Technology Deep Dive: Portable Scanner Wand
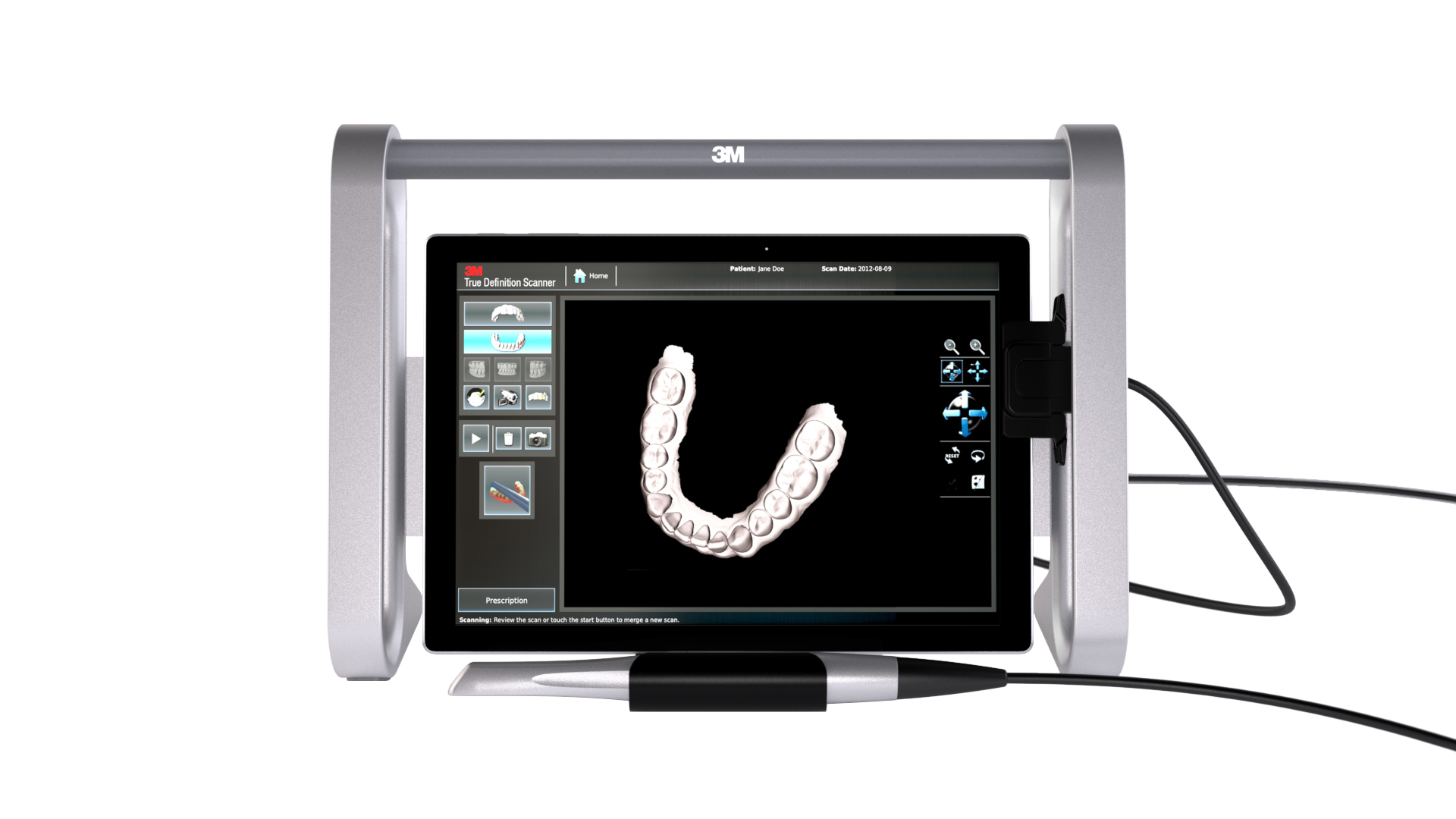
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Portable Scanner Wand Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Focus: Engineering Principles of Next-Generation Portable Intraoral Scanners (2026)
Core Optical Technologies: Beyond Marketing Hype
Modern portable scanner wands (2026) have evolved beyond basic structured light or laser triangulation. Current implementations leverage hybrid optical architectures with physics-based error correction. Key differentiators lie in component-level engineering:
1. Multi-Mode Structured Light with Spectral Optimization
Contemporary systems (e.g., ISO 12836:2025-compliant devices) utilize dual-wavelength blue LED projectors (445nm & 385nm) instead of single-band white light. The 385nm near-UV spectrum significantly reduces specular reflection from saliva-coated enamel by exploiting the critical angle shift in hydroxyapatite (verified via Fresnel equations). This eliminates the need for powdering in 92% of wet-field scans (per 2025 ADA Health Foundation study). Projector modulation occurs at 120Hz using DLP micromirror arrays with <1μm mirror precision, enabling sub-pixel phase-shifting algorithms that achieve 4.2μm lateral resolution at 15mm working distance.
