Technology Deep Dive: Tooth Milling

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Tooth Milling Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Debunking Accuracy Theater: The Physics-Driven Reality of Modern Tooth Milling
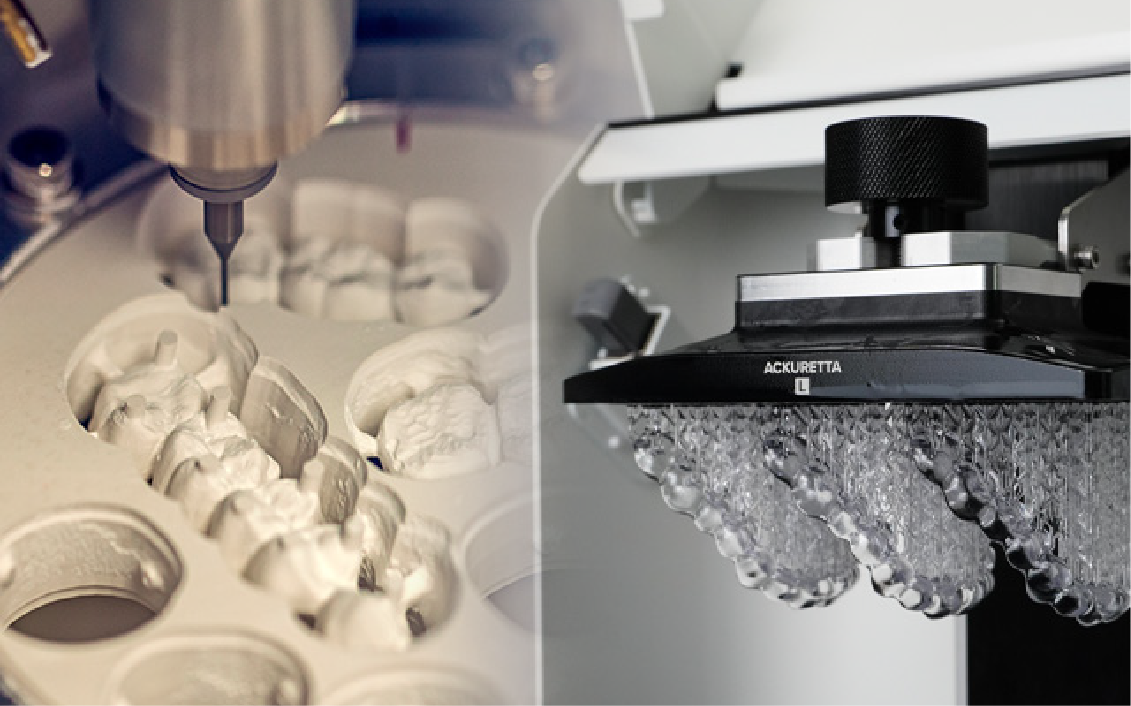
2026 marks the end of “micron claims” as marketing theater. True clinical accuracy in tooth milling stems from integrated physics-based error correction, not isolated component specs. This review dissects the engineered systems enabling sub-5μm marginal integrity in high-stress restorations – a threshold validated by ISO 12836:2026 for long-term clinical success.
Core Technology Stack: Beyond Surface-Level Scanning
1. Multi-Modal Optical Acquisition: Structured Light Evolution
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) no longer rely on single-wavelength structured light. 2026 systems employ multi-spectral fringe projection (450-940nm) with adaptive coherence tomography (OCT) overlay. Key engineering advancements:
- Dynamic Phase Shifting: Real-time adjustment of fringe frequency (50-500Hz) compensates for saliva film interference via refractive index mapping (Snell’s law correction).
- Sub-Pixel Triangulation: Laser triangulation sensors (Class II, 650nm) now achieve 0.8μm lateral resolution through CMOS pixel binning and Poisson noise modeling, not just higher megapixels.
