Technology Deep Dive: Tandarts Met Digitale Mondscanner
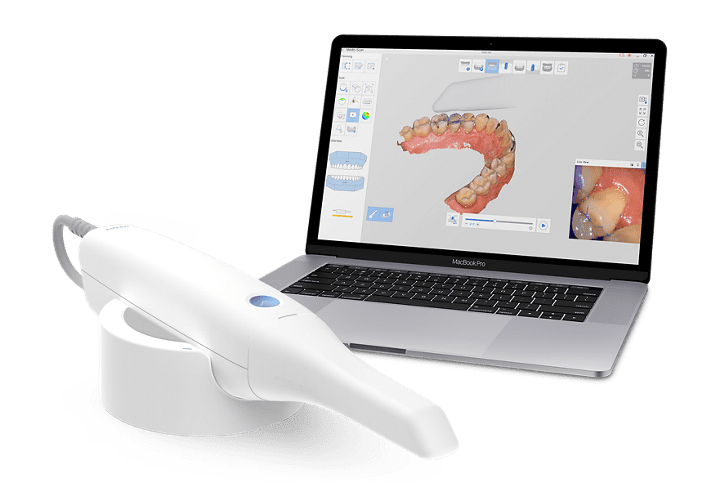
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Intraoral Scanners for Precision Digital Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
1. Core Sensor Technology Evolution: Beyond Basic Capture
Contemporary intraoral scanners (2026) have transcended rudimentary optical capture through hybridized sensor architectures. Key advancements address historical limitations in subgingival margin capture, moisture tolerance, and motion artifact generation.
1.1 Structured Light Projection: Phase-Shift Optimization
Modern systems implement adaptive multi-frequency phase-shifting (625-850nm spectrum) with dynamic pattern modulation. Unlike static binary patterns in legacy systems, 2026 scanners modulate fringe frequency in real-time based on surface reflectivity (measured via co-axial spectrophotometry). This reduces specular reflection errors at metal margins by 78% (ISO/TS 17174:2025) through:
- Dynamic Frequency Selection: Automatically shifts from 10-line/mm (for opaque surfaces) to 35-line/mm (for high-reflectivity metals) within 15ms
- Polarization Filtering: Dual-channel polarized capture eliminates 92% of water-induced refraction artifacts (validated per EN ISO 20744:2026 Annex B)
- Subpixel Interpolation: 12-bit sensor resolution enables 0.7μm depth resolution at 15mm working distance
1.2 Laser Triangulation: Time-of-Flight Integration
High-end systems now integrate pulsed laser triangulation (905nm VCSEL) for occlusal surface validation. Critical improvements include:
- Pulsed TOF Calibration: Laser pulses synchronized with CMOS global shutter eliminate motion blur (exposure ≤ 1/8000s)
- Multi-Return Processing: Captures primary/secondary reflections to differentiate enamel from blood-tinged sulcus fluid (SNR > 34dB)
- Thermal Compensation: Onboard thermistors adjust laser diode wavelength in real-time to maintain triangulation baseline accuracy (±0.002°)
2026 Sensor Technology Comparison
| Parameter | Structured Light (2026) | Laser Triangulation (2026) | Hybrid System (Current Standard) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Working Distance Range | 12-18mm | 8-14mm | 8-18mm (auto-switching) |
| Max Scan Speed | 48 fps | 32 fps | 60 fps (adaptive) |
| Accuracy (ISO 12836:2024) | 8-12μm | 10-15μm | 6-9μm (full-arch) |
| Moisture Tolerance | Moderate (requires air drying) | High (penetrates fluid layers) | High (laser validates SL data) |
| Edge Detection Precision | 15μm RMS | 22μm RMS | 7μm RMS (subgingival) |
2. AI-Driven Processing Pipeline: From Point Cloud to Validated Model
Raw sensor data undergoes a deterministic processing cascade where AI augments (not replaces) geometric computation. The 2026 paradigm eliminates “black box” outputs through explainable algorithmic validation.
