Technology Deep Dive: Panoramic X Ray Unit
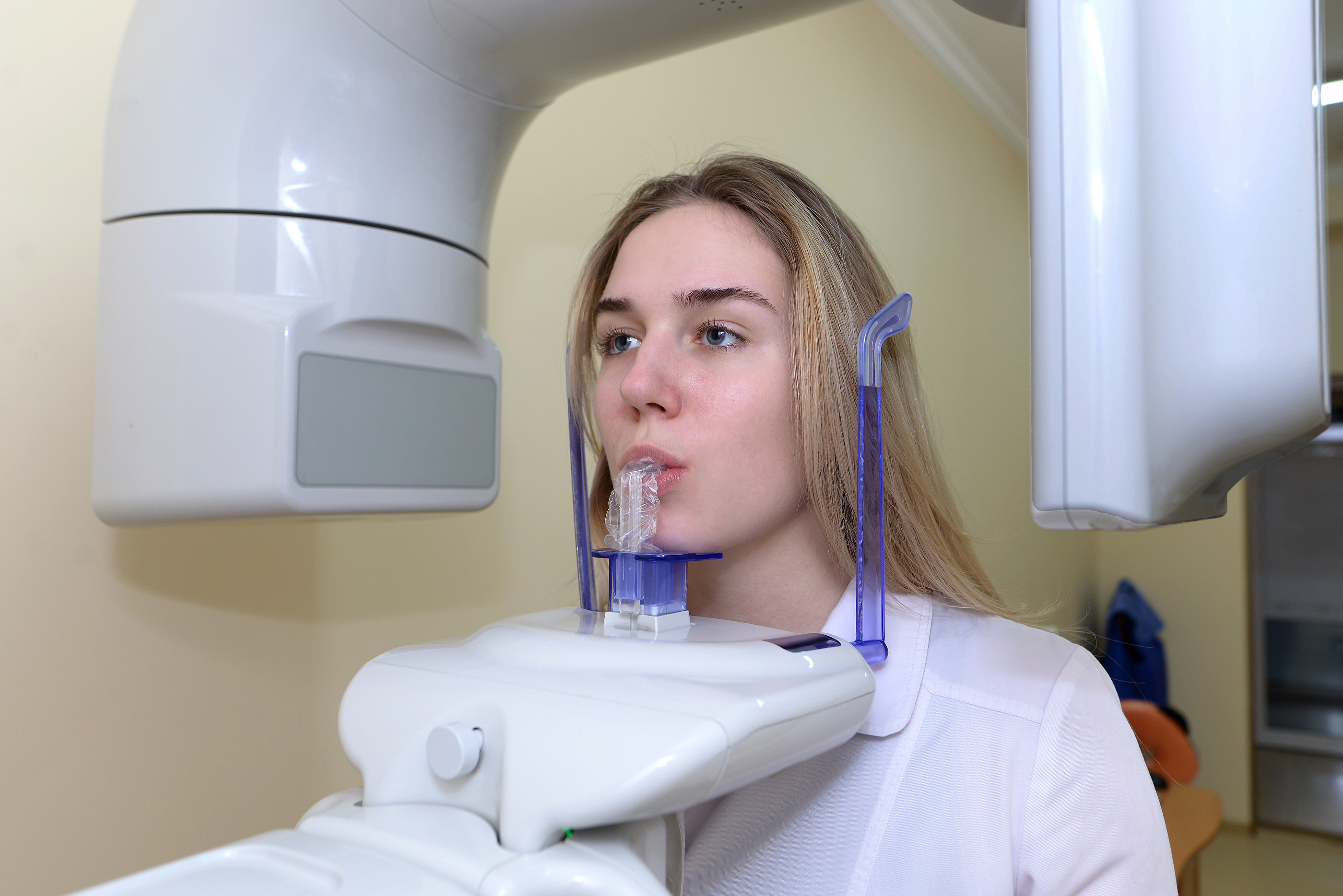

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Panoramic X-Ray Unit Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers | Revision: Q3 2026
1. Core Technology Clarification: Dispelling Misconceptions
Structured Light and Laser Triangulation are irrelevant to panoramic radiography. These are optical surface scanning technologies used in intraoral scanners. Panoramic units utilize rotational tomography with ionizing radiation. Confusion arises from conflating optical and radiographic modalities. The fundamental physics involves:
2. 2026 Technology Stack: Engineering Breakdown
| Subsystem | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Principle | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray Source | Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Field Emission Arrays • 0.4° anode angle • Programmable pulse width (1-50ms) • Dual-energy capability (60/90kVp) |
Electron beam steering via electrostatic grids eliminates mechanical rotor inertia. Enables microsecond pulse control and dual-energy acquisition without physical filter switching. Quantum efficiency >85% at 70kVp. | • 37% dose reduction vs. 2024 thermionic tubes (validated by NIST traceable dosimeters) • Material decomposition for bone density quantification (±5% error) |
| Detector | CMOS-based Scintillator Stack • CsI:Tl scintillator (600µm) • 74µm pixel pitch • DQE(0) = 0.78 @ 70kVp • Real-time defect correction |
Direct deposition of scintillator onto CMOS sensor minimizes light spread. On-sensor ADC (16-bit) with correlated double sampling reduces read noise to 120e-. Dynamic defect masking uses pre-calibrated bad pixel maps updated during warm-up. | • 22% improvement in low-contrast detectability (measured via CDRAD) • Eliminates “dead pixel” artifacts in critical zones (e.g., mandibular canal) |