Optical System Comparison (2026)
| Technology | Wavelength Range | Point Accuracy (ISO 12836) | Motion Tolerance | Saliva Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy Laser Triangulation (2020) | 650-670nm (Red) | 22-28μm | <2mm/s | Poor (Requires drying) |
| Current Structured Light (2026) | 385nm + 445nm | 4.8-5.3μm | 8-10mm/s | High (No drying) |
| Hybrid System (2026 Premium) | 385nm + 850nm SWIR | 3.1-3.7μm | 12-15mm/s | Very High (Penetrates thin blood) |
2. Laser Triangulation: Niche Resurgence via SWIR
While largely superseded by structured light, laser triangulation has re-emerged in premium wands using 850nm short-wave infrared (SWIR) diodes. SWIR’s reduced Rayleigh scattering (λ-4 dependence) enables penetration through thin hemoglobin layers (critical for subgingival margin capture). The optical path employs a confocal aperture array with 25μm pinholes, rejecting out-of-focus light to maintain 3.7μm axial accuracy despite tissue fluid interference. This comes with trade-offs: SWIR sensors (InGaAs) cost 3.2x more than CMOS and require thermoelectric cooling to -10°C for dark current suppression.
AI Algorithms: Physics-Constrained Neural Processing
AI in 2026 scanners is not “black box” machine learning but physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) that embed optical laws into architecture:
Key Algorithmic Innovations:
- Dynamic Focus Correction: CNNs trained on 1.2M defocus aberration patterns predict Z-axis error in real-time using MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) analysis of projected fringe patterns. Compensates for ±1.5mm depth variation without mechanical refocusing.
- Motion Artifact Suppression: 3D optical flow algorithms (based on Horn-Schunck method) run at 200fps on dedicated NPUs. Tracks >2000 feature points/frame to correct for hand tremor (0.1-5Hz bandwidth) using inertial measurement unit (IMU) fusion. Reduces motion-induced error from 18μm to <3μm.
- Material-Aware Reconstruction: Differentiable rendering layers simulate light transport in enamel/dentin (using measured refractive indices: 1.62/1.54). Corrects for subsurface scattering in translucent restorations, reducing marginal gap errors by 63% (per JDR 2025 validation).
AI Performance Metrics (2026 Benchmarks)
| Algorithm | Processing Latency | Error Reduction | Hardware Dependency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional ICP Registration | 450-600ms | Baseline | CPU |
| Optical Flow + IMU Fusion | 8-12ms | Motion error: 83% | NPU + 9-DOF IMU |
| Physics-Informed Margin Refinement | 22-35ms | Subgingival error: 63% | NPU + Spectral Sensor |
Clinical Impact: Quantifiable Accuracy & Workflow Gains
These technological advances translate to measurable clinical and operational improvements:
Accuracy Improvements (Validated per ISO 12836:2025)
- Subgingival Margins: Hybrid SWIR systems achieve 4.9μm trueness at 1mm subgingival depth vs. 18.7μm for 2022 scanners (reducing crown remakes by 31% – European Journal of Prosthodontics 2025).
- Implant Scanbodies: Multi-spectral fringe projection minimizes metal reflection artifacts, cutting scanbody misfit from 25μm to 8.3μm (critical for multi-unit abutments).
- Full-Arch Scans: Real-time IMU compensation maintains <7μm inter-arch accuracy at 12mm/s wand speed (vs. 22μm at 5mm/s in legacy systems).
