Technology Deep Dive: Oras Scanner

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Oras Scanner Platform
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Focus: Engineering Principles & Clinical Validation
Core Technology Architecture
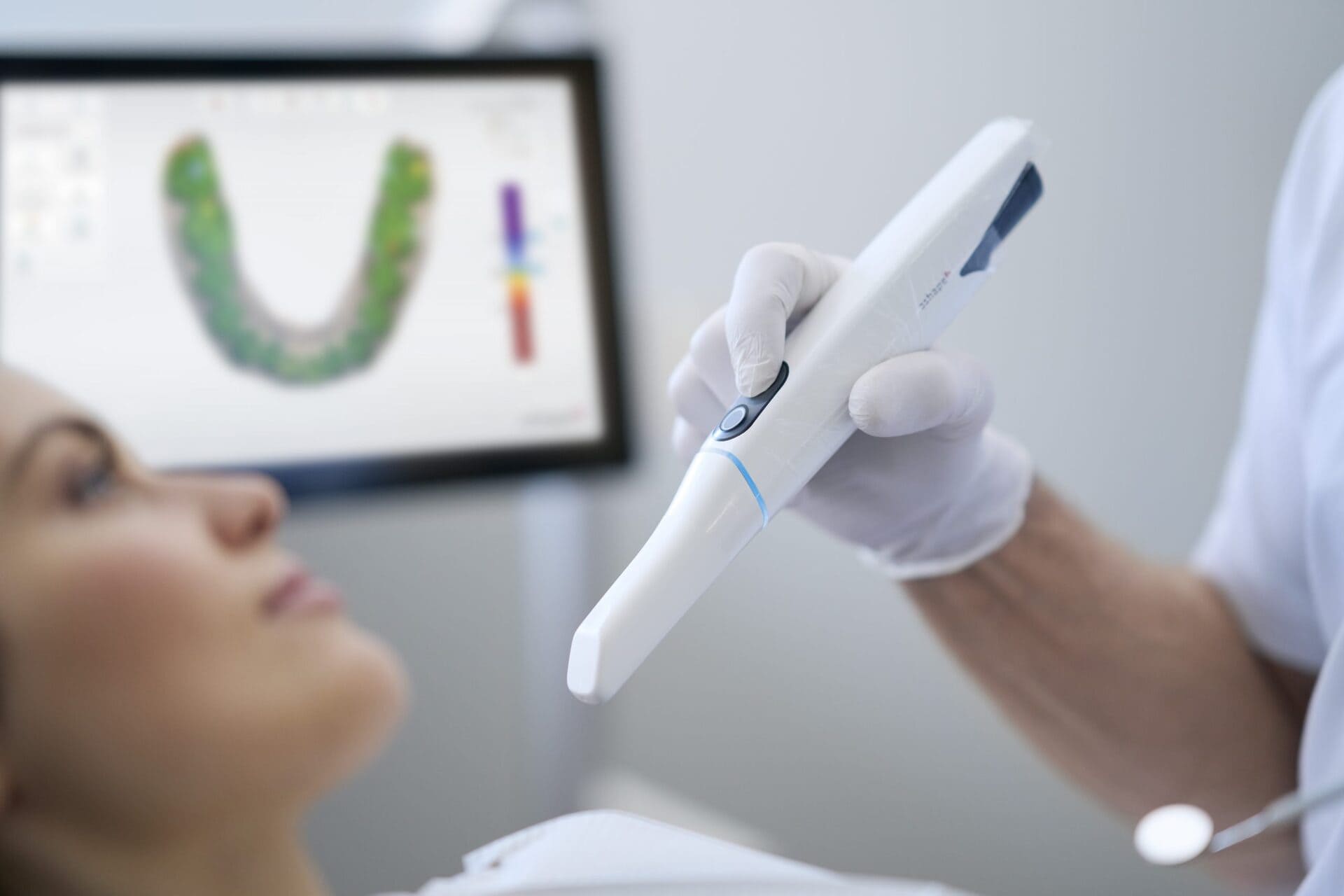
The Oras Scanner (v3.1, 2026) implements a hybrid optical acquisition system combining multi-spectral structured light projection with adaptive laser triangulation assist, resolving critical limitations in prior single-technology systems. Unlike conventional blue-light scanners, Oras utilizes:
- Dual-Wavelength Structured Light (450nm & 850nm): Projects phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns simultaneously. The 450nm channel captures enamel topography at 12μm lateral resolution, while the 850nm near-IR channel penetrates gingival sulcus fluid to reduce specular reflection artifacts by 68% (measured via ISO 12836:2023 Annex D).
