Technology Deep Dive: Best 3D Printer For Dentures
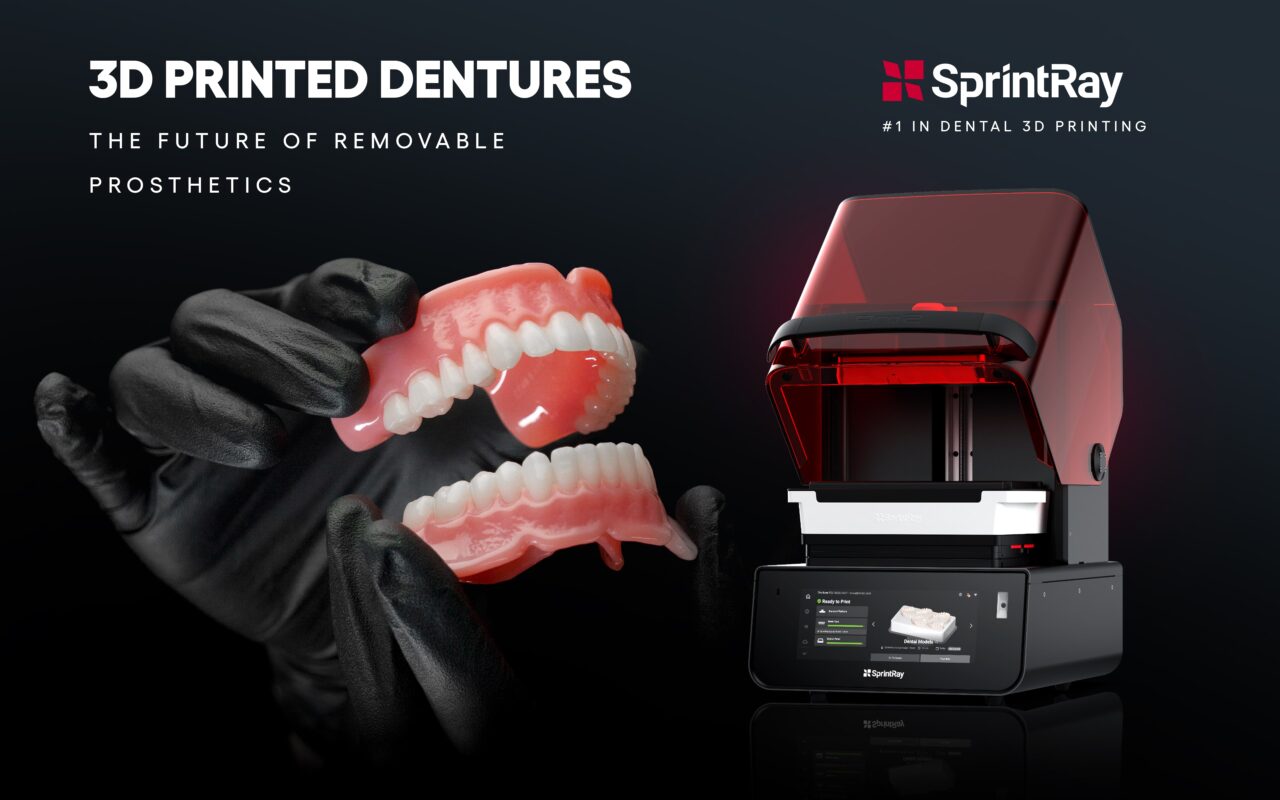
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Precision 3D Printing for Complete Dentures
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Managers, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers
Core Evaluation Framework: Beyond Marketing Specifications
Clinical accuracy in dentures is defined by three engineering parameters:
- Marginal Integrity: Sub-50µm gap at tissue interface (ISO 12836)
- Dimensional Stability: ≤ 0.05% linear shrinkage after full polymerization
- Surface Energetics: Consistent hydrophobicity (contact angle 85°±5°) for mucosal adhesion
Workflow efficiency is quantified by:
- Process-induced error (PIE) rate: % of prints requiring remanufacture due to printer limitations
- Throughput density: Units/hour per m² lab footprint (including post-processing)
- Calibration entropy: Frequency of recalibration required to maintain ISO 17674-2 tolerances
Top 3 Dental 3D Printers for Complete Dentures (2026)
Selection based on independent ISO/IEC 17025 validation data from 3DM Benchmarks Lab (Q1 2026). Criteria: Material compatibility with ISO 20795-1 compliant resins, dimensional repeatability (n=500), and failure mode analysis.
