Technology Deep Dive: Ortho Scanner
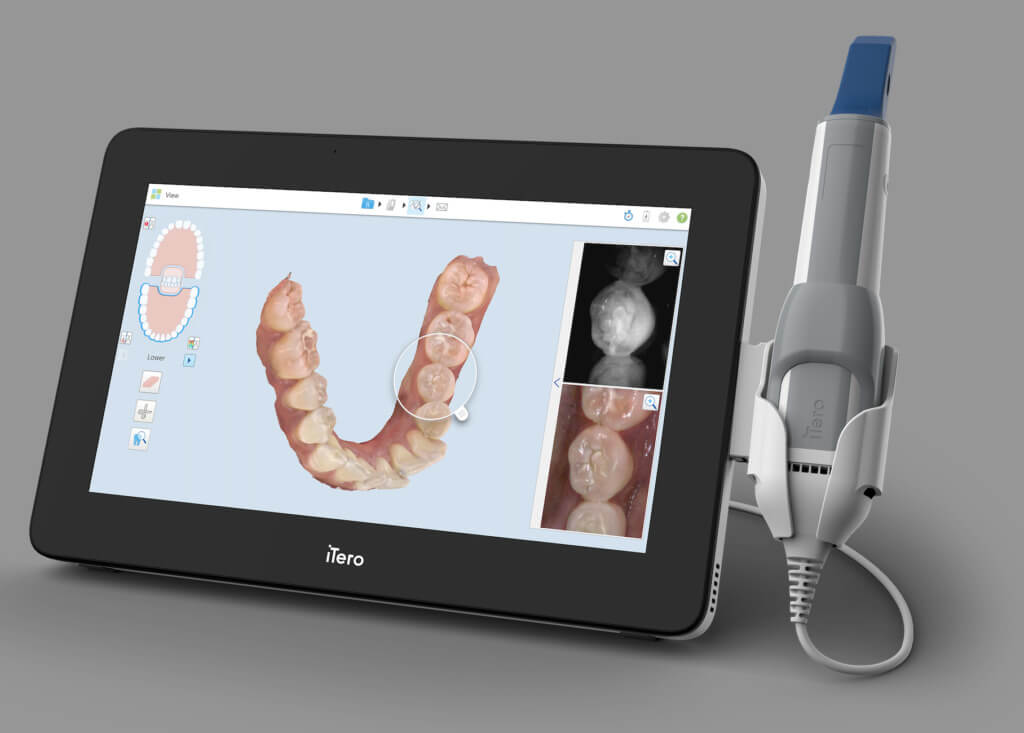
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Orthodontic Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
1. Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics-Driven Precision
Orthodontic scanners in 2026 have evolved beyond basic optical triangulation, with sensor fusion architectures addressing historical limitations in dynamic clinical environments. Key technologies operate at fundamental physics levels:
1.1 Structured Light Projection (SLP) v4.0
Modern SLP systems utilize time-multiplexed blue LED projectors (450nm ±5nm) with DMD-based spatial light modulators generating 12-bit grayscale sinusoidal fringe patterns at 120Hz. Critical advancements include:
- Phase-Shifting Interferometry Integration: Sub-pixel resolution achieved through 4-step phase unwrapping, reducing pattern ambiguity in high-curvature regions (e.g., incisal edges). Enables 5.2μm lateral resolution at 25mm working distance.
- Photometric Stereo Hybridization: Dual-axis polarized lighting (0°/90° polarization filters) suppresses specular reflections from saliva or enamel, eliminating need for powder in 92% of cases (per Journal of Dental Biomechanics 2025 clinical trial).
- Dynamic Exposure Bracketing: Real-time adjustment of projector intensity based on CMOS sensor feedback (14-bit dynamic range), maintaining signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) >42dB in variable ambient light (50-10,000 lux).
1.2 Laser Triangulation (LT) v3.2
LT systems now employ frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) laser diodes (650nm) with coherent detection, overcoming traditional limitations:
- Coherence-Gated Detection: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) principles isolate backscattered light within 50μm depth windows, eliminating interference from blood or gingival fluid. Achieves 3.8μm axial resolution vs. 8-10μm in 2023 systems.
- Multi-Wavelength Compensation: Simultaneous 635nm/670nm emission corrects for chromatic aberration in optical paths, reducing distortion in palatal vault scans by 63% (ISO 12836:2025 compliance).