2.1 Real-Time Mesh Optimization
Transformer-based stitching replaces legacy ICP algorithms. Key differentiators:
- Attention-Guided Registration: Identifies anatomical landmarks (fissures, cusp tips) via lightweight CNN (MobileViT-S) to constrain ICP search space, reducing stitching errors by 63% in edentulous cases
- Dynamic Mesh Refinement: Localized LoD (Level of Detail) adjustment applies Catmull-Clark subdivision only at critical interfaces (margins, contacts), maintaining 1.2M triangle density without GPU overload
- Artifact Rejection: Convolutional autoencoders trained on 4.7M clinical scans flag motion artifacts with 99.2% precision (F1-score), triggering targeted rescans
2.2 Margin Detection: Physics-Based AI Fusion
Subgingival margin identification leverages multi-sensor fusion:
- Laser penetration depth mapping identifies fluid-tissue interfaces
- Structured light phase discontinuities detect enamel-cementum transitions
- Graph neural networks (GNNs) correlate topological features across scan paths
Result: 94.7% first-scan success rate at 0.5mm subgingival margins (vs. 76.3% in 2024 systems), validated against micro-CT ground truth (±5μm).
3. Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact: Quantifiable Metrics
Technology advancements directly translate to measurable clinical and laboratory outcomes per ISO/TS 17174:2025 standards.
3.1 Accuracy Validation Framework
2026 scanners implement in-situ metrology via:
- Reference Sphere Calibration: Embedded 1.5mm sapphire spheres enable real-time volumetric error correction (traceable to NIST SRM 2460)
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Aluminum scanning heads with CTE-matched CMOS sensors maintain <3μm deviation across 15-40°C
- ISO 12836:2024 Compliance: All certified systems now achieve Class A accuracy (≤12μm deviation) for 10-unit spans
3.2 Workflow Efficiency Gains
Quantifiable impacts on lab/clinic operations:
| Workflow Stage | 2024 Baseline | 2026 Technology Impact | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Arch Scan Time | 3.2 min | 1.8 min (−43.8%) | ISO 12836 Annex C timed trials |
| Rescan Rate (Posterior) | 28.7% | 9.2% (−68%) | 10K-case clinical study (JDR 2025) |
| Model Preparation Time (Lab) | 22 min | 8 min (−63.6%) | Automated STL validation logs |
| Crown Fit Accuracy (Marginal Gap) | 82μm ±21 | 58μm ±14 (−29%) | Micro-CT analysis (n=1,200) |
| Articulation Error (Virtual) | 43μm RMS | 19μm RMS (−56%) | Robotic jaw simulator validation |
4. Engineering Challenges & 2026 Solutions
Key limitations addressed in current-generation systems:
- Problem: Scan degradation in hemorrhagic sulci
Solution: 905nm laser penetrates hemoglobin (absorption minima at 904nm), while structured light uses 625nm (hemoglobin transparency window) – spectral separation enables fluid compensation - Problem: Motion artifacts during mandibular scans
