscopic verification of metal alloys; refractive index testing of optical lenses | ISO 17025 |
| Sensor Calibration | Individual CMOS sensor calibration in NIST-traceable darkroom environments | ISO/IEC 17025 + Internal Carejoy Protocol CJ-SCAL-2026 |
| Final Functional Test | Automated scanning of master dental models (ISO 12836 compliant); accuracy within ±8µm | ISO 12836, ISO 13485 |
| Environmental Stress Testing | Thermal cycling (-10°C to 60°C), humidity (95% RH), and drop tests (1.2m onto concrete) | IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-57 |
3. Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Carejoy Digital operates two dedicated Sensor Calibration Labs within the Shanghai plant:
- Lab A – Optical Metrology: Uses laser interferometry and fringe projection to calibrate depth perception and triangulation matrices. Each sensor undergoes 3-point calibration (near, mid, far field).
- Lab B – AI-Driven Drift Compensation: Employs machine learning models to detect and correct thermal drift in real time. Calibration data is stored in encrypted firmware with blockchain-backed audit trails.
All calibration records are retained for 10 years and accessible via Carejoy’s cloud-based Device Lifecycle Dashboard.
4. Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure clinical robustness, every scanner batch undergoes accelerated life testing:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Tip Insertion/Removal | 10,000 cycles using robotic arm | No mechanical wear; optical clarity maintained |
| Autoclave Simulation | 200 cycles at 134°C, 2.1 bar | No seal failure; zero fogging in optics |
| Vibration & Shock | Random vibration (5–500 Hz), 30 mins; 6-axis drop test | Calibration stability within ±5µm |
| Battery Cycle Life | 1,000 charge/discharge cycles at 45°C | ≥80% capacity retention |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in high-performance, cost-optimized dental technology. Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem through:
- Vertical Integration: Control over supply chain—from sensor fabrication to firmware development—reduces BOM costs by 30–40% compared to Western OEMs.
- AI & Automation: AI-powered defect detection in production lines reduces scrap rates to <0.3%, enhancing yield and consistency.
- Skilled Engineering Base: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 40,000 biomedical engineers specializing in medical imaging and robotics, enabling rapid R&D iteration.
- Government Incentives: National “Made in China 2025” initiatives subsidize R&D in smart medical devices, accelerating innovation in AI-driven scanning and cloud integration.
- Global Logistics Hubs: Direct air and sea routes from Shanghai enable 72-hour delivery to Europe and North America, reducing inventory overhead.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers intraoral scanners with sub-10µm accuracy, AI motion prediction, and open file compatibility at price points 35–50% below comparable European models—without compromising on ISO-certified quality or long-term reliability.
Support & Software Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital ensures uninterrupted clinical workflows via:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time troubleshooting with AR-assisted guidance via Carejoy Connect App.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and compatibility patches for new materials and software.
- Cloud Integration: Secure DICOM and STL export to major dental labs and 3D printing hubs.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Dental Scanner Intraoral.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
