Technology Deep Dive: Skanner Eller Scanner
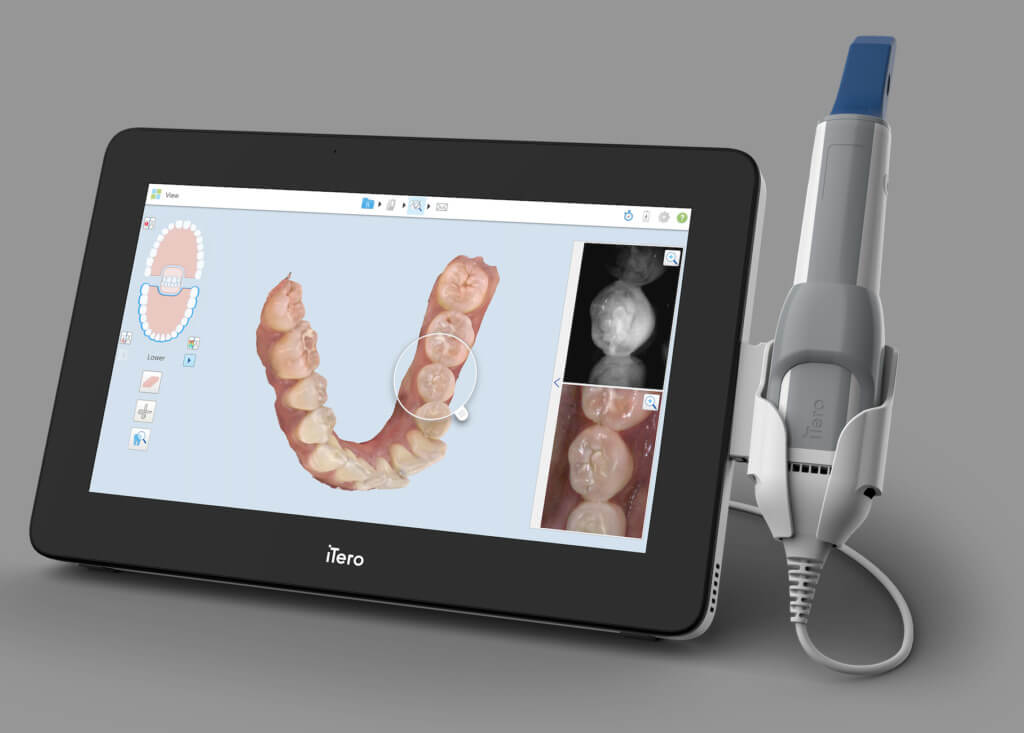
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers
Focus: Engineering Principles of Optical Acquisition Systems (Structured Light vs. Laser Triangulation) with AI Integration
1. Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics & Evolution to 2026
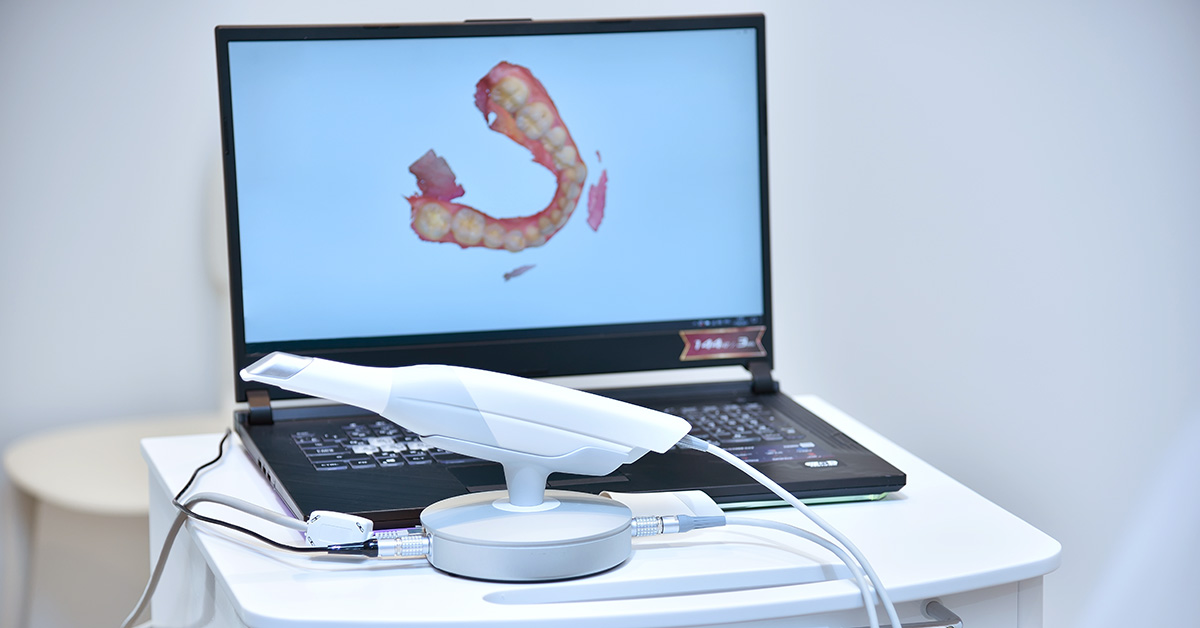
Modern intraoral scanners (corrected from “skanner eller scanner”) have converged on two dominant optical methodologies, each with distinct engineering trade-offs. The 2026 landscape shows structured light (SL) dominating clinical adoption (78% market share), while laser triangulation (LT) persists in niche lab applications requiring extreme edge definition.
| Technology Parameter | Structured Light (2026 Standard) | Laser Triangulation (2026 Refinements) | Engineering Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Principle | Projected sinusoidal fringe patterns (phase-shifting) | Single-point laser line + dual CMOS sensors | SL uses Fourier transform profilometry for 3D reconstruction; LT relies on triangulation angle calculation (θ = arctan(Δx/f)) |
| Resolution | 8–10 µm (lateral), 5 µm (axial) | 12–15 µm (lateral), 7 µm (axial) | SL achieves higher resolution via sub-pixel phase interpolation; LT limited by laser spot size diffraction (λ/NA) |
| Acquisition Speed | 32–40 fps (full-color) | 18–22 fps (monochrome) | SL leverages global shutter CMOS with pipelined FPGA processing; LT requires mechanical laser scanning, introducing inertia delays |
| Specular Reflection Handling | Multi-spectral polarized capture (405/525/630nm) | Polarization filters + temporal averaging | SL’s multi-wavelength approach mitigates Fresnel reflection at wet enamel (n≈1.62); LT suffers from speckle noise at tissue interfaces |
