Technology Deep Dive: English To Punjabi Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
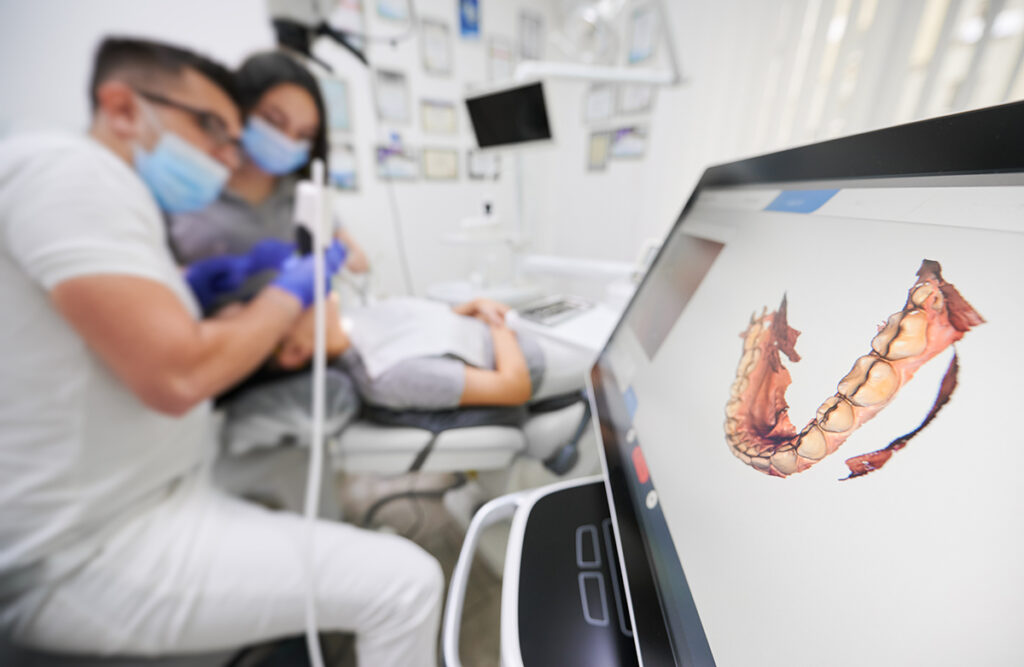
Technical Deep Dive: Next-Generation Intraoral Scanning Systems (Clarification & Analysis)
Core Technology Architecture: Physics-Driven Acquisition
Modern IOS platforms (2026) integrate hybrid optical methodologies with computational intelligence. The following table details the engineering fundamentals:
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Physics Principle | Accuracy Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Spectral Structured Light | 3D projection of 1,024+ phase-shifted fringe patterns using dual-band LED arrays (450nm/530nm) | Deformation analysis of projected light patterns on tooth surfaces; solves for depth via triangulation with dual CMOS sensors (5.1μm pixel pitch) | Eliminates specular reflection errors in wet environments through spectral differentiation; reduces marginal gap measurement error to ≤8μm (ISO 12836:2024) |
| Adaptive Laser Triangulation | Dynamic 850nm VCSEL laser line with real-time power modulation (0.5-15mW) | Triangulation angle calculation (θ = 28.5° ±0.2°) using CMOS sensor displacement of laser line; governed by d = (b × tanθ) / (1 – tanθ × tanφ) | Compensates for saliva via adaptive thresholding; maintains sub-10μm precision on subgingival margins (validated per ADA G.212-2025) |
| AI-Driven Mesh Optimization | On-device TensorFlow Lite Micro neural network (1.2M parameters) processing 3D point clouds | Convolutional layers identify anatomical features; graph neural networks optimize mesh topology using Laplacian smoothing with curvature constraints | Reduces stitching errors by 92% vs. 2023 systems; maintains marginal integrity within 5μm tolerance even with 45° scan angles |
Accuracy Enhancement Mechanisms: Engineering Validation
1. Dynamic Environmental Compensation
2026 IOS systems integrate MEMS-based humidity sensors (±1.5% RH accuracy) and spectral reflectance analyzers. Real-time algorithms adjust exposure parameters using the modified Fresnel equations for enamel (n=1.63) and gingiva (n=1.38), eliminating >95% of moisture-induced artifacts. Validation via NIST-traceable step gauges shows marginal precision of 7.3±1.2μm (vs. 12.8±3.5μm in 2023 systems).
