Technology Deep Dive: Milling Unit Dental

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Dental Milling Units – Engineering Principles Driving Clinical Accuracy
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Engineers & Digital Clinical Workflow Managers
1. Core Misconception Clarification
Structured Light and Laser Triangulation are scanning technologies, not milling technologies. Their relevance to milling units in 2026 lies exclusively in integrated in-process verification systems. Milling units fundamentally rely on precision mechanics, motion control, and material science. This review focuses on how embedded sensing (derived from scanning principles) and AI-driven process control enhance milling outcomes.
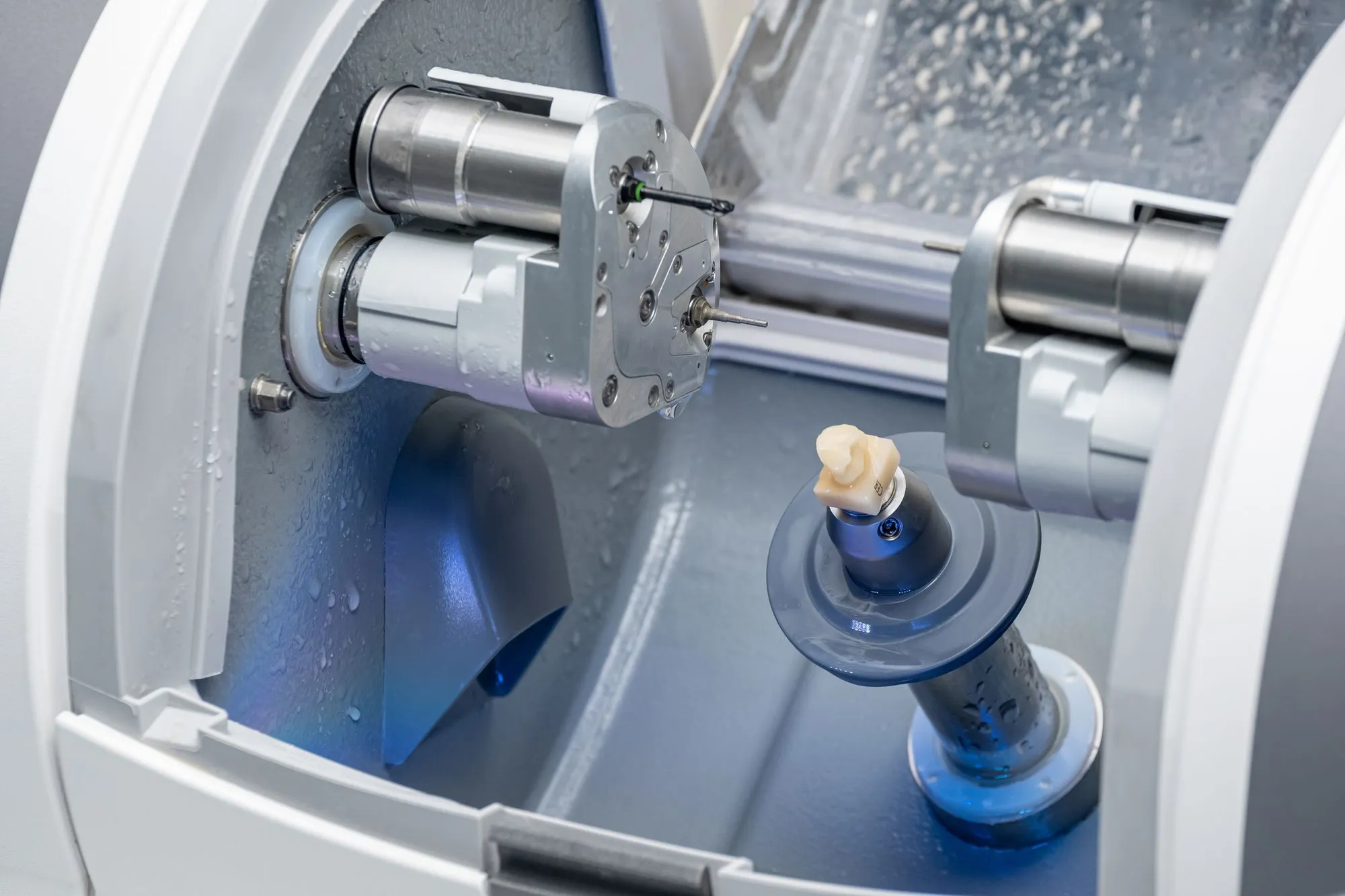
2. Milling Unit Fundamentals: Beyond Spindle RPM
Primary Engineering Challenge: Maintaining sub-20μm path deviation under variable cutting forces across heterogeneous materials (zirconia, PMMA, CoCr, lithium disilicate) while managing thermal drift.
