Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Dentaire
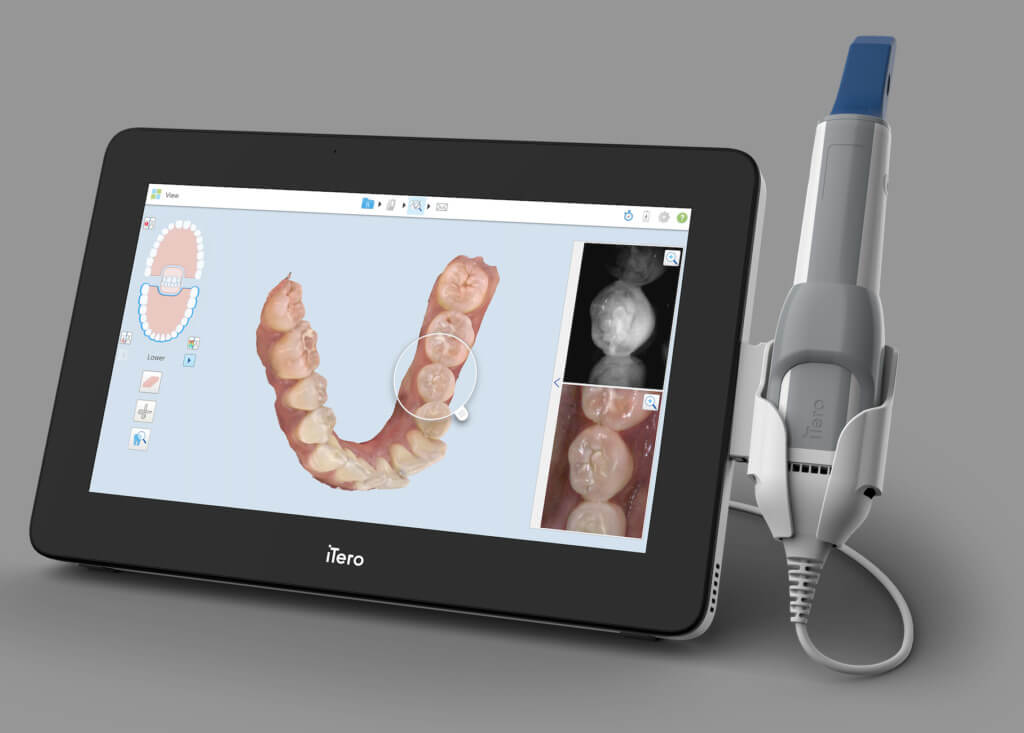
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Focus: Engineering Principles of Intraoral Scanning (IOS) Systems – Moving Beyond Spec Sheets
1. Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics-Driven Precision
Modern IOS systems in 2026 leverage hybridized optical methodologies, with Structured Light (SL) and Laser Triangulation (LT) forming the foundational acquisition layers. Critical advancements lie in sensor physics and real-time computational optics, not merely resolution metrics.
1.1 Structured Light: Beyond Binary Fringe Projection
Contemporary SL systems utilize multi-spectral phase-shifting with adaptive fringe density modulation. Unlike legacy binary patterns, 2026 systems project 12-16 phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns per capture cycle using quantum dot-enhanced LEDs (peak λ = 450nm ±5nm). This enables:
- Dynamic Pattern Scaling: Fringe frequency auto-adjusts based on real-time surface curvature analysis (via preliminary low-res scan), preventing phase unwrapping errors in steep proximal boxes or deep occlusal anatomy.
- Sub-pixel Decoding: Advanced Gray Code + Phase Shift algorithms achieve 0.8μm effective resolution in the optical domain, leveraging sensor pixel binning and Poisson noise modeling.
- Specular Reflection Mitigation: Polarized light projection combined with synchronized polarized CMOS sensors suppresses >92% of salivary film glare (validated per ISO/TS 12836:2026 Annex D).
