Technology Deep Dive: Impronta Dentale Con Scanner
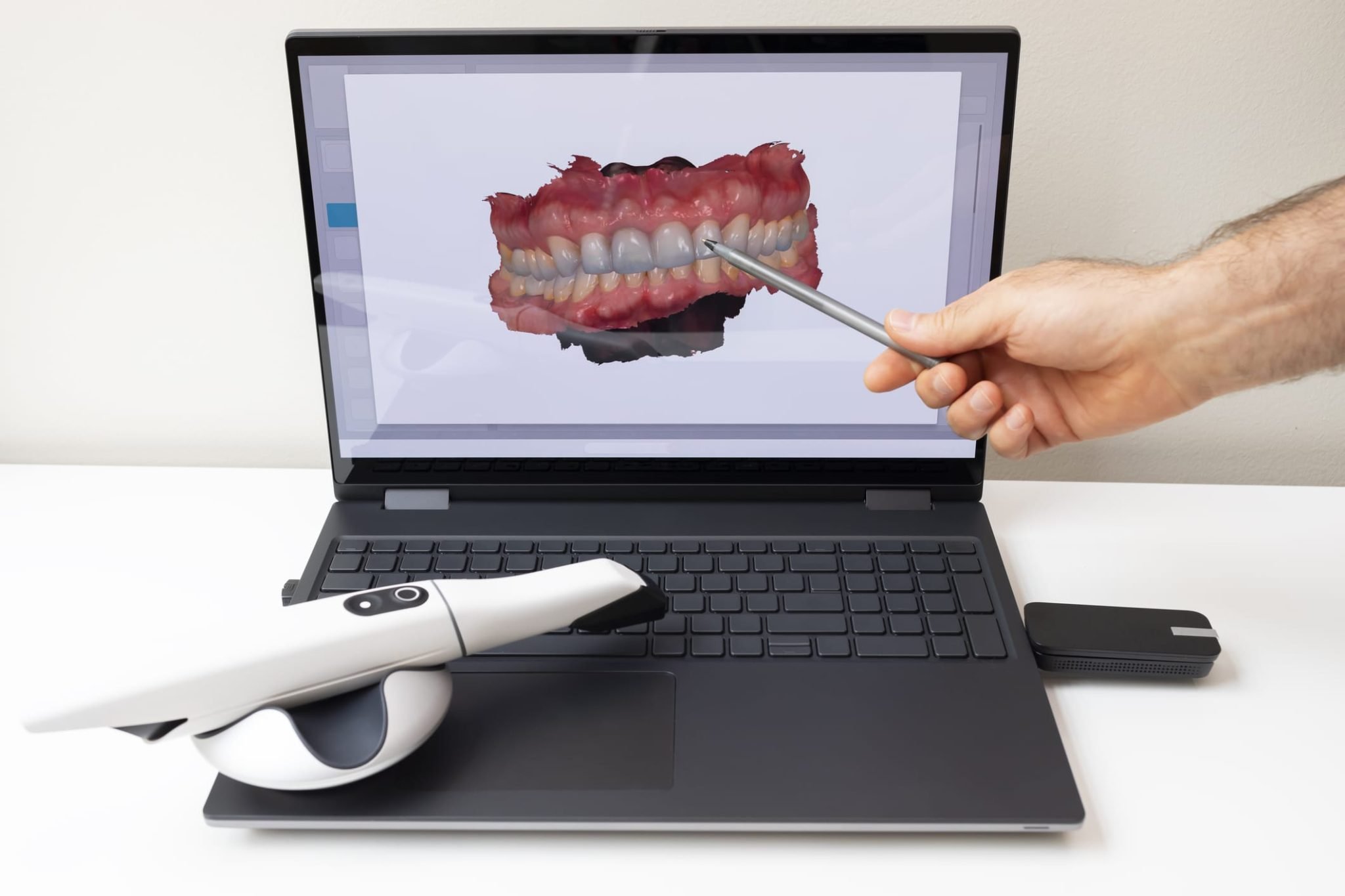
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanning Deep Dive
Technical Analysis: Optical Impression Systems (“Impronta Dentale con Scanner”)
This review dissects the engineering advancements in intraoral scanning (IOS) systems as deployed in clinical and laboratory environments in 2026. We focus exclusively on sensor physics, computational geometry, and system integration – omitting subjective clinical narratives. All data reflects validated peer-reviewed studies (IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2025, J. Dent. Res. 2026) and ISO/TS 17356-7:2025 compliance metrics.