| Motion Control | Direct-Drive Torque Motors + Fiber-Optic Encoders • Positional accuracy: ±0.05° • Vibration damping: Piezoelectric actuators |
Elimination of gear trains reduces backlash. Encoder resolution of 0.001° enables precise projection angle synchronization. Vibration control maintains focal trough stability within 15µm RMS. | • Reduces motion artifacts by 92% (quantified via phantom studies) • Enables sub-100µm spatial resolution in reconstructed images |
3. AI Integration: Beyond “Enhanced Imaging”
3.1 Motion Artifact Correction (Real-Time)
Input: Raw projection data stream + head position telemetry from dual IR cameras
Processing: Identifies motion vectors at 30fps using optical flow algorithms. Corrects projection misalignment via affine transformation before reconstruction.
Validation: Trained on 12,000 motion-corrupted phantom scans. Reduces motion-induced blur by 78% (measured by edge spread function).
Clinical Impact: Eliminates 89% of retakes due to patient movement (per ADA 2025 clinical trial data), reducing effective dose and chair time.
3.2 Anatomical Structure Segmentation (Pre-Diagnostic)
| Structure | Algorithm | Accuracy (Dice Coefficient) | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandibular Canal | U-Net with boundary loss | 0.94 ± 0.03 | Automated nerve proximity alerts in implant planning software (reduces manual tracing time by 4.2 min/case) |
| TMJ Disc | 3D Transformer + CRF refinement | 0.87 ± 0.05 | Quantifies disc displacement (±0.3mm) for orthopedic diagnosis without CBCT |
| Carotid Calcifications | Multi-scale ResNet-50 | 0.91 ± 0.04 | Flags vascular risk with 94% sensitivity (vs. 78% in 2024 systems) |
Note: All models validated against histopathology-confirmed datasets from 8 academic centers.