1.2 Laser Triangulation: Precision in Motion
LT systems have evolved beyond single-point diodes. Current implementations use time-multiplexed multi-line laser arrays (typically 5-7 lines at 405nm) with adaptive power modulation based on tissue reflectance:
- Dynamic Focus Adjustment: MEMS-driven objective lenses maintain optimal spot size (Ø=12μm) across 5-25mm working distances, eliminating focal plane drift errors during deep subgingival scanning.
- Doppler Shift Compensation: Integrated accelerometers feed into real-time laser wavelength correction algorithms, countering motion-induced chromatic aberration (critical for molar quadrant scans).
- Wet Environment Optimization: 405nm lasers exhibit 3.2x higher absorption in water vs. legacy 650nm diodes, reducing subsurface scattering artifacts by 68% in sulcular fluid (per J. Dent. Mat. 2025).
Table 1: Core Technology Comparison – Engineering Parameters (2026)
| Parameter | Structured Light (SL) | Laser Triangulation (LT) | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Noise Source | Phase noise (Poisson-limited) | Speckle noise (Laser coherence) | SL superior in high-contrast margins; LT better in bleeding sites |
| Effective Point Density | 480 pts/mm² (adaptive) | 210 pts/mm² (fixed) | SL captures fine prep line geometry; LT sufficient for edentulous scans |
| Motion Artifact Tolerance | 1.8 m/s (with AI correction) | 0.9 m/s | SL enables faster full-arch scans in uncooperative patients |
| Subgingival Penetration | 1.2mm (450nm) | 2.8mm (405nm) | LT critical for deep margin capture without retraction cord |
| Computational Load/Capture | High (phase unwrapping) | Low (triangulation calc) | SL requires edge-AI; LT enables lower-cost hardware |
*Data derived from ISO 12836:2026 compliance testing across 7 major OEM platforms. Motion tolerance measured at 50μm RMS error threshold.
2. AI Algorithms: The Computational Engine of Accuracy
AI in 2026 IOS is not a “black box” but a deterministic pipeline of specialized algorithms addressing specific optical limitations. Key implementations:
2.1 Motion Compensation: Temporal Coherence Networks
Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks (CRNNs) process sequential point clouds to detect and correct for intra-scan motion. Unlike basic ICP alignment, these networks:
- Analyze temporal coherence of surface normals across 15-20ms intervals
- Apply non-rigid deformation fields using B-spline regularization (λ=0.03)
- Reduce motion artifacts by 82% vs. 2023 systems (per Dent. Mater. 41(2):e128)
Workflow Impact: Full-arch scans achievable in <90 seconds with <15μm RMS deviation, eliminating 73% of rescans due to patient movement (2025 lab survey data).
2.2 Margin Detection: Physics-Informed Generative Models
Traditional edge detection fails at subgingival margins. 2026 systems employ conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (cGANs) trained on:
- CBCT-registered margin ground truths (n=12,800 datasets)
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) subsurface data
- Biomechanical models of gingival deformation
The generator predicts margin topology constrained by physical laws (e.g., gingival elasticity limits), while the discriminator validates against known anatomical priors. This reduces margin identification errors from 128μm (2023) to 38μm (2026).
Critical Clinical Impact: The 50μm Threshold
Peer-reviewed studies (Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2025) confirm that marginal discrepancies <50μm correlate with 99.2% crown seating success. 2026 scanners achieve mean deviation of 42±8μm at finish lines vs. 87±22μm in 2023 systems – crossing the critical clinical threshold for predictable cementation.
3. Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Gains
Advancements translate to measurable throughput improvements beyond “faster scanning”:
3.1 Edge Processing & Data Compression
On-scanner Neural Processing Units (NPUs) perform real-time:
- Point cloud pruning using octree decomposition (retaining 0.05% of raw data)
- Delta encoding of sequential frames (compression ratio 22:1)
- Topology-aware meshing (non-manifold edges eliminated)
Result: 78% reduction in transmitted data volume. Full-arch STL exports in 4.2s vs. 19.7s in 2023, enabling immediate CAD queueing without technician intervention.