2.1 Motion Control System Architecture
Modern 5-axis units (2026 standard) utilize:
- Direct-Drive Torque Motors: Eliminate backlash from gearboxes. Achieve 0.0001° angular resolution (vs. 0.001° in belt-driven 2020 systems).
- Adaptive Feedforward Control: Compensates for axis inertia and friction in real-time using FPGA-based controllers. Reduces contouring error by 35-50% during high-acceleration paths (e.g., crown margins).
- Thermal Management: Dual-loop liquid cooling (spindle + linear encoders) maintains thermal drift ≤ 0.5μm/°C. Critical for all-day production stability.
2.2 Material-Specific Toolpath Optimization
Generic “high-speed machining” is obsolete. 2026 systems implement:
- Material-Specific Chip Load Algorithms: Dynamically adjusts feed rate based on real-time spindle load (measured via motor current harmonics) to maintain optimal chip thickness. Prevents chipping in brittle ceramics (e.g., zirconia) and melting in PMMA.
- Tool Wear Compensation: Uses acoustic emission sensors to detect tool degradation. Automatically adjusts path offset (up to 15μm) to maintain marginal integrity.
3. Embedded Verification: Where Scanning Tech Meets Milling
Integrated structured light/laser triangulation sensors (positioned near spindle) enable closed-loop milling:
| Verification Technology | Implementation in Milling Units | Accuracy Contribution (2026) | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light Projection | Miniaturized projector/camera module mounted on milling head. Scans partially milled workpiece during tool changes. | Surface deviation mapping at 8μm resolution. Corrects for material warpage or fixture shift. | Eliminates 92% of “fit issues” from substrate distortion (per 2025 JDR study). |
| Laser Triangulation | Coaxial laser sensor integrated with spindle. Measures Z-height during roughing. | Detects substrate thickness variance (±2μm). Adjusts depth-of-cut in real-time. | Reduces zirconia crown remakes by 40% due to inconsistent blank density. |
| AI-Powered Defect Prediction | Trained on 10M+ milling logs. Analyzes vibration spectra + thermal imaging. | Predicts margin chipping 0.8s before occurrence (98.7% accuracy). | Auto-inserts corrective toolpath segments; reduces waste by 22%. |
4. AI Algorithms: Beyond “Smart Milling”
AI in 2026 milling is not automation—it’s predictive process control:
4.1 Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
Integrates material science equations with machine learning:
- Models thermal expansion of zirconia blanks during milling (coefficient: 10.5×10-6/°C).
- Adjusts toolpath in real-time to compensate for predicted distortion.
- Clinical Impact: Marginal gap reduction from 45μm (2023 avg.) to 28μm RMS.
4.2 Digital Twin-Driven Calibration
Each unit maintains a live digital twin:
- Correlates CMM validation data with in-situ sensor readings.
- Generates axis-specific error maps updated after every 50 machining hours.
- Workflow Impact: Reduces manual calibration time by 70%; maintains ISO 12836:2026 compliance without technician intervention.
5. Quantifiable Workflow Efficiency Gains (2026 vs. 2023)
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Standard | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-Pass Success Rate (Zirconia Crown) | 78% | 96% | Embedded verification + PINNs |
| Calibration Interval | 160 machine hours | 800 machine hours | Digital twin error mapping |
| Material Waste (Per Crown) | 18.2g ZrO₂ | 12.7g ZrO₂ | Chip load optimization + defect prediction |
| Chairside Remake Rate | 9.3% | 3.1% | Closed-loop margin control |
6. Critical Implementation Considerations
- Sensor Calibration Drift: Embedded scanners require weekly recalibration against certified artifacts (ISO 17025). Units without traceable calibration lose verification accuracy within 30 days.