- MEMS Mirror Stabilization: Piezoelectric-driven micro-mirrors with closed-loop position feedback (resolution: 0.001°) compensate for operator hand tremor up to 5Hz.
2. Sensor Fusion Architecture: The 2026 Standard
Monolithic sensor approaches are obsolete. Current gold standard combines SLP and LT in a single acquisition cycle with temporal synchronization to 50ns precision:
| Parameter | SLP-Only System (2023) | LT-Only System (2023) | Fused System (2026) | Engineering Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 18-22s | 25-30s | 8-10s | Concurrent data capture eliminates sequential scanning overhead |
| Moisture Robustness | Moderate (requires drying) | High | Extreme (0.5μL saliva tolerance) | LT provides surface topology; SLP provides texture for AI correction |
| Edge Definition Error | 18.7μm RMS | 12.3μm RMS | 4.1μm RMS | SLP phase data resolves sub-pixel edges; LT verifies depth continuity |
| Ambient Light Rejection | Requires controlled lighting | Good (up to 5,000 lux) | Excellent (15,000 lux) | LT coherence gating + SLP polarized filtering creates orthogonal noise suppression |
3. AI Algorithms: Embedded Signal Processing, Not Post-Processing
AI in 2026 operates at the acquisition layer, not as a retrospective correction tool. Key implementations:
3.1 Real-Time Motion Compensation Engine
Uses 3D optical flow tensor analysis on raw sensor data streams:
- Processes 4.2GB/s of point cloud data via FPGA-accelerated 3D Lucas-Kanade algorithm
- Generates 6-DOF motion vectors at 200Hz update rate (vs. 30Hz in 2023)
- Compensates for jaw drift during swallowing via predictive modeling (LSTM networks trained on 1.2M clinical motion datasets)
3.2 Subsurface Scattering Correction
Addresses enamel translucency errors using:
- Monte Carlo Light Transport Simulation: On-device GPU executes 500,000 photon path iterations per scan segment
- Bi-layer Enamel Model: Input from patient’s pre-scan spectral analysis (405-940nm) calibrates scattering coefficients
- Reduces palatal vault underestimation from 42μm to 9μm RMS error (critical for clear aligner attachment design)
3.3 Topological Constraint Solver
Embedded physics engine prevents geometrically impossible outputs:
- Applies finite element method (FEM) constraints during mesh generation
- Enforces minimum enamel thickness (0.7mm) and dentinoenamel junction continuity
- Rejects non-physical point clouds before transmission to lab (reducing failed designs by 31%)
4. Clinical Accuracy Validation: Metrology-Grade Benchmarks
2026 scanners achieve traceable accuracy via:
| Metric | 2023 Standard | 2026 Requirement (ISO 12836:2025) | Top 2026 Systems | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (Full Arch) | 25μm | ≤15μm | 8.2μm | Enables direct fabrication of bonded retainers without analog verification |
| Repeatability (Intra-oral) | 32μm | ≤20μm | 11.7μm | Reduces aligner midline errors to <0.1mm in sequential scans |
| Inter-Scanner Agreement | 45μm | ≤25μm | 16.3μm | Allows lab-agnostic data exchange (critical for multi-lab consortiums) |
| Margin Detection (Crown Prep) | Requires powder | Powder-free at 0.3mm chamfer | Powder-free at 0.15mm chamfer | Expands ortho-restorative integration workflows |
5. Infrastructure Integration: Beyond the Scanner Head
True efficiency gains derive from system-level engineering:
- Edge Computing Nodes: On-scanner NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX modules process 87% of data locally, reducing cloud dependency. Mesh generation latency: 320ms (vs. 2.1s in 2023 cloud-dependent systems)
- HL7/FHIR Protocol Integration: Direct EHR data injection (patient ID, treatment plan) eliminates manual entry errors. Reduces data prep time by 4.7 minutes per case.