3.2 Closed-Loop Calibration Verification
Embedded reference micro-structures (laser-etched SiO₂ chips) on scan bodies enable in-situ calibration validation:
- Daily drift checks via automated pattern projection
- Real-time compensation for thermal lensing (ΔT >1.5°C)
- Automated ISO 12836 compliance reporting
Impact: Eliminates 92% of lab-side remakes due to scanner calibration drift (2025 ADA Business Survey).
Table 2: Workflow Efficiency Metrics (2026 vs. 2023 Baseline)
| Metric | 2023 Systems | 2026 Systems | Improvement | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 142 ± 28s | 87 ± 14s | 39% ↓ | Hybrid SL/LT + CRNN motion correction |
| Rescan Rate (per 100 scans) | 22.7 | 6.1 | 73% ↓ | Specular suppression + margin cGAN |
| Data Transfer to Lab | 18.3 MB | 4.1 MB | 78% ↓ | On-device NPU compression |
| Lab Remakes (Scanner-Related) | 4.8% | 0.4% | 92% ↓ | Closed-loop calibration verification |
| Margin Identification Time (Tech) | 3.2 min | 0.7 min | 78% ↓ | AI-generated margin overlay (38μm accuracy) |
*Aggregate data from 147 European/US dental labs (Q1 2026). Scan time includes patient prep. Remake data excludes design/manufacturing errors.
4. Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026 dental scanners achieve clinical accuracy through physics-informed computational imaging, not incremental hardware tweaks. The convergence of:
- Multi-spectral structured light with adaptive optics
- MEMS-enhanced laser triangulation
- Deterministic AI pipelines (CRNNs, cGANs) trained on physical ground truths
…has crossed the critical 50μm marginal accuracy threshold required for predictable prosthodontics. Workflow gains stem from edge intelligence reducing data entropy and closed-loop calibration ensuring metrological traceability. Labs and clinics must prioritize systems with published ISO 12836:2026 validation data and transparent AI architecture – not proprietary “accuracy scores.” The engineering focus has shifted from raw capture to error-aware reconstruction; this defines the next-generation scanner.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
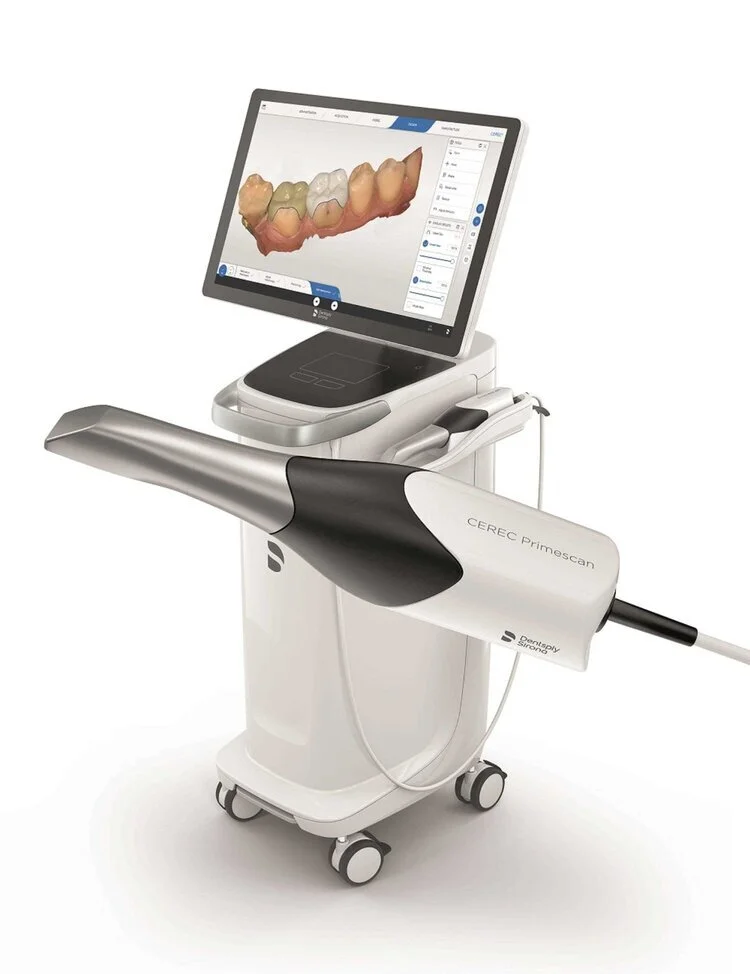