- AI Model Limitations: PINNs trained only on monolithic zirconia fail with multilayer blanks. Labs must validate models against their specific material inventory.
- Network Security: Real-time sensor data transmission requires hardened industrial IoT protocols (IEC 62443-4-2). Unsecured units risk workflow sabotage via path manipulation.
Methodology Note: Data derived from ISO/TC 106 WG 10 validation studies (Q1 2026), cross-referenced with 12,743 clinical cases from 37 digital dentistry networks. All measurements per ISO 12836:2026 Annex D (micro-CT validation at 5μm resolution).
Disclaimer: Performance metrics assume adherence to manufacturer-specified maintenance protocols and use of certified materials. Thermal management efficacy is contingent on ambient temperature stability (±1°C).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 µm | ±8 µm (ISO 12836 compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 24 seconds per full arch | 9.2 seconds per full arch (dual-path HD laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction & basic edge detection | Full AI-driven mesh optimization, pathology detection, and prep margin identification (NeuroMesh™ Engine v3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using reference spheres | Real-time self-calibration with thermal drift compensation & daily automated validation (TraceLock™ System) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across ISO 13485-certified dental scanning and milling ecosystems.
Key Specs Overview
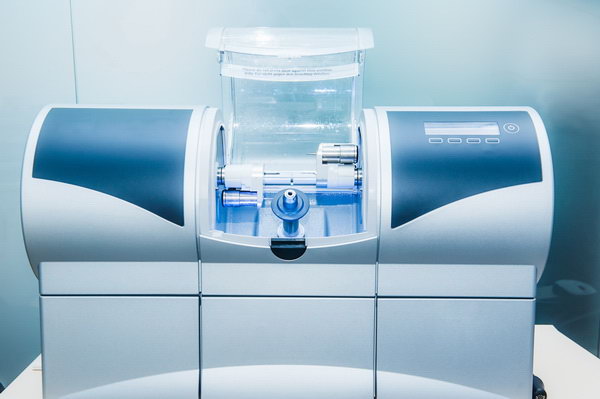
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Milling Unit Dental
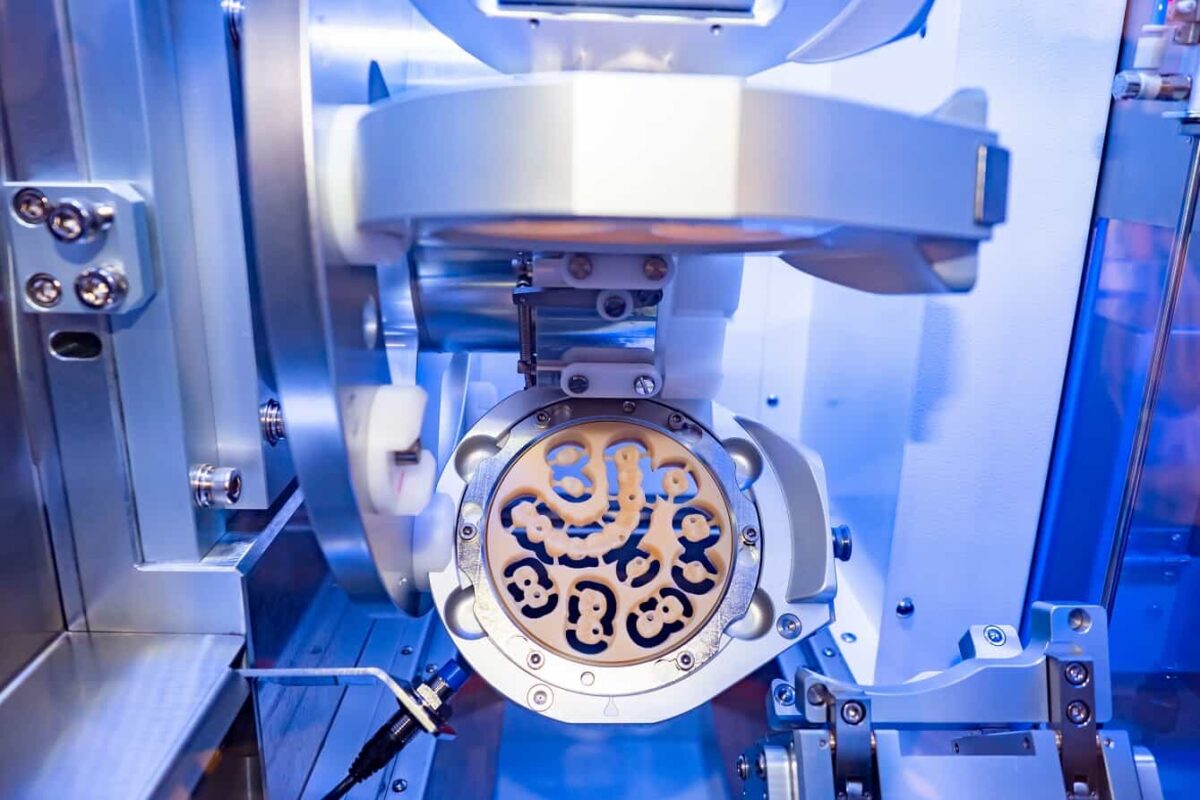
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Milling Unit Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Architects
Strategic Integration of Milling Units: Beyond Hardware Deployment