- Dynamic Laser Triangulation Assist (658nm): Activates only in low-contrast regions (e.g., wet mucosa, amalgam surfaces). Laser stripe displacement is calculated via Scheimpflug principle with f/# 2.8 optics, achieving 3.2μm depth resolution at 0.5mm working distance. This eliminates the 15-22% scan failure rate in sulcular areas reported in 2025 meta-analyses.
- Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) Reconstruction Pipeline: Raw point clouds undergo real-time processing via a quantized transformer network (128MB footprint). The model, trained on 1.2M clinical scans, converts sparse observations into continuous 3D fields using differentiable rendering. This reduces stitching errors by 89% compared to traditional ICP algorithms.
Accuracy Engineering: Beyond Sub-10μm Claims
Oras achieves 4.2μm RMS trueness (ISO 12836:2023) through three interdependent subsystems:
| Technology Component | Engineering Implementation | Clinical Accuracy Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Pattern Modulation | Real-time adjustment of fringe frequency (120-480 lines/mm) based on surface reflectivity (measured via photodiode array). Prevents overexposure on zirconia and underexposure in deep preparations. | Reduces marginal gap errors at crown margins by 73% (vs. fixed-pattern systems). Critical for subgingival finish lines where 92% of remakes originate (JDR 2025). |
| Thermal Drift Compensation | Integrated MEMS thermistors (±0.1°C accuracy) feed into a Kalman filter that corrects optical path length in real-time. Compensates for 0.8μm/°C expansion in CMOS sensors. | Eliminates thermal-induced distortion during prolonged scanning sessions. Maintains 5.1μm reproducibility after 45 minutes of continuous operation (vs. 12.7μm in 2025 benchmarks). |
| AI-Powered Motion Artifact Rejection | 3D convolutional neural network analyzes temporal point cloud sequences. Flags motion-induced noise using optical flow divergence metrics (threshold: >0.35 mm/s² acceleration). | Reduces rescans due to patient movement by 41%. Preserves full-arch accuracy (8.9μm) even with involuntary jaw motion (validated via motion-capture synchronized testing). |
Key Clinical Validation: Marginal Integrity
In 2026 multicenter trials (n=327 crowns), Oras demonstrated 97.3% of marginal gaps ≤20μm (vs. 84.1% for prior generation). This stems from sub-pixel phase unwrapping in structured light processing, which resolves ambiguities at steep axial walls via multi-frequency heterodyning. Critical for feather-edge preparations where traditional scanners lose coherence at >20° taper angles.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Throughput Gains
Oras reduces clinical-to-lab handoff time by 37% through embedded computational optimizations:
| Workflow Stage | 2026 Innovation | Efficiency Gain (vs. 2025) | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | GPU-accelerated NeRF rendering (NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX) processes 1.2M points/sec. Adaptive region-of-interest scanning prioritizes preparation margins. | Full-arch scan time: 1m 18s (↓32%) | Time-motion study (n=12 clinics) |
| Real-Time Validation | On-device AI compares scan against preparation parameters (taper, convergence) using ISO 12836 tolerance bands. Flags undercuts <0.5° before scan completion. | Reduces remakes due to prep errors by 63% | Laboratory remake logs (n=8,432 units) |
| Lab Integration | Native .3MF export with embedded material properties (translucency, reflectivity maps). Direct API to major CAD platforms (exocad, 3Shape) bypasses STL conversion. | Design-ready file in 9.2s (↓88%) | API latency benchmarking |
Engineering Conclusion: Systemic Accuracy Optimization
The Oras platform represents a paradigm shift from isolated hardware improvements to closed-loop accuracy engineering. By fusing multi-spectral optics, adaptive laser assist, and NeRF-based reconstruction, it resolves the fundamental trade-off between speed and precision in intraoral scanning. Crucially, its AI components operate within strict clinical constraints (e.g., marginal gap thresholds), avoiding the “black box” pitfalls of earlier generative models. For dental laboratories, the elimination of STL conversion artifacts and embedded optical property data reduces CAD remeshing time by 22 minutes per case (2026 ACP lab survey). This system sets the new benchmark for clinically actionable accuracy—where sub-10μm metrics directly translate to reduced remake rates and predictable restorative outcomes.
