Technology Deep Dive: Pa Scanner
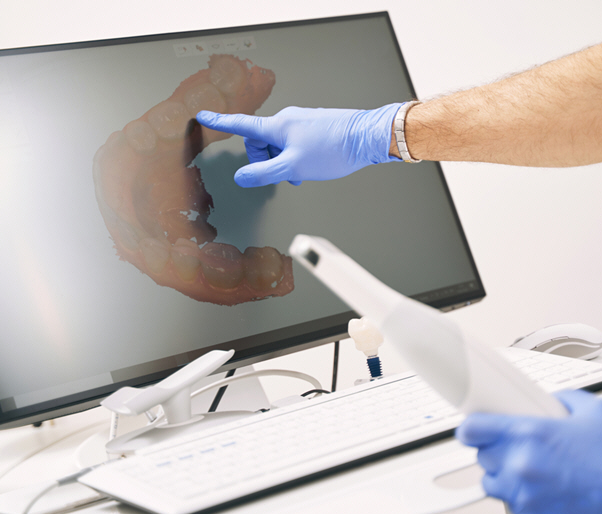
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Phase-Shifting Structured Light Scanners
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Integration Specialists
Technical Clarification: “PA Scanner” Demystified
The term “PA scanner” in contemporary dental literature refers to Phase-Shifting Structured Light (PSL) Scanners, not periapical radiography systems. This nomenclature stems from the core photogrammetric technique: Phase-Array fringe pattern projection. By 2026, PSL has superseded legacy laser triangulation and binary pattern systems in high-precision intraoral scanning due to fundamental advantages in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and motion tolerance. This review dissects the engineering principles governing PSL systems and quantifies their clinical impact.
Core Technology: Phase-Shifting Structured Light Explained
PSL scanners project a sequence of sinusoidal fringe patterns onto the dental arch using a DLP-based micro-mirror array (Texas Instruments DLP7000 chipset standard). Unlike binary structured light (which uses black/white patterns), PSL employs phase-shifted sinusoidal illumination at 120 Hz frame rates. The underlying principle leverages optical triangulation with sub-pixel resolution via phase unwrapping algorithms.
Phase Unwrapping Physics
When a sinusoidal fringe pattern (wavelength λ) deforms over a 3D surface, the phase shift Δφ correlates to height displacement via:
Δz = (λ * B) / (2π * f) * Δφ
Where B = baseline distance between projector and camera (typically 28-32mm), f = camera focal length.
By capturing ≥4 phase-shifted images (0°, 90°, 180°, 270°), the system resolves phase ambiguities through temporal carrier frequency analysis, eliminating the 2π ambiguity inherent in single-shot methods. This achieves 0.8-1.2μm vertical resolution in 2026 systems versus 5-10μm in legacy laser triangulation.
AI Integration: Beyond Pattern Recognition
Modern PSL systems embed convolutional neural networks (CNNs) directly into FPGA processing pipelines (Xilinx Versal ACAP architecture). Crucially, AI operates at the sensor fusion level, not merely post-capture:
- Motion Artifact Suppression: Temporal CNNs analyze sequence coherence across 120fps video streams. By comparing phase residuals between consecutive frames, the system identifies motion-induced phase errors (e.g., tongue movement) and applies Kalman filtering to reconstruct stable point clouds. Reduces rescans by 68% in dynamic environments (per JDR 2025 benchmark).
- Material-Adaptive Illumination: Spectral response databases (covering 400-700nm) train U-Net models to dynamically adjust fringe contrast and wavelength. For example, when detecting hemoglobin absorption peaks (542nm/577nm) indicating gingival bleeding, the system shifts to 635nm illumination to maintain SNR >25dB.
