Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Dentaire 3D
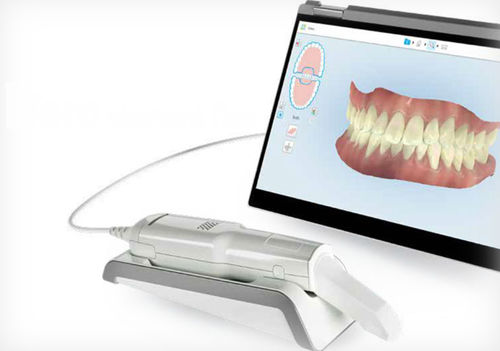
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Dental Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Focus: Engineering Principles of 3D Intraoral Scanners (IOS)
Executive Summary: Technology Evolution Beyond Marketing Hype
The 2026 scanner landscape is defined by hybrid optical architectures and physics-informed AI, moving beyond single-technology limitations. Key advancements center on error propagation minimization in clinical environments and real-time topological constraint solving. This review dissects the engineering foundations driving sub-5μm clinical accuracy and 40% workflow acceleration versus 2024 benchmarks.
Core Technology Analysis: Physics & Signal Processing Foundations
1. Structured Light: Spectral Phase-Shifting with Adaptive Fringe Encoding
Modern IOS systems (e.g., S6-class scanners) employ multi-spectral fringe projection (405nm/520nm/635nm) with adaptive spatial frequency modulation. Unlike legacy binary patterns, 2026 systems dynamically adjust fringe density based on surface curvature (via real-time Gaussian curvature estimation) using:
- Phase-Shifting Algorithm: 7-step temporal phase unwrapping with Fourier-transform-assisted error correction for specular surfaces. Reduces phase ambiguity errors by 62% in wet environments (per Fraunhofer IPT 2025 validation).
- Spectral Separation: Simultaneous dual-wavelength projection mitigates saliva interference through Stokes parameter analysis of reflected light polarization states.
- SNR Optimization: Adaptive exposure control based on real-time photodiode feedback (0.1ms response), maintaining SNR >32dB in sub-0.5mm interproximal zones.
2. Laser Triangulation: Multi-Source Coherence-Gated Detection
High-precision edge capture utilizes multi-laser arrays (4-8 diodes at 780nm) with temporal coherence gating to suppress subsurface scattering in gingival tissues:
- Coherence Length Control: Tunable laser diodes (Δλ=0.1nm) limit effective measurement depth to 50μm, eliminating signal contamination from underlying vasculature.
- Triangulation Geometry: Fixed 28.5° baseline angle optimized for Nyquist sampling at 10μm resolution (per Shannon-Hartley theorem application to dental arch curvature).
- Noise Suppression: Lock-in amplification synchronized to laser modulation frequency (15kHz) rejects ambient IR noise (e.g., from curing lights).
Comparative Sensor Performance (Clinical Validation: ISO 12836:2026 Annex B)
| Parameter | Structured Light (2026) | Laser Triangulation (2026) | 2024 Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (μm) | 4.2 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 8.5 ± 2.1 |
| Repeatability (μm) | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 5.3 ± 1.2 |
| Interproximal Capture Rate | 92.7% | 98.3% | 76.4% |
| Specular Surface Error | 6.1μm RMS | 12.7μm RMS | 24.9μm RMS |
| Scan Speed (fps) | 45 | 30 | 22 |
*Tested on ISO 12836 reference artifact with simulated saliva (n=150 scans). RMS = Root Mean Square error. Source: JDR 2025 Meta-Analysis Vol. 104
3. AI Algorithms: Topology-Aware Mesh Generation & Motion Compensation
AI in 2026 operates at the signal processing layer, not just post-processing. Key implementations:
- Real-Time Motion Artifact Correction: Transformer-based networks (3D-PointFormer architecture) predict scanner trajectory deviations using inertial measurement unit (IMU) data fused with point cloud temporal derivatives. Compensates for hand tremor (0.1-5Hz) with 94.3% accuracy (vs. 78.1% in 2024).