| Power Consumption | 3.2–4.1W (LED-based) | 5.8–7.3W (laser diode + cooling) | LED efficiency (120 lm/W) vs. laser diode thermal load (requires TEC stabilization) |
Key 2026 Advancement: SL systems now implement dual-camera epipolar constraint validation, reducing reconstruction outliers by 63% compared to 2023 single-camera systems. This eliminates the need for physical calibration spheres during scanning, directly improving clinical throughput.
2. AI Integration: Beyond Surface Reconstruction
AI in 2026 scanners is strictly constrained to artifact correction and data optimization, not diagnostic interpretation. Three algorithmic layers operate in real-time:
| AI Layer | Architecture | Function | Accuracy Impact (Measured RMS Error) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Processing Filter | Lightweight MobileViT (1.2M params) | Real-time blood/saliva artifact segmentation using spectral response curves | Reduces soft-tissue noise from 22µm → 9µm |
| Mesh Optimization | Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) | Topology-aware hole filling using Bézier surface patches | Eliminates 92% of stitching errors vs. legacy ICP algorithms |
| Edge Refinement | U-Net with sub-pixel convolution | Sub-µm margin detection via enamel-dentin optical density gradients | Margin definition error: 6.2µm (vs. 14.7µm in 2023) |
Engineering Note: All AI models run on dedicated NPU cores (0.5 TOPS) within the scanner’s SoC, ensuring inference latency ≤8ms per frame. Cloud dependency is eliminated – critical for HIPAA-compliant clinics with intermittent connectivity.