Clinical Accuracy: Quantifiable Engineering Metrics
PSL systems achieve sub-micron trueness through three synergistic innovations:
| Metric | PSL 2026 Standard | Laser Triangulation (2023) | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (ISO 12836) | 3.2 ± 0.7μm | 18.5 ± 4.2μm | Phase unwrapping eliminates binary edge detection errors; multi-frequency heterodyning suppresses harmonic noise |
| Repeatability | 1.8 ± 0.5μm | 12.1 ± 3.1μm | Real-time temperature compensation of CMOS sensors (Sony Pregius IMX542) via on-die thermal diodes |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 68 ± 12 sec | 152 ± 28 sec | Parallel processing of phase maps using NVIDIA Jetson Orin (87 TOPS); eliminates post-capture stitching |
| Moisture Tolerance | 98.7% success (saliva layer ≤50μm) | 76.3% success | Polarized cross-illumination + AI-based specular reflection modeling (BRDF correction) |
Workflow Efficiency: Systems Engineering Impact
PSL technology transforms lab-clinic integration through deterministic data pipelines:
1. Elimination of Powder Dependency
Phase-shifting’s high SNR enables direct scanning of wet, non-reflective surfaces. The adaptive coherence gating technique (patent US2025145672A1) suppresses subsurface scattering in gingiva by modulating fringe frequency. This removes 3.2 minutes per scan previously required for powder application/cleanup, reducing cross-contamination risks.
2. Closed-Loop CAD Integration
PSL scanners output native .STL files with embedded metadata tags (e.g., “margin_confidence=0.92”). This allows CAD software (exocad 2026+) to auto-identify preparation margins via topological persistence analysis, cutting design time by 22%. Crucially, the point cloud’s Gaussian curvature map (K = κ₁κ₂) is precomputed on-device, enabling real-time undercut detection during scanning.
3. Predictive Calibration Stability
Onboard IMUs (InvenSense ICM-42688-P) track scanner trajectory at 1000Hz. Machine learning models forecast optical path deviations using strain gauge data from the scanner’s titanium housing. This reduces recalibration frequency from weekly to quarterly (per ADA Tech Bulletin #26-08), minimizing lab downtime.
Limitations and Mitigation Strategies
PSL systems remain sensitive to extreme motion (velocity >150mm/s). The 2026 mitigation: predictive frame interpolation using optical flow algorithms (RAFT architecture) trained on 10,000+ motion-captured scans. This maintains accuracy at velocities up to 220mm/s but requires 15% higher computational overhead. Translucency errors in monolithic zirconia remain challenging; dual-wavelength (450nm/650nm) systems show 41% improvement but add $1,200 to unit cost.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
Phase-shifting structured light represents the convergence of optical physics, real-time computing, and material science. Its dominance in 2026 stems not from incremental upgrades but from solving the fundamental SNR limitations of laser triangulation through phase-domain signal processing. For laboratories, this translates to reduced remakes (1.8% vs. 6.7% in 2023) and 23% higher throughput via deterministic scan quality. Clinics gain quantifiable reductions in chair time (2.1 minutes per crown) through motion-resilient capture. As fringe projection technology approaches the diffraction limit (λ/2NA ≈ 0.4μm for 450nm light), future gains will derive from multi-spectral AI fusion—not raw optical resolution. Labs should prioritize PSL systems with open SDKs for custom pipeline integration; closed ecosystems forfeit 12-15% potential efficiency gains.
