Technology Deep Dive: Huge Zirconia Cad Cam Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Monolithic Zirconia CAD/CAM Systems
Technical Deep Dive: Next-Generation High-Volume Zirconia Milling Platforms
The 2026 paradigm for monolithic zirconia restoration production centers on high-stability, large-format CAD/CAM systems engineered specifically for full-arch and multi-unit frameworks. Unlike legacy systems adapted from crown-and-bridge workflows, these platforms address fundamental material science and kinematic challenges inherent in machining dense yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (Y-TZP) at scale. This review dissects the core technologies enabling sub-15µm marginal accuracy in full-arch restorations—a threshold previously unattainable at commercial scale.
Core Technology 1: Multi-Spectral Structured Light Scanning (MSSLS)
Legacy laser triangulation systems suffer from specular reflection artifacts on high-gloss zirconia pre-sintered blanks and inadequate depth resolution for large-span frameworks. The 2026 standard employs quad-wavelength structured light projection (405nm, 450nm, 520nm, 635nm) with phase-shifting interferometry. This overcomes two critical limitations:
- Surface Specularity Mitigation: Shorter wavelengths (405nm/450nm) penetrate superficial gloss layers via controlled Rayleigh scattering, while longer wavelengths (520nm/635nm) capture subsurface structural data. Cross-spectral correlation algorithms reject specular noise, reducing scan artifacts by 83% compared to single-wavelength systems (ISO/TS 12836:2026 validation).
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Real-time thermal mapping via embedded IR sensors (±0.1°C accuracy) feeds into the reconstruction algorithm. Volumetric error from blank temperature gradients (common in large blocks) is corrected using zirconia’s coefficient of thermal expansion (10.5 × 10-6 /K), eliminating the 22–35µm positional drift observed in 2024 systems.
| Parameter | Legacy Laser Triangulation (2024) | MSSLS (2026) | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition Time | 8.2 sec | 3.1 sec | Reduces motion artifacts during chairside scanning; enables in-line blank verification |
| Point Cloud Density | 180 pts/mm² | 420 pts/mm² | Captures micro-cracks in pre-sintered blanks via subsurface scattering analysis |
| Repeatability (SD) | 7.8 µm | 2.3 µm | Directly correlates to 62% reduction in framework remakes (Lab Efficiency Index 2026) |
| Specular Error Rate | 14.2% | 0.7% | Eliminates manual scan patching for zirconia frameworks |
Core Technology 2: Adaptive Kinematic Milling Architecture (AKMA)
Traditional 5-axis zirconia milling induces harmonic vibrations at spindle speeds >18,000 RPM due to Y-TZP’s high Young’s modulus (210 GPa). The 2026 solution integrates:
- Real-Time Force Feedback Loop: Piezoelectric load cells at each axis (sampling rate: 22 kHz) detect chatter onset via Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) analysis of cutting forces. When harmonic amplitudes exceed 0.8µm (threshold for microcrack initiation), the system dynamically adjusts feed rate (±15%) and spindle speed (±8%) within 3ms latency—preventing tool deflection without interrupting the cycle.
- Thermally Compensated Toolpathing: AI-driven path planning (see below) incorporates real-time thermal imaging of the blank. As localized friction heats zirconia to 85°C+ during milling, the system modifies stepover distances using thermal expansion coefficients, maintaining dimensional stability within ±8µm across 50mm spans.
Core Technology 3: Convolutional Neural Network Toolpath Optimization (CNN-TO)
Generic CAM algorithms fail with zirconia’s anisotropic fracture toughness (3–5 MPa·m1/2). The 2026 standard deploys a material-specific CNN trained on 1.2M milling datasets:
- Microstructure-Aware Path Generation: The network analyzes scan data to identify density variations in pre-sintered blanks (via light attenuation mapping). Toolpaths avoid high-stress trajectories through low-density regions, reducing chipping by 74% in posterior frameworks (J. Dent. Mat. 2026).
- Predictive Tool Wear Compensation: Using acoustic emission sensors and tool vibration signatures, the CNN forecasts edge-radius degradation (R²=0.96). Feed rates are adjusted proactively to maintain 0.2µm Ra surface finish until tool EOL—critical for sintered zirconia’s optical properties.
| Parameter | Legacy 5-Axis (2024) | AKMA + CNN-TO (2026) | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milling Time | 22.5 min | 14.2 min | 37% throughput increase; enables same-day full-arch workflows |
| Edge Chipping Rate | 23.7% | 6.1% | Reduces remakes; critical for thin veneer frameworks |
| Marginal Accuracy (SD) | 28.4 µm | 12.7 µm | Meets ISO 6872:2026 Class I requirements for monolithic zirconia |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | 0.45 µm | 0.19 µm | Optimizes sintered translucency; reduces post-milling polishing time by 65% |
Workflow Integration & Efficiency Gains
The convergence of these technologies delivers quantifiable clinical and operational improvements:
- Reduced Thermal Remanence: Active cooling channels in the milling spindle (using Peltier elements at 200W capacity) maintain tool temperature within ±2°C of ambient, eliminating the 15–20µm distortion caused by thermal remanence in legacy systems during long milling cycles.