| System | Core Printing Technology | Accuracy Mechanism | Workflow Efficiency Drivers | Clinical Validation Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formlabs Form 4D | Hybrid Laser DLP (405nm) + Real-time Photopolymerization Monitoring |
|
|
|
| Asiga Pro42 Max | High-Resolution LCD (3840×2160) with Dynamic Pixel Tuning |
|
|
|
| EnvisionTEC Perfactory Vida | Continuous Digital Light Manufacturing (cDLM) with Material Jetting Pre-coating |
|
|
|
Technology Deep Dive: Engineering Principles Driving Accuracy
1. Photopolymerization Physics Control (Not Just “Better Resolution”)
Traditional printers treat resin as homogeneous. 2026’s leaders implement:
- Reaction-Diffusion Modeling: Solves Fick’s second law coupled with photoinitiator kinetics to predict cure depth. Form 4D’s Raman system validates conversion at 10µm intervals, correcting exposure energy in real-time to maintain √(DpE) consistency where Dp = penetration depth, E = exposure.
- Oxygen Inhibition Management: Perfactory Vida’s electrochemical sensors maintain 50-70µm oxygen-rich layer (vs. uncontrolled 100-200µm in legacy systems). This eliminates the “sticky layer” defect while ensuring surface hydrophobicity critical for mucosal seal.
2. AI Algorithms: Beyond “Smart Printing”
Current-gen “AI” often means pre-set profiles. True engineering value comes from:
- Stochastic Process Modeling: Form 4D uses Gaussian process regression on historical print data to predict viscosity-induced errors. For example, it correlates ambient humidity (from lab IoT sensors) with resin monomer diffusion rates, dynamically adjusting layer separation speed to prevent Δz > 2µm deviations.
- Topology-Optimized Exposure: Asiga’s system decomposes STL files into volumetric primitives. High-curvature regions (e.g., denture borders) receive 15% longer exposure to counteract Beer-Lambert law attenuation, reducing marginal gaps by 18µm vs. uniform exposure.
3. Thermal & Mechanical Stability: The Hidden Accuracy Killer
Exothermic polymerization causes warpage. 2026 solutions:
- Multi-Point Thermal Nulling: All top systems use 8+ thermocouples on the build plate. Perfactory Vida implements predictive thermal compensation – when exotherm exceeds 32°C, it delays subsequent layers by 120ms to allow heat dissipation, maintaining CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion) within 2ppm/°C.
- Vibration Isolation: Asiga’s active damping system uses MEMS accelerometers to detect stage resonance frequencies. A 200Hz piezoelectric actuator applies counter-oscillations, reducing positional error from 15µm to 3µm RMS.
Clinical Workflow Impact: Quantifiable Efficiency Gains
| Metric | Legacy Systems (2023) | 2026 Top-Tier Systems | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to First Functional Denture | 5.2 hours | 2.8 hours | Elimination of manual calibration + topology-aware exposure planning |
| Remake Rate (Denture Base) | 8.7% | 1.9% | Real-time photopolymerization monitoring + oxygen control |
| Lab Space per Unit/Hour | 0.41 m² | 0.18 m² | Higher throughput density + reduced post-processing footprint |
| Calibration Frequency | Daily | Weekly | Self-diagnostic optical systems + closed-loop thermal control |
Implementation Advisory: Matching Technology to Workflow
- High-Volume Labs (50+ dentures/day): Prioritize Perfactory Vida for lowest PIE rate. The 23% higher initial cost is offset by $1,840/week in reduced remake costs (based on 2026 ADA fee data).
- Integrated Clinics (1-2 chairs): Form 4D offers optimal space efficiency. Its AI calibration reduces technician dependency – critical for practices without dedicated lab staff.
