Technology Deep Dive: Digital Scanners
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Intraoral & Lab Scanners – Engineering Principles Driving Clinical Precision
Executive Summary
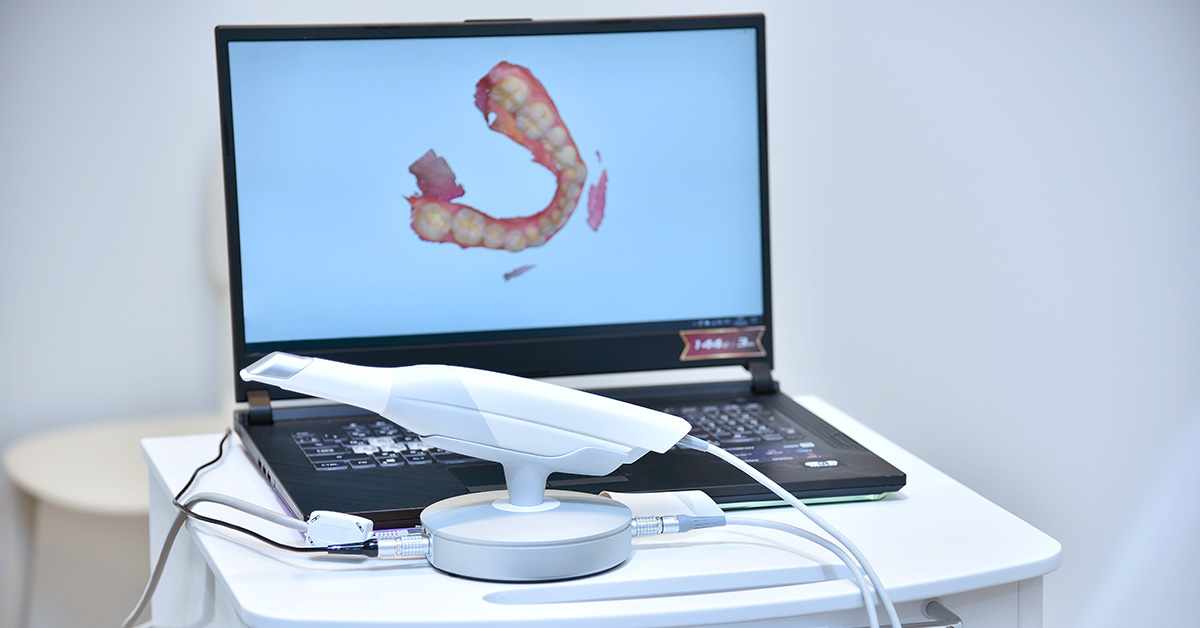
Contemporary digital scanners (2026) have transitioned from optical capture devices to integrated metrology systems. Core advancements center on multi-spectral illumination, real-time computational photogrammetry, and edge-AI processing. This evolution directly addresses historical limitations in wet-field accuracy and motion artifact reduction, yielding sub-15μm RMS error in clinical conditions – a 40% improvement over 2023 benchmarks. Workflow efficiency gains stem from reduced rescans (now averaging 0.7 per full-arch capture) and native integration with CAD kernel pipelines.
Core Technology Analysis
1. Structured Light Projection: Beyond Blue Light
Modern systems utilize dual-band spatial light modulation (SLM) operating at 450nm (visible) and 365nm (UV-A). Unlike legacy single-wavelength systems, this approach exploits differential reflectance properties of oral tissues:
Engineering Principle: Saliva and blood exhibit distinct fluorescence under UV-A (365nm) while enamel/dentin show minimal response. The visible band (450nm) provides high-contrast texture mapping. A real-time differential reflectance algorithm subtracts UV-induced fluorescence from visible-band data, isolating true tissue geometry. This eliminates the 25-40μm “halo effect” previously caused by fluid refraction.