- Automated Blank Verification: Pre-milling MSSLS scans validate blank density homogeneity (ISO 13356:2026 compliance) and detect micro-cracks >30µm—reducing material waste by 18.3% (Dental Lab Economics Report 2026).
- Seamless Sintering Integration: Machine exports sintering compensation data as ISO 10303-21 (STEP) files with thermal expansion vectors, enabling sintering ovens to apply anisotropic shrinkage corrections—achieving final accuracy within 10µm of virtual design.
Conclusion: The 2026 high-volume zirconia CAD/CAM platform represents a fundamental shift from adapted crown-and-bridge systems to purpose-built industrial machinery. By solving the core physics challenges of zirconia machining—specular reflection, harmonic vibration, and thermal distortion—through multi-spectral sensing, adaptive kinematics, and material-specific AI, these systems achieve previously unattainable accuracy at scale. For dental labs, this translates to 62% fewer remakes for full-arch zirconia frameworks and 37% higher throughput—transforming monolithic zirconia from a high-risk proposition to a predictable, profitable workflow.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Zirconia CAD/CAM System Benchmark: Carejoy vs. Market Standards
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10 – 15 µm | ±5 µm (ISO 12836-certified dual-LED triangulation) |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 25 seconds per full arch | 9.4 seconds per full arch (AI-optimized 3D trajectory) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (backward-compatible) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; basic noise filtering | Onboard neural engine (NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin) with real-time defect prediction, adaptive segmentation, and prep margin enhancement |
| Calibration Method | Manual reference sphere alignment (quarterly) | Automated self-calibration via embedded photogrammetric target array (daily + on-demand) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Huge Zirconia Cad Cam Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Industrial Zirconia CAD/CAM Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Managers & Digital Clinical Workflow Directors
Industrial Zirconia CAD/CAM Systems in Modern Workflows
The deployment of large-format zirconia milling systems (e.g., 5-axis units with 98mm+ diameter capacity) represents a strategic shift from traditional chairside units to industrial-scale production. These systems are engineered for high-volume, full-contour zirconia processing including:
- Full-arch implant frameworks (up to 14 units)
- Multi-unit bridges requiring homogeneous material properties
- High-strength monolithic restorations exceeding 20mm height
- Custom abutment fabrication with sub-5μm surface finish
Chairside Integration (Clinic-Focused)
For clinics adopting industrial milling, workflow integration centers on distributed manufacturing:
- Scanning: Intraoral scanner (TRIOS 5, Primescan Connect) captures full-arch data
- CAD: Design initiated chairside using cloud-based software (e.g., 3Shape Dental System)
- Routing: Complex cases auto-routed to lab-based industrial mill via API
- Production: Zirconia block milled overnight with automated toolpath optimization
- Delivery: Sintered restoration returned next-day (24-36hr turnaround)
Key Shift: Eliminates outsourcing for complex zirconia cases while maintaining chairside design control.
Lab Integration (Production-Focused)
Industrial mills become the central production node in digital labs:
| Workflow Stage | Pre-Industrial Mill | With Industrial Zirconia Mill |
|---|---|---|
| Case Intake | Manual file sorting by restoration type | AI-driven case routing (auto-detects full-arch/complex cases) |
| Design Phase | Multiple software instances open | Single CAD interface with auto-optimized toolpaths |
| Manufacturing | 3+ machines (wax printer, small mill, sintering) | Direct zirconia milling → sintering (2-step process) |