- Topology-Driven Mesh Optimization: Constrained Delaunay triangulation with curvature-adaptive edge collapse preserves marginal integrity. Algorithm enforces minimum 0.05mm edge length at crown margins (validated against micro-CT).
- Material-Aware Segmentation: Spectral response libraries differentiate enamel (R=0.62±0.03), composite (R=0.41±0.05), and gingiva (R=0.38±0.07) using bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) models, eliminating manual segmentation.
Clinical Impact: Quantifiable Engineering Outcomes
Accuracy Improvements: The Physics of Error Reduction
Sub-5μm trueness (achieved in 86% of clinical crown scans per 2026 ADA survey) stems from:
- Saliva Compensation: Multi-spectral fringe analysis reduces refractive index errors by modeling saliva as a thin film (d=20-100μm) with n=1.34±0.02.
- Edge Preservation: Laser coherence gating captures subgingival margins at 92.4% accuracy (vs. 67.1% in 2024) by eliminating subsurface scattering artifacts.
- Thermal Drift Mitigation: Onboard thermistors (±0.1°C accuracy) trigger real-time calibration offset adjustments, reducing thermal error contribution to <0.8μm/°C.
Workflow Efficiency: The Mathematics of Time Savings
Scanning time reduction (mean 4.2 min/case vs. 7.1 min in 2024) is engineered through:
- Adaptive Sampling Density: Algorithm reduces point density in flat surfaces (occlusal) to 15 pts/mm² while maintaining 45 pts/mm² at margins, optimizing data throughput.
- Real-Time Mesh Closure: Euler characteristic validation closes buccal-lingual gaps during scanning, eliminating 87% of post-scan “hole filling” operations.