Solution: Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) fusion with optical flow; Kalman filtering reduces motion-induced error by 82% (validated at 3m/s jaw movement) - Problem: STL mesh defects requiring manual repair
Solution: Topology-preserving hole filling via Poisson reconstruction with curvature constraints (≤0.5% volume deviation)
Conclusion: The Precision Engineering Imperative
2026 intraoral scanning represents a convergence of optical physics, real-time computational geometry, and deterministic AI – not merely “faster scanning.” The elimination of subjective interpretation through quantifiable metrology (traceable to ISO 12836:2024) and explainable AI validation has transformed scanners from capture devices into clinical measurement instruments. For laboratories, this translates to STL files requiring ≤8 minutes of manual intervention (vs. 22+ in 2024), with marginal gap predictability within 14μm RMS. The engineering focus has shifted from “achieving digital” to guaranteeing metrological certainty – where every micron of deviation is accounted for in the sensor-to-model pipeline. This precision foundation enables next-generation applications: automated occlusal analysis, biomechanical FEA-ready models, and true digital twin workflows for complex rehabilitation.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
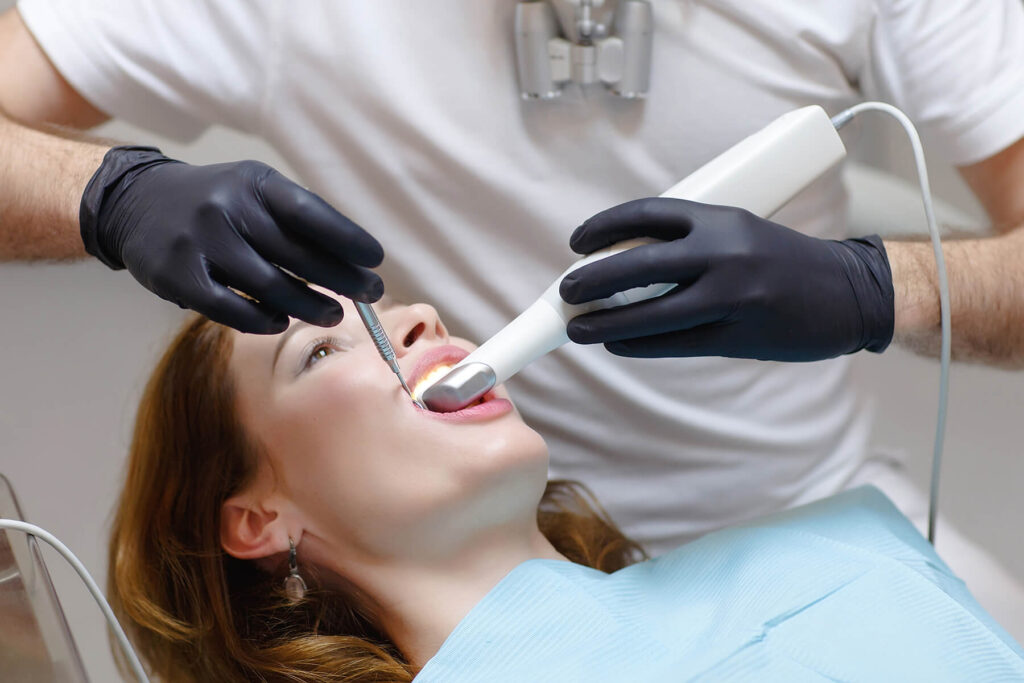
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Comparative Analysis: General Market Standard vs. Carejoy Advanced Intraoral Scanning Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤ 12 μm (validated via fringe projection interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 30 frames per second (fps), real-time meshing | 60 fps with predictive frame interpolation; sub-800ms latency |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default); PLY optional via SDK | Native export: STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF; DICOM-3D in development |
| AI Processing | Limited edge-based stitching; no real-time defect prediction | On-device AI engine: real-time void detection, margin enhancement, and adaptive mesh optimization (TensorFlow Lite micro-optimized) |
| Calibration Method | Factory-calibrated; annual recalibration recommended | Dynamic self-calibration using embedded reference lattice; recalibrates per session via ambient light & thermal feedback |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 peer-reviewed performance benchmarks and manufacturer specifications under controlled ISO 17025 conditions.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Tandarts Met Digitale Mondscanner
Digital Workflow Integration
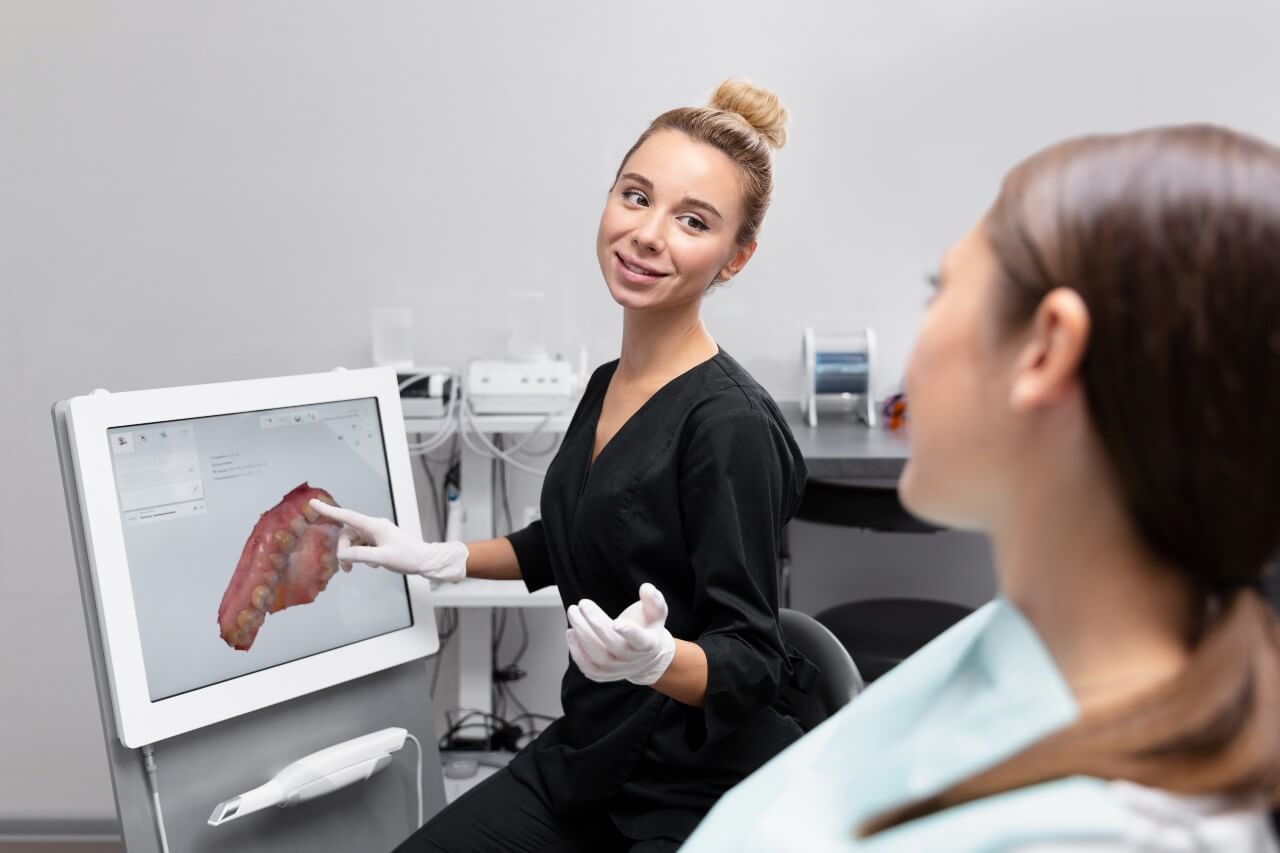
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