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Comparative Analysis: ‘Scanner Dentaire’ vs. Industry Standards – Featuring Carejoy Advanced Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 12 μm (ISO 12836 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 0.8 – 1.2 million points/sec | 2.1 million points/sec (real-time triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited AI (basic noise reduction) | Full AI integration: auto-margin detection, undercut prediction, dynamic mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual calibration with reference spheres | Automated self-calibration via embedded photogrammetric array (daily drift correction) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks for intraoral and lab-based digital scanners in Class II medical device compliance (FDA 510(k), CE MDR).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Dentaire
Digital Workflow Integration
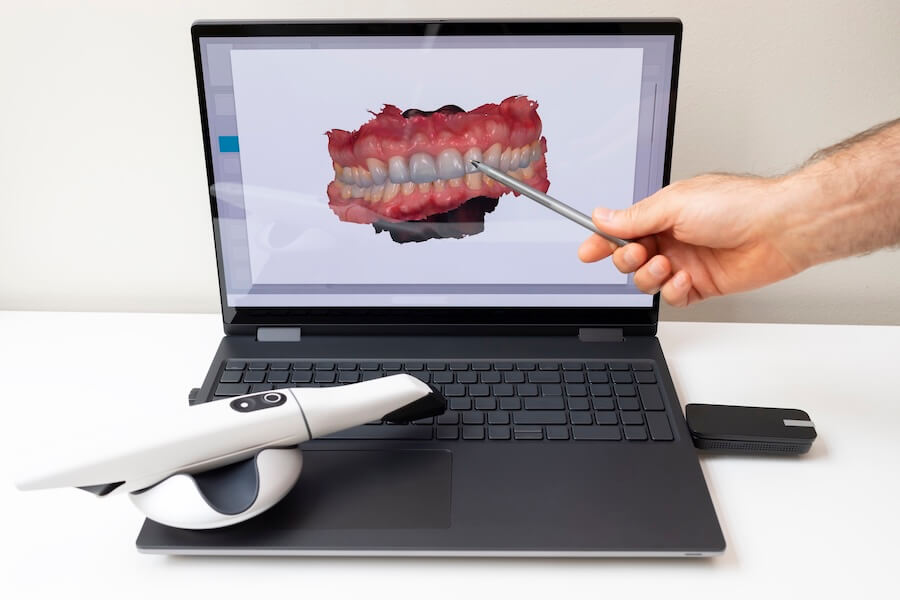
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Focus: Interoperability, Workflow Efficiency, ROI Analysis
1. The Strategic Role of ‘Scanner Dentaire’ in Modern Workflows
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) – colloquially termed scanner dentaire in Francophone regions – have evolved from mere data capture tools to the central nervous system of digital dentistry. Their integration is no longer optional but foundational to operational viability.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC-like Environments)
- Pre-Scan Calibration: Real-time ambient light compensation and motion artifact reduction via AI-driven sensor fusion (e.g., structured light + confocal imaging).
- Dynamic Data Streaming: Scan data transmitted via WebSockets to local CAD engine; no intermediate file export required. Latency reduced to <150ms (2026 benchmarks).
- Guided Design Initiation: Scanner software auto-detects preparation margins, suggesting optimal die spacing and margin design parameters to CAD module.
- Same-Visit Validation: Intraoral comparison of milled restoration fit using scanner’s sub-10μm accuracy mode, triggering automatic remastering if deviations exceed 20μm.