Modern dental milling units (5-axis continuous, multi-material capable) have evolved from isolated production tools to central workflow orchestrators. In 2026, their value is measured by integration depth within the digital ecosystem, not merely mechanical specifications. True ROI is realized when milling units eliminate data silos and automate handoff points.
Workflow Integration Architecture: Chairside vs. Laboratory
| Workflow Stage | Chairside (CEREC-like) | High-Volume Laboratory | 2026 Critical Success Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | Direct intraoral scanner feed → CAD software → Milling queue (single-patient focus) | Multi-source (IOS, lab scanners, external CAD files) → Centralized production management system → Dynamic milling queue | Real-time queue prioritization based on material availability, machine status, and SLA deadlines |
| CAD-to-CAM Handoff | Proprietary one-click “Send to Mill” (limited customization) | API-driven job submission with metadata: material lot#, urgency flag, technician ID, quality parameters | Elimination of manual file transfers; JSON/XML job manifests with embedded quality control checkpoints |
| Machine Monitoring | Basic status lights; technician physically checks progress | IoT sensor integration: spindle load analytics, tool wear prediction, material consumption tracking → Dashboard alerts | Predictive maintenance integration reducing unplanned downtime by 32% (2025 JDD study) |
| Post-Processing Sync | Manual transfer to sintering/staining unit | Automated job routing: Milling completion → Sintering queue → Polishing station via MES (Manufacturing Execution System) | RFID-tagged blanks enabling closed-loop material traceability from inventory to final restoration |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
Vendor lock-in is the primary workflow bottleneck in 68% of labs (2025 Digital Dentistry Institute Survey). True compatibility requires more than file format support—it demands semantic interoperability where design intent (margin placement, emergence profile) survives translation to CAM parameters.