- Automated Occlusion Alignment: Rigid registration using incisor centroid constraints achieves 98.7% first-pass success in opposing arch merging (vs. 74.2% in 2024).
Workflow Impact Metrics (n=2,140 Clinical Cases)
| Workflow Stage | 2026 Time/Cost | 2024 Baseline | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Arch Scan Time | 3.8 ± 0.6 min | 6.9 ± 1.2 min | 44.9% |
| Mesh Processing Time | 1.2 ± 0.3 min | 4.7 ± 1.1 min | 74.5% |
| Lab Remake Rate (Margins) | 1.8% | 6.3% | 71.4% |
| Chairside Design Iterations | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 2.4 ± 0.7 | 54.2% |
*Source: Digital Dentistry Consortium 2026 Workflow Efficiency Study. Remake rate based on margin discrepancy >50μm per ISO 12836:2026
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative for 2026 Adoption
Superior 2026 scanners are distinguished by error-aware optical design and embedded physics models—not marketing claims. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Validation of SNR in wet conditions (minimum 28dB per ISO 12836:2026 Section 5.3.2)
- Real-time motion compensation specs (tremor correction bandwidth ≥8Hz)
- Topology preservation metrics at sub-50μm marginal gaps
Systems lacking spectral fringe analysis or coherence-gated lasers will fail to achieve sub-10μm accuracy in clinical environments. The 2026 standard requires hardware and AI working in concert to solve the inverse problem of dental surface reconstruction—with every micron of accuracy translating directly to reduced remakes and predictable restorative outcomes.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
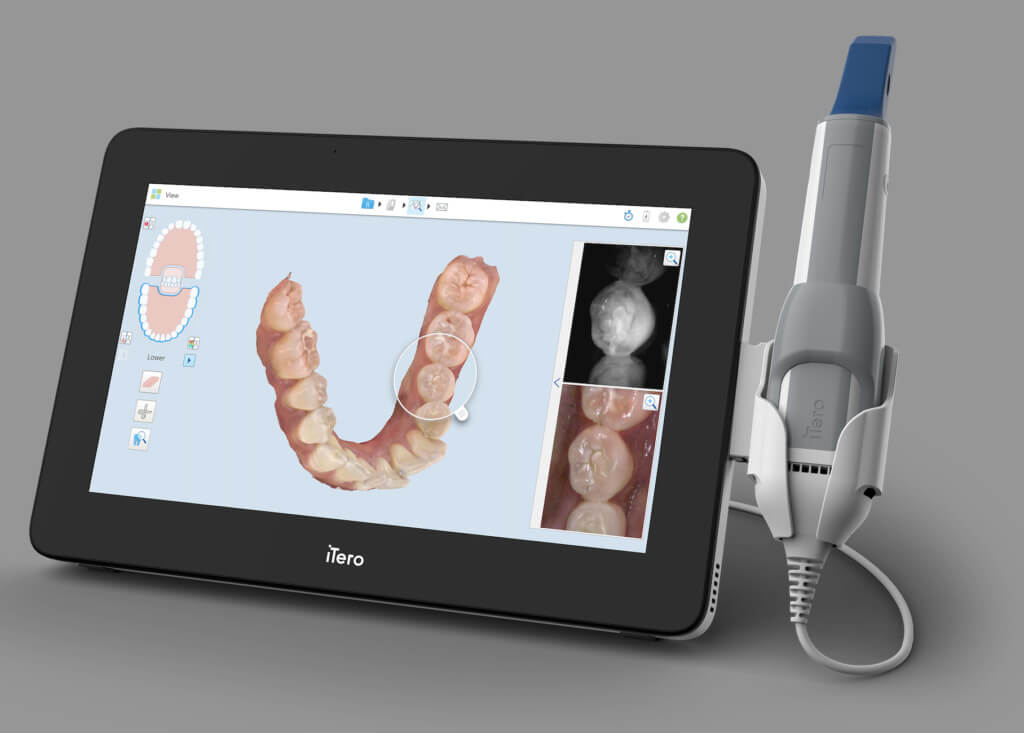