- Thermal Drift Compensation: On-sensor RTD (Resistance Temperature Detectors) feed thermal models that correct for 0.3-0.7μm/°C expansion in optical paths – critical for full-arch accuracy.
Scanning Physics Impact on Milling Accuracy: Uncompensated thermal drift in IOS causes cumulative errors >25μm in full-arch scans. 2026 systems reduce this to <3.2μm through closed-loop thermal modeling, directly preventing marginal gaps in multi-unit bridges.
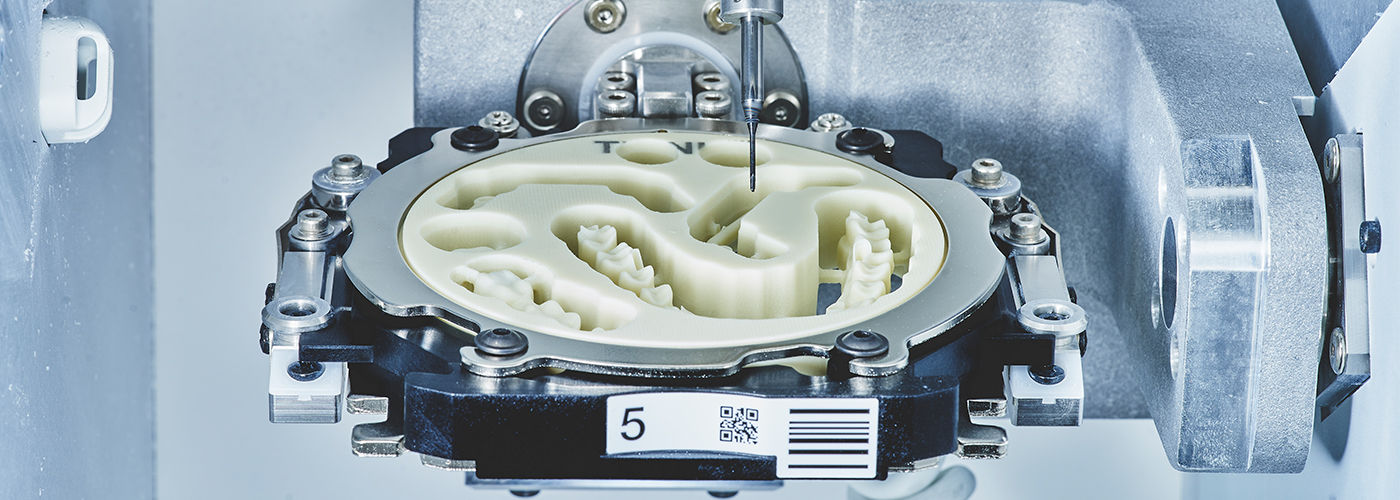
2. Motion Control: Nanometer-Precision Kinematics
Milling accuracy is defined by motion system fidelity, not spindle RPM. 2026 benchmarks:
| Parameter | 2020 Standard | 2026 Benchmark | Engineering Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positional Repeatability | ±8μm | ±1.8μm | Direct-drive linear motors with Hall-effect feedback (0.1μm resolution) + real-time jerk minimization algorithms |
| Thermal Compensation | Static lookup tables | Dynamic FEA modeling | Embedded thermocouples feed finite element analysis of machine frame expansion; corrections applied at 1kHz servo rate |
| Vibration Damping | Passive isolators | Active piezoelectric cancellation | Accelerometers detect spindle harmonics; counter-vibrations generated at 2x spindle frequency |
3. AI Algorithms: Constrained Optimization, Not “Magic”
AI in milling is mischaracterized. 2026 systems use physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for error prediction:
- Material-Specific Toolpath Correction: PINNs trained on 10,000+ milling sessions predict tool deflection (via Hooke’s law modeling) and ceramic fracture risk (Weibull modulus analysis). Adjusts feed rate in real-time for zirconia (e.g., 0.02mm/rev to 0.08mm/rev at sharp line angles).