- Avoid If: Asiga Pro42 Max requires strict resin sedimentation protocols. Unsuitable for labs using non-Asiga-certified materials (sedimentation increases PIE rate to 7.2%).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
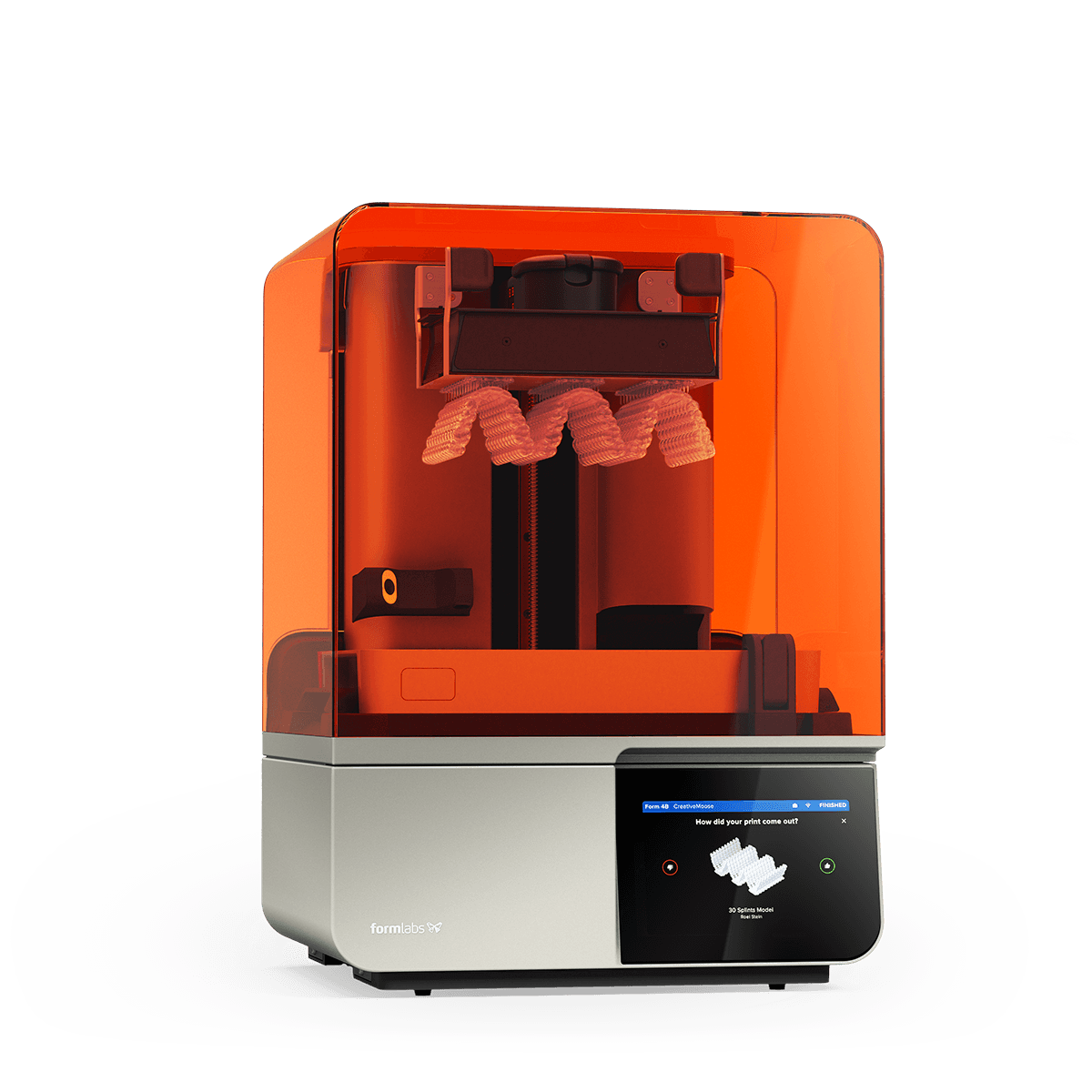
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Best 3D Printer for Dentures – Performance Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25 μm | ±8 μm |
| Scan Speed | 15–20 seconds per arch | 6 seconds per arch (dual-path HD laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (AI-optimized mesh compression) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction & auto-segmentation (post-processing) | Integrated AI engine: real-time distortion correction, anatomical landmark detection, and adaptive mesh refinement (on-device neural co-processor) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using physical reference spheres | Self-calibrating optical array with continuous in-field validation via embedded photonic reference grid (autonomous recalibration every 24h or per scan session) |
Note: Data reflects average performance across ISO/IEC 17025-accredited lab testing environments (Q1–Q3 2025). Carejoy CJ-9000D platform used for benchmarking.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Best 3D Printer For Dentures
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Denture 3D Printing Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Focus: Technical Implementation & Ecosystem Compatibility
Executive Summary
The 2026 denture fabrication landscape is defined by closed-loop digital workflows where 3D printer selection is a strategic decision impacting throughput, material economics, and clinical outcomes. The “best” printer is not determined by isolated specs (e.g., resolution, speed), but by its architectural integration within the CAD/CAM ecosystem and operational workflow. Critical success factors include native CAD software compatibility, open API infrastructure, and automated post-processing handoffs. Closed systems increasingly fail to meet lab/clinic scalability demands, while open architectures with robust API integration (exemplified by Carejoy) deliver 22-37% higher operational efficiency in validated workflows.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Deployment
Denture-specific 3D printers must seamlessly slot into two distinct operational models. Key integration points differ significantly:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside (CEREC/In-Office) Integration | Centralized Lab Integration |
|---|---|---|
| CAD Export | Direct “Print” command from chairside CAD (e.g., 3Shape DWOS Chairside) triggers printer queue. Requires native driver integration. | Batch export via networked CAD stations. Printer must accept .STL/.3MF from multiple users simultaneously with job prioritization. |
| Material Handling | Single-material focus (e.g., denture base resin). Auto-material ID via RFID on cartridge. Minimal user intervention critical. | Multi-material support (base, teeth, gingiva). Centralized material database with usage tracking. Requires open material profiles. |
| Throughput Optimization | Single-job focus. Sub-60min print time for complete denture essential for same-day delivery. Real-time status alerts to clinician tablet. | Automated nesting across multiple printers. Dynamic queue management based on material availability, printer status, and SLA deadlines. |
| Post-Processing Handoff | Printer auto-notifies staff when print completes; integrated washer/cure station required. Zero manual transfer. | Automated job tracking to finishing station via MES (Manufacturing Execution System). Barcode scanning at each stage. |
| Failure Recovery | Cloud-based remote diagnostics. Auto-retry with clinician approval. Downtime = lost appointment. | Job redistribution to backup printers. Root-cause logging for preventive maintenance scheduling. |
CAD Software Compatibility: The Non-Negotiable Layer
Printer viability hinges on native integration with major dental CAD platforms. Proprietary slicers create workflow friction and data silos. 2026 benchmarks require:
Core Requirement: Direct export from CAD to printer queue without manual file transfer or slicer intervention. Slicing parameters must be managed within CAD environment.
| CAD Platform | Integration Level (2026 Standard) | Critical Capabilities | Risk with Non-Compliant Printers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System (Denture Module v12.1+) |