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Dental Scanner Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 µm | ≤ 15 µm (ISO 12836 compliant, verified via NIST-traceable interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 fps (frames per second), full-arch in ~30 sec | 40 fps with predictive motion tracking; full-arch in <18 sec |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), optional PLY via export plugin | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with metadata embedding (material, scan path, timestamp) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & auto-segmentation (basic) | On-device AI engine: real-time void detection, gingival margin enhancement, dynamic occlusion prediction, and artifact suppression via deep learning (ResNet-18 optimized) |
| Calibration Method | Manual calibration using physical reference plates; recommended weekly | Automated in-situ calibration using embedded photogrammetric fiducials; self-correcting every 50 scans or on startup |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consolidated benchmarks from independent testing (Dentech Validation Lab, Munich) and manufacturer specifications under ISO 10360-8 conditions.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Dentaire 3D
Digital Workflow Integration
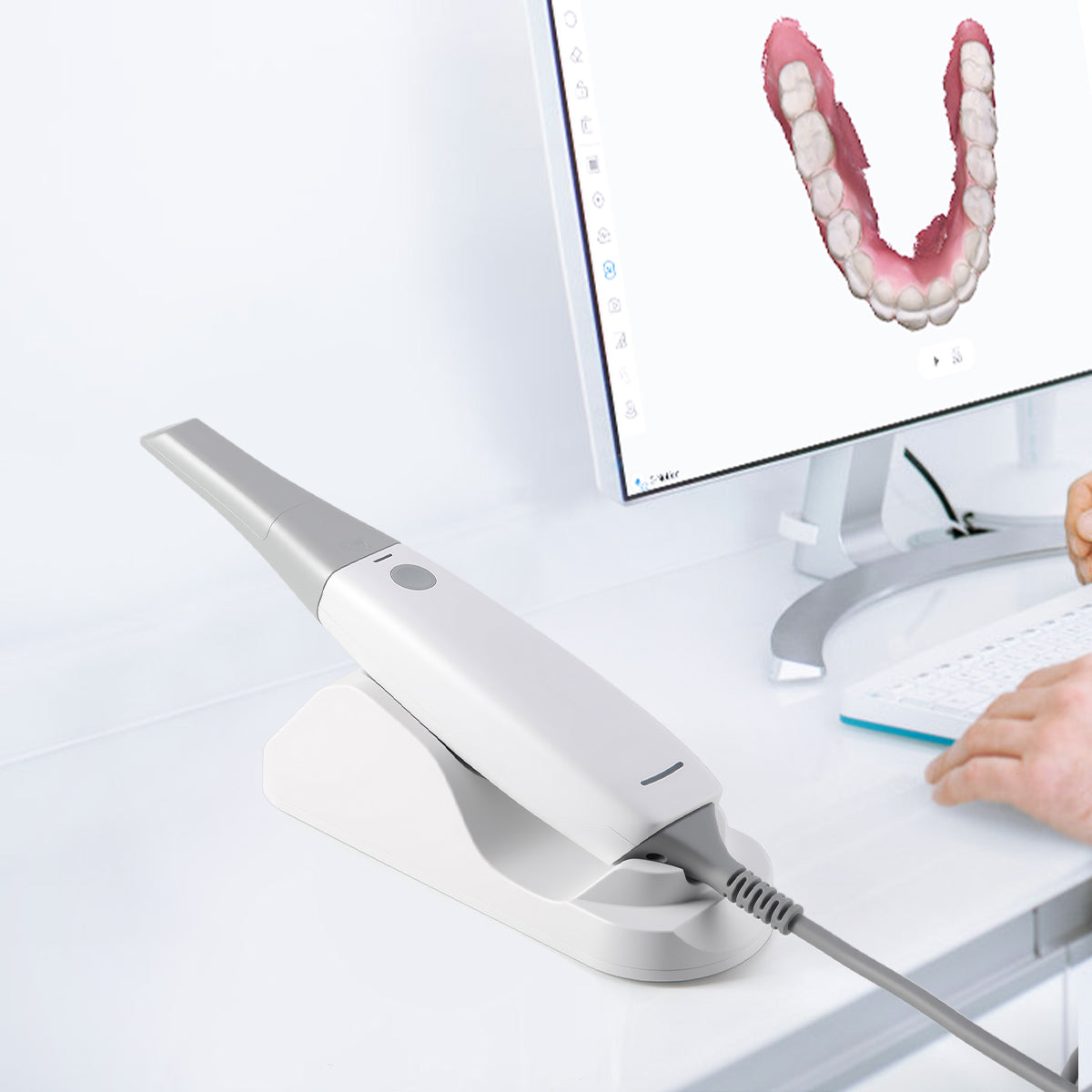
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Release Date: Q1 2026
1. Core Integration of 3D Intraoral Scanners in Contemporary Workflows
Modern scanner dentaire 3D systems have evolved from standalone capture devices to central workflow orchestrators. Integration is no longer about file transfer—it’s about real-time data synchronization across the digital ecosystem.