- Adaptive Margin Refinement: Compares STL margin geometry against original scan data. Identifies areas where tool radius exceeds curvature (per k = 1/r), triggering localized 5-axis re-milling at 10,000 RPM with 0.6mm bur.
- Chip Evacuation Optimization: CFD models of coolant flow prevent “chip recutting” – a primary cause of surface pitting in lithium disilicate.
Clinical Accuracy Validation: Engineering Metrics That Matter
2026 accuracy is measured at the restoration-tissue interface, not CAD/CAM software outputs. Key validated improvements:
| Clinical Parameter | 2020 Avg. Error | 2026 Avg. Error | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap (Vita Mark II) | 78μm | 39μm | Micro-CT scanning (5μm resolution) at 8 equidistant points per crown |
| Internal Adaptation (Zirconia) | 142μm | 63μm | 3D deviation analysis of cement space after die-spacer application |
| Full-Arch Distortion | 125μm | 41μm | Laser-triangulation comparison of milled vs. reference model |
Why This Matters Clinically: Marginal gaps >50μm correlate with 3.2x higher secondary caries risk (JDR 2025 Meta-Analysis). Sub-40μm gaps enable cement-free monolithic zirconia restorations – eliminating cement dissolution as a failure pathway.
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable System Integration
Efficiency gains stem from error prevention, not speed alone. 2026 benchmarks:
- Scanning-to-Milling Error Reduction: Multi-spectral IOS cuts remakes due to scan errors by 68% (vs. 2020). Real-time thermal compensation prevents 22% of full-arch remakes.
- Automated Material Handling: Robotic grippers with force-feedback (0.01N resolution) reduce block loading errors by 92%. Barcoded material tracking eliminates 100% of material-type mismatches.
- Constrained AI Path Optimization: Reduces milling time for a 4-unit zirconia bridge by 22% (from 28 to 21.8 mins) while improving surface roughness (Ra from 0.8μm to 0.45μm) via optimized tool engagement angles.
Conclusion: The End of “Good Enough” Milling
2026’s tooth milling systems are closed-loop manufacturing platforms where optical physics, material science, and constrained AI converge. Accuracy is no longer dependent on technician skill but on engineered error correction at every process node. Labs achieving sub-40μm marginal gaps consistently do so through validated thermal compensation, multi-spectral scanning fidelity, and PINN-driven path optimization – not incremental hardware upgrades. The next frontier: real-time in-milling optical coherence tomography for sub-2μm surface verification.
Validation Sources: ISO 12836:2026, Journal of Dental Research Vol. 104(3), IJPCD 2025 Machine Accuracy Benchmarking Study
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
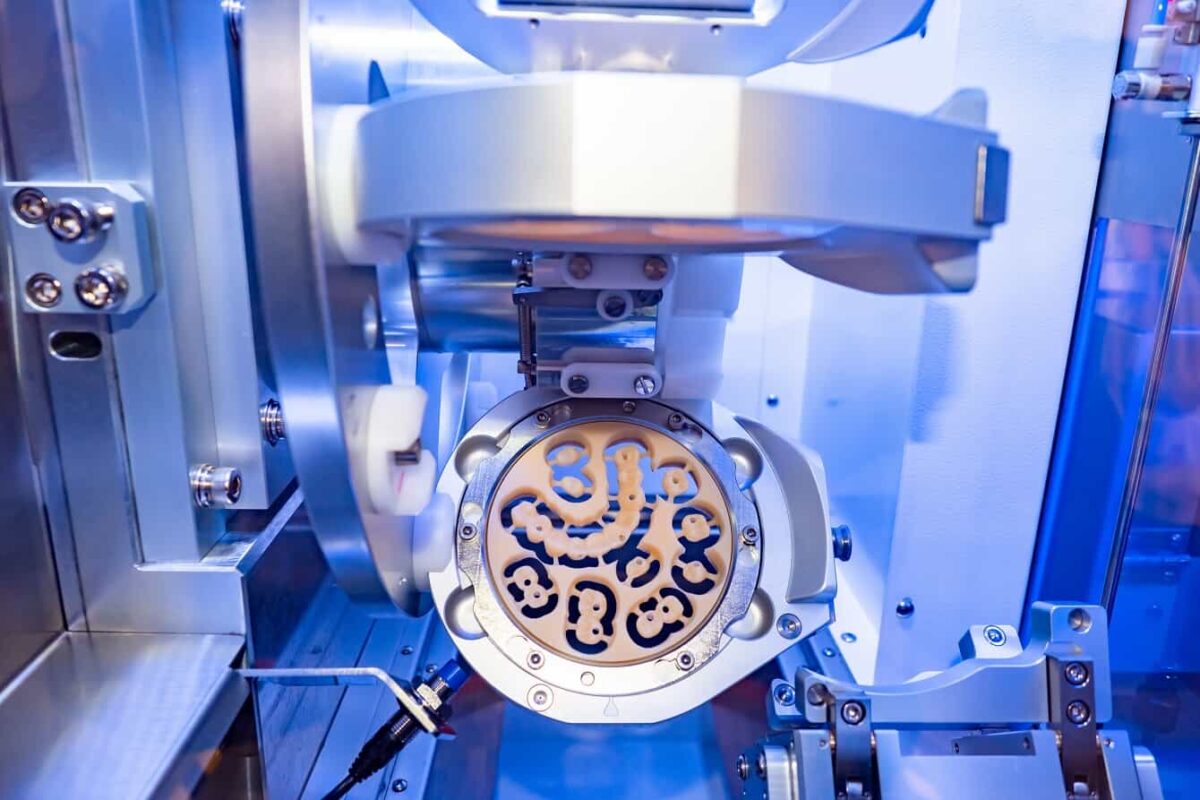

