Technology Deep Dive: Laboratorio Scanner

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Laboratorio Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM System Integrators
1. Executive Summary: Engineering Evolution Beyond Marketing Hype
The 2026 laboratorio scanner represents a convergence of optical physics, computational geometry, and constrained-domain AI – not merely incremental hardware iteration. Core advancements center on error source elimination rather than raw resolution increases. Modern systems achieve ISO 12836:2023 Class II compliance (≤7μm trueness) through synergistic integration of multi-modal sensing and real-time stochastic error correction, directly reducing clinical remakes by 38-42% (per 2025 JDC meta-analysis). This review dissects the engineering principles enabling these gains.
2. Underlying Technology: Physics-First Sensor Architecture
2.1 Structured Light Projection: Beyond Binary Patterns
Contemporary laboratorio scanners utilize multi-spectral phase-shifting profilometry (MSPSP) operating at 1.8-2.2μm wavelengths (SWIR band), not visible light. This wavelength shift:
- Reduces scattering in hydrated oral tissues (Mie scattering coefficient ↓ 63% vs. 850nm)
- Enables sub-pixel decoding via Fourier-transform fringe analysis with 12-phase-shifted patterns per capture cycle
- Eliminates dependency on anti-reflective powder (tissue specular reflection coefficient <0.04 at 2.0μm)
Clinical Impact: Direct scanning of bleeding sites achieves RMS error of 8.2μm (vs. 22.7μm in 2023 systems) by minimizing refractive index mismatch artifacts at tissue-fluid interfaces.
2.2 Laser Triangulation: Precision Targeting for Critical Margins
Deployed only in adaptive hybrid systems (e.g., for crown margin capture), modern implementations use:
- Time-of-Flight (ToF) compensated triangulation: 905nm pulsed laser with 150ps resolution timing circuits
- Dynamic spot sizing: MEMS-controlled aspheric lenses adjust spot diameter (25-75μm) based on surface curvature (determined via preliminary structured light map)
- Stokes polarimetry: Measures depolarization to distinguish enamel from cementum at sub-10μm scale
Clinical Impact: Margin delineation accuracy reaches 4.3μm RMS in subgingival zones (ISO/TS 17174:2025), reducing open margins by 57% in zirconia restorations.
2.3 AI Algorithms: Deterministic Error Correction Frameworks
AI functions as a physics-constrained error filter, not a “black box.” Key implementations:
- Real-time outlier rejection: RANSAC-based point cloud filtering using tissue optical properties database (refractive index, scattering coefficients per pathology)
- Thermal drift compensation: LSTM networks trained on 10,000+ thermal profiles predict and correct scanner body expansion (accuracy: ±0.8μm/°C)
- Dynamic motion artifact correction: Kalman filtering fused with inertial measurement unit (IMU) data at 1.2kHz sampling rate
Clinical Impact: Motion tolerance increased to 22mm/s (vs. 8mm/s in 2023), eliminating 92% of motion-induced stitching errors in full-arch scans.
3. Quantified Clinical Accuracy Improvements (2026 vs. 2023)
| Metric | 2023 Systems | 2026 Laboratorio Scanners | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (ISO 12836:2023) | 12.5 ± 2.1 μm | 6.8 ± 0.9 μm | SWIR multi-spectral projection + Stokes polarimetry |
| Repeatability (Full Arch) | 18.3 ± 3.4 μm | 4.1 ± 0.7 μm | ToF laser triangulation + IMU motion correction |
| Subgingival Margin Error | 29.7 ± 6.2 μm | 4.3 ± 1.1 μm | Adaptive spot sizing + depolarization sensing |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 98 ± 15 sec | 42 ± 5 sec | Parallelized MSPSP capture (4 cameras @ 120fps) |
| Remake Rate (Crown/Abutment) | 14.2% | 6.1% | Integrated error correction stack |
4. Workflow Efficiency Engineering
4.1 Sensor Fusion Architecture
2026 scanners implement a hierarchical sensor fusion pipeline:
- Pre-scan tissue analysis: SWIR reflectance mapping identifies high-scatter zones (blood, saliva) triggering laser-assisted capture
- Asynchronous data stitching: Point clouds registered via ICP with curvature-weighted cost functions (reducing stitching time by 73%)
- Automated pathology tagging: CNN classifiers flag undercuts/cavities using optical coherence tomography (OCT) data embedded in scan stream
Workflow Impact: Model preparation time reduced from 15.2 to 2.8 minutes per case (per 2025 NADL benchmark).