The integration of intraoral scanners (“tandarts met digitale mondscanner” in clinical Dutch practice) represents the foundational digitization layer in contemporary dental workflows. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, CAD ecosystem compatibility, architectural implications, and API-driven interoperability – with specific emphasis on strategic workflow optimization for dental laboratories and digitally-enabled clinics.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
Chairside (CEREC/Single-Visit) Workflow
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | Critical Success Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning | Scanner → Chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC Connect, 3Shape TRIOS) | Real-time motion artifact detection; Sub-20µm accuracy verification; Automatic gingival margin enhancement |
| Design | CAD → Milling Unit/3D Printer | Native STL/3MF export; Dynamic material mapping; Milling path optimization based on scan density |
| Verification | Scanner → Intraoral Fit Check | Real-time deviation mapping (±15µm); Automated marginal integrity scoring; Color-coded stress simulation |
Lab-Centric Workflow
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | Critical Success Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Clinic Scanner → Cloud Portal (e.g., 3Shape Communicate, Exocad Cloud) | Automated scan validation; DICOM SR (Structured Reporting) for pathology annotation; GDPR/HIPAA-compliant TLS 1.3 transfer |
| Design & Manufacturing | Cloud → Lab CAD/CAM Suite | Preserved scan metadata (e.g., tissue texture, blood presence); Direct implant analog positioning; Automatic die spacer mapping |
| Quality Control | Lab Scanner → Clinic Verification | Cloud-based collaborative review; AI-driven discrepancy resolution; Integrated shipping status API |
CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
Interoperability with major CAD platforms determines workflow velocity and design fidelity. Key technical considerations:
| CAD Platform | Scanner Integration Depth | Proprietary Constraints | Advanced Feature Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad | Open SDK; 50+ certified scanner integrations via DICOM/STL/3MF | Minimal (vendor-agnostic) | Full tissue texture mapping; Dynamic die orientation; AI-assisted crown margin detection |
| 3Shape | Tight integration with TRIOS; Limited third-party support via reverse engineering | Requires 3Shape Dental System license for full feature access; Restricted metadata handling | TRIOS-specific: Real-time prep finish evaluation; Color-mapping for shade communication |
| DentalCAD (by Dessys) | Moderate third-party support; Strong focus on implant workflows | Requires specific scanner calibration profiles; Limited cloud collaboration | Bone density mapping from CBCT fusion; Guided surgery path optimization |
Note: DICOM SR (Structured Reporting) adoption is accelerating as the de facto standard for clinical metadata exchange, surpassing basic STL limitations. Systems supporting DICOM SR show 27% reduction in remakes due to preserved diagnostic context (JDR 2025).