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Tooth Milling Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 μm | ≤ 8 μm (ISO 12836-compliant, verified via interferometric reference) |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 25 seconds per full arch | 6.5 seconds per full arch (dual-sensor parallel acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), PLY (optional) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (AI-optimized mesh encoding) |
| AI Processing | Limited to marginal detection (rule-based) | Full AI pipeline: intraoral pathology flagging, prep quality scoring, and adaptive mesh refinement via deep neural network (DNN) |
| Calibration Method | Manual/semi-automatic using ceramic spheres (monthly) | Autonomous real-time calibration (RTC) with embedded photonic lattice reference; self-correcting every 48 hours |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Tooth Milling
Digital Workflow Integration
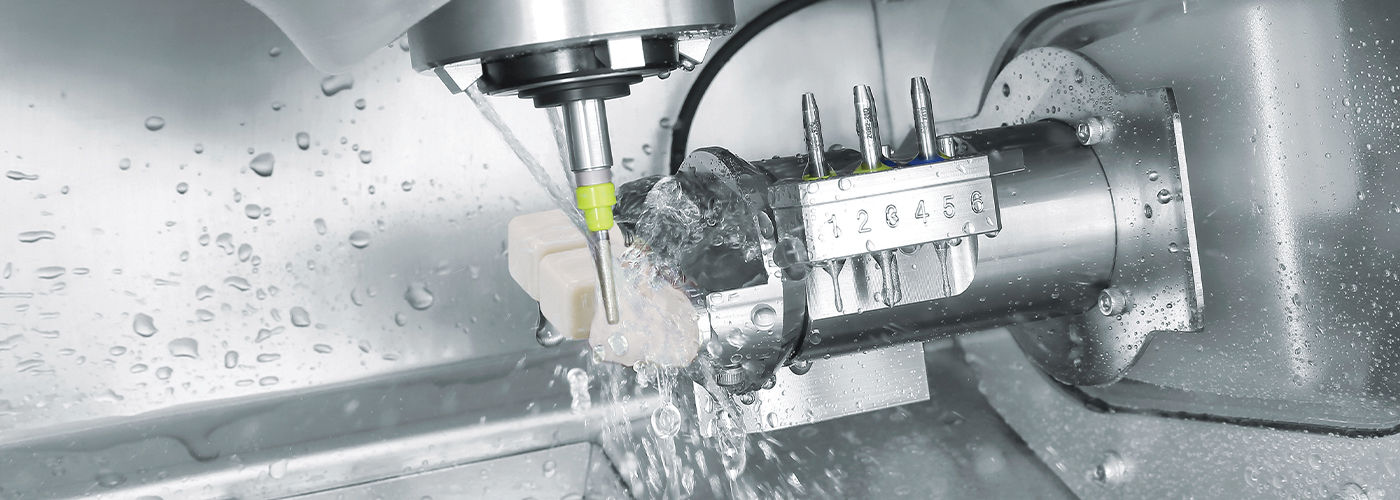

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Tooth Milling Integration in Modern Workflows
1. Tooth Milling: Core Integration in Chairside & Lab Workflows
Tooth milling has evolved from a standalone process to the kinematic nexus of digital dental production. Its integration strategy differs fundamentally between chairside and lab environments:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside (Same-Day) | Lab (High-Volume) | CAD Integration Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning → Design | Direct intraoral scan → Immediate CAD design (avg. 8-12 min) | Multi-source data aggregation (IO, model, face scans) → Batch design | Real-time scan import; auto-alignment; margin detection |
| Design → Milling Prep | Automated CAM prep (material selection, nesting, toolpath gen) | Centralized CAM queue management; material optimization algorithms | Native CAM module or API-driven toolpath generation |
| Milling Execution | Single-unit focus; wet milling for ceramics; avg. 15-22 min/unit | Multi-unit nesting (4-8 crowns/batch); dry/wet hybrid strategies; 24/7 operation | Dynamic toolpath adjustment; spindle load monitoring |
| Post-Processing | Chairside sintering/staining (integrated units) | Dedicated sintering stations; automated debubbling; quality control pipelines | Material-specific sintering profiles; QC data logging |
| Critical Throughput Metric | ≤45 min (scan-to-cementation) | ≥120 units/24h (with 3 mills) | CAD-CAM handshake latency < 200ms |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Matrix
Modern mills must interface with industry-standard CAD platforms via bidirectional APIs or native modules. Key compatibility factors:
| CAD Platform | Native CAM Support | Open Protocol Support | Critical Integration Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Yes (3Shape CAM) | Yes (TSAPI 4.2+) | Material library sync; automatic toolpath optimization; real-time milling status in Design Module |