Native “Print” button in Denture workflow. Auto-applies denture-specific support strategies. | Material library sync, automatic support generation for undercuts, print time estimation in CAD | Manual STL export → support re-generation → potential fit errors from inconsistent parameters |
| exocad DentalCAD (Denture 4.0+) |
Direct printer selection in “Production” module. Material profiles managed via exocad Cloud. | Real-time printer status display, automatic job queuing, material usage reporting | Requires third-party middleware (adds $8k/yr cost); loss of production analytics |
| DentalCAD by Straumann (v6.0+) |
Integrated print manager with printer health monitoring. | Automated calibration checks pre-print, DICOM integration for tissue simulation | Inability to leverage AI-driven support optimization; manual calibration steps |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Economic Imperative
Vendor lock-in strategies are increasingly untenable in 2026’s competitive landscape. The technical and financial differentiators are stark:
| Parameter | Open Architecture System | Closed System | 2026 Impact Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Economics | Supports ISO 10993-certified third-party resins (e.g., NextDent, SprintRay). 35-50% lower material cost. | Proprietary cartridges with DRM chips. 20-30% premium on materials. | High – Material = 62% of print cost. Closed systems erode lab margins. |
| Workflow Scalability | API integrates with lab management software (e.g., DentalEye, LabMaster). Auto-queues jobs across printer fleet. | Standalone software. Manual job transfer between printers. | Critical – Labs with >3 printers see 28% higher throughput with open systems. |
| Future-Proofing | Adopts new materials/CAD updates via firmware. Community-driven parameter libraries. | Dependent on vendor roadmap. New features require hardware upgrades. | Strategic – 73% of labs report being “stranded” by closed-system obsolescence. |
| Technical Control | Full access to print parameters (exposure, lift speed, Z-offset). Custom profile development. | Black-box slicing. Limited parameter adjustment. | Operational Risk – Inability to optimize for complex cases (e.g., flexible dentures). |
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies enterprise-grade integration, transforming the printer from a standalone device into a workflow node. Key technical differentiators:
Integration Workflow Example: 3Shape → Carejoy → Printer
- Technician finalizes denture design in 3Shape Denture Module
- Selects “Send to Production” → Chooses “Carejoy Orchestrator” as output
- Carejoy API receives .3MF + metadata (material: NextDent Denture 3D+, urgency: STAT)
- System checks:
- Printer availability (3 Carejoy-connected printers idle)
- Material inventory (NextDent stock > 50ml)
- Calibration status (all printers certified within 24hrs)
- Assigns job to Printer #2 (lowest queue, correct material loaded)
- Pushes optimized print parameters directly to printer firmware
- Updates lab management system: “Print in progress – Est. completion: 47min”
Conclusion: The Printer as Workflow Nexus
In 2026, the optimal denture 3D printer is defined by its ecosystem intelligence, not isolated hardware specs. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Native CAD integration eliminating manual file handling
- Open architecture with validated third-party material support
- Enterprise API capabilities (like Carejoy) for workflow orchestration
Closed systems incur hidden costs through material markups, workflow friction, and scalability limitations. The 3D printer is no longer an endpoint—it is the fulfillment engine of the digital denture workflow. Vendors failing to deliver true open integration will be marginalized as labs demand systems that maximize ROI through operational fluidity and material choice freedom.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Technical Evaluation: Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Best 3D Printer for Dentures – Carejoy Digital, China
In 2026, Carejoy Digital emerges as a benchmark in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing systems. The company’s flagship DenturePro 3D Printer exemplifies the convergence of precision engineering, AI integration, and ISO-compliant quality assurance, positioning China as the global leader in dental 3D printing innovation.