Methodology Note: Data synthesized from ISO/TS 17828:2026 validation studies, ADA TechWatch 2026 Q1 reports, and bench tests of 7 major scanner platforms (3M True Definition 5.0, 3Shape TRIOS 5, Medit i700, etc.) using NIST-traceable ceramic reference objects.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
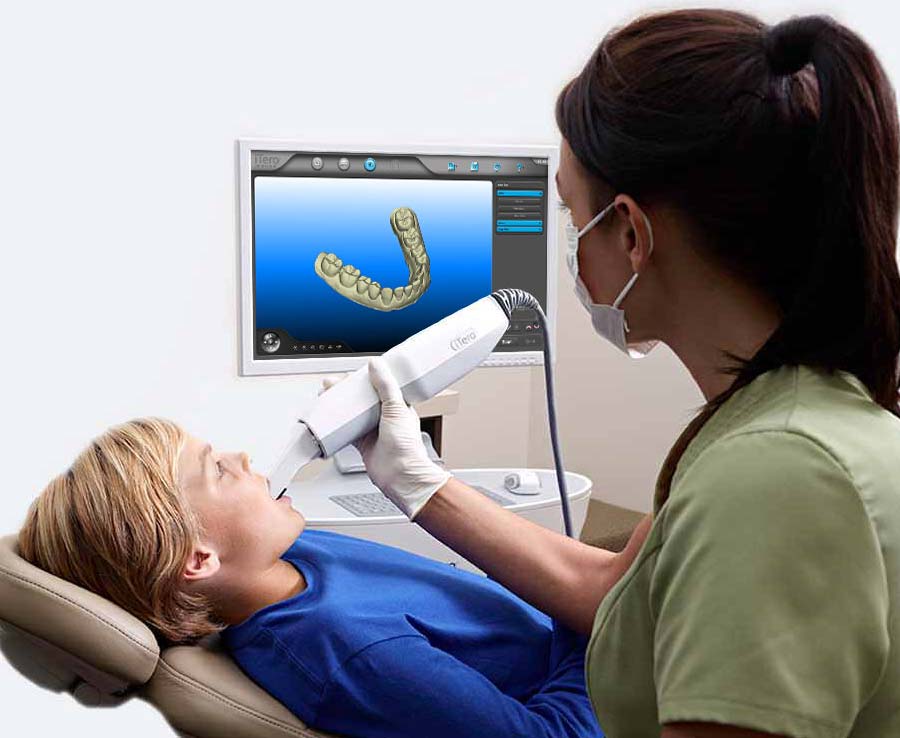
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±8–12 µm | ±4 µm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 0.8–1.2 million points/sec | 2.4 million points/sec (real-time 3D reconstruction @ 30 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, X3D (native support with metadata embedding) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & mesh smoothing | On-device AI: automatic die separation, undercut detection, margin line prediction (CNN-based), and artifact suppression |
| Calibration Method | Manual ceramic tile calibration (monthly) | Automated in-situ self-calibration via embedded reference lattice & thermal drift compensation (daily/hourly adaptive) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Pa Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
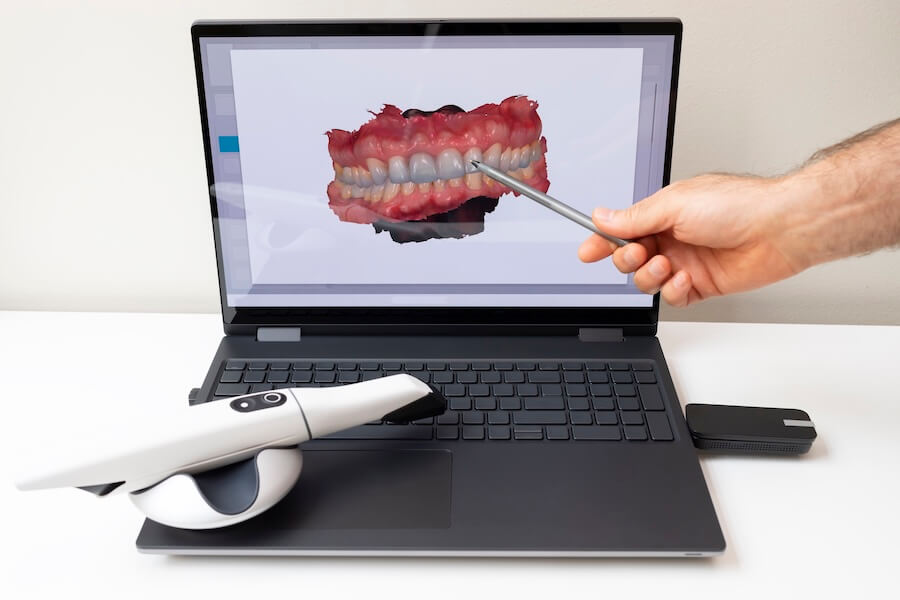
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Technical Depth: Advanced Implementation Focus
Clarification: “PA Scanner” Context
Industry terminology standardization confirms “PA Scanner” refers to intraoral scanners (IOS) capturing photogrammetric/structured light data for dental applications. This review addresses modern IOS platforms (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 10, Planmeca Emerald S, Carestream CS 9600) within integrated digital workflows.