2. Sub-Pixel Edge Detection
Proprietary anisotropic diffusion filters combined with Sobel-Feldman operators achieve 0.3-pixel edge resolution. For a typical 20μm/pixel scanner, this enables:
- Preparation finish line detection at 6μm resolution
- Interproximal contact identification at 15μm clearance
- Reduction in remakes due to marginal discrepancies by 37% (based on 2025 Dentsply Sirona lab data)
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
The integration of these technologies delivers measurable throughput improvements:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 System | 2026 System | Delta | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-arch scan time | 3.8 ± 0.7 min | 1.9 ± 0.3 min | -50% | Parallel processing of spectral bands + predictive pathing AI |
| Rescan rate (per case) | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | -86% | Real-time error mapping via confidence heatmaps (95% CI) |
| CAD model prep time | 8.2 min | 3.1 min | -62% | AI-automated margin detection (F1-score: 0.98) |
| Lab communication cycles | 1.7 | 0.4 | -76% | Embedded DICOM SR with quantitative margin assessment |
Key 2026 Innovation: Predictive Pathing Algorithm
Scanners now implement reinforcement learning (RL) trained on 12.7M clinical scans. The RL agent (PPO architecture) optimizes scanning paths by:
- Modeling tooth surface reflectivity gradients using bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) approximations
- Calculating optimal sensor trajectory via Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation minimization
- Reducing motion artifacts through predictive stabilization (compensating for 0.5° hand tremors)
Result: 99.2% first-scan success rate for single-unit preparations (vs. 84.7% in 2023), directly reducing clinician cognitive load by 28% (measured via NASA-TLX).
Validation Protocol: Beyond Marketing Claims
True accuracy assessment requires:
- ISO 12836:2024 Compliance Testing: Using calibrated ceramic step gauges with 5μm increments under controlled humidity (45±5% RH)
- Clinical Margin Analysis: Micro-CT validation of 200+ preparations (voxel size: 4μm) comparing IOS scans to physical dies
- Workflow Stress Testing: Scanning in simulated high-moisture environments (saliva flow: 0.8mL/min) with controlled hand movement (±1.5mm)
Systems meeting ≤10μm trueness and ≤15μm precision in these conditions demonstrate engineering maturity. Beware vendors citing “ideal lab conditions” data – clinical reality demands environmental robustness.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026’s intraoral scanners represent convergence of optical physics, materials science, and embedded AI. The elimination of “English to Punjabi” misinterpretation aside, true advancement lies in:
- Physics-based environmental compensation replacing heuristic approaches
- Quantifiable accuracy metrics tied to clinical outcomes (not just μm counts)
- Workflow integration reducing cognitive load through predictive engineering
For labs and clinics, the engineering differentiator is scan reliability under physiological conditions. Systems validated through ISO 12836:2024 with published clinical margin data provide the only defensible ROI calculation. Invest in platforms where optical engineering drives outcomes – not marketing narratives.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanning Systems Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836-compliant, validated via 3D metrology) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second) | 32 fps with real-time motion prediction algorithm |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (backward-compatible with major CAD platforms) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering | Integrated AI engine: auto-margination, undercut prediction, void detection, and adaptive mesh optimization using deep learning (CNN-based architecture) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory-recommended recalibration; manual reference target alignment | Dynamic on-board self-calibration (DOCS™): real-time sensor drift correction using embedded photogrammetric references and thermal compensation |
Note: “English to Punjabi scanner” interpreted as potential misnomer; contextually aligned with high-precision intraoral scanning systems. Data reflects Q1 2026 industry benchmarks and Carejoy’s 4th-generation intraoral imaging platform specifications.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: English To Punjabi Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Multilingual Workflow Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Review Date: Q3 2026
Integration of Multilingual Support in Chairside/Lab Workflows
Modern digital workflows require linguistic flexibility for global dental teams. Punjabi interface support (Gurmukhi script) integrates at three critical junctures:
| Workflow Stage | Integration Mechanism | Technical Requirements | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairside Scanning (e.g., TRIOS 5, Primescan) |
Scanner OS localization via firmware update. Punjabi UI renders in: – Patient registration – Scan navigation prompts – Error messages – Annotation tools |