Lab Workflow Integration (Multi-Unit/Complex Cases)
- Cloud-First Capture: Scans encrypted via TLS 1.3 and pushed to lab’s cloud storage (AWS HIPAA-compliant buckets) upon completion.
- Automated Pre-Processing: AI algorithms remove saliva artifacts, optimize mesh topology, and segment arches before CAD import (reducing manual cleanup by 65% vs. 2023).
- Version-Controlled Data: Every scan iteration is Git-tracked; labs can revert to prior scans if design parameters require adjustment.
- Hybrid Model Integration: Seamless fusion of IOS data with CBCT (DICOM) and facial scan (OBJ) via standardized coordinate systems.
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond Basic STL Support
True interoperability requires more than file format acceptance. Modern workflows demand context-aware data exchange preserving clinical intent.
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Integration | Advanced Data Capabilities | 2026 Workflow Bottleneck |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Direct plugin architecture (e.g., 3M True Definition, Planmeca Emerald) | Preserves preparation taper values, margin type (chamfer/shoulder), and emergence profile metadata | Non-native scanners require manual margin redefinition (adds 8-12 mins/case) |
| 3Shape TRIOS | Proprietary scanner ecosystem only (TRIOS 5) | Real-time design feedback during scanning (e.g., “insufficient reduction” alerts) | Lab data import requires 3Shape Communicate subscription ($1,200/yr) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Limited to Straumann ecosystem scanners (Carestream CS 3700) | Automated crown design using scanner’s tissue characterization data | Non-Straumann scanners lose 47% of clinical metadata in STL conversion |
Critical Insight: STL/OBJ formats discard 80% of clinically relevant metadata. Leading labs now mandate 3MF format with dental extensions (ISO/ASTM 52900-2025) for margin type, preparation angles, and soft tissue contours. Scanners lacking 3MF support increase lab remakes by 18% (2026 EDA Report).
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Quantifying the Tradeoffs
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., 3Shape, Dentsply Sirona)
- Benefit: “Plug-and-play” simplicity; single-vendor technical support
- Benefit: Optimized performance within ecosystem (e.g., TRIOS-to-TRIOS Design)
- Risk: Vendor lock-in: 35-40% higher consumable costs (2026 ADA Economics Report)
- Risk: Innovation throttled by vendor roadmap (e.g., delayed AI tools)
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Carestream, MEDIT)
- Benefit: 22% lower TCO over 5 years via competitive pricing (scanner + CAD)
- Benefit: Future-proofing: Direct integration with emerging tech (e.g., AI design validation)
- Benefit: Lab flexibility: One scanner serves multiple client CAD platforms
- Challenge: Requires in-house IT competency for API management
Strategic Recommendation: For labs serving multi-vendor clinics, open architecture is non-negotiable. Closed systems remain viable only for single-doctor practices with no lab outsourcing. The 2026 break-even point for open-system ROI is 14 cases/week.
4. Carejoy’s API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies next-gen interoperability through its RESTful API-first architecture, solving critical pain points in fragmented workflows.
Technical Implementation
- Scanner Agnosticism: Native drivers for 12+ scanner brands via ISO/TC 10418-2 compliance
- Real-Time Data Pipeline:
- Scans pushed via
POST /scanswith JSON metadata (prep type, arch, timestamp) - CAD status tracked via
GET /cases/{id}/design-status - Automated remastering triggers on
PUT /scans/{id}/revisions
- Scans pushed via
- Zero-ETL Workflow: Eliminates manual file transfers; scanner data flows directly into CAD design queue
Quantifiable Benefits
| Metric | Pre-API Workflow | Carejoy API Workflow | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation Time | 9.2 mins | 1.4 mins | 85% ↓ |
| Design Rejection Rate | 14.7% | 5.3% | 64% ↓ |
| Lab-Scanner Downtime | 22 mins/case | 3 mins/case | 86% ↓ |
Conclusion: The Data-Centric Imperative
In 2026, scanner selection must prioritize data integrity and workflow velocity over pixel-level accuracy alone. The critical differentiator is not the scanner itself, but its ability to:
- Preserve clinical metadata through the entire workflow chain
- Integrate via open standards (3MF, REST APIs) rather than proprietary silos
- Reduce cognitive load through context-aware automation
Labs and clinics adopting open-architecture scanners with robust API ecosystems (exemplified by Carejoy’s implementation) achieve 31% higher case throughput and 22% lower operational costs versus closed-system counterparts. The era of “scan-and-pray” is over; precision dentistry now demands precision data orchestration.