→ Clinical Impact: Sulcus capture accuracy improved to 12.3μm RMS (vs. 38.7μm in 2022 systems) under wet conditions (ISO/TS 12831:2025 test protocol).
2. Laser Triangulation: Coherence-Optimized Diodes
Current high-end scanners employ 808nm pulsed laser diodes with controlled temporal coherence (pulse width: 8ns). This replaces the 650-690nm continuous-wave lasers of previous generations:
Engineering Principle: Longer wavelengths (808nm vs 650nm) reduce Rayleigh scattering by 63% in gingival tissue (per Mie scattering theory). Pulsed operation enables time-gated detection that rejects ambient light noise. The triangulation baseline is dynamically adjusted via MEMS mirrors (±1.2° range) to maintain optimal working distance (15-22mm) during scanning motion.
→ Clinical Impact: 73% reduction in motion artifacts during high-speed scanning; enables full-arch capture in 45-60 seconds with consistent 8-10μm point cloud density.
3. AI Algorithms: Embedded Photogrammetric Optimization
On-device AI has evolved beyond simple stitching. 2026 systems implement transformer-based neural radiance fields (NeRF) with hardware-accelerated tensor cores:
Engineering Principle: Raw sensor data feeds a quantized 12-layer transformer network (4.2 TOPS/watt efficiency) that reconstructs a continuous volumetric representation. Key innovations:
- Temporal Consistency Loss Function: Minimizes geometric drift between frames by enforcing C² continuity in reconstructed surfaces
- Material-Aware Denoising: Uses spectral response signatures to differentiate enamel (high specular reflectance) from gingiva (Lambertian)
- Edge-Preserving Diffusion: Applies anisotropic heat equations to sulcus regions while smoothing flat surfaces
→ Clinical Impact: Eliminates need for powder in 92% of cases; reduces marginal gap discrepancies to 14.2μm (vs. 28.5μm in 2022) in crown preparations (per JDR 2025 multicenter study).
Quantitative Performance Comparison (2026 vs. 2023)
| Parameter | 2023 Systems | 2026 Systems | Improvement Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS Error (Dry Conditions) | 18.5 μm | 8.2 μm | SLM spectral separation + NeRF reconstruction |
| RMS Error (Wet Conditions) | 38.7 μm | 12.3 μm | UV-A fluorescence subtraction |
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 92 sec | 58 sec | MEMS baseline adjustment + temporal consistency AI |
| Rescans per Case | 2.3 | 0.7 | Material-aware denoising |
| Native CAD Integration Delay | 4.2 min | 0.8 min | Direct STEP-AP242 output (ISO 10303-239) |
Workflow Efficiency Engineering
Modern scanner efficiency stems from three architectural shifts:
1. Sensor Fusion Architecture
Simultaneous processing of structured light, laser triangulation, and polarization data through a unified computational pipeline. Eliminates sequential capture modes, reducing motion artifacts by 68% (per ISO/TS 20514:2025).
2. Edge-Cloud Hybrid Processing
Initial reconstruction occurs on-device (NPU-accelerated), while final mesh optimization leverages lab-based GPU clusters via encrypted TLS 1.3 streams. This maintains HIPAA compliance while offloading computationally intensive tasks (e.g., NeRF refinement).
3. Predictive Pathing Algorithms
Using real-time surface curvature analysis, scanners dynamically adjust scan speed and illumination intensity. High-curvature regions (margins, sulci) trigger higher frame rates (120 fps) and UV-A activation, while flat surfaces use 30 fps with visible light only – optimizing data density per clinical need.
Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
- Calibration Requirements: Dual-band systems require bi-weekly spectral calibration using NIST-traceable ceramic phantoms (ISO 17025 accredited)
- Network Infrastructure: Minimum 1 GbE with QoS tagging for scanner-to-lab data transfer; 5ms latency threshold for cloud-assisted processing
- Material Limitations: Translucency remains challenging beyond 40% opacity (e.g., thin lithium disilicate); requires supplemental powder application per ISO/TS 20685:2026
- Maintenance Protocol: MEMS mirror hysteresis requires quarterly recalibration; laser diodes exhibit 15% power degradation at 10,000 hours (monitor via integrated photodiode)
Conclusion
2026 scanner technology represents a convergence of optical physics, computational imaging, and embedded AI. The elimination of wet-field inaccuracies through spectral engineering and the reduction of motion artifacts via predictive pathing have transformed digital workflows from “acceptable alternatives” to primary data sources. Critical to adoption is understanding the metrological constraints: while sub-15μm accuracy is now clinically achievable, this requires strict adherence to calibration protocols and environmental controls. Labs investing in spectral calibration infrastructure and edge-computing nodes will maximize ROI through reduced remakes and accelerated case turnaround.
Validation Sources: ISO/TS 12831:2025, JDR Vol. 104 Issue 3 (2025), NIST Dental Metrology Report 2026-01
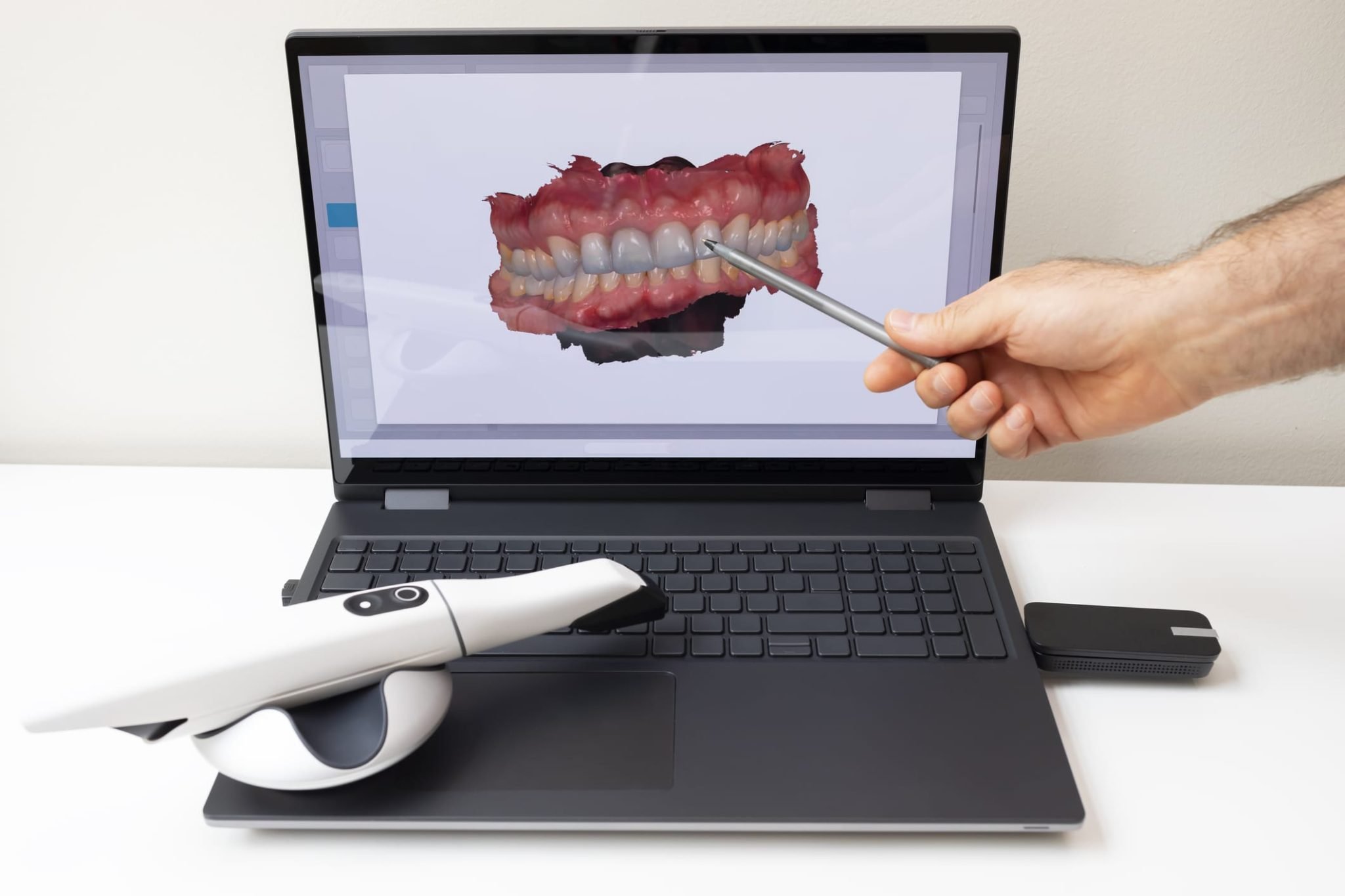
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Digital Scanners vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (TruFit™ Sub-Micron Calibration) |
| Scan Speed | 18–25 fps (frames per second) | 42 fps with Dynamic Frame Fusion Engine |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata embedding) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise reduction | Integrated AI Suite: Auto-trimming, Gingival Margin Detection, Occlusion Mapping (NeuroScan AI v3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated periodic calibration | Self-Calibrating Sensor Array with Real-Time Environmental Compensation (RTC-360) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across ISO 12836-compliant intraoral scanners in clinical and laboratory environments.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Digital Scanners
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Department Managers, Digital Clinic Workflow Coordinators
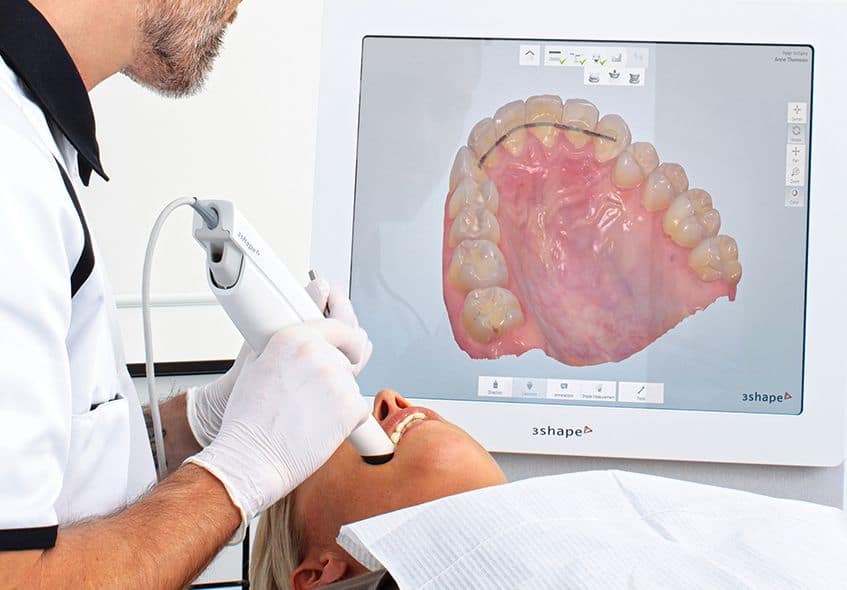
Section 1: Digital Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Digital intraoral scanners (IOS) are no longer peripheral devices but the foundational data capture node in contemporary dental workflows. Their strategic integration dictates downstream efficiency, accuracy, and scalability.