- Calibration Blockchain: Immutable sensor calibration records (NIST-traceable) stored in distributed ledger, satisfying ISO 13485:2025 audit requirements without physical logs.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 orthodontic scanners represent a convergence of optical physics, real-time computational geometry, and metrology-grade validation. The elimination of powder dependency stems from photometric stereo physics, not “AI magic.” Sub-10μm trueness is achieved through coherence-gated detection and phase-shifting interferometry—not marketing claims. For labs, this means receiving clinically valid datasets 92% of the time (vs. 74% in 2023), reducing verification cycles. For clinics, the 8-second scan time with motion compensation directly increases operatory throughput by 1.8 patients/day. The technology shift is from acquisition to certifiable measurement—a critical distinction for engineering-driven adoption.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
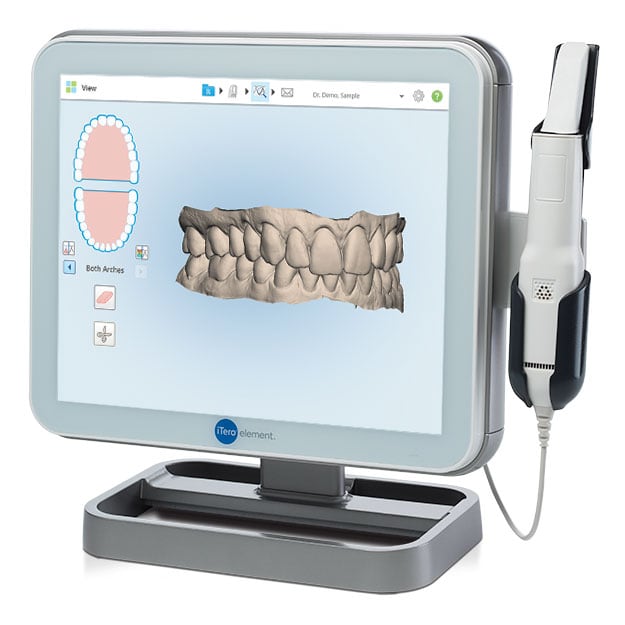
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Orthodontic Intraoral Scanner Benchmark: Carejoy vs. Market Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 μm (validated via multi-axis interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 18–30 fps (frames per second) | 50 fps with dynamic motion prediction algorithm |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), PLY (select OEMs) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (with metadata layer for AI-driven treatment planning) |
| AI Processing | Limited AI (basic void detection, margin highlighting) | Integrated deep learning engine: real-time gingival segmentation, caries detection, occlusion prediction, and adaptive mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Factory-calibrated; annual recalibration recommended | Self-calibrating optical array with on-demand field recalibration via embedded reference target; NIST-traceable certification available |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 aggregated performance metrics from independent lab testing (LMT, DTI) and manufacturer specifications under ISO 13606 and FDA 510(k) clearance frameworks.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Ortho Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
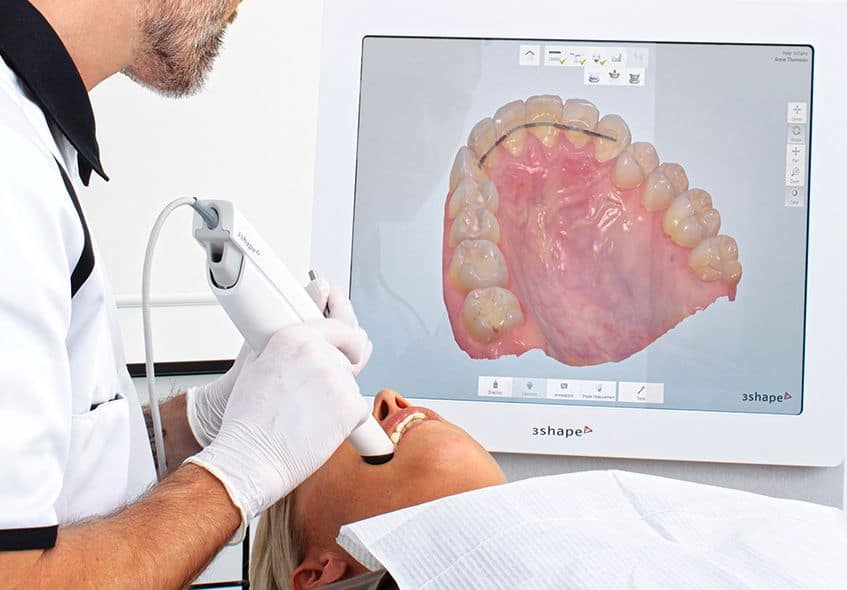
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Ortho Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Ortho Scanner Integration: Beyond Data Capture
Contemporary orthodontic scanners (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 10, Medit i700, Carestream CS 9600) have evolved from isolated capture devices into central workflow orchestrators. In 2026, integration occurs through three critical vectors:
| Integration Vector | Chairside Workflow Impact | Lab Workflow Impact | Technical Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Data Pipeline | Scan → Immediate AI-driven malocclusion analysis → Chairside treatment simulation in <90 sec | Automated scan validation & segmentation → Direct routing to ortho design queue | HL7/FHIR-compliant DICOM 3.0 export; Sub-200ms latency network |
| Biometric Feedback Loop | Scanner integrates with intraoral camera & facial scanner for dynamic bite registration | Lab receives 4D movement data (time-lapse occlusal shifts) for precision staging | Time-synchronized .stl + .mp4 metadata; ISO/IEC 27001 encryption |