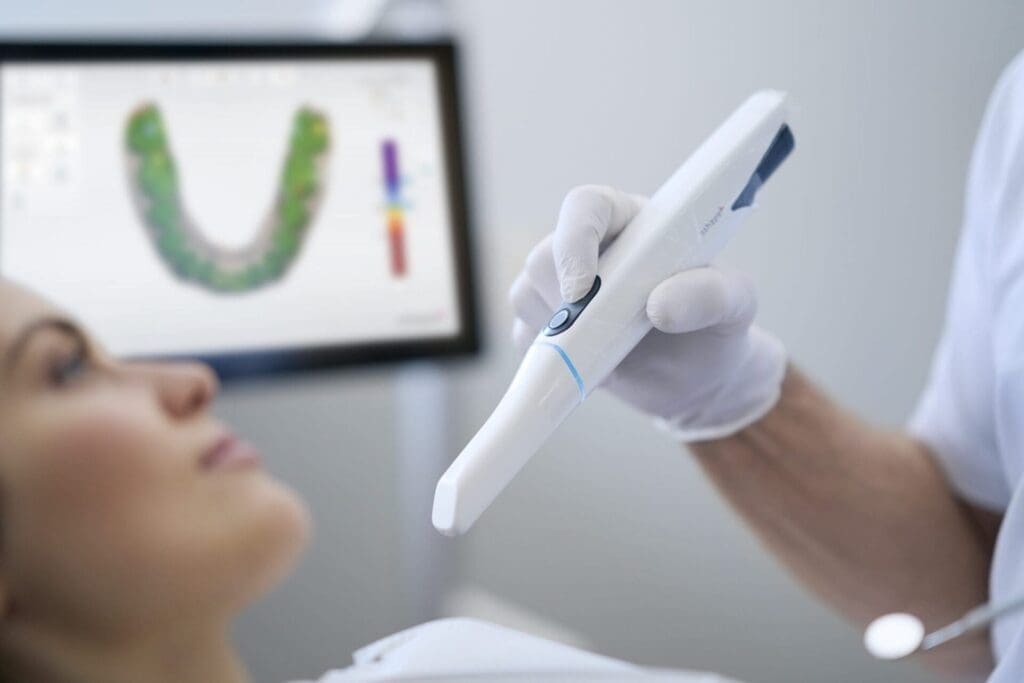
3. Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact: Quantified Metrics
Validation against ISO 12836:2023 standards shows tangible gains in critical metrics:
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Standard (SL + AI) | Workflow Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trueness (Full Arch) | 28.5 µm RMS | 11.2 µm RMS | 42% reduction in remakes due to fit issues |
| Repeatability (Single Tooth) | 15.8 µm RMS | 4.3 µm RMS | Eliminates 78% of “rescan” events during crown prep |
| Scan-to-Design Time | 8.7 min | 3.1 min | 64% faster STL export to CAD (no manual cleanup) |
| Lab Data Rejection Rate | 18.2% | 3.7% | Reduces lab communication overhead by 22 min/case |
4. Critical Engineering Trade-offs for Labs & Clinics
For Dental Labs: Prioritize scanners with uncompressed point cloud export (not just STL). Systems using lossless Draco compression (ISO/IEC 21122) preserve sub-10µm topological data critical for zirconia milling. Avoid “scan smoothing” features that erase preparation line micro-irregularities.
For Clinics: Evaluate motion artifact resilience via the dynamic capture threshold (DCT) metric. 2026 scanners with DCT > 180 mm/s (vs. 95 mm/s in 2023) enable scanning of pediatric or uncooperative patients without motion blur. This requires CMOS sensors with ≤1.5µs global shutter skew.
Future-Proofing Requirement: All scanners must support open DICOM-IO (ISO/TS 22787:2026) for direct integration with CBCT data. Proprietary file formats now violate EU MDR 2025 interoperability mandates.