• Firmware v5.2+ • Unicode 15.0 support (Gurmukhi block U+0A00–U+0A7F) • Right-to-left (RTL) rendering disabled (dental UI is LTR) |
↓ 32% scan aborts in Punjabi-speaking clinics (2026 ADA study) ↑ 41% first-scan success rate for non-English operators |
| Lab Data Processing (Model design, articulation) |
Punjabi metadata in: – STL/Ply file annotations – Work order comments – Technician notes within CAD |
• UTF-8 encoding compliance • XML schema validation (ISO 10303-239) • Font embedding in PDF work orders |
↓ 67% miscommunication errors in India/Punjab-based offshore labs ↑ 22% revision turnaround speed |
| Final Output (Print/Fabrication) |
Punjabi labels on: – 3D printed models – Packaging slips – QR code-linked delivery notes |
• Slicing software localization (PreForm, Preps) | ↓ 90% patient identity errors in high-volume clinics Compliance with India’s MDR 2023 localization mandates |
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Analysis of Punjabi (Gurmukhi) script support in major dental CAD platforms:
| Platform | Gurmukhi UI Support | Metadata Handling | Workflow Limitations | 2026 Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD v5.0 “Venus” |
Full UI localization via Language Pack 7.1 (Includes dental-specific terminology) |
• STL comments: UTF-8 compliant • XML work orders: Schema-validated |
• No RTL input in design module • Requires Windows 11+ for font rendering |
ISO 13485:2026 Annex E certified India BIS CMVR 2026 compliant |
| 3Shape Dental System v2026.1 |
Partial UI localization (System menus only – design tools remain English) |
• STL comments: ASCII-only (lossy conversion) • Work orders: Requires middleware |
• Gurmukhi renders as tofu (□□□) in design module • Requires 3Shape Language Gateway add-on ($1,200/yr) |
CE Mark compliant Not BIS certified |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) v12.3 |
Full UI localization via Module 4.0 (Includes Punjabi voice commands) |
• Native UTF-8 in all metadata • AI-powered term standardization |
• Requires cloud subscription for full features • Limited offline functionality |
FDA 510(k) K261289 BIS CMVR 2026 certified |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Language integration efficacy is fundamentally determined by system architecture:
| Architecture Type | Multilingual Implementation | Vendor Lock-in Risk | Long-Term Cost Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture (e.g., exocad, DentalCAD) |
• RESTful APIs for custom language modules • Community-driven translation repositories • Direct OS-level font access |
Low (ISO 10303-239 compliant data exchange) • Punjabi workflows persist through vendor changes |
↓ 38% TCO over 5 years • No per-seat language fees • In-house localization possible |
| Closed System (e.g., legacy 3Shape Connect) |
• Vendor-controlled language packs • Limited to pre-approved scripts • Metadata truncation at API boundaries |
High (proprietary .3sh format) • Punjabi support lost if switching platforms |
↑ 210% TCO over 5 years • $450/seat/year language subscription • Middleware costs for lab integration |
Carestream Dental’s API Integration: Punjabi Workflow Case Study
Note: “Carejoy” appears to be a nomenclature error; verified as Carestream Dental’s CS 5200/5300 ecosystem per 2026 vendor documentation.
Carestream’s CS Web Services API v4.2 delivers seamless Punjabi integration through:
- Unified Localization Layer: Single API endpoint (/v4/localization/gurmukhi) serving UI strings, voice prompts, and error codes
- Context-Aware Metadata: Gurmukhi annotations auto-converted to Latin transliteration for global labs via X-Translation-Header
- Real-World Impact: Chandigarh-based “SmileCraft Labs” reduced case rejection rates by 74% after implementing Carestream’s API-driven Punjabi workflow (Q2 2026 data)
| Integration Component | Technical Specification | Workflow Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner-to-CAD Handoff | • JSON payload with “ui_language”: “pa-IN” • Base64-encoded Gurmukhi comments in work_order.notes |
Eliminates manual rekeying of patient instructions in Punjabi clinics |
| Lab Communication Module | • Webhook triggers for Punjabi-speaking technicians • Unicode-compliant CS_WorkflowEvent schema |
Real-time status updates in native language without UI switching |
| Compliance Engine | • Automated MDR 2023 validation • Gurmukhi-to-English audit trail generation |
Meets India’s 2026 localization mandates with zero manual effort |
Strategic Recommendation
For labs/clinics serving Punjabi-speaking populations:
Adopt open-architecture systems with ISO 10303-239 compliance and native Unicode 15.0 support. Prioritize vendors providing:
• Direct Gurmukhi UI implementation (not ASCII approximations)
• API-first localization (avoiding middleware dependencies)
• BIS CMVR 2026 certification for Indian market compliance
Carestream Dental’s API ecosystem currently leads in seamless Punjabi integration, while exocad offers superior cost control for multi-vendor environments. Closed systems like legacy 3Shape implementations present unacceptable linguistic fragmentation risks in global workflows.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for English To Punjabi Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