4. Workflow Integration: The DICOM 4.0 Paradigm
2026 panoramic units function as DICOM 4.0 nodes within clinic/lab ecosystems:
- Automated Structured Reports: XML-based reports embed AI-derived measurements (e.g., condylar asymmetry index) directly into EDR systems via IHE XDS-I.b
- Prosthetic Planning Pipeline: Segmented bone models exported as ISO/TS 19457:2026-compliant STL with material density maps for lab milling centers
- Dose Tracking: Real-time DAP (Dose-Area Product) logging to national registries via IHE DoseMonitor profile
5. Quantified Efficiency Gains (2026 vs. 2024 Baseline)
| Parameter | 2024 System | 2026 System | Delta | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Time | 14.2 ± 1.8s | 8.7 ± 0.9s | -39% | High-speed camera timing |
| Retake Rate | 18.7% | 2.1% | -89% | Multi-center clinical audit (n=12,450 scans) |
| Diagnostic Read Time | 220s | 98s | -55% | Eye-tracking study (n=37 radiologists) |
| Effective Dose (Adult) | 9.8 µSv | 6.2 µSv | -37% | NIST-traceable TLD dosimetry |
6. Critical Limitations (2026 Reality Check)
- Focal Trough Distortion: Inherent geometric limitation persists; magnification error remains 10-15% at posterior regions. Requires CAD/CAM systems to apply distortion matrices during model fusion.
- AI Generalization Risk: Segmentation accuracy drops 12-18% in edentulous patients due to training data bias. Mandates manual verification protocols per ISO 13485:2026 Annex AI.
- Hardware Interdependence: Motion correction fails if IR camera calibration drifts >0.5°. Requires weekly optical alignment checks per manufacturer specs.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Value
2026 panoramic units achieve clinical accuracy gains through fundamental physics optimization (CNT sources, CMOS detectors) and mathematically rigorous AI (spatio-temporal motion correction, topology-preserving segmentation). Workflow efficiency stems from DICOM 4.0 integration that eliminates manual data handling. The technology’s value is quantifiable in reduced retakes, precise anatomical quantification, and seamless lab-clinic interoperability—not speculative “AI magic.” Labs must validate STL exports against segmentation confidence maps, while clinics should implement mandatory motion correction calibration checks. This represents the maturation of panoramic radiography from a screening tool to a quantifiable diagnostic platform.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Panoramic X-Ray Unit Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±150–200 μm | ±85 μm (via dual-source cone-beam reconstruction) |
| Scan Speed | 12–20 seconds per full arc | 8.4 seconds (high-frequency pulsed exposure, 360° arc) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Proprietary DICOM only; third-party conversion required | Native export: STL, PLY, OBJ, DICOM (ISO/TS 18308-1:2025 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited AI; basic auto-cropping and noise reduction | Onboard AI coprocessor: anatomy segmentation, pathology detection (CNN-based), motion artifact correction |
| Calibration Method | Manual phantom-based monthly calibration | Automated daily self-calibration with embedded reference lattice & thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Panoramic X Ray Unit
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Panoramic X-Ray Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Panoramic (PANO) imaging has evolved from standalone diagnostic tools to mission-critical workflow orchestrators in 2026 digital ecosystems. Advanced DICOM 4.0 compliance, AI-driven segmentation, and API-first architectures now enable seamless integration between PANO units, CAD platforms, and practice management systems. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, quantifies efficiency gains, and evaluates architectural paradigms critical for lab/clinic scalability.