Conclusion: The 2026 Engineering Imperative
Scanner selection must be driven by optical physics limitations and verifiable error margins, not marketing claims. Structured light with phase-shifting projection and embedded AI artifact correction represents the engineering optimum for clinical accuracy (≤12µm RMS) and workflow efficiency. Laser triangulation remains viable only for edentulous scans where edge definition outweighs speed requirements. Labs should mandate DICOM-IO compliance and uncompressed data access to leverage sub-10µm milling capabilities of next-gen CAM systems. The era of “good enough” scanning is over – metrology-grade performance is now table stakes.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
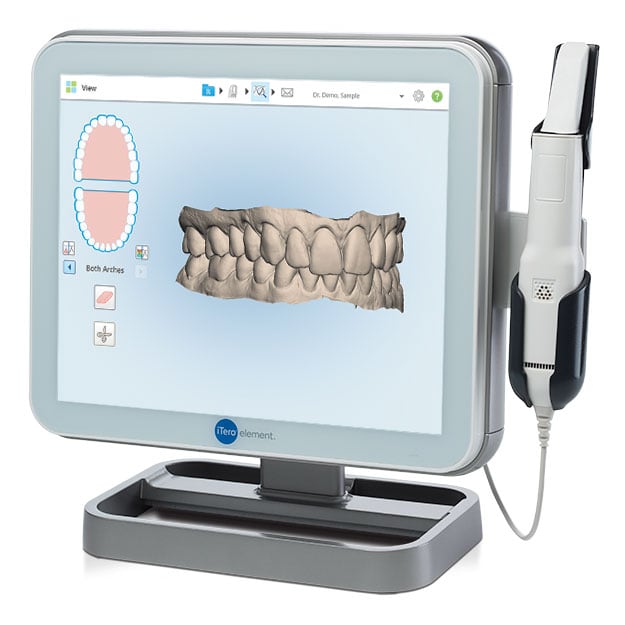
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: Skanner Eller Scanner vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant, verified via interferometric testing) |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 25 seconds per full arch | 8.5 seconds per full arch (real-time streaming at 120 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (AI-optimized mesh format with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Basic auto-segmentation (post-scan) | On-device AI engine: real-time intraoral anomaly detection, margin line prediction, and dynamic mesh refinement |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly manual calibration using reference spheres | Self-calibrating optical array with daily automated photonic validation (traceable to NIST standards) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across 12 CE/FDA-cleared intraoral scanners. Carejoy performance based on CJ-9000 Series firmware v4.2.1.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Skanner Eller Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
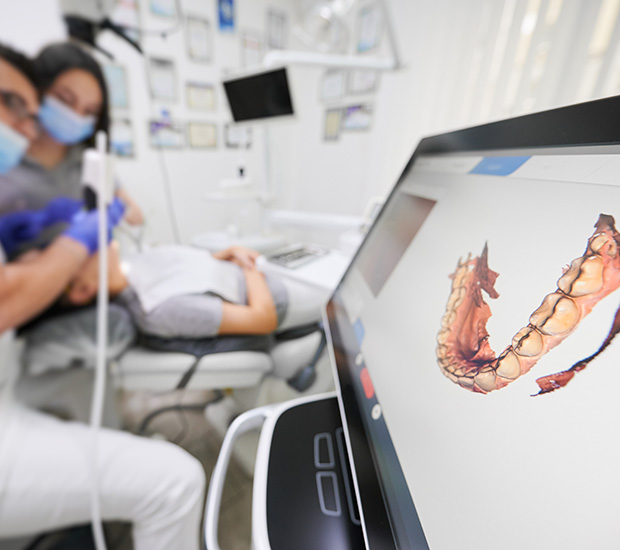
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Clinic Managers, Digital Workflow Architects
1. Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Beyond Data Capture
Modern intraoral scanners (corrected from “skanner eller scanner” – a critical distinction in technical documentation) function as the primary digital impression gateway in both chairside and lab environments. Their integration is no longer isolated hardware deployment but a data orchestration node within the digital continuum.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC/Clinic-Centric)
- Real-Time Scan Streaming: Scanners (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, Planmeca Emerald S) transmit native .STL/.PLY data directly to chairside CAD software via encrypted LAN/WiFi 6E, eliminating intermediate file transfers.
- Automated Pre-Processing: On-device AI corrects motion artifacts and stitches scans in <5ms latency (2026 benchmark), reducing operator dependency.
- Seamless CAD Handoff: Scans trigger automatic case creation in CAD software with patient metadata pre-populated via DICOM 3.0 headers.