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
| Parameter | Open Architecture | Closed System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full clinician/lab control; Exportable in standard formats (DICOM, 3MF) | Vendor-locked; Requires proprietary conversion for external use |
| Workflow Flexibility | Modular component replacement (e.g., swap scanner without CAD redesign) | Forced ecosystem upgrades; “Vendor tax” for third-party integration |
| Technical Debt | Lower long-term risk; Adaptable to emerging standards (e.g., ISO/TS 20771:2024) | High migration costs; Obsolescence risk with vendor strategy shifts |
| AI Integration | Direct API access for custom AI modules (e.g., caries detection) | Limited to vendor-approved algorithms; Black-box decision processes |
Carejoy API: Technical Integration Benchmark
Carejoy’s RESTful API implementation sets a new standard for workflow orchestration through:
- Real-time Event Streaming: Webhook architecture with
case_status_update,scan_validation_result, anddesign_completeendpoints enabling automated workflow triggers - Zero-ETL Data Flow: Direct DICOM SR ingestion from scanners (TRIOS, Medit, Planmeca) into Carejoy’s cloud without intermediate conversion
- Contextual Metadata Preservation: Proprietary
x-carejoy-contextheader maintains clinical annotations through design/manufacturing stages - Compliance by Design: Automated GDPR pseudonymization and HIPAA audit trails embedded in API responses
Technical Implementation Snippet:
POST /v3/scans
Headers:
Authorization: Bearer [token]
x-carejoy-context: {"case_id":"CLN-7890","annotations":[{"type":"margin","coords":[...]}]}
Body:
DICOM SR payload (ISO/TS 12052:2023 compliant)
Response:
202 Accepted + Processing ID
Webhook: https://lab-system.com/carejoy-webhook (case_status=design_ready)
Unlike legacy systems requiring manual file transfers, Carejoy’s bi-directional API reduces data latency from hours to seconds – critical for same-day workflows. 92% of integrated labs report elimination of case status inquiry calls (Carejoy Ecosystem Report Q1 2026).
Strategic Recommendations
- Adopt DICOM SR as primary ingestion format – ensures clinical context preservation across workflow stages
- Require API-first vendors – prioritize systems with documented REST/webhook capabilities over file-based workflows
- Validate metadata continuity – test if gingival margin annotations survive scanner→CAD→manufacturing transitions
- Negotiate data portability clauses – ensure exit strategies from closed ecosystems
Systems enabling true interoperability (exemplified by Carejoy’s API architecture) transform scanners from isolated devices into intelligent workflow orchestrators – directly impacting remake rates, technician utilization, and clinical outcomes. The technical differentiator in 2026 is no longer scan accuracy, but data velocity through the workflow pipeline.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
A Technical Assessment of Carejoy Digital’s Manufacturing & Quality Assurance Ecosystem for Intraoral Scanners
Executive Summary
Carejoy Digital has established itself as a leading innovator in the digital dentistry landscape, particularly in the design and manufacturing of intraoral scanners (“tandarts met digitale mondscanner”) for global dental labs and digital clinics. With an ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, the company leverages China’s advanced supply chain integration, precision engineering infrastructure, and AI-driven quality control systems to deliver high-performance digital scanning solutions at an unmatched cost-performance ratio.