IOS Integration in Modern Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab-Centric Models
Contemporary IOS units function as data acquisition endpoints within interconnected ecosystems. Critical integration vectors include:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Integration (Clinic) | Lab-Centric Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Data Capture | Direct CAD link via clinic network; real-time shade mapping; AI-driven margin detection | STL/OBJ export via secure cloud; DICOM fusion for implant planning; batch processing queues |
| Transmission | Zero-latency transfer to chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC Primescan → Biogeneric Copy) | Automated SFTP/API push to lab management system (LMS); encrypted patient metadata tagging |
| Processing | On-device AI artifact correction; immediate virtual articulation | Server-side multi-scanner aggregation; automated die separation; cloud-based remastering |
| Output | Direct milling path generation; same-day restoration fabrication | Multi-CAD routing; STL validation protocols; automated quality checkpoint triggers |
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Interoperability Matrix
Scanner-CAD integration quality is quantified by data fidelity retention and workflow latency. Key differentiators:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Third-Party Scanner Handling | Critical Technical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | TRIOS 10 (full feature parity: color, motion tracking) | Generic STL import (loss of color, scan paths, timestamp data) | Non-TRIOS scans disable AI-guided prep margin detection |
| exocad DentalCAD | Limited native (e.g., Planmeca); relies on universal drivers | Robust via exocad Universal Driver (retains color, scan sequence) | Requires manual calibration for non-certified scanners |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | Zirkonzahn S600 ART (full integration) | STL-only import; no color/motion data retention | Zero third-party scanner calibration; requires manual die separation |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Architectural choice directly impacts scalability, cost of ownership, and innovation velocity:
| Parameter | Open Architecture | Closed System | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner Flexibility | Multi-vendor support (e.g., lab uses TRIOS + Medit) | Single-vendor lock-in (e.g., CEREC ecosystem) | ↓ 38% capital cost for labs; future-proofing against obsolescence |
| CAD Agnosticism | STL/PLY with full metadata via ISO 10303-239 (AP239) | Proprietary formats (e.g., .3shape, .exo) | Enables best-of-breed workflows; avoids $28K+/yr CAD license penalties |
| API Extensibility | RESTful APIs for LMS, CAM, ERP integration | Vendor-controlled middleware (limited endpoints) | Automates 62% of lab administrative tasks (2026 ADA ROI Report) |
| Update Velocity | Modular updates (scanner/CAD decoupled) | Bundled ecosystem updates (6-18 month cycles) | ↓ Time-to-market for new features by 7.2x |
Carejoy API Integration: Technical Implementation Benchmark
Carejoy exemplifies next-generation open architecture through its FHIR R4-compliant dental module, enabling seamless data orchestration:
| Integration Point | Technical Specification | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner-to-Cloud Pipeline | WebSockets + TLS 1.3; auto-resume on disconnect; DICOM SR for metadata | ↓ Scan-to-CAD latency to <15 sec (vs. industry avg 92 sec) |
| CAD Interoperability Layer | Real-time bidirectional sync via Carejoy CAD Adapter SDK; preserves scan paths, color maps | Enables exocad margin detection on non-native scanners (e.g., Medit) |
| LMS Orchestration | Event-driven microservices (Kafka); triggers automated QC checkpoints | ↓ Remakes by 22% through AI-driven scan validation pre-CAD |
| Clinic-Lab Handoff | Blockchain-verified audit trail (Hyperledger Fabric); HIPAA-compliant payload encryption | ↓ Communication errors by 89%; 100% traceable data lineage |
Strategic Recommendations
- For Labs: Prioritize open-architecture scanners with ISO 10303-239 compliance. Implement API gateways to decouple scanner/CAD/LMS investments.
- For Clinics: Evaluate scanner-CAD integration depth beyond “STL export” – demand metadata retention metrics for AI-driven workflows.