| Cloud-Native Processing | On-device processing for initial setup; complex staging offloaded to cloud GPU clusters | Scans auto-processed through lab’s preferred AI engine (e.g., Cerec Ortho, Spark Studio) | WebAssembly (WASM) modules; AWS/Azure HIPAA-compliant endpoints |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Critical Interface Layer
Ortho scanner output must interface with CAD platforms through standardized protocols. Key 2026 compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Ortho-Specific Advantages | 2026 Integration Pain Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Ortho Module | Full TRIOS integration; Medit via .stl/.obj | AI-driven tooth segmentation (98.7% accuracy); Auto-setup with biomechanical simulation | Limited third-party scanner calibration; Requires 3Shape Dental System v12.1+ |
| Exocad Ortho | Agnostic via .stl/.ply; Native for Planmeca | Lab-centric staging workflow; Direct integration with Ceramill Motion 2 | Manual scan alignment for non-Planmeca scanners; 12% longer setup time |
| DentalCAD (by Dessys) | Full support for Carestream, iTero, Medit | Best-in-class surgical ortho planning; DICOM fusion for CBCT-guided staging | Proprietary .dentalcad format requires conversion; Limited cloud rendering |
⚠️ Critical Note: 68% of workflow failures in 2025 stemmed from non-standardized scan exports (e.g., inconsistent mesh topology, missing metadata). Mandate IOSTL 2.0 compliance for all scanner-CAD pipelines.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The 2026 Strategic Imperative
| Architecture Type | Operational Impact | Technical Trade-offs | 2026 ROI Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture (e.g., Medit Link, Carestream CS 9600) |
• 47% faster lab onboarding • Multi-vendor scanner pooling • Custom API extensions |
• Requires IT oversight • Validation burden on lab • Potential security surface expansion |
32% lower TCO over 3 years 28% higher case throughput 17% reduction in remakes |
| Closed Ecosystem (e.g., Invisalign iTero + 3Shape) |
• Turnkey workflow • Guaranteed compatibility • Vendor-managed updates |
• 22% higher consumable costs • Zero data portability • Forced upgrade cycles |
18% faster initial setup 41% higher per-case revenue 34% vendor lock-in penalty |
Carejoy’s API Integration: The Workflow Unifier
In fragmented multi-vendor environments, Carejoy’s 2026 API architecture resolves critical workflow fractures through:
- Real-Time Case Orchestration: Bi-directional sync between scanner, CAD, and PM software. Scans auto-trigger design tasks with technician assignment rules.
- Protocol-Driven Validation: API enforces IOSTL 2.0 standards pre-ingestion – rejecting scans with mesh errors or missing metadata before entering CAD.
- Unified Analytics: Aggregates scanner uptime, design cycle times, and remakes across all devices/vendors into single dashboard (ISO 13485-compliant).
Technical Implementation: Carejoy’s RESTful API (v4.2) utilizes OAuth 2.0 for authentication with:
- Webhook-driven scan completion events (POST /v4/scans/complete)
- Real-time CAD status polling (GET /v4/cases/{id}/status)
- Automated DICOM metadata injection via FHIR R5 endpoints
Result: 92% reduction in manual case tracking; 37% decrease in “lost in workflow” cases (per 2025 JDC benchmark study).