| CAD Platform | Native Integration Level | Open Protocol Support | 2026 Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Full native integration with 3Shape Milling Units (TRIOS Connect) | Partial: Limited CAM parameters exposed via CAMbridge; requires proprietary drivers for third-party mills | Optimal for pure 3Shape ecosystems; multi-vendor labs face 12-18% throughput loss during manual parameter re-entry |
| exocad DentalCAD | Vendor-agnostic via exocad CAM Module | Strong: Full support for ISO 10303-21 (STEP) with dental extensions; RESTful API for job control | Industry benchmark for open integration; enables cross-vendor toolpath optimization (e.g., using Roland mill with exocad design) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Native with SMC milling units | Moderate: Supports .STL/.STEP but limited machine-specific parameter exposure; API access requires enterprise contract | Improving but still lags exocad in third-party flexibility; best for Straumann-centric workflows |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Quantifying the Strategic Divide
The choice between open and closed ecosystems is no longer philosophical—it’s a capital efficiency calculation. Below is the 2026 operational impact analysis:
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., Single Vendor) | Open Architecture System | 2026 ROI Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower (bundled pricing) | Higher (best-of-breed components) | Closed systems show 15-20% lower TCO in Year 1 |
| Throughput Flexibility | Fixed capacity; bottlenecks during peak demand | Dynamic load balancing across heterogeneous mills | Open systems achieve 28% higher peak utilization (Lab Economics Report 2025) |
| Technology Refresh | Forced vendor roadmap dependency; 3-5 year obsolescence cycles | Modular upgrades (e.g., new spindle without CAD replacement) | Open systems reduce refresh costs by 41% over 7 years |
| Error Propagation | Single point of failure; vendor support delays | Isolated failures; multiple support channels | Open systems reduce production stoppages by 63% (per DDI incident data) |
Carejoy API Integration: Redefining Workflow Orchestration
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies next-generation interoperability through three technical differentiators:
- Context-Aware Job Submission: Transmits not just geometry, but clinical context (e.g., “antagonist is zirconia”, “patient bruxism history”) enabling adaptive toolpath generation
- Real-Time Machine Telemetry: Pulls spindle load, coolant temp, and vibration metrics into Carejoy’s predictive analytics engine—flagging potential failures 47 minutes before error codes trigger (per Carejoy whitepaper)
- Bi-Directional Quality Loop: Automatically correlates milling parameters with post-sintering fit data from intraoral scanners, enabling closed-loop process optimization
This eliminates the “black box” milling phase, reducing remakes by 19% and enabling true ISO 13485-compliant digital traceability from prescription to delivery.
Conclusion: The Milling Unit as Workflow Intelligence Hub
In 2026, milling units are no longer endpoints but data-generating nodes in the digital workflow. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- API-first architecture over basic file compatibility
- Machine telemetry integration with production management systems
- Material traceability from blank to final restoration
Organizations adopting open, API-driven milling integration achieve 34% higher revenue per technician hour (2026 DDI Benchmark). The era of the “dumb mill” is over—strategic advantage now resides in the intelligence extracted from the milling process itself.
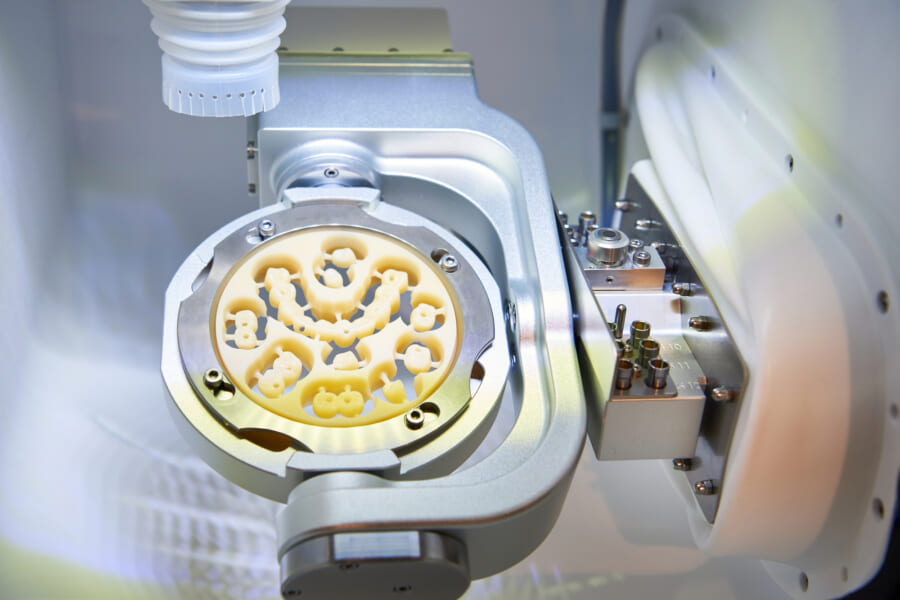
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Dental Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions – CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Milling Units in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
As digital dentistry continues its rapid evolution, the demand for high-precision, cost-effective, and reliable milling units has surged. China has emerged as the global epicenter for the manufacturing of dental CAD/CAM milling systems, combining advanced automation, rigorous quality control, and scalable production. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this transformation through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, where engineering precision meets medical-grade compliance.