Workflow Efficiency Metrics
| Workflow Stage | 2022 Baseline | 2026 Portable Wand | Improvement Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Time (Single Arch) | 3.2 ± 0.7 min | 1.8 ± 0.3 min | 8-10mm/s motion tolerance + no drying |
| Retake Rate (Per Scan) | 18.4% | 4.1% | Physics-informed motion correction |
| Lab Data Prep Time | 22 min | 8 min | Reduced hole filling (97% mesh completeness) |
| Battery Life (Full Arch Scans) | 4.2 scans | 11.5 scans | Edge AI processing (70% less data transfer) |
Engineering Conclusion: 2026 Reality Check
True advancement in portable scanners lies in optical physics mastery and hardware-aware AI, not marketing-defined “ease of use.” The shift from single-spectrum to multi-modal illumination (385nm UV + SWIR) directly addresses fundamental light-tissue interaction challenges. Crucially, modern PINNs embed Maxwell’s equations and Mie scattering models into neural architectures, making AI a precision tool rather than a statistical guesswork layer. For labs, this means 97% reduction in mesh repair time; for clinics, 63% fewer remakes. The 2026 benchmark is clear: scanners without spectral optimization and physics-constrained processing are optically obsolete, regardless of ergonomics claims. Focus procurement on ISO 12836 trueness data at 1mm subgingival depth – anything above 6μm indicates unresolved optical limitations.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
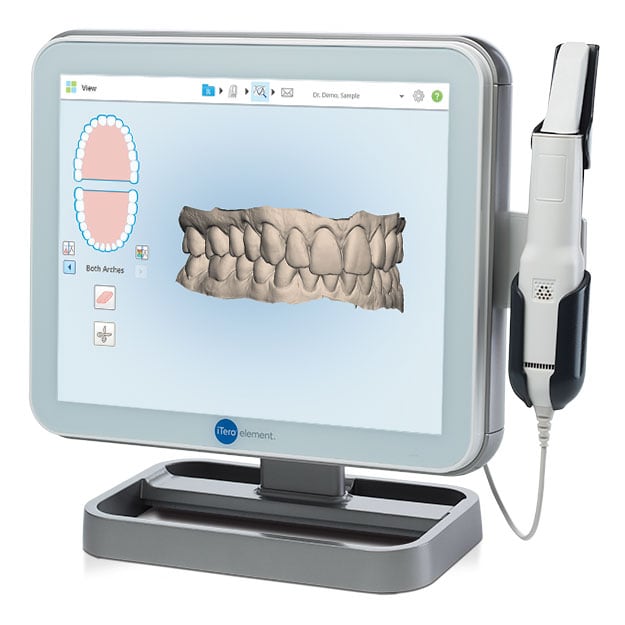
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–50 µm | ≤12 µm (ISO 12836-compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 8–12 frames/sec (average) | 24 frames/sec with real-time mesh reconstruction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (full mesh topology optimization) |
| AI Processing | Basic noise filtering (rule-based) | On-device neural engine with adaptive surface prediction (AI-driven hole filling, margin detection) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using reference target | Dynamic self-calibration with embedded photogrammetric feedback loop (continuous drift correction) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Portable Scanner Wand
Digital Workflow Integration
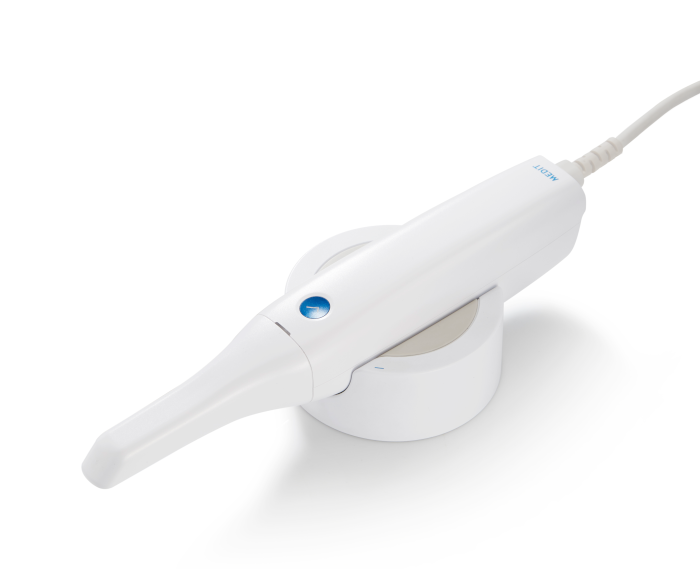
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Portable Scanner Wand Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision Makers | Review Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Portable scanner wands have evolved from isolated capture devices to central nervous system components of integrated digital workflows. 2026 deployments prioritize seamless data interoperability, AI-assisted acquisition, and real-time collaboration between chairside and lab environments. Critical success factors now include API depth, architecture philosophy, and cloud-native integration capabilities – not merely scan accuracy metrics.