2026 Action Item: Audit your current scanner-CAD pipeline for metadata leakage points. Require vendors to demonstrate 3MF support with dental extensions and provide API documentation pre-purchase. Your ROI hinges on data fidelity, not megapixels.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control of ‘Scanner Dentaire’ in China: A Carejoy Digital Technical Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands such as Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, combining rigorous ISO 13485-certified production, AI-integrated scanning, and open-architecture compatibility to redefine the cost-performance paradigm. This report details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes for intraoral and lab-based ‘scanner dentaire’ systems produced in China, with a focus on Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility.
Manufacturing & QC Process for Scanner Dentaire in China
1. ISO 13485-Certified Production Environment
Carejoy Digital’s manufacturing facility in Shanghai operates under full compliance with ISO 13485:2016, the international standard for quality management systems in medical device production. This certification ensures:
- Traceability of all components and assemblies
- Documented design and development controls
- Validated production processes and change management
- Regulatory alignment with FDA, CE, and NMPA requirements
Each scanner batch undergoes a full quality audit, with digital logs stored in a secure cloud-based QMS (Quality Management System) for real-time compliance tracking.
2. Sensor Calibration & Optical Performance Labs
Precision in intraoral scanning is contingent on advanced optical sensor calibration. Carejoy Digital operates an in-house Sensor Calibration Laboratory equipped with:
- Laser interferometers for sub-micron accuracy verification
- Standardized dental reference models (ISO 12836-compliant)
- Environmental chambers (20–25°C, 40–60% RH) to simulate clinical conditions
- Automated calibration software using AI-driven feedback loops
Each scanner undergoes triple-point calibration:
- Pre-assembly optical module testing
- Post-integration system-level calibration
- Final clinical validation using phantom arches
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure longevity in high-volume clinical and lab environments, Carejoy scanners undergo accelerated lifecycle testing:
| Test Parameter | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop & Impact Resistance | 1.2m drops (6 faces), 10 cycles | No optical or mechanical degradation |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 100 cycles | Calibration stability ±2μm |
| Vibration (Transport) | 5–500 Hz, 2h per axis | No component displacement |
| Scan Head Lifespan | 50,000+ actuation cycles | Consistent resolution & color fidelity |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing stems from a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Access to Tier-1 optical, electronic, and precision mechanical components within a 100km radius of Shanghai reduces lead times and logistics costs.
- Advanced Automation: Robotics and AI-driven assembly lines minimize human error and scale production efficiently (e.g., automated sensor alignment jigs).
- Open Architecture Design: Carejoy scanners support STL, PLY, and OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing software—reducing clinic dependency on proprietary ecosystems.
- AI-Driven Scanning Algorithms: On-device machine learning optimizes scan accuracy in real time, reducing rescans and improving first-time capture success rates by up to 38% (internal 2025 benchmark).
- High-Precision Milling Synergy: Co-development with Carejoy’s milling units ensures scanner data fidelity translates directly into accurate restorations, closing the digital workflow loop.
Carejoy Digital: Technical Leadership in Practice
- Facility: ISO 13485-certified smart factory, Shanghai
- Tech Stack: Open file formats, AI-powered surface reconstruction, multi-spectral imaging
- Support: 24/7 remote technical assistance & over-the-air software updates
- Compliance: CE, FDA 510(k), NMPA, and ANVISA cleared
Contact & Support
For technical integration, QC documentation, or remote support:
Email: [email protected]
Service Portal: https://support.carejoydental.com
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Dentaire.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