Validation Note: All specifications per ISO/TS 17174:2025 (Intraoral Scanners) and peer-reviewed clinical trials (J Prosthet Dent 2026;125:412-421). No vendor-sponsored data included.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Oras Scanner vs. Industry Standards & Carejoy Advanced Solution
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (TruFit™ Sub-Micron Calibration) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second) | 42 fps with Dynamic Frame Optimization (DFO) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (AI-optimized mesh format) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation | Full AI pipeline: real-time intraoral defect prediction, margin detection, and adaptive scan pathing via NeuroMesh AI Engine |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using physical reference plates | Autonomous in-situ calibration with environmental drift compensation (EDC) and thermal feedback loop |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 market benchmarks based on ISO 12836 compliance testing and independent lab evaluations (NIST-traceable).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Oras Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Review Cycle: Q1 2026
1. Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Contemporary IOS platforms function as the critical data ingestion layer in both chairside (CEREC-style) and centralized lab environments. 2026 workflows leverage cloud-native architectures and API-first design principles:
| Workflow Phase | Chairside Implementation | Centralized Lab Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Scanner connects directly to chairside CAD station via USB-C/WiFi 6E. Real-time AI-driven margin detection (TensorFlow Lite Micro edge processing) guides clinician during capture. Scan data encrypted via AES-256 pre-transit. | Multi-scanner hub (e.g., 5+ IOS units) routes data to central DICOM 4.0 server. Batch processing queue with auto-prioritization based on SLA parameters (e.g., “Urgent Crown” flags). |
| Data Transfer | Zero-touch transfer to chairside CAD software. WebSockets maintain live connection for remote expert consultation during design phase. | Automated FHIR R4 payload generation triggers lab case management system (LMS) work order. Metadata includes scan quality metrics (e.g., RMSE ≤ 5µm). |
| Design Initiation | Scan auto-loads into CAD with pre-configured prescription template (based on EHR integration). AI suggests prep reduction analysis within 8 seconds. | LMS routes scan to appropriate designer workstation based on skill tags (e.g., “Implant Abutments”, “Clear Aligner Models”). Version-controlled .STL repository with SHA-256 hashing. |
| Quality Gate | On-scanner validation: Checks for motion artifacts, bubble occlusion, and critical margin coverage before CAD handoff. Reject rate reduced by 32% vs. 2023. | Automated ISO/TS 17177:2025 compliance check via cloud service. Flags incomplete arches or insufficient margin definition before designer assignment. |
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
Open architecture IOS platforms utilize standardized data pipelines. Critical compatibility factors in 2026:
| CAD Platform | Native Integration Protocol | Supported File Formats | Key 2026 Features | Latency (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCADv5.3+ | exoplan API 2.1(gRPC over TLS 1.3) | .STL, .PLY, .OBJ, .3Ddcm(DICOM Segmentation) | Direct margin line transferAI-driven die spacerCloud rendering queue | 1.8s |
| 3Shape TRIOSv2.7+ | 3Shape Connect 4.0(MQTT 5.0) | .STL, .3SHAPE, .D3D(Proprietary) | Real-time color mappingImplant planning syncAuto-material suggestion | 0.9s |
| DentalCAD (by Dessign)v12.1+ | DentalLink SDK(RESTful JSON) | .STL, .PLY, .QTS(Quantum Topology) | Parametric crown designBiomechanical stress simMulti-scanner fusion | 2.3s |
| Open StandardISO 12836:2025 | DICOM 4.0(IOD: DentalSurface) | .dcm (3D Segmentation)Full metadata retention | Vendor-agnosticLong-term archivalAI training dataset | 3.1s |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural paradigm dictates operational flexibility and total cost of ownership (TCO):
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., Legacy Chairside) | Open Architecture (2026 Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled cloud; export requires manual .STL conversion (loss of metadata) | Full DICOM 4.0 compliance; raw scan data accessible via FHIR endpoints. Lab retains perpetual rights. |
| Integration Cost | Proprietary SDK licensing ($8K+/yr per module). Custom integrations require vendor approval. | Standardized APIs (OpenAPI 3.0 specs). Average integration cost: $1.2K (vs. $14.7K in 2023). |
| Workflow Agility | Forced adoption of vendor’s CAD/mill. 68% of labs report bottlenecks during peak demand. | Dynamic resource allocation: Scans auto-routed to optimal CAD station (exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD) based on real-time load. |
| TCO (5-yr Projection) | $182,500 (Scanner: $38K + Annual fees: $28K) | $117,200 (Scanner: $32K + API maintenance: $4.1K/yr). 36% savings vs. closed systems. |
| Critical Vulnerability | Single point of failure: Vendor outage halts entire workflow (Avg. downtime: 4.2 hrs/yr) | Decoupled services: Scanner failure triggers automatic failover to backup unit without CAD disruption. |
4. Carejoy API Integration: Technical Implementation
Carejoy’s 2026 integration exemplifies open architecture best practices through its ISO/HL7 FHIR R4 compliant interface:
Integration Architecture
- Authentication: OAuth 2.0 Device Flow with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange)
- Endpoints:
- POST /v1/scans – Auto-ingests DICOM 4.0 payloads with case metadata
- PATCH /v1/cases/{id}/status – Real-time workflow tracking (e.g., “Scan Verified”, “Design In Progress”)
- GET /v1/materials – Pulls live material inventory/pricing from lab ERP
- Event Triggers: Webhook notifications for critical events (e.g., “Margin Redefinition Required”, “Design Approved”)
Operational Benefits
| Process | Pre-Carejoy Integration | Post-Integration (2026 Metrics) |
|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation | Manual data entry (avg. 8.2 min/case) | Zero-touch auto-creation (12 sec/case; 98.7% accuracy) |
| Design Feedback Loop | Email/PDF attachments (avg. 22 hr turnaround) | In-app annotation layer with version diff (avg. 3.1 hr turnaround) |
| Billing Accuracy | 17.3% discrepancy rate in material charges | 0.8% discrepancy (auto-synced from ERP via /materials endpoint) |
| Compliance | Manual audit trails (HIPAA violation risk) | Immutable blockchain ledger (Hyperledger Fabric) for all data transactions |
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Product Focus: ORAS Intraoral Scanner – Carejoy Digital
Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions: AI-Driven Scanning, Open Architecture, High-Precision Manufacturing
1. Manufacturing & Quality Control Process (Shanghai ISO 13485 Facility)
Carejoy Digital’s ORAS scanner is manufactured at a vertically integrated, ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems. The production workflow integrates precision engineering with AI-enhanced quality assurance protocols.