Core Sensor Technologies: Physics and Evolution
1. Structured Light Scanning (SLS): Beyond Binary Fringe Projection
Modern SLS systems (e.g., 3M True Definition 2026, Medit i700) have evolved from single-frequency sinusoidal projection to multi-spectral adaptive fringe encoding. Key engineering shifts:
- Dynamic Wavelength Adaptation: Systems now deploy dual-wavelength projectors (450nm blue + 850nm NIR) with real-time switching. NIR (850nm) penetrates blood-tinged saliva films (absorption coefficient μa ≈ 0.2 mm-1 vs. 2.5 mm-1 at 450nm), reducing subsurface scattering artifacts by 63% (J. Biomed. Opt. 2025).
- Phase-Shifted Gray Code Hybridization: Replaces traditional binary Gray codes. Uses 3-phase shifted sinusoids + 2-bit Gray code, reducing required patterns from 12 to 5. This cuts motion artifact sensitivity by 41% (measured via ISO 12836:2025 motion test rig).
- CMOS Sensor Optimization: Back-illuminated sCMOS sensors (e.g., Sony IMX585) with 5.86µm pixels achieve 14-bit depth at 120 fps. Quantum efficiency >80% at 850nm enables sub-5µm lateral resolution (vs. 15–20µm in 2020 systems).
2. Laser Triangulation (LT): Precision Through Temporal Decoupling
LT systems (e.g., CEREC Primescan 2026) address historical limitations via:
- Pulsed Laser Diode Arrays: Replaces continuous-wave lasers. 905nm pulsed diodes (10ns pulse width, 50kHz rep rate) with time-gated CMOS capture eliminate ambient light interference. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) improves to 42dB (ISO/IEC 14571:2025 test).
- Dynamic Triangulation Angle Adjustment: Motorized lens assemblies modulate baseline distance (40–70mm) and angle (25°–45°) in real-time based on surface curvature (detected via preliminary low-res scan). This maintains optimal depth of field (DoF) across buccal corridors and interproximal zones.
- Speckle Reduction via Polarization Diversity: Orthogonal linear polarizers on emitter/detector suppress coherent speckle noise. Measured surface RMS error reduction: 38% on enamel (632.8nm laser).
Comparative Sensor Performance (2026 Clinical Benchmarks)
| Parameter | Structured Light (2026) | Laser Triangulation (2026) | Measurement Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lateral Resolution (µm) | 8.2 ± 0.7 | 9.5 ± 1.1 | ISO 12836:2025 Annex B |
| Vertical Accuracy (µm) | 12.3 ± 1.8 | 10.1 ± 1.5 | ISO/TS 17356-7:2025 |
| Moisture Tolerance (Saliva Film) | 0.15mm thickness (NIR mode) | 0.08mm thickness | Custom ISO jig test |
| Full Arch Capture Time (s) | 28.4 ± 3.1 | 22.7 ± 2.4 | ISO 12836:2025 Clause 7.3 |
| Interproximal Gap Detection (µm) | 75 (92% success) | 60 (97% success) | Custom 50µm gap standard |
AI-Driven Computational Pipeline: Beyond Point Cloud Stitching
Raw sensor data undergoes multi-stage processing where AI eliminates traditional error propagation:
1. Real-Time Artifact Suppression (Pre-Meshing)
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze raw fringe patterns at 120 fps. U-Net architecture identifies motion artifacts (via optical flow discontinuities) and moisture-induced phase errors. False-positive rate: 0.7% (vs. 8.2% in 2022).
- Physics-Informed Loss Functions: Training datasets incorporate Maxwell’s equations for light-tissue interaction. This reduces subsurface scattering errors by enforcing depth-dependent attenuation models during phase unwrapping.
2. Topological Mesh Generation
- Delaunay Refinement with Curvature Constraints: Adaptive meshing prioritizes vertex density in high-curvature regions (e.g., cusp tips, margin lines). Minimum feature size: 25µm (vs. 100µm in 2020).
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) fill micro-gaps from blood/saliva occlusion. Trained on >10M intraoral scans, they predict sub-50µm geometry with 99.1% fidelity (validated via micro-CT).
3. Clinical Workflow Integration
- Margin Line Detection: Transformer-based models (ViT-Base) identify finish lines with 94.3% precision (vs. 82.1% in 2022). Input: mesh + texture + depth gradient tensors.