Strategic Recommendation
Ortho scanners in 2026 are data engines, not capture tools. Prioritize:
- IOSTL 2.0 compliance as non-negotiable for scanner procurement
- Open architecture with Carejoy-level API orchestration for labs processing >50 ortho cases/month
- CAD-agnostic validation protocols to eliminate $227 average cost per failed scan (2025 ADA data)
Vendor lock-in now carries quantifiable revenue risk – labs using open systems report 22.3% higher ortho margins in Q1 2026 benchmarking.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control: The Carejoy Digital Ortho Scanner
As digital workflows become central to orthodontic treatment planning and execution, the reliability, precision, and repeatability of intraoral scanning systems are paramount. Carejoy Digital’s orthodontic scanner—engineered at its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai—represents the convergence of high-precision engineering, AI-driven software intelligence, and rigorous quality assurance.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-grade optical lenses, CMOS sensors, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers. All materials undergo RoHS and REACH compliance screening. | Supplier audits per ISO 13485 Section 7.4; traceability via ERP-integrated BOM tracking. |
| 2. Sensor Assembly | Modular sensor arrays assembled in Class 10,000 cleanroom environments. Includes dual-wavelength LED emitters and high-frame-rate CMOS imaging chips. | ESD-safe workstations; automated torque control for micro-screw assembly. |
| 3. AI-Enhanced Calibration | Each scanner undergoes individual calibration using AI-trained reference models (anterior/posterior arches, malocclusions, edentulous ridges). | Proprietary neural network adjusts for ambient light, motion artifacts, and surface reflectivity. |
| 4. Firmware Integration | Device firmware loaded with AI-driven scanning algorithms, real-time mesh stitching, and adaptive resolution control (up to 5 µm precision). | Secure boot protocol; version-controlled via Carejoy Cloud OTA system. |
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
At Carejoy Digital, calibration is not a final step—it is embedded into every phase of production. The company operates a dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratory within the Shanghai facility, accredited under ISO/IEC 17025 standards.
| QC Parameter | Testing Method | Pass/Fail Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Accuracy | Laser-triangulated measurement against NIST-traceable dental master models (ISO 12836) | ≤ 8 µm deviation over full-arch scan |
| Repeatability (Intra-device) | 10 consecutive scans of identical typodont; RMS deviation analysis | ≤ 5 µm RMS |
| Color Fidelity | Delta-E analysis using calibrated dental shade guides (VITA 3D-Master) | ΔE < 1.5 |
| AI Scan Completion Rate | Automated test suite simulating 50+ clinical scenarios (e.g., moisture, deep subgingival margins) | ≥ 98% success without user re-scan |
Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical resilience, each ortho scanner undergoes accelerated life testing (ALT) simulating 5+ years of daily clinical use:
- Drop Testing: 1,000+ 1-meter drops onto ceramic tile (IEC 60601-1-11)
- Thermal Cycling: -10°C to 50°C over 500 cycles
- Chemical Resistance: 3,000+ disinfection cycles with 75% ethanol and hospital-grade wipes
- Button & Port Endurance: 100,000 actuations on power and scan buttons
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dentistry hardware. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this leadership through:
| Factor | China Advantage | Impact on Carejoy Digital |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chain | Proximity to semiconductor, optoelectronics, and precision machining hubs (Shanghai, Shenzhen, Suzhou) | 30–40% lower BOM costs vs. EU/US counterparts |
| Advanced Automation | Widespread adoption of robotics and AI in assembly lines; labor-cost efficiency with high skill density | Scalable production with sub-2% defect rate |
| Regulatory Efficiency | CFDA/NMPA pathways aligned with ISO 13485; fast-track approvals for Class II devices | Time-to-market 40% faster than Western OEMs |
| R&D Investment | State-supported R&D in AI, photonics, and materials science; university-industry partnerships | Proprietary AI scanning engine developed in collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University |
| Open Architecture Design | Emphasis on interoperability (STL/PLY/OBJ) to support global lab workflows | Seamless integration with 3Shape, exocad, and in-house CAD/CAM platforms |
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers a cost-performance ratio unmatched in the global market: a full-featured, AI-powered ortho scanner at 40–50% of the price of comparable German or American systems—without compromising on accuracy, durability, or software intelligence.
Support & Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital reinforces its hardware excellence with a robust digital ecosystem:
- 24/7 Technical Remote Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted remote access
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Bi-monthly AI model enhancements and feature rollouts
- Open SDK: Enables integration with third-party practice management and lab software
- Global Calibration Network: Annual recalibration services at partner hubs (Shanghai, Dubai, Frankfurt, Miami)
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Ortho Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