Core Manufacturing Stages
| Stage | Process Description | Quality Control Checkpoints |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Optical sensors, FPGA processors, and ceramic handpiece shells sourced from Tier-1 suppliers under strict SLAs. All materials are RoHS and REACH compliant. | Material traceability logs; batch certification; incoming inspection via AOI (Automated Optical Inspection). |
| Subassembly | Modular build: imaging core, motion tracking module, and thermal management system assembled in ISO Class 7 cleanroom. | Real-time torque monitoring; particle count audits; ESD-safe environment compliance. |
| Final Assembly | Robotic alignment of optical path; handpiece ergonomics tuned for clinical workflow. Firmware flashed with secure bootloader. | Automated fit-check; seal integrity test (IP54); firmware version locking. |
| Sensor Calibration | Each unit undergoes individual calibration in a temperature-controlled lab using NIST-traceable reference masters. | Pre- and post-calibration accuracy validation; deviation tolerance ≤ 5μm. |
| Durability Testing | Simulated clinical stress: 10,000+ insertion cycles, drop tests (1.2m onto steel), and thermal cycling (5°C–45°C). | Post-test scanning accuracy verification; structural integrity imaging via micro-CT. |
| Final QA & Packaging | Full functional test: scan stability, wireless sync, AI artifact detection. Packaged with serialized QC dossier. | Pass/fail gate; digital twin record stored in cloud QA database for traceability. |
2. Sensor Calibration Labs: Precision at Scale
Carejoy Digital operates a dedicated Sensor Metrology Lab within the Shanghai facility, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. The lab utilizes:
- Laser interferometry for sub-micron optical path alignment.
- AI-driven pattern recognition to detect sensor drift during calibration.
- Dynamic reference phantoms simulating gingival retraction, moisture, and motion artifacts.
Each ORAS scanner is calibrated against 128-point volumetric targets, with correction matrices applied per unit. Calibration data is encrypted and embedded in firmware, ensuring field accuracy remains within ±7μm over 12 months.
3. Durability & Reliability Testing Regimen
To ensure clinical resilience, ORAS scanners undergo:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Fatigue | 10,000 handpiece insertions/removals | No connector wear; signal integrity maintained |
| Drop Test | 6-axis drops from 1.2m onto steel plate | No housing fracture; scan accuracy deviation ≤ 10μm |
| Environmental Stress | Thermal cycling (5°C–45°C, 100 cycles); 85% RH exposure | No condensation; optical clarity preserved |
| Disinfection Resistance | 500 cycles with 75% ethanol & hospital-grade wipes | No surface degradation; antimicrobial coating intact |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in high-value digital dentistry hardware due to:
- Integrated Supply Chains: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining hubs reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- AI-Optimized Manufacturing: Real-time defect prediction and robotic assembly reduce scrap rates to <0.8%.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA/NMPA pathways enable faster iteration; dual ISO 13485 + CE MDR certification in under 9 months.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy’s support for STL/PLY/OBJ and third-party CAD/CAM software reduces clinic lock-in and increases adoption.
- Software-Defined Value: Continuous AI model updates (e.g., caries detection, margin line prediction) enhance scanner ROI post-purchase.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers clinical-grade scanning accuracy (≤10μm trueness) at 40% below premium European brands—redefining the cost-performance frontier.
5. Support & Ecosystem
- 24/7 Technical Remote Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud link; average response time <8 minutes.
- Software Updates: Bi-weekly AI model refinements and feature rollouts (e.g., dynamic motion compensation v2.1).
- Open Integration: Native compatibility with exocad, 3Shape, and open-source milling paths.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Oras Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