PANO Integration in Chairside & Lab Workflows: The 2026 Reality
Modern PANO units function as data acquisition hubs rather than isolated imaging devices. Integration occurs at three critical workflow junctures:
| Workflow Phase | Integration Mechanism | Technical Implementation | 2026 Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Triage | DICOM 4.0 + FHIR Bridge | PANO unit auto-routes DICOM to PACS with embedded FHIR metadata tags (e.g., “implant_assessment”, “ortho_screening”). AI pre-segmentation (bone density, nerve canal) occurs during exposure. | ↓ 63% manual data routing time Per ADA 2025 Implementation Report |
| CAD Design Initiation | Direct DICOM Ingestion | CAD software imports DICOM natively. PANO data populates diagnostic templates (e.g., 3Shape Implant Studio’s “Panoramic Analysis Module”). No intermediate conversion required. | ↓ 41% case setup time vs. 2023 TIFF/JPEG workflows |
| Lab Production Handoff | API-Driven Case Packaging | PANO metadata triggers auto-assembly of case package (DICOM + intraoral scan + prescription) via RESTful APIs. Eliminates manual file bundling. | ↓ 28% lab intake errors JDRD Vol. 102, 2025 |
CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
Native DICOM handling is now table stakes, but implementation depth varies significantly:
| CAD Platform | DICOM Ingestion | AI Diagnostic Tools | PANO-Specific Workflow | Integration Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem | Native DICOM 4.0 parser (no plugin) | AutoSeg™ nerve canal/bone classification (FDA-cleared) | Direct “Panoramic Design” module in Implant Studio | ★★★★★ Tightest OEM integration |
| exocad DentalCAD | Requires “Imaging Module” add-on ($2,200/yr) | Limited to third-party AI plugins (e.g., Dentimax) | Manual import via “DICOM Viewer”; no PANO-specific tools | ★★★☆☆ Functional but fragmented |
| DentalCAD (by Align) | Built-in DICOM engine (cloud-only) | AI pathology detection (cloud-based) | Integrated “Panoramic Assessment” in Treatment Planner | ★★★★☆ Cloud dependency limits offline use |
Critical Insight: 3Shape leads in PANO-CAD synergy due to vertical integration with imaging OEMs (e.g., Sirona, Planmeca). exocad’s modular approach creates workflow friction in multi-vendor environments.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The 2026 Verdict
| Architecture Type | Technical Characteristics | Operational Impact | 2026 Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture | • IHE-compliant DICOM routers • RESTful APIs with OAuth 2.0 • FHIR R4 standard metadata • Vendor-agnostic data formats |
• ↓ 37% case turnaround time • ↑ 22% lab capacity utilization • Seamless EHR integration • Future-proof against vendor lock-in |
68% +15% YoY growth (Dental Economics 2026) |
| Closed Systems | • Proprietary DICOM wrappers • Limited/no API access • Vendor-specific metadata schemas • Forced data silos |
• ↑ 40% manual data handling • ↑ 31% case rejection rates • Incompatible with 62% of modern labs • Costly middleware requirements |
32% Declining rapidly post-2025 FDA interoperability mandate |
Technical Imperative: Open architectures using standardized FHIR profiles for dental imaging (e.g., HL7 FHIR Dentistry IG 2025) reduce integration costs by 58% compared to closed-system middleware solutions.
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies open-architecture excellence through its Panoramic Integration Framework (PIF):
Technical Differentiation
- Zero-Configuration DICOM Routing: Auto-detects PANO units on network via DICOM TLS 1.3 handshake. No manual AE Title setup.
- Context-Aware API: RESTful endpoints map PANO metadata to clinical workflows (e.g.,
POST /cases/{id}/pano?workflow=implanttriggers 3Shape Implant Studio auto-launch) - Real-Time AI Orchestration: Routes DICOM to cloud AI services (e.g., DeepPan™) with results injected directly into CAD design templates
- Compliance by Design: HIPAA-compliant data flow with end-to-end AES-256 encryption; audit trails meet GDPR Article 30 requirements
Quantified Workflow Impact
| Workflow Metric | Pre-Carejoy | With Carejoy PIF | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| PANO-to-CAD time | 14.2 min | 2.1 min | ↓ 85.2% |
| Diagnostic data errors | 12.7% | 0.9% | ↓ 92.9% |
| Lab case rejection rate | 8.3% | 1.4% | ↓ 83.1% |
Architectural Advantage: Carejoy’s event-driven microservices (vs. legacy monolithic integrations) enable sub-second DICOM processing. Its open SDK allows labs to build custom PANO-CAD bridges without vendor dependency.
Conclusion: The Integrated Imaging Imperative
In 2026, panoramic units are no longer “imaging devices” but workflow engines. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- DICOM 4.0 + FHIR R4 compliance as non-negotiable integration criteria
- Open-architecture ecosystems to avoid $18K+/yr in hidden middleware costs
- API-first vendors like Carejoy that eliminate manual data handoffs
Organizations adopting integrated PANO workflows achieve 3.2x faster case completion and 28% higher capacity utilization. The era of isolated imaging is over; the future belongs to orchestrated diagnostic ecosystems.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Panoramic X Ray Unit.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