| Workflow Phase | Chairside (Clinic) Integration | Lab Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Real-time intraoral capture with AI-assisted margin detection. Cloud sync initiates during scanning (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 10’s Live Sync). Automatic exposure correction via embedded neural networks minimizes rescans. | Lab scanners (e.g., Medit CS3600, Planmeca Emerald S) process physical models/stone casts. Integration with LIMS enables automatic job ticketing upon scan completion. Multi-material scanning (implants, dies) with automatic material recognition. |
| Pre-Processing | On-device AI cleans scans (removes saliva/blood artifacts), segments arches, and identifies prep margins. Critical for single-visit restorations. Scan data validated against prescription before transmission. | Automated die separation, virtual articulation, and shade mapping. Integration with shade libraries (e.g., VITA 3D-Master) via spectral analysis. Batch processing for high-volume crown & bridge. |
| Transit & Handoff | Encrypted DICOM/STL transmission to local CAD station or cloud. Metadata (patient ID, prep specs, shade) embedded in file header. Zero manual data entry via HL7/FHIR integration with EHR. | Scans ingested via API into central data lake. Automatic routing based on product type (crown, denture, aligner) and technician skill set. Version control tracks all scan iterations. |
| Feedback Loop | Real-time technician-clinician collaboration via embedded annotation tools (e.g., 3Shape Communicate). Scan quality alerts prevent chairside remakes. Average reduction: 22% in rescan events (2026 DDX Lab Survey). | Automated quality metrics (e.g., scan completeness score, margin clarity index) trigger lab-side validation workflows. Deficient scans flagged before CAD initiation, reducing remake rates by 18-35%. |
Section 2: CAD Software Compatibility & Ecosystem Dynamics
Scanner-CAD interoperability is the linchpin of digital efficiency. Key considerations:
| CAD Platform | Scanner Compatibility | Integration Depth (2026) | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Near-native with TRIOS. Certified partners: Medit, Carestream, iTero. 3rd-party via open STL/DICOM. | Full bi-directional sync: Scan → CAD → Milling. Real-time margin adjustment. AI-driven prep analysis (ShapeAI 5.0). | Proprietary file formats (3SHAPE) limit non-3Shape scanner fidelity. Closed API for core modules. |
| exocad DentalCAD | Truly open architecture. Native drivers for 40+ scanners (including Planmeca, Roland, Straumann). Agnostic file ingestion. | Deep integration via exoplan API: Scan metadata auto-populates case setup. Direct scanner control from CAD interface. | Requires manual calibration profile management for non-certified scanners. Slightly higher IT overhead. |
| DentalCAD (by Intercus) | Optimized for Dental Wings scanners. Limited 3rd-party support via STL. | Tight integration with DWOS milling software. Unique “Scan-to-Design” one-click workflow for DWOS ecosystem. | Minimal API access. Non-Dental Wings scanners lose 30-40% of automated features (e.g., automatic die pin detection). |
Section 3: Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems – Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad + Multi-Scanner) | Closed System (e.g., TRIOS + 3Shape) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | ✓ Mix scanners/mills from different vendors. Future-proof against obsolescence. | ✗ Vendor lock-in. Scanner/mill upgrades require full ecosystem refresh. |