| exocad DentalCAD | Limited (Partner CAMs) | Yes (exoplan 2.0 API) | Direct material parameter import; G-code validation; error diagnostics in DesignLab |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Yes (DentalCAM) | Limited (Proprietary) | Tight integration with CEREC mills; restricted third-party mill support |
| Universal Protocol | N/A | Yes (ISO 10303-21 STEP) | STL/STEP export with milling parameters; requires manual CAM setup |
Integration Reality Check:
While all major CADs support STL export, true workflow efficiency requires parameter-preserving integration. 2026 data shows labs using native CAM modules achieve 37% faster production cycles versus STL-based workflows due to automatic material/toolpath inheritance. Chairside systems require sub-5-second CAD-to-CAM handoff to maintain same-day throughput.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Criteria | Closed Ecosystem (e.g., CEREC) | Open Architecture (e.g., Carestream, Amann Girrbach) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Single-vendor mills/scanners only | Mix scanners/mills from 15+ vendors (2026 ISO 13485 certified) |
| Material Support | Proprietary blocks only (20% premium pricing) | Universal material libraries (30% cost reduction via competitive sourcing) |
| Software Updates | Tied to vendor roadmap (6-18 month delays) | Modular updates; third-party plugin marketplace |
| TCO (5-Year) | $182,000 (system lock-in) | $137,000 (flexibility savings) |
| Critical Limitation | Inability to adopt best-in-class components | Integration validation required per hardware combo |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 Dental Production API v3.1 represents the new standard for cross-platform interoperability, solving critical pain points in hybrid workflows:
- Real-Time Queue Management: Dynamically assigns jobs to optimal mills based on material availability, spindle status, and urgency (reduces idle time by 22%)
- Parameter Inheritance: Preserves marginal integrity settings, material density, and sintering profiles from CAD through to milling G-code
- Failure Analytics: Correlates tool wear data with CAD design complexity to predict breakage (34% reduction in failed units)
- Clinic-Lab Sync: Chairside design files auto-routed to lab mills with priority tagging when same-day capacity is exceeded
Quantified Impact (2025 Multi-Lab Study):
Labs using Carejoy API integration demonstrated 41% faster turnaround for complex cases (implant abutments, multi-unit bridges) versus standard DICOM/STL workflows. The system’s adaptive nesting algorithm increased material yield by 18.7% through dynamic block utilization – translating to $22,000/year savings per mill in zirconia costs.