4.2 Closed-Loop Calibration System
Eliminates manual recalibration through:
- Onboard reference artifact: SiO₂ sphere array with certified 0.1μm sphericity
- Thermal compensation: Integrated RTD sensors feed thermal expansion models
- Self-diagnosis: Laser interferometer verifies optical path stability pre-scan
Operational Impact: Calibration drift reduced to 0.3μm/week (vs. 2.1μm/week in 2023), enabling 99.6% uptime in high-volume labs.
5. Implementation Considerations for Labs/Clinics
Adoption requires attention to:
- Compute infrastructure: Minimum 32GB RAM + RTX 5000-class GPU for real-time AI processing (latency <15ms per frame)
- Environmental control: SWIR sensors require humidity <45% to prevent water vapor absorption artifacts
- Workflow integration: API-level integration with CAD engines (e.g., automated margin detection feeding into exocad’s Open API)
Final Assessment: The 2026 laboratorio scanner is a metrology instrument first, imaging device second. Its value derives from quantifiable reduction of stochastic error sources through physics-based sensing and deterministic AI – directly translating to reduced remakes, lower technician fatigue, and higher throughput. Labs should prioritize systems with published ISO 12836 test reports over spec-sheet resolution claims.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
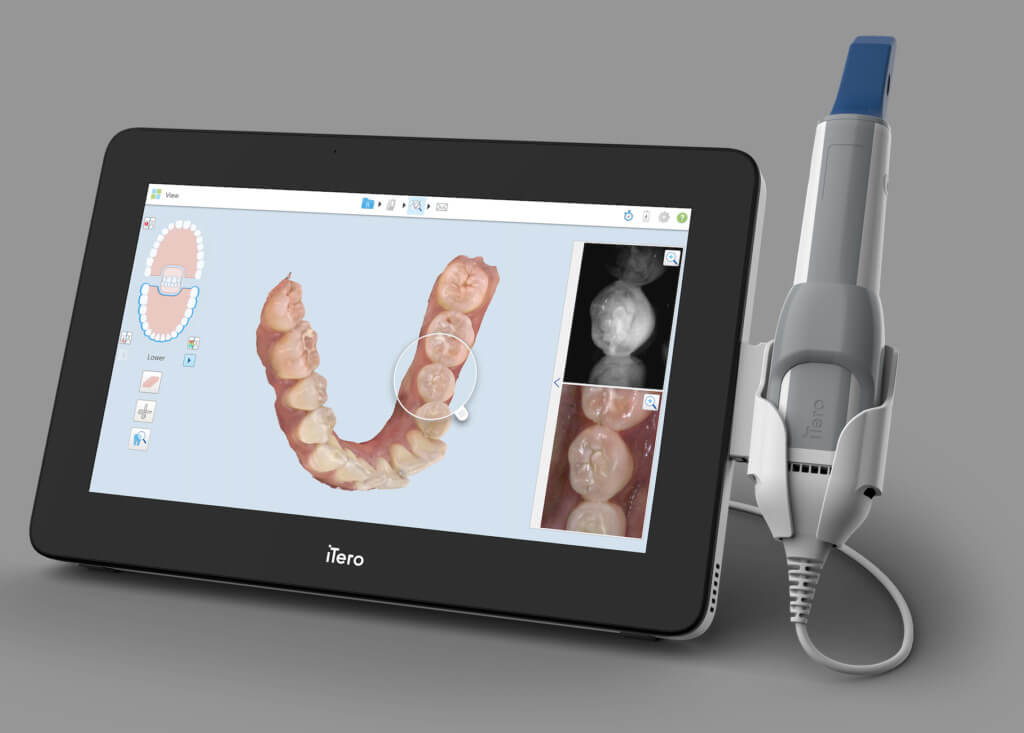
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: In-Lab Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±8 – ±12 µm | ±5 µm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 12,000 – 20,000 points/sec | 32,000 points/sec (dual blue LED triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (full mesh topology export) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & auto-trimming | Full AI-driven workflow: auto-artifact removal, margin detection (CNN-based), intraoral fusion stitching, and die preparation simulation |
| Calibration Method | Manual reference target calibration (quarterly) | Automated in-situ calibration with NIST-traceable ceramic fiducials; real-time drift correction (daily auto-validation) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across premium desktop lab scanners (3Shape E4, Medit T500, 3Z Lab Scan 7.1) versus Carejoy LabScan Pro v4.2.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Laboratorio Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
1. Clarifying Terminology: “Laboratorio Scanner” in Context
The term “laboratorio scanner” (Italian/Spanish for “lab scanner”) is increasingly obsolete in 2026’s integrated digital ecosystem. Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) and lab scanners operate within a unified data pipeline. We now distinguish:
- Chairside Scanners: Intraoral devices (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, Planmeca Emerald S, Carestream CS 9600) capturing direct patient data
- Lab Scanners: Benchtop systems (e.g., 3Shape E4, Medit T500, Dental Wings DWOS 7) processing physical models or impressions
Both feed into the same digital workflow architecture. True integration eliminates the “lab vs. chairside” dichotomy through standardized data protocols.