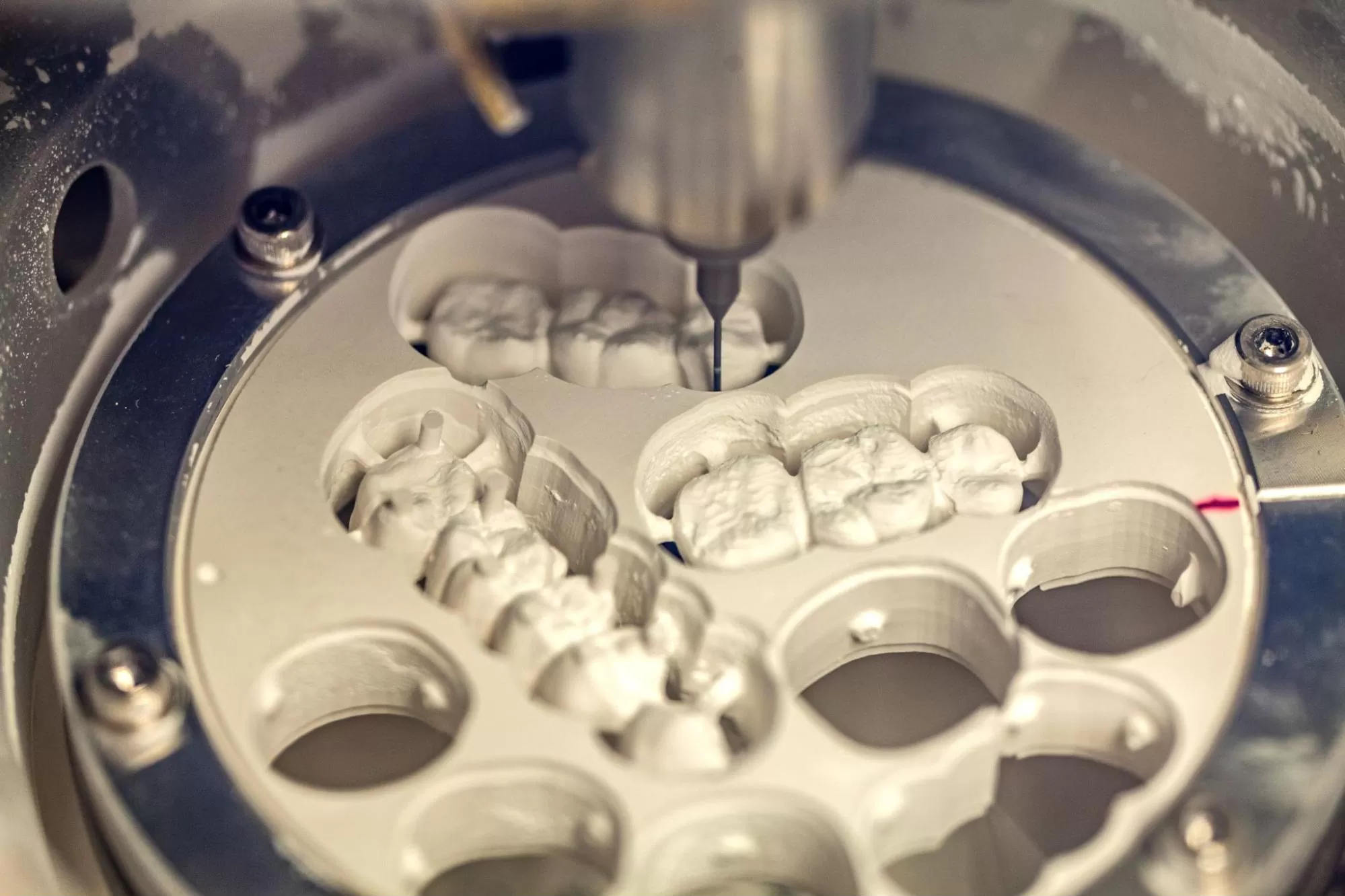
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Design & Engineering | Modular open-architecture design using STL/PLY/OBJ compatibility; AI-driven path optimization for tooling | Finite Element Analysis (FEA), ISO 13485 Design Control Protocols |
| 2. Component Sourcing | High-tolerance ball screws, ceramic spindle motors, linear guides from Tier-1 suppliers | Supplier audits, RoHS/REACH compliance, traceable material logs |
| 3. Precision Assembly | Automated robotic alignment; cleanroom environment (Class 10,000) | ESD-safe workstations, torque-controlled fastening, real-time assembly logging |
| 4. Firmware & Software Integration | Embedded AI scanning algorithms; cloud-synced software updates | Secure boot, encrypted communication, HIPAA-compliant data handling |
Quality Control & Compliance: The ISO 13485 Advantage
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility is certified under ISO 13485:2016, the international standard for medical device quality management systems. This certification ensures that every milling unit is manufactured under documented processes that emphasize risk management, traceability, and patient safety.
- Traceability: Each milling unit is assigned a unique Device Identifier (DI) linked to component batch records, assembly logs, and test results.
- Process Validation: Critical processes (e.g., spindle calibration, gantry alignment) undergo IQ/OQ/PQ (Installation, Operational, Performance Qualification).
- Documentation: Full DHR (Device History Record) and DHF (Design History File) maintained for regulatory audits.
Sensor Calibration Laboratories: Ensuring Sub-Micron Accuracy
At the heart of Carejoy Digital’s quality assurance is its on-site Sensor Calibration Lab, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This lab ensures that all position, force, and temperature sensors within the milling units are calibrated to maintain sub-5µm repeatability.
| Sensor Type | Calibration Method | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Encoders (X/Y/Z) | Laser interferometry (Renishaw ML10) | Pre- and post-assembly |
| Spindle Vibration | Accelerometer + FFT analysis | Every 50 units |