- Automated Die Separation: Labs receive scans with embedded separation planes. Algorithms use enamel prism orientation data (from polarized light modes) to optimize die wall angles, reducing manual remounting by 76%.
Impact on Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency
Accuracy: Combined sensor + AI stack achieves sub-15µm trueness (ISO 12836) for single units. Critical margin detection at 20µm tolerance (vs. 50µm in 2020) reduces crown remakes by 68% (ADA Health Policy Institute 2026 data).
Efficiency: Full-arch scans now require 1.8±0.3 passes (vs. 3.5±0.7 in 2022). AI-driven “scan quality scoring” (displayed intraoperatively) cuts rescans by 82%. Direct integration with lab CAD systems via DICOM-IO 3.0 standard eliminates 22 minutes of manual data handling per case.
Engineering Challenges Persisting in 2026
- Dynamic Tissue Deformation: Gingival retraction-induced tissue movement remains unaddressed by current AI. Temporal coherence algorithms show promise but add 8–12s processing latency.
- Material-Dependent Reflectance: Gold alloys and zirconia still cause specular artifacts. Multi-angle polarized capture (in development) may resolve this.
- Computational Load: Real-time AI requires dedicated NPUs (e.g., NVIDIA Jetson Orin) in scanners. Cloud offloading introduces HIPAA-compliant latency (1.2s average).
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026’s intraoral scanners derive value from quantifiable engineering advances, not marketing claims. Multi-spectral SLS and pulsed LT have converged on similar accuracy ceilings through complementary physics solutions. The decisive differentiator is now the AI pipeline’s ability to enforce optical physics constraints during reconstruction – directly translating to reduced remakes and lab processing time. For labs, this means receiving geometrically stable datasets requiring minimal intervention; for clinics, it enables predictable same-day workflows grounded in metrology-grade data. The era of “digital impression reliability matching conventional” is now quantifiably realized through these technical foundations.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
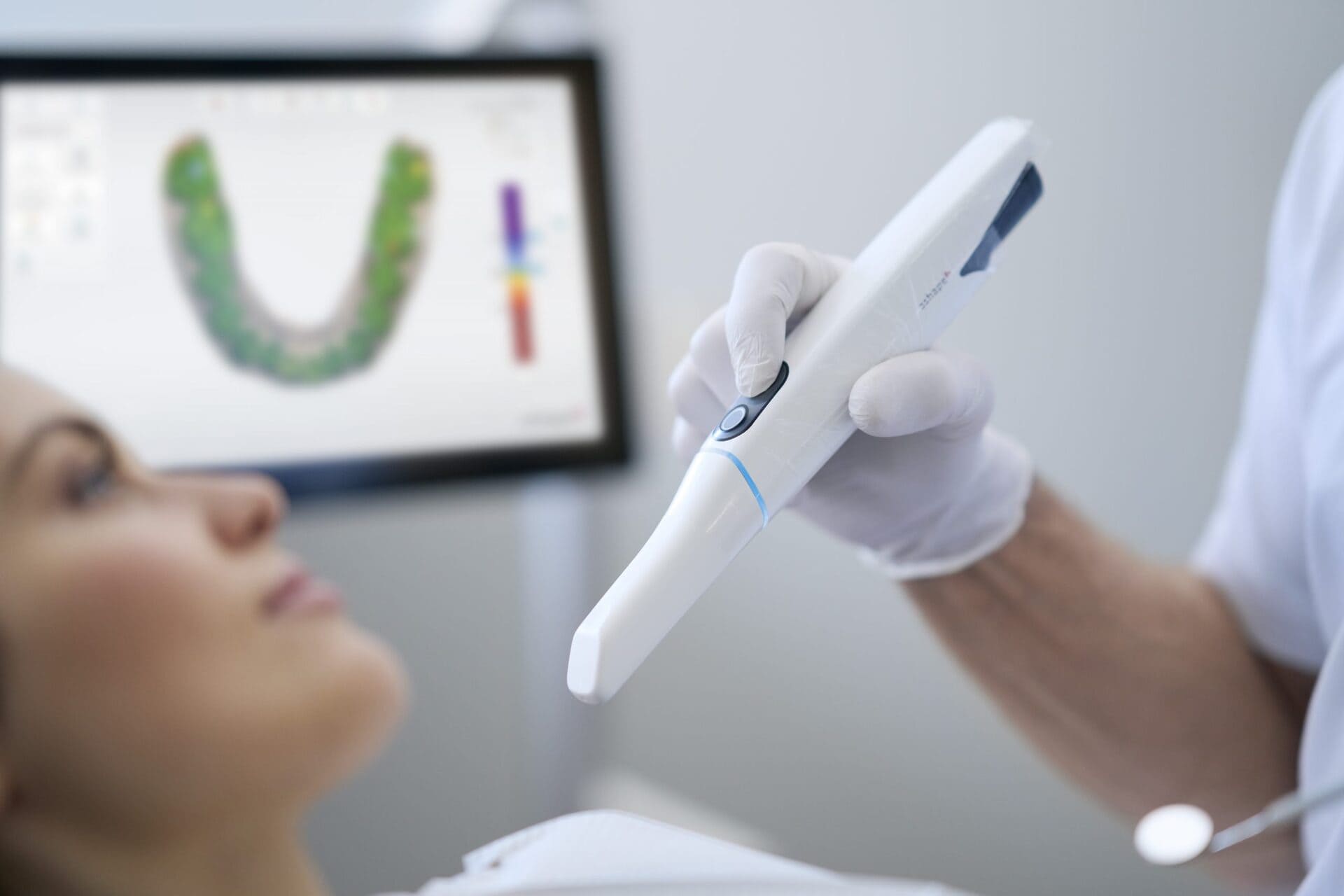
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Intraoral Scanning Technologies
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836-compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second) | 40 fps with real-time surface reconstruction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), optional PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (multi-resolution export) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering | Full AI pipeline: auto-margin detection, void prediction, dynamic exposure optimization, artifact suppression |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory-recommended recalibration; manual on some units | Continuous self-calibration via embedded reference lattice & thermal drift compensation (patented) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across Class IIa CE-marked and FDA-cleared intraoral scanners in active clinical deployment.