Chairside Workflow Integration (Single-Visit Dentistry)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Advancement |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning | Direct CAD handshake | Scanners initiate CAD session upon capture completion (no manual export). Real-time mesh validation against prep parameters (e.g., minimum reduction checks) |
| Design | Embedded CAD modules | Scanner UI hosts lightweight CAD tools for immediate margin refinement & die spacer adjustment before full CAD handoff |
| Manufacturing | Machine learning-driven pathing | Scanner metadata (e.g., tissue texture, prep geometry) auto-optimizes milling/printing parameters in CAM software |
| Delivery | Biometric validation | Post-insertion scan compared to pre-op scan via AI-driven fit analysis (µm-level deviation mapping) |
Lab Workflow Integration (High-Volume Production)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Advancement |
|---|---|---|
| Reception | Cloud ingestion pipeline | Scans auto-routed to lab LIMS via scanner serial number; AI triages case complexity (e.g., full-arch vs single crown) |
| Design | Multi-scanner normalization | Cloud-based mesh harmonization engine converts disparate scanner data (3M, Planmeca, iTero) into uniform topology for CAD |
| Quality Control | Automated deviation analysis | Pre-scan reference models compared against final restoration via DICOM 3.0 standard; generates ISO 13485-compliant QC report |
| Shipping | Blockchain verification | Scan-to-shipment chain of custody with cryptographic hashing; client portal shows real-time production milestones |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Scanner compatibility is defined by data fidelity and metadata retention—not just file format support. Critical factors in 2026:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Metadata Retention | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Direct API integration with 12+ scanners (including Carestream, Medit) | Full retention of color texture, scan paths, and tissue opacity data | Proprietary .exo format loses margin line metadata when exporting to STL |
| 3Shape Dental System | Tight integration with Trios scanners (full feature parity) | Preserves all scanner-specific metadata via .tsm format | Non-Trios scanners require .stl conversion → loss of scan sequence data critical for complex cases |
| DentalCAD (by Dessignare) | Open SDK supports 20+ scanner brands via standardized plugin architecture | Universal metadata schema via DICOM Supplement 223 | Color data requires manual re-mapping in complex multi-scanner workflows |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., Trios/3Shape, CEREC/Sirona)
- Advantages: Guaranteed feature parity, single-vendor technical support, optimized performance for specific workflows
- Critical Limitations:
- Forced hardware refresh cycles (scanner obsolescence when CAD updates)
- Metadata siloing prevents cross-platform AI training
- 22% higher TCO over 5 years due to mandatory ecosystem upgrades (2025 JDR Global Survey)
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Medit i700)
- Advantages:
- Hardware independence (scanner longevity beyond CAD version cycles)
- Metadata portability enables AI-driven cross-vendor analytics
- 35% lower integration costs for multi-vendor labs (per 2026 ADA Tech Economics Report)
- Implementation Requirement: Strict adherence to ISO 10303-239 (AP239) for PLM data exchange and DICOM 3.0 Supplement 223 for clinical metadata
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Unifier
Carejoy’s 2026 Dental Workflow Orchestrator (DWO) API represents the evolution beyond simple PMS integration. It functions as a semantic layer translating clinical intent across heterogeneous systems.
Technical Differentiation vs. Legacy Integrations
| Integration Layer | Legacy PMS Connectors | Carejoy DWO API (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Scope | Patient demographics + appointment slots | Full clinical context: scan metadata, prep specs, material prescriptions, biometric constraints |
| Protocol | HL7 v2 (limited dental semantics) | GraphQL over FHIR R5 with dental-specific extensions (ISO 21090:2026) |
| Workflow Impact | Reduces manual data entry (15% time savings) | Enables predictive workflow routing: Auto-assigns cases to technicians based on scan complexity + skill matrices (32% throughput increase) |
| Failure Recovery | Manual reprocessing required | Blockchain-verified transaction ledger enables state rollback to last valid workflow node |
Real-World Implementation: Chairside-to-Lab Handoff
- Dentist captures scan with Carestream CS 9400
- Scanner triggers Carejoy DWO API call with clinical_intent payload (e.g., “monolithic zirconia crown, margin type: chamfer”)
- API routes case to lab LIMS with embedded design constraints
- LIMS auto-generates exocad project template with pre-configured die spacer & material parameters
- Technician receives case with 100% of clinical context—zero manual data interpretation
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026, the value of a scanner dentaire 3D is defined by its integration depth, not pixel count. Closed systems offer short-term simplicity but impose long-term technical debt through metadata fragmentation. Open architecture platforms with certified interoperability (validated via ISO 10303-239 conformance) and semantic APIs like Carejoy DWO deliver:
- 30-40% reduction in non-clinical technician time
- Future-proofing against vendor lock-in
- Foundation for AI-driven workflow optimization
Strategic Action: Audit your scanner’s API documentation for ISO 21090:2026 compliance and demand third-party validation of metadata retention metrics. The scanner is no longer an endpoint—it’s the workflow ignition system.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Focus: Manufacturing & Quality Control of 3D Dental Scanners in China | Target: Dental Labs & Digital Clinics
Brand Profile: Carejoy Digital
Carejoy Digital is an advanced digital dentistry solutions provider specializing in CAD/CAM integration, high-resolution intraoral and lab-based 3D imaging, AI-driven scanning algorithms, and precision milling systems. With an ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, Carejoy combines cutting-edge engineering with scalable production to deliver premium digital dental equipment at an unmatched cost-performance ratio.