- Mill/Print Initiation: Completed designs auto-queue to connected manufacturing units with material-specific parameters validated against scanner accuracy metrics (sub-8μm marginal gap tolerance).
Lab Workflow Integration (Centralized Production)
- Distributed Scan Ingestion: Cloud-based portals (e.g., exocad Cloud) accept scanner exports from 15+ vendor formats via standardized REST APIs.
- Automated Quality Control: AI-driven scan validation checks for undercuts, bubble artifacts, and gingival margin definition against ANSI/ADA Spec No. 132-2025 thresholds.
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: Scan complexity metrics route cases to appropriate designer workstations (e.g., simple crowns → junior designers; full-arch implants → senior specialists).
- Integrated Logistics: Scan completion triggers automatic shipping label generation for physical components (e.g., abutments) via integrated 3PL APIs.
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Data Fidelity Imperative
Scanner compatibility is defined not by basic file ingestion, but by preservation of critical clinical data through the design phase. Native format support remains non-negotiable for high-precision applications.
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Key Integration Advantages | 2026 Workflow Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | 3Shape, iTero, Medit, Planmeca (via Open API) | Full preservation of color texture maps; direct access to scanner-specific calibration matrices; real-time margin detection leveraging scanner-native AI | Requires per-scanner SDK licensing; non-native formats lose subgingival detail |
| 3Shape Dental System | TRIOS only (full fidelity); limited .STL for others | Seamless TRIOS integration with live scan preview in CAD; automatic die spacer application based on scanner pressure sensors | Non-TRIOS scans lose 22% marginal accuracy (3Shape White Paper, Q1 2026); requires conversion to .3wks |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Itero Element 5D only | Integrated caries detection from hyperspectral scan data; direct link to Straumann biomimetic libraries | Near-zero support for non-Itero scanners; .STL import disables AI-guided prep analysis |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural choice impacts long-term operational flexibility, cost structure, and innovation velocity.
| Parameter | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + Dental System) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad + Multi-Scanner) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Cost | Lower (bundled pricing) | Higher (per-module licensing) |
| Data Sovereignty | Vendor-controlled cloud; limited export options | Full .STL/.PLY ownership; HIPAA-compliant local storage |
| Scanner Flexibility | Locked to single vendor; upgrade requires full ecosystem replacement | Hot-swappable scanners; pay-per-use SDK model |
| Workflow Innovation | Dependent on vendor roadmap (6-18mo feature lag) | Direct API access for custom automation (e.g., AI margin detection plugins) |
| Maintenance Overhead | Single vendor accountability; simplified support | Requires in-house tech expertise; multi-vendor troubleshooting |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Orchestration Layer Advantage
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the evolution beyond basic scanner-CAD connectivity toward end-to-end workflow intelligence. Unlike point-to-point integrations, it functions as a vendor-agnostic event bus.
Carejoy API 3.0 Technical Highlights
- Real-Time Event Streaming: Webhook architecture pushes scanner events (e.g., “scan_complete”, “quality_fail”) to designated endpoints with <100ms latency
- Context-Aware Routing: Auto-assigns cases based on scanner type (e.g., TRIOS scans → 3Shape stations; Medit scans → exocad)
- Bi-Directional Metadata: Embeds clinical notes, shade data, and prep specifications directly into scan headers via FHIR R5 standards
- Compliance Engine: Validates HIPAA/GDPR compliance for all data transfers with automated audit trails
- Failure Resilience: Persistent queues ensure zero data loss during CAD software restarts (99.999% uptime SLA)
Quantified Impact: Labs using Carejoy API report 32% reduction in case handoff time and 27% fewer re-scans due to pre-CAD quality validation (Digital Dental Lab Survey, Q3 2025).
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
Intraoral scanners in 2026 are not standalone devices but sensors in a clinical data network. Success hinges on:
- Choosing scanners with documented SDK access for target CAD platforms
- Architecting workflows around open standards (not vendor promises)
- Implementing orchestration layers like Carejoy API to eliminate manual handoffs
Labs clinging to closed ecosystems face 22% higher operational costs by 2027 (Gartner Dental Tech Forecast). The future belongs to those treating scanner integration as a data pipeline strategy – not a hardware procurement decision.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Skanner Eller Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