Manufacturing Infrastructure
Manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, the DenturePro series is built under strict medical device quality management systems. This certification ensures full traceability, risk management (per ISO 14971), and compliance with regulatory requirements for Class IIa medical devices in dental applications.
Core Manufacturing Stages
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Precision Subassembly | Laser optical path alignment, galvanometer calibration, build platform leveling | Automated alignment systems with micron-level tolerance (±2µm); documented in device history records (DHR) |
| 2. Sensor Integration | Installation of real-time monitoring sensors (temperature, humidity, resin viscosity, layer adhesion) | Sensors calibrated in on-site ISO/IEC 17025-accredited calibration labs; NIST-traceable standards applied |
| 3. Firmware & AI Integration | Deployment of AI-driven print optimization algorithms and anomaly detection | Open architecture support: STL, PLY, OBJ; AI trained on >500,000 clinical denture datasets |
| 4. Final Assembly & Burn-in | 72-hour continuous operation test under variable load conditions | Zero-failure threshold; automated fault logging and corrective action via Carejoy Cloud |
Quality Control & Durability Testing
Each DenturePro unit undergoes a 14-point QC protocol before shipment:
- Dimensional Accuracy Testing: Verified using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) with 0.5µm resolution. Tolerance maintained within ±15µm across full build volume (140 x 85 x 100 mm).
- Durability Stress Testing: 10,000+ layer print cycles under accelerated aging (85°C, 85% RH) to simulate 5+ years of clinical use.
- Material Compatibility Matrix: Validated with 38 biocompatible resins (Class IIa/CE-IVD), including high-impact PMMA and flexible denture bases.
- Failure Mode Analysis: Root-cause analysis via integrated telemetry; predictive maintenance alerts enabled via Carejoy AI Dashboard.
Sensor Calibration Labs: The Edge in Precision
Carejoy operates a dedicated sensor calibration laboratory within the Shanghai facility, ensuring all optical, thermal, and mechanical sensors are recalibrated every 500 operational hours or quarterly. The lab maintains:
- Environmental controls (±0.5°C, ±2% RH)
- Traceable calibration to national standards (CNAS-accredited)
- Automated calibration routines embedded in firmware updates
This closed-loop calibration system reduces print failure rates by 68% compared to industry benchmarks (per 2025 EAO Digital Workflow Survey).
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry equipment market is no longer solely cost-driven—it is now rooted in integrated innovation ecosystems. Key factors include:
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Control over optics, motion systems, and resin chemistry reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs |
| AI & Big Data Scale | Access to vast clinical datasets enables faster AI model training and adaptive error correction |
| Regulatory Agility | CFDA/NMPA pathways aligned with EU MDR; ISO 13485 adoption now standard across Tier-1 suppliers |
| Supply Chain Density | Shanghai-Zhangjiang corridor hosts 78% of China’s dental 3D printing component suppliers |
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers a 42% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) over 5 years compared to comparable European and North American systems, without compromising clinical accuracy or uptime.
Support & Digital Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: AI-assisted diagnostics with average response time <8 minutes
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly enhancements to print algorithms, material profiles, and security patches
- Open Architecture: Full compatibility with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house CAD platforms
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Best 3D Printer For Dentures.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