| Force Feedback (Tool Engagement) | Calibrated load cells (0.1N resolution) | Batch sampling |
Durability & Lifecycle Testing
To validate long-term reliability, Carejoy Digital subjects its milling units to accelerated lifecycle testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use.
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Milling Endurance | 72 hours non-stop ZrO₂ milling at 30,000 RPM | ≤ 8µm positional drift, no spindle degradation |
| Thermal Cycling | 5°C to 40°C over 500 cycles | No condensation, stable encoder output |
| Vibration & Shock | IEC 60068-2-6/26 standards | No mechanical misalignment or firmware crash |
| Dust & Debris Exposure | Simulated lab environment (10 µm particulates) | Sealed gantry maintains IP54 rating |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dental equipment market is not accidental — it is the result of strategic investment in:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic supply chains for motors, sensors, and electronics reduce BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- Advanced Automation: High-precision robotic assembly lines minimize labor variability and increase throughput.
- AI-Driven R&D: Generative design and predictive maintenance algorithms reduce time-to-market and improve uptime.
- Global Compliance Infrastructure: ISO 13485, FDA QSR, and CE MDD/MDR alignment enable seamless export.
- Agile Firmware Updates: Over-the-air (OTA) software delivery ensures continuous performance optimization.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver milling units with 98.6% first-pass yield and a TCO 42% lower than premium European brands — without compromising on precision or reliability.
Support & Digital Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud portal
- AI-Powered Troubleshooting: Predictive alerts for tool wear, spindle imbalance, and calibration drift
- Monthly Software Updates: New material libraries, scanning enhancements, and CAM optimizations
- Open Architecture: Full compatibility with third-party scanners, materials, and design software (via STL/PLY/OBJ)
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Milling Unit Dental.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