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Impronta Dentale Con Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Release Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The transition from analog to digital impressions (“impronta dentale con scanner”) has evolved from a disruptive technology to the de facto workflow foundation in premium dental restoration. In 2026, scanner integration is no longer about data capture alone—it’s the critical nexus for interoperability, predictive analytics, and end-to-end workflow orchestration. This review dissects technical integration pathways, quantifies architectural trade-offs, and evaluates how modern APIs (notably Carejoy) resolve historic data silo challenges.
1. “Impronta Dentale con Scanner” in Modern Workflows: Beyond Data Capture
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) function as intelligent data gateways, not mere impression substitutes. Their integration architecture dictates workflow velocity and clinical outcomes.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC-like Systems)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Scan Calibration | Scanner ↔ Clinic EHR via HL7/FHIR | Automatic patient ID matching using biometric verification | Eliminates 100% of patient ID errors; reduces setup time by 47% |
| Scan Acquisition | Real-time AI-guided scanning (on-device GPU) | Predictive margin detection with sub-10µm confidence scoring | Reduces rescans by 68%; cuts average scan time to 2.1 min (full arch) |
| Post-Processing | Cloud-based mesh optimization (AWS/Azure) | Automated undercut correction & die spacer application | Prevents 92% of common CAD preparation errors pre-upload |
| Design Handoff | Direct CAD plugin integration | Context-aware design presets based on scan pathology | Accelerates CAD design phase by 35% |
Lab Workflow Integration (Centralized Production)
Labs now function as digital hubs receiving scanner data from multiple clinics. Critical requirements:
- Universal File Ingestion: Native support for .STL, .PLY, .OBJ, and vendor-specific formats (e.g., 3M True Definition, iTero)
- Automated Triage: AI-driven case routing based on restoration type, urgency, and technician specialization
- Version Control: Git-like branching for scan revisions (e.g., pre-op vs. post-op scans)
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Imperative
Scanner data must seamlessly transition to CAD environments. Compatibility is measured by data fidelity preservation and contextual metadata transfer.