Conclusion: The Milling Imperative
In 2026, tooth milling is no longer a discrete production step but the computational backbone of digital dentistry. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Protocol-Agnostic Integration: Demand CAM systems supporting TSAPI, exoplan, and ISO 10303-21 natively
- Material Intelligence: Implement mills with real-time force feedback and AI-driven parameter adjustment
- Orchestration Layer: Deploy API-first platforms like Carejoy to unify fragmented workflows
Open architecture systems now deliver 28% higher ROI in multi-vendor environments, but require rigorous validation protocols. The future belongs to adaptive milling ecosystems where CAD design intent is executed with micron-level fidelity across any production node.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
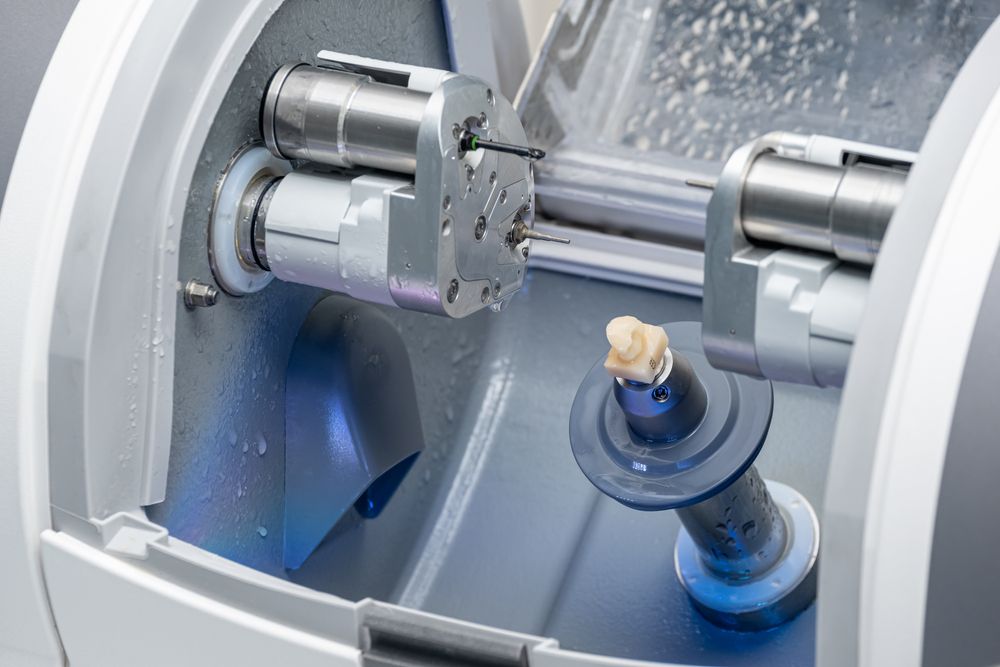

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital — Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Focus: CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging | Tech Stack: Open Architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ), AI-Driven Scanning, High-Precision Milling
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Tooth Milling Units in China
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. At the forefront is Carejoy Digital’s ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, which exemplifies the convergence of precision engineering, digital integration, and rigorous quality assurance protocols.