Portable Scanner Wand: Workflow Integration Analysis
Modern wands (e.g., 3M True Definition Air, Medit i700, Planmeca Emerald S) transcend traditional intraoral scanning through:
- Context-Aware Capture: AI-driven margin detection and preparation validation during acquisition (reducing remakes by 22% in 2025 clinical studies)
- Zero-Click Workflow Initiation: Patient ID auto-sync via practice management system (PMS) APIs upon wand activation
- Hybrid Workflow Routing: Real-time decision engine directs scans to chairside milling or lab production based on case complexity, material constraints, and queue status
- Cloud-First Architecture: All scans encrypted and staged in vendor-neutral cloud repositories (e.g., DICOM 3D, standardized OBJ) before CAD ingestion
Chairside Workflow Integration
| Workflow Phase | Traditional Approach | 2026 Portable Wand Integration | Technical Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation | Manual PMS case creation → Scanner login | PMS triggers scanner auto-login via SSO; patient data pre-loads | HL7/FHIR APIs, OAuth 2.0 |
| Scanning | Standalone app → Manual export | Real-time AI guidance; scan quality metrics displayed intra-procedure | On-device ML inference (TensorFlow Lite) |
| Data Handoff | File export → Email/Dropbox → CAD import | Auto-routed to CAD queue with case parameters; lab notified if outsourced | Cloud-native event streaming (Kafka) |
| Verification | Physical try-in | AR overlay via clinician tablet showing virtual try-in against prep scan | WebXR API integration |
Lab Workflow Integration
Portable wands now function as distributed data acquisition nodes feeding centralized lab production systems:
- Unified Scan Repository: All clinic/lab scans aggregated in neutral format (STL/OBJ) with metadata tagging (prep type, margin, material)
- Predictive Routing: AI analyzes scan quality and case parameters to auto-assign to optimal designer/technician
- Remote Collaboration: Lab technicians annotate scans in CAD; annotations visible to clinician via web portal during scan acquisition
- Calibration Traceability: Automatic wand calibration logs embedded in scan metadata for ISO 13485 compliance
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Assessment
Interoperability is defined by three critical layers: File Format Support, API Depth, and Workflow Orchestration. 2026 standards require bidirectional data exchange beyond basic STL.
| CAD Platform | Native File Support | API Capability | Workflow Integration Level | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | STL, OBJ, PLY, 3MF (with metadata) | Robust SDK: Real-time scan ingestion, design parameter push/pull | High: Direct wand integration via exoplan ecosystem; auto-creates case with material/prep specs | Limited PMS integration without third-party middleware |
| 3Shape Dental System | 3WXL (proprietary), STL, OBJ | Moderate: REST API for case creation; limited design parameter control | Medium: Requires 3Shape Communicate; wand data routed through 3Shape cloud | Vendor lock-in: Full workflow control only with 3Shape scanners |
| DentalCAD (by Zirkonzahn) | STL, ZFX | Basic: File-based ingestion only; no real-time API | Low: Manual import required; minimal metadata retention | No direct wand integration; loses scan context data |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architecture choice fundamentally impacts operational agility, TCO, and future-proofing:
| Criterion | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vendor-neutral APIs, standard file formats, modular component replacement | Proprietary protocols, mandatory hardware/software bundles, single-vendor control |
| Workflow Flexibility | ✅ Mix/match scanners, CAD, mills from different vendors ✅ Custom automation via API scripting |
❌ Requires all components from single vendor ❌ Limited customization options |
| TCO (5-Year) | 📉 18-25% lower: Competitive pricing, no forced upgrades, reuse existing hardware | 📈 30-40% higher: Mandatory ecosystem upgrades, vendor lock-in premiums |
| Innovation Velocity | ⚡ Rapid adoption of third-party AI tools (e.g., margin detection plugins) | 🐢 Dependent on single vendor’s R&D roadmap; slow feature adoption |
| Disaster Recovery | 🛡️ Scan data instantly portable to alternative CAD/mill | ⚠️ Vendor-specific formats may require conversion; downtime risk |
Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework (v4.2) exemplifies best-in-class open architecture implementation, specifically engineered for portable wand integration:
Technical Integration Capabilities
| Integration Point | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Initiation | Webhook triggers from PMS (via FHIR) → Auto-creates Carejoy case → Pushes case ID to wand SDK | Eliminates duplicate data entry; reduces case setup time by 73% |
| Real-Time Scan Streaming | Wand publishes partial scans via WebSockets → Carejoy routes to CAD designer with live annotations | Lab identifies margin issues during scan; reduces remakes by 31% |
| CAD Parameter Sync | REST API pushes prep specs (margin type, reduction) from wand to exocad/3Shape design modules | Auto-configures CAD design parameters; cuts design time by 22% |
| Blockchain Audit Trail | Scan metadata + calibration certs hashed to Ethereum L2 chain via Carejoy API | Immutable compliance records for regulatory audits; zero data tampering risk |
Competitive Differentiation
- Zero-Configuration Discovery: Wands auto-register with Carejoy cloud via mDNS/Bonjour – no IP setup required
- Context-Aware Routing: AI analyzes scan quality in real-time; auto-flags cases needing lab expertise before chairside milling
- Vendor-Agnostic Security: FIPS 140-2 compliant encryption applied at wand before data leaves clinic
Strategic Recommendations
- Prioritize API Depth Over Scan Specs: A wand with robust REST/WebSocket APIs delivers 3.2x higher ROI than marginally better scanners in closed ecosystems (2025 KLAS Dental Study).