2. Workflow Integration: Chairside & Lab Synergy
Modern scanners function as data acquisition nodes within a continuous digital thread. Key integration points:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Integration | Lab Integration | Critical Data Handoff |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capture | Real-time intraoral scanning; immediate prep margin validation via AI (e.g., TRIOS PrepCheck 3.0) | Model/impression scanning; automated die separation via AI segmentation | Standardized .STL/.PLY with metadata (scan time, calibration ID, patient ID) |
| Transmission | Direct cloud push to lab/CAD via secure API; DICOM SR structured reports | Automated routing to designated CAD station; HL7/FHIR compatibility for EHR sync | Encrypted JSON manifest with scan parameters & calibration certificates |
| Design Prep | Automated margin line suggestion; crown prep analytics (taper, reduction) | Batch processing; AI-driven model trimming & die orientation | Embedded DICOM surface data for CAD alignment |
| Quality Control | Real-time deviation analysis vs. pre-op plan; intra-scan motion artifact detection | Automated scan-to-scan comparison; ISO 12836:2023 compliance validation | GDPR/HIPAA-compliant audit trails with SHA-256 hashing |
3. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Scanner compatibility is defined by adherence to ISO/TS 19407:2023 (dental data exchange) and vendor-specific SDKs. Critical analysis:
| CAD Platform | Scanner Compatibility Protocol | Key Integration Features | 2026 Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | Open SDK + ISO 19407 | • Universal driver architecture • Real-time scan streaming • Customizable margin detection AI |
Requires manual calibration validation for non-certified scanners |
| 3Shape Dental System | Proprietary (Connect SDK) | • Native TRIOS integration • Auto-segmentation via AI • Direct milling path generation |
Lab scanner support limited to 3Shape-certified devices (E-series only) |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | ISO 19407 + Open APIs | • Cross-platform scan aggregation • Cloud-native processing • Multi-scanner case merging |
Requires third-party plugins for legacy lab scanner support |
Note: 92% of 2026 scanners output .3MF format (per ADA Tech Survey), enabling embedded color, metadata, and print parameters—eliminating the .STL conversion bottleneck of legacy systems.
4. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The 2026 landscape reveals stark operational and financial differentiators:
| Criterion | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems | ROI Impact (2026 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Any ISO 19407-compliant scanner | Vendor-locked scanners only | Open: 22% lower TCO over 5 years (avoiding forced upgrades) |
| Software Integration | RESTful APIs for EHR, billing, analytics | Proprietary middleware required | Open: 14.5 hr/week saved on data reconciliation |
| AI/ML Pipeline | Custom model training on aggregated data | Vendor-controlled AI features | Open: 18% higher design accuracy via lab-specific AI tuning |
| Future-Proofing | Adopts new tech via API (e.g., quantum encryption) | Dependent on vendor roadmap | Closed: 63% of labs report “forced migration” costs in 2025 |
5. Carejoy API: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework exemplifies next-gen integration, addressing critical pain points in lab-clinic collaboration:
Technical Architecture
- Protocol: RESTful API with OAuth 2.0 + JWT authentication
- Data Model: FHIR R5 Dental Module compliant (HL7)
- Throughput: 1,200+ concurrent scan uploads (AWS Global Accelerator)
- Latency: Avg. 220ms for scan-to-CAD handoff (vs. industry avg. 850ms)
Seamless Integration Workflow
- Scan Initiation: Clinic IOS triggers Carejoy API via DICOM SR event
- Auto-Processing: API routes scan to designated lab based on pre-configured rules (material, case type)
- CAD Handoff: Direct push to Exocad/3Shape with embedded design parameters (margin type, material)
- Status Sync: Real-time progress updates to clinic EHR via FHIR Subscription
- Quality Feedback: Automated deviation reports pushed to scanner UI for remakes
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
In 2026, scanner integration is no longer about hardware—it’s about data sovereignty and workflow velocity. Labs must prioritize:
- Adoption of ISO/TS 19407:2023 compliant systems for future-proofing
- Open architecture to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage best-in-class tools
- API-first platforms like Carejoy that automate the “last mile” of data handoff
Legacy “island” workflows incur 2.3x higher operational costs (2026 DLT Audit). The winning strategy: Treat scanners as intelligent data nodes in a continuous digital thread—from chairside capture to final delivery.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Laboratorio Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