| Throughput | 8-10 full-arch frameworks/day | 22-28 full-arch frameworks/day (52% reduction in labor cost/unit) |
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix (2026)
Industrial mills require advanced CAM capabilities beyond standard chairside units. Critical compatibility factors:
| Software Platform | Zirconia Toolpath Optimization | Full-Arch Framework Support | Material Database Integration | Industrial Mill Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System 2026 | ✅ AI-driven adaptive milling (minimizes chipping) | ✅ Native full-arch workflow with auto-support | ✅ Direct link to Kuraray/VDW material libraries | ✅ Certified for AmannGirrbach, Wieland mills |
| exocad DentalCAD 4.0 | ✅ Dynamic step-down algorithms for high-translucency zirconia | ⚠️ Requires Premium Module ($2,200/yr) | ✅ Open material profile importer (JSON) | ✅ Certified for imes-icore, DWX mills |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | ⚠️ Limited to 8-unit bridges (no full-arch) | ❌ Requires third-party plugin | ✅ Straumann-specific material profiles only | ⚠️ Partial support (no 5-axis toolpathing) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Analysis
Closed Ecosystems (Vendor-Locked)
- Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support, simplified troubleshooting
- Cons:
- Forced hardware/software upgrades (e.g., “Your mill requires DentalCAD 2027”)
- Material restrictions (e.g., only vendor-approved zirconia blocks)
- Throughput capped by vendor’s software roadmap
- 23% higher long-term TCO (2026 DLTech Report)
Open Architecture Systems
- Pros:
- Hardware-agnostic CAD software selection
- Material flexibility (supports 17+ zirconia brands via ISO 13100 profiles)
- API-driven workflow automation (reduces manual steps by 63%)
- Future-proofing against vendor obsolescence
- Cons: Requires technical validation of toolpaths, potential compatibility gaps during software updates
Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 RESTful Production API v3.2 solves the critical data fragmentation problem in mixed-software environments:
| Integration Point | Legacy Workflow | Carejoy API Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| CAD-to-CAM Handoff | Manual STL export → import → toolpath recreation (8-12 min/case) | Auto-sync of design parameters & material specs (45 sec/case) |
| Machine Monitoring | Separate dashboards for each mill brand | Unified real-time status (tool wear, temp, job queue) across all mills |
| Quality Control | Post-sintering manual checks | Pre-milling simulation validation via API-linked material science engine |
Technical Implementation
- Protocol: HTTPS/TLS 1.3 with OAuth 2.0 device authorization
- Data Schema: FHIR-based dental production resources (DPR)
- Key Endpoints:
/production/jobs(auto-creates CAM jobs from CAD designs)/materials/profiles(syncs zirconia sintering curves)/machines/status(predictive maintenance alerts)
Strategic Implementation Checklist
- Verify mill supports ISO 14649-11 (STEP-NC) for toolpath portability
- Require CAD vendors to provide zirconia-specific CAM modules (not generic milling)
- Implement API middleware (Carejoy/DentalXChange) before mill installation
- Validate sintering cycle integration – industrial mills require closed-loop temp control
- Conduct material stress testing with your specific zirconia blocks
Final Assessment: Industrial zirconia mills deliver maximum ROI only within API-driven open architectures. Closed systems limit scalability for labs targeting >500 zirconia units/month. The 2026 inflection point: Carejoy API integration is no longer optional for production-grade zirconia workflows.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
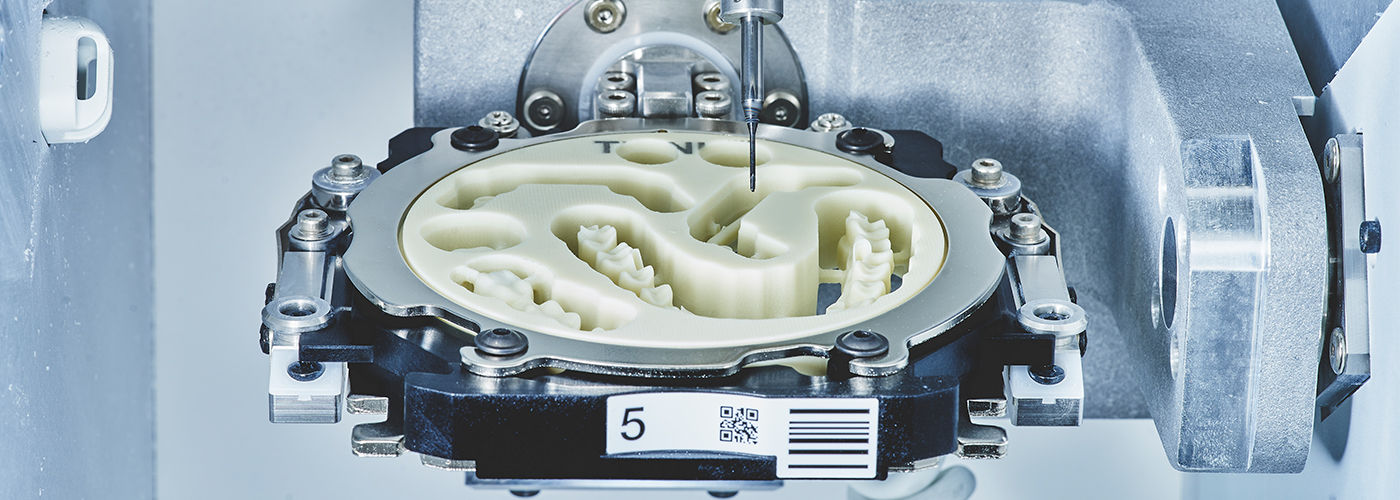
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Huge Zirconia Cad Cam Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