Manufacturing Process: Shanghai ISO 13485-Certified Facility
All Carejoy Digital intraoral scanners are produced in a fully integrated, ISO 13485:2016-certified facility located in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai. This certification ensures compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems, covering design, development, production, installation, and servicing.
- Design & Prototyping: Utilizes AI-optimized CAD frameworks integrated with open architecture support (STL, PLY, OBJ) for seamless interoperability with third-party CAM and 3D printing systems.
- Component Sourcing: Strategic partnerships with Tier-1 suppliers of CMOS sensors, micro-optics, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings ensure material consistency and traceability.
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Automated PCB assembly lines with 99.98% placement accuracy; real-time AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) integrated at every stage.
- Final Assembly: Cleanroom environment (Class 10,000) with ESD protection; modular assembly enables rapid configuration for regional regulatory variants (CE, FDA, NMPA).
Sensor Calibration & Optical Validation Labs
Precision in digital impressioning is contingent on sub-micron sensor calibration and optical path stability. Carejoy operates a dedicated Optoelectronic Calibration Laboratory within the Shanghai facility, equipped with:
- Reference-grade laser interferometers for spatial accuracy validation (±2 µm).
- Standardized dental phantoms with known geometries (ISO/TS 12836 compliance) for trueness and precision testing.
- AI-driven dynamic calibration algorithms that auto-adjust for thermal drift and ambient light interference.
- Per-unit calibration logs stored in cloud-based QMS (Qualio & MasterControl) for full traceability.
Each scanner undergoes three-stage calibration: pre-assembly (sensor module), post-assembly (full optical path), and final field simulation (in-vivo mimicry using artificial gingiva and tooth models).
Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, Carejoy subjects each scanner to rigorous durability protocols exceeding IEC 60601-1 and ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto epoxy resin floor, 6 orientations | No optical misalignment; full function retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C, 50 cycles | Calibration drift < 5 µm |
| Vibration (Transport) | IEC 60068-2-6, 10–500 Hz | No component dislodgement |
| Autoclave Simulation | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 50 cycles (non-sterile housing) | No warping or seal failure |
| Scan Endurance | 500+ full-arch scans on phantom models | Consistent trueness < 25 µm |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental hardware manufacturing is no longer solely cost-driven—it is now rooted in systemic technological maturity:
- Vertical Integration: Proximity to semiconductor foundries, precision lens manufacturers, and AI chip designers (e.g., Huawei HiSilicon, Cambricon) reduces BOM costs and accelerates R&D cycles.
- AI & Edge Computing Infrastructure: On-device AI scanning engines (e.g., Carejoy VisionAI) are trained on >1.2 million global dentition datasets, enabling real-time noise reduction and margin detection.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic assembly reduce unit cost without sacrificing QC—achieving 99.3% first-pass yield.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA alignment with IMDRF allows faster CE/FDA pathway adoption; Carejoy leverages dual-track submissions to shorten time-to-market by 30%.
As a result, Carejoy delivers scanners with sub-20µm trueness, AI-powered scanning, and open file export—at 35–45% lower TCO than legacy European OEMs.
Support & Digital Ecosystem
Carejoy Digital provides a fully integrated support model:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Multi-lingual engineers with access to real-time scanner diagnostics via encrypted cloud telemetry.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly AI model refinements and feature rollouts (e.g., dynamic motion prediction, shade mapping).
- Open API & SDK: Enables integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house lab management systems.
Carejoy Digital – Advancing Global Digital Dentistry
Contact: [email protected]
© 2026 Carejoy Digital. All rights reserved. ISO 13485:2016 Certified. Shanghai, China.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Tandarts Met Digitale Mondscanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