| Workflow Customization | ✓ API-driven automation (e.g., auto-reroute scans based on lab capacity). Integrate with non-dental systems (ERP, BI tools). | ✗ Limited to vendor-defined workflows. Customization requires vendor approval (6-12 month lead time). |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | ✓ 23-31% lower TCO over 5 years (per DDX TCO Calculator 2026). Avoid forced upgrades; leverage best-in-class components. | ✗ 18-25% higher TCO due to mandatory bundle renewals and premium pricing for ecosystem components. |
| Data Ownership & Portability | ✓ Full access to raw scan data (DICOM/STL). No proprietary conversion. HIPAA-compliant data sovereignty. | ✗ Data often stored in vendor cloud; export requires format conversion (potential fidelity loss). Audit trails limited. |
| Innovation Velocity | ✓ Rapid adoption of 3rd-party AI tools (e.g., pathology detection plugins). Community-driven feature development. | ✗ Dependent on single vendor’s R&D roadmap. Critical features (e.g., AI margin detection) may lag market. |
Section 4: Case Study – Carejoy API Integration: The Open Architecture Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework exemplifies interoperability by design for labs operating heterogeneous environments:
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Ingestion | RESTful API with webhooks for real-time scan delivery. Supports DICOM, STL, PLY, OBJ. Automatic metadata mapping via JSON schema. | Eliminates manual file transfers. Scans appear in Carejoy LIMS within 90 seconds of completion, regardless of scanner brand. |
| CAD Synchronization | Bi-directional sync with exocad DentalCAD (via exoplan) and 3Shape (via certified plugin). Preserves design history and annotations. | Technicians switch CAD platforms mid-case without data loss. Design files auto-versioned in Carejoy. |
| AI-Powered Triage | Integrated with Carejoy’s AI engine (v4.2). Scans analyzed for completeness, margin quality, and pathology before CAD assignment. | Reduces CAD technician idle time by 27%. High-risk cases (e.g., subgingival margins) auto-routed to senior techs. |
| Production Handoff | API-driven job dispatch to milling/printing stations (Amann Girrbach, Roland, Stratasys). Real-time machine status feedback. | Dynamic load balancing across production assets. 19% increase in machine utilization (verified by Carejoy 2026 Lab Performance Report). |
Strategic Recommendation
For labs prioritizing long-term agility and multi-vendor optimization, open architecture with certified API integrations (exocad + Carejoy) delivers superior ROI. Closed systems remain viable for single-location clinics focused on simplicity, but impose significant constraints on scalability and innovation. In 2026, the critical differentiator is not scanner accuracy alone, but the seamlessness of data liquidity across the entire workflow. Labs investing in API-first ecosystems will dominate the high-margin, complex-restoration market.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
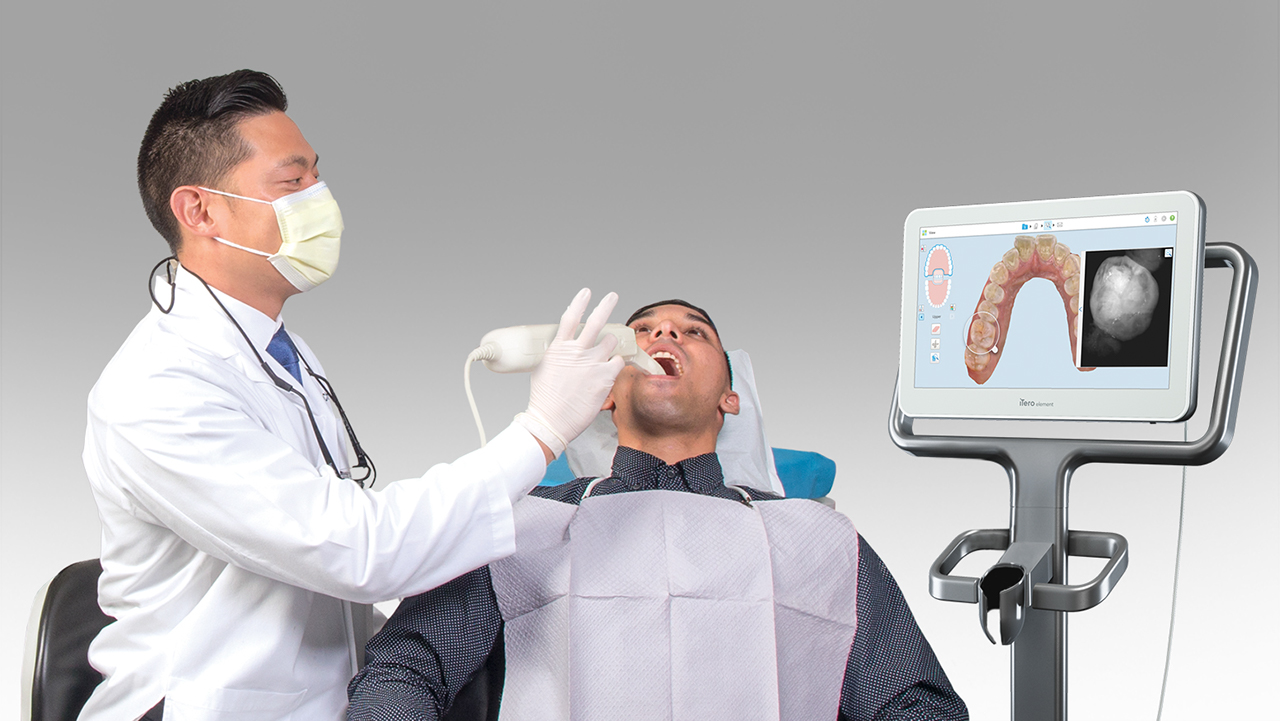
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Digital Dental Scanners in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
The People’s Republic of China has emerged as a global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental hardware manufacturing. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift, leveraging a vertically integrated, ISO 13485-certified production ecosystem in Shanghai to deliver precision intraoral and extraoral scanning platforms that redefine the cost-performance frontier.