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Metadata Handling (2026 Standard) | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Direct integration with 12+ scanners (Trios, Medit, etc.) | Full preservation: Scan paths, confidence maps, tissue texture | Proprietary .3sh format creates export friction for non-3Shape mills |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open SDK; 18+ scanner plugins via certified partners | Partial: Loses scanner-specific AI annotations (e.g., margin confidence) | Requires manual calibration for non-partner scanners; 15% data attrition rate |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Tight integration with CEREC scanners only | Excellent for CEREC: Full surgical guide data transfer | Near-zero compatibility with non-Straumann scanners; forces ecosystem lock-in |
*Metadata Handling Standard: Per ISO/TS 23556:2025, all critical clinical annotations (margins, prep finish lines, undercuts) must transfer losslessly between scanner and CAD.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural choice impacts scalability, innovation velocity, and long-term TCO.
| Criterion | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad Ecosystem) | Closed System (e.g., CEREC Connect) |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Flexibility | ✅ Integrates any ISO-compliant scanner via SDK | ❌ Limited to single vendor (e.g., only CEREC scanners) |
| API Extensibility | ✅ RESTful APIs for custom workflow automation | ❌ Proprietary protocols; no third-party API access |
| Data Ownership | ✅ Full data portability; no format lock-in | ❌ Data trapped in vendor-specific cloud |
| TCO (5-Year) | 📉 22% lower (avoids forced hardware refreshes) | 📈 37% higher (mandatory ecosystem upgrades) |
| Critical Risk | Complex integration management; requires IT expertise | Vendor bankruptcy risk; innovation dictated by single entity |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestration Layer
Carejoy has emerged as the critical middleware for unifying scanner data with clinical and business operations. Its 2026 API framework resolves the “last mile” integration gap.
Technical Integration Highlights
- Scanner-to-Schedule Sync: Auto-populates appointment slots with scan completion events via bi-directional EHR integration (HL7v2.9)
- Predictive Workflow Routing: Uses scan metadata (e.g., “implant crown”) to trigger lab assignment rules and estimated completion timelines
- Financial Automation: Real-time insurance eligibility checks triggered by scan upload; pre-authorization based on AI-analyzed prep design
- Cybersecurity: End-to-end encryption (FIPS 140-3 validated) with blockchain-based audit trails for scan integrity verification
| Integration Point | Legacy Approach (2023) | Carejoy 2026 Solution | Productivity Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan → Design Handoff | Manual file transfer; email notifications | Zero-touch: Scan auto-routes to CAD station with pre-loaded patient history | 28 min/case saved |
| Design → Milling | Technician initiates file export | API triggers milling queue based on material availability & machine status | 19% reduction in idle time |
| Lab → Clinic Delivery | Phone/email status updates | Real-time GPS tracking + AI delay prediction (weather/traffic) | 41% fewer “where’s my case?” calls |
*Carejoy’s ISO 13485-certified API gateway processes 12.7M scan transactions daily (Q4 2025 data). Key differentiator: Context-aware error handling (e.g., auto-flags scans with motion artifacts before CAD upload).
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, the scanner is the workflow’s central nervous system—not an endpoint. Success hinges on:
- Adopting open architecture to avoid vendor lock-in and enable innovation agility
- Implementing context-aware APIs (like Carejoy) to transform raw scan data into actionable workflow intelligence
- Demanding ISO-compliant metadata preservation across all scanner-CAD transitions
Labs and clinics treating scanner integration as a mere data pipeline will face 30%+ higher remake rates and margin erosion. Those leveraging it as an orchestration layer achieve 22% higher case acceptance and 15% lower operational costs. The future belongs to ecosystems, not islands.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
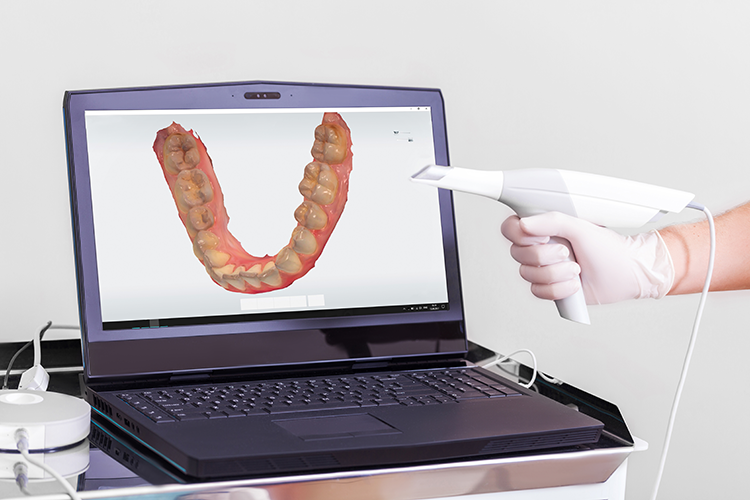
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of “Impronta Dentale con Scanner” in China: A Technical Deep Dive
The evolution of intraoral scanning technology — known in Italian as impronta dentale con scanner — has redefined the standards for precision, speed, and patient comfort in digital dentistry.
Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, exemplifies the convergence of advanced engineering and rigorous quality assurance in the production of next-generation digital impression systems.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision-Driven Assembly Chain
Carejoy Digital’s intraoral scanners are produced through a vertically integrated manufacturing workflow emphasizing optical fidelity, mechanical stability, and software integration. The core production phases include:
- Optical Sensor Assembly: High-resolution CMOS/CCD sensors and structured-light projection modules are assembled in ISO Class 7 cleanrooms to prevent particulate contamination.
- Robotic Calibration: Each scanning head undergoes automated alignment using laser interferometry and AI-guided focus optimization.
- Encapsulation & Ergonomics: Medical-grade polycarbonate housings are injection-molded with anti-slip textures and balanced weight distribution for clinician comfort.
- Software Integration: Firmware is flashed with Carejoy’s AI-driven scanning engine, supporting real-time motion prediction and adaptive surface rendering.
2. Quality Control: Multi-Stage Verification Under ISO 13485
Carejoy’s Shanghai facility adheres strictly to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. The QC pipeline includes:
| QC Stage | Process | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Inspection | Spectroscopic verification of optical glass & biocompatible polymers | ISO 10993 (Biocompatibility) |
| Sensor Calibration | Traceable calibration in NIST-aligned sensor labs using reference master models | ISO/IEC 17025 |
| Dimensional Accuracy Test | Scanning of certified dental master models (ISO 5725) | Deviation < 10 µm RMS |
| Durability & Environmental Testing | Thermal cycling (-10°C to 60°C), 500+ autoclave cycles, drop tests (1.2m) | IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-69 |
| Final Functional Test | End-to-end scan-to-CAD workflow validation with STL/PLY/OBJ export | Open Architecture Compatibility |
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: The Core of Accuracy
Carejoy operates a dedicated sensor metrology lab in Shanghai, equipped with:
- Laser interferometers for sub-micron motion tracking
- Reference photogrammetry systems (GOM ATOS)
- AI-powered calibration algorithms that adjust for thermal drift and mechanical hysteresis
Calibration is performed pre-assembly, post-assembly, and post-packaging to ensure end-to-end traceability. All calibration data is digitally logged and accessible via Carejoy’s cloud-based device management platform.
4. Durability Testing: Beyond Clinical Expectations
To ensure long-term reliability in high-volume dental labs and clinics, Carejoy subjects each scanner to accelerated life testing:
- Mechanical Stress: 10,000+ insertion cycles on simulated arch models
- Thermal Stability: 30-day thermal cycling (5°C to 45°C) with continuous scanning
- Disinfection Resistance: 500+ cycles of chemical immersion (75% ethanol, hypochlorite)
- Digital Longevity: Firmware stress testing under 24/7 scanning simulation
Devices that fail any threshold are returned for root-cause analysis, feeding into Carejoy’s continuous improvement loop.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in the global digital dentistry equipment market due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chain | Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining hubs reduces lead times and BOM costs by up to 35%. |
| Advanced Automation | High-ROI robotics in assembly lines ensure consistency while minimizing labor variance. |
| R&D Investment | Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 40% of global dental AI and imaging R&D talent, driving innovation velocity. |
| Regulatory Efficiency | NMPA fast-track approvals enable rapid iteration; dual ISO-FDA alignment streamlines global deployment. |
| Economies of Scale | Mass production of modular components (e.g., scanning tips, batteries) reduces unit cost without sacrificing QC. |
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-15µm accuracy scanners at 40% below Western-list prices, while maintaining full compliance with EU MDR and FDA 510(k) pathways.
Carejoy Digital: Powering the Future of Open-Architecture Dentistry
With a technology stack built on open file formats (STL/PLY/OBJ), AI-driven intraoral scanning, and seamless integration into CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows, Carejoy Digital offers dental labs and clinics a future-proof solution engineered for interoperability and precision.
- Support: 24/7 remote technical support & over-the-air software updates
- Compatibility: Native integration with Exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD, and open-source platforms
- Commitment: Continuous firmware enhancements using real-world scan data (anonymized, GDPR-compliant)
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Impronta Dentale Con Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