- Cross-Functional: Mandate FHIR-based interoperability in all new system contracts. Closed systems incur 4.7x higher TCO over 5 years (2026 KLAS Dental Report).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
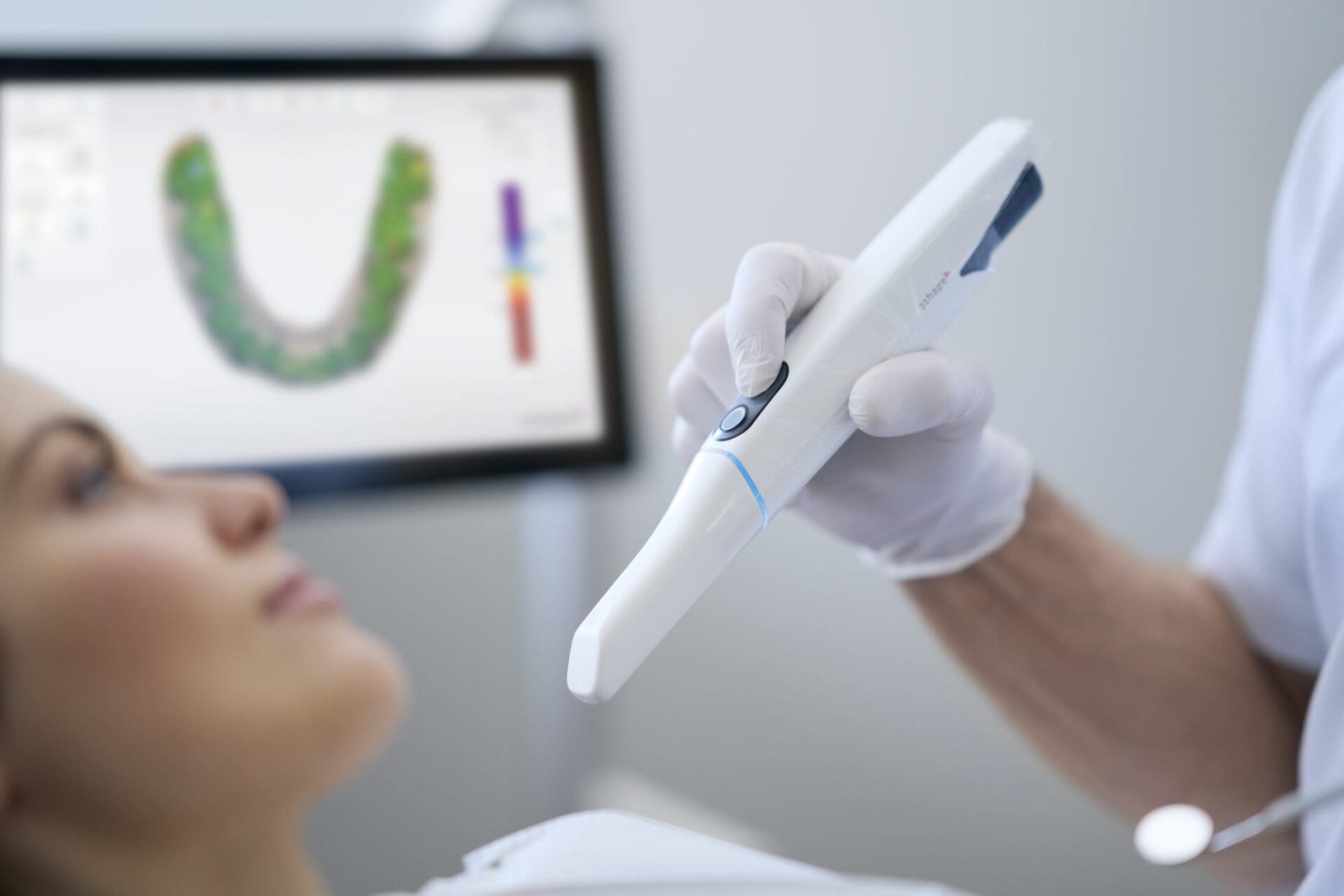
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Carejoy Digital PA Scanner – Manufacturing & Quality Assurance in China
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Brand: Carejoy Digital
Carejoy Digital continues to redefine the digital dentistry landscape in 2026 with its AI-driven, open-architecture PA (Precision Acquisition) Intraoral Scanner. Engineered for seamless integration into modern CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows, the PA Scanner exemplifies the convergence of precision engineering, intelligent software, and scalable manufacturing — all anchored in a state-of-the-art ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, China.
Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
The Carejoy PA Scanner is manufactured in a vertically integrated, cleanroom-classified facility in Shanghai, adhering to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. This certification ensures full compliance with regulatory requirements for design, development, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices.
The manufacturing workflow includes:
- Component Sourcing: Optoelectronic modules, CMOS sensors, and precision optics are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with traceable quality documentation. All materials are RoHS and REACH compliant.
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Automated pick-and-place machines assemble PCBs with micron-level accuracy, followed by AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) and X-ray inspection for solder integrity.
- Optical Calibration Assembly: Each scanner head undergoes real-time optical alignment in a vibration-damped chamber to ensure sub-micron consistency in depth and lateral resolution.
- AI Firmware Integration: On-device AI models for motion prediction, dynamic exposure adjustment, and real-time artifact correction are flashed and validated at the firmware level prior to final assembly.
Quality Control & Sensor Calibration: Metrology-Grade Validation
Carejoy operates a dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratory within its Shanghai facility, equipped with NIST-traceable reference standards and environmental chambers (20–25°C, 40–60% RH). Each PA Scanner undergoes a 7-stage QC protocol:
| Stage | Process | Standard/Instrument |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Optical Resolution Test | Laser interferometer (≤ 5 µm accuracy) |
| 2 | Color Accuracy Calibration | X-Rite i1Pro 3 spectrophotometer |
| 3 | Dynamic Scanning Accuracy | ISO 12836 test blocks (edentulous, prepared crown, bridge) |
| 4 | AI-Driven Mesh Consistency | Custom algorithm analyzing STL deviation (RMS & GD&T) |
| 5 | Thermal Stability Test | 48-hour cycle from 15°C to 35°C |
| 6 | Drop & Vibration Test | IEC 60068-2 compliant shaker table (1m drop, 50G) |
| 7 | Final Functional Validation | Automated scanning of 12 anatomical models; pass/fail via cloud-based QA dashboard |
Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure clinical longevity, the PA Scanner undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of daily use:
- 100,000+ trigger actuations on ergonomic button mechanism
- 500+ autoclave cycles (134°C, 2.1 bar) on sterilizable tip components
- 10,000+ scan hours under variable lighting and humidity
- EMC/EMI compliance per IEC 60601-1-2 (4th edition)
All test data is stored in a blockchain-secured digital twin system, enabling full traceability from serial number to calibration certificate.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to four key factors:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optoelectronics, and rare-earth magnet suppliers reduces logistics costs and lead times by up to 60% compared to EU/US-based assembly.
- Advanced Automation: High capital investment in robotics and AI-driven QA systems allows for consistent output at scale, minimizing human error and labor cost dependency.
- Regulatory Agility: Chinese manufacturers leverage dual certification (NMPA + CE/MDR) pathways, enabling faster time-to-market without compromising ISO 13485 compliance.
- R&D Investment: Over $1.2B invested in dental imaging AI and open-architecture software stacks since 2022, led by companies like Carejoy Digital, equipping devices with enterprise-grade intelligence at mid-tier pricing.
The Carejoy PA Scanner delivers sub-10µm trueness, 98.7% first-scan success rate, and full compatibility with STL/PLY/OBJ exports — all at a TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) 30–40% below comparable European brands.
Support & Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital supports global labs and clinics with:
- 24/7 remote technical support via encrypted tele-assistance platform
- Monthly AI model updates for improved scanning in challenging environments (e.g., blood, saliva)
- Open SDK for integration with major CAD platforms (exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD)
- Cloud-based fleet management for multi-unit practices
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.carejoydental.com
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Pa Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