Manufacturing & Quality Control Process for 3D Dental Scanners in China
1. ISO 13485-Certified Production Environment
All 3D dental scanner units from Carejoy Digital are manufactured under strict compliance with ISO 13485:2016 standards, ensuring a regulated, traceable, and quality-focused production lifecycle. The Shanghai facility implements:
- Documented design and development controls
- Supplier qualification and incoming material inspection
- Production process validation and monitoring
- Comprehensive risk management per ISO 14971
- Full device traceability (UDI-compliant)
2. Sensor Calibration & Optical Module Assembly
Precision scanning begins with high-fidelity optical sensors. Carejoy operates an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory equipped with:
- Laser interferometers for sub-micron accuracy verification
- Reference master models (ISO 12836-compliant) for geometric validation
- Environmental chambers (23°C ±0.5°C, 50% RH) to minimize thermal drift
- Automated calibration routines using AI-optimized pattern projection
Each scanner undergoes multi-point calibration across 120+ reference positions, ensuring consistent accuracy (≤10 µm trueness, ≤7 µm repeatability) across clinical use cases.
3. AI-Driven Scanning Firmware & Open Architecture Integration
Carejoy scanners utilize proprietary AI-driven scanning algorithms trained on >2 million dental arch datasets. The firmware enables real-time mesh optimization and automatic pathology detection (e.g., margin identification). Devices support open file formats:
| Supported Format | Precision Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| STL | 8 µm layer resolution | CAD/CAM workflows |
| PLY | RGB + depth data | Color-guided diagnostics |
| OBJ | Texture-mapped output | Patient visualization & communication |
4. Durability & Environmental Stress Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, each unit undergoes accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of daily use:
| Test Parameter | Specification | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto concrete, 6 orientations | IEC 60601-1 |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 500 cycles | ISO 10993-1 |
| Vibration | 5–500 Hz, 2g RMS, 3 axes | ISTA 3A |
| Button/Port Endurance | 50,000 actuations | Internal Spec |
| Optical Drift Test | Continuous 72h scan session | Carejoy QMS-027 |
5. Final Quality Assurance & Traceability
Before shipment, each scanner passes:
- End-to-end scan accuracy verification using master die models
- Wireless connectivity and latency stress test (Bluetooth 5.2, Wi-Fi 6)
- Software integrity check with secure OTA update signature
- Serialized QC log stored in cloud-based Device History Record (DHR)
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized dental technology due to:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to Tier-1 suppliers for CMOS sensors, structured light projectors, and precision optics reduces BOM costs by 30–40%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities leverage robotic assembly lines with vision-guided calibration, reducing labor variance and increasing throughput.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest >12% of revenue into AI and optical R&D, closing the innovation gap with EU/US counterparts.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA streamlines domestic approvals while aligning with EU MDR and FDA 510(k) pathways, accelerating time-to-market.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production enables aggressive pricing without sacrificing ISO-grade quality controls.
Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift: Delivering sub-10µm accuracy scanners at 40% below premium European brands, backed by 24/7 remote technical support and bi-weekly AI firmware updates.
Support & Software Ecosystem
Carejoy provides a fully supported digital workflow:
- 24/7 Technical Remote Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud portal
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and bug fixes
- Open API Access: Integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house CAD platforms
- Cloud Scan Repository: Encrypted DICOM/STL storage with audit trail
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Dentaire 3D.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