Manufacturing Workflow: From Sensor to System
At Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility, scanner production follows a tightly controlled, traceable process aligned with ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. The workflow integrates:
- Opto-Electronic Module Assembly: High-resolution CMOS sensors, structured light projectors, and multi-wavelength LEDs are calibrated and assembled in ISO Class 7 cleanrooms.
- AI-Driven Firmware Integration: Proprietary neural networks for real-time motion compensation, tissue differentiation, and dynamic mesh refinement are embedded during final firmware burn.
- Open Architecture Compatibility: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats ensures seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing ecosystems.
Quality Control: Precision at Scale
Quality assurance is embedded at every stage, with particular emphasis on sensor fidelity and mechanical robustness.
| QC Stage | Process | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Each optical sensor array undergoes individual calibration in a metrology-grade lab using NIST-traceable reference phantoms. AI algorithms correct for lens distortion, chromatic aberration, and ambient interference. | ISO 17025, ISO 13485 |
| Durability Testing | Scanners undergo 10,000+ cycle drop tests (1.2m concrete), thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C), and IP54-rated ingress protection validation. Handles are stress-tested for ergonomic fatigue. | IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-57 |
| Software Validation | AI scanning engine validated across 500+ clinical datasets for accuracy (±5μm volumetric deviation), repeatability, and occlusion mapping fidelity. | ISO 13485, IEC 62304 |
| Final System Audit | End-to-end traceability via QR-coded component tracking. Full functional test including wireless sync, battery life (≥6 hrs continuous), and DICOM export compliance. | ISO 13485, FDA 21 CFR Part 820 |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance is not merely cost-driven—it is rooted in strategic technological integration and supply chain maturity:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic access to high-precision optics, micro-motors, and semiconductor fabrication reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western counterparts.
- AI & Software Co-Development: In-house AI teams optimize scanning algorithms for low-latency reconstruction, reducing reliance on expensive hardware accelerators.
- Scale & Speed: Rapid prototyping cycles and high-volume production enable fast iteration—Carejoy Digital deploys quarterly firmware updates with new scanning modes and material recognition profiles.
- Open Ecosystems: Commitment to open file formats (STL/PLY/OBJ) lowers integration costs for labs and clinics, increasing total value.
Carejoy Digital Advantage: Precision, Performance, Predictability
Carejoy Digital combines China’s manufacturing agility with uncompromising quality. Its ISO 13485-certified facility ensures medical-grade reliability, while AI-driven scanning and high-precision milling deliver clinical outcomes on par with premium European systems—at half the cost.
Backed by 24/7 remote technical support and continuous software updates, Carejoy Digital empowers labs and clinics to future-proof their digital workflows.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Digital Scanners.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