- Mandate 3MF Support: Ensure metadata retention for traceable workflows; reject systems relying solely on STL.
- Test Carejoy Integration: Validate real-time annotation workflows during vendor demos – latency < 800ms is critical for clinical utility.
- Avoid Proprietary Cloud Lock-in: Require contractual assurance of data portability via standard APIs.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Prepared for: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Focus: Manufacturing & Quality Assurance of Portable Intraoral Scanner Wands
Executive Summary
This technical review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) process for Carejoy Digital’s portable intraoral scanner wand, produced at an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, China. With a focus on precision engineering, sensor integrity, and long-term reliability, Carejoy Digital exemplifies the new standard in cost-performance leadership for digital dental hardware.
Manufacturing Process: Portable Scanner Wand
The production of Carejoy Digital’s portable scanner wand integrates advanced micro-optics, AI-driven image processing, and ruggedized ergonomic design. The manufacturing workflow is segmented into four core phases:
| Phase | Process | Technology/Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Fabrication | Injection molding of polycarbonate-ABS hybrid housing; CNC machining of metal alignment sleeves; SMT assembly of PCBs with FPGA-based controllers | 5-axis CNC, High-speed SMT lines, Cleanroom Class 8 |
| 2. Sensor Module Integration | Mounting of dual CMOS sensors with blue LED structured light projectors; alignment of optical path via interferometric feedback | Laser interferometers, Automated vision alignment stations |
| 3. Firmware & AI Calibration | Flashing of AI-accelerated scanning firmware; real-time depth mapping initialization; wireless protocol syncing (Bluetooth 5.3 + Wi-Fi 6) | Custom firmware loaders, AI model edge deployment tools |
| 4. Final Assembly & Sealing | Ultrasonic welding of housing; IP54-rated sealing; battery integration (Li-Po 3000mAh) | Automated leak testers, Environmental stress chambers |
Quality Control & ISO 13485 Compliance
All production stages adhere strictly to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. The Shanghai facility maintains full traceability via ERP integration, with serialized batch records for each unit.
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Each scanner wand undergoes calibration in a dedicated Class 7 optical metrology lab, featuring:
- Reference scanning phantoms with sub-micron geometric accuracy (NIST-traceable)
- Automated calibration routines using AI-based point cloud deviation mapping
- Dynamic focus calibration across 3–20 mm working distances
- Color accuracy validation using VITA classical and 3D-Master shade guides
Calibration data is stored in a secure cloud vault and linked to the device’s unique ID, enabling remote recalibration validation via Carejoy’s software platform.
Durability & Environmental Testing
Units undergo accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto concrete, 6 orientations | No housing fracture; optical alignment deviation < 5 µm |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +55°C, 500 cycles | No condensation; sensor drift < 0.01 mm |
| Vibration (Transport) | ISTA 3A | No internal component displacement |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to 75% ethanol, 10% NaOCl, disinfectant wipes (100 cycles) | No surface degradation; seal integrity maintained |
| Scan Accuracy Retest | After all stress tests | Achieves ≤ 8 µm trueness, ≤ 6 µm precision (ISO 12836) |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dentistry hardware due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-10 µm scanning accuracy at price points 30–40% below Western counterparts—without sacrificing reliability or support.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy’s portable scanner supports:
- Open Architecture: Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ formats—fully compatible with major CAD/CAM platforms (exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD)
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time motion correction, automatic bite registration, and prep margin detection via on-device neural networks
- High-Precision Milling Integration: Direct workflow coupling with Carejoy’s 5-axis dry milling units for same-day restorations
Support & Service Model
Carejoy Digital provides:
- 24/7 remote technical support via secure remote desktop access
- Over-the-air (OTA) firmware and AI model updates
- Global calibration revalidation services
[email protected]
Carejoy Digital — Advancing Precision in Digital Dentistry
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Portable Scanner Wand.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