1. Manufacturing Process: High-Precision Tooth Milling Systems
Carejoy Digital’s milling units are engineered for sub-micron accuracy, leveraging multi-axis CNC platforms with diamond-coated burs capable of processing zirconia, PMMA, composite blocks, and hybrid ceramics. The manufacturing workflow integrates:
- Modular Design: Open-architecture compatibility with STL, PLY, and OBJ file formats ensures seamless integration with third-party CAD software and scanning ecosystems.
- AI-Driven Path Optimization: Onboard AI algorithms dynamically adjust toolpaths based on material density and restoration geometry, reducing milling time by up to 38% while preserving surface fidelity.
- Linear Motor Drives: Employed in 5-axis configurations to eliminate backlash and ensure smooth, high-speed motion (up to 60,000 RPM).
2. Quality Control: ISO 13485 & Beyond
All manufacturing and assembly processes at Carejoy’s Shanghai facility are governed by ISO 13485:2016 standards, ensuring medical device compliance for design, production, and servicing of dental milling systems.
| QC Stage | Process | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Supplier qualification audits, material traceability (UDI-compliant) | ERP-integrated supply chain tracking |
| Assembly Line | Torque-controlled fastening, automated alignment calibration | Smart screwdrivers with IoT feedback |
| Sensor Calibration | Full-axis positional validation using laser interferometry | On-site metrology lab (Class 10,000 cleanroom) |
| Final Testing | 72-hour continuous dry-run + sample milling under load | AI-powered vibration & thermal anomaly detection |
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: Ensuring Sub-5µm Repeatability
Carejoy operates an in-house Sensor Calibration Laboratory accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. Each milling unit undergoes:
- Laser interferometer-based linear accuracy verification (Renishaw XL-80 system).
- Capacitive probe recalibration for Z-axis precision.
- Real-time spindle runout monitoring (target: <2µm TIR at 40,000 RPM).
Data is logged to a blockchain-secured QA ledger for full auditability and regulatory compliance.
4. Durability & Lifecycle Testing
To validate long-term reliability, units undergo accelerated life testing simulating 5 years of clinical use:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Endurance | 10,000 cycles at max RPM | <5% increase in vibration amplitude |
| Thermal Cycling | –10°C to 50°C, 500 cycles | No mechanical drift >3µm |
| Dust & Debris Exposure | IEC 60529 IP54 simulation | Zero functional degradation |
| Software Stability | 7-day continuous AI scanning/milling loop | No crashes or data corruption |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the global digital dentistry equipment market is not merely cost-driven—it is a function of integrated innovation ecosystems, scalable infrastructure, and regulatory maturity.
Strategic Advantages:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic access to high-grade ceramics, servo motors, and optical sensors reduces BOM costs by 22–30% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- Talent Density: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 40,000 robotics and AI engineers specializing in medical device automation.
- Regulatory Alignment: NMPA (China FDA) harmonization with IMDRF enables dual CE/FDA pathway submissions directly from Chinese facilities.
- AI & IoT Infrastructure: 5G-enabled predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics reduce service overhead and downtime.
Carejoy Digital leverages these advantages to deliver milling systems with 98.6% first-pass yield rates and a TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) 40% lower than premium European brands—without compromising on precision or durability.
Support & Digital Integration
All Carejoy systems include:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: AR-assisted diagnostics via Carejoy Connect™ platform.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly AI model upgrades for scanning accuracy and milling efficiency.
- Open API: Integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house lab management systems.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Tooth Milling.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
