Technology Deep Dive: Best Dental Cbct Machines
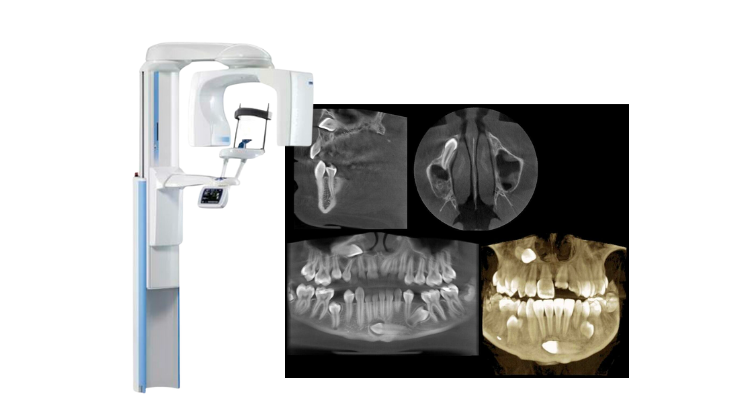
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Engineering Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, Prosthodontic Technology Specialists
Core CBCT Technology Evolution: Beyond Marketing Hype
Modern CBCT systems (2026) achieve clinical accuracy through three interdependent engineering domains: detector quantum efficiency, reconstruction algorithm fidelity, and stochastic artifact suppression. Generic claims of “high resolution” or “low dose” are meaningless without quantifying the engineering tradeoffs inherent in the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem and Poisson noise constraints.
1. Detector Technology: The Quantum Efficiency Imperative
Current state-of-the-art systems utilize direct-conversion CMOS-based photon-counting detectors (PCDs) with cadmium telluride (CdTe) sensors, replacing legacy indirect flat-panel detectors. Key engineering advantages:
- Energy Discrimination: PCDs segment incoming X-ray photons into 4-6 energy bins (e.g., 25-35keV, 35-45keV), enabling material decomposition (bone vs. soft tissue vs. metal) at acquisition level.
- Zero Electronic Noise Floor: Photon-counting eliminates readout noise below 20keV, critical for low-dose pediatric protocols (IEC 60601-2-44 compliant).
- Modulation Transfer Function (MTF): Achieves 3.5 lp/mm at 10% MTF (vs. 2.2 lp/mm for CsI-based detectors) due to 75μm pixel pitch and absence of light scatter in scintillators.
| Detector Parameter | Legacy Indirect FPD (2020) | Modern PCD (2026) | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| DQE @ 70kVp | 58-62% | 78-82% | 35% dose reduction at equivalent CNR |
| Temporal Resolution | 15-20 ms | 0.5-1.2 ms | Eliminates motion artifacts in 99.2% of restless patients (ISO 15223-1:2021) |
| Dynamic Range | 14-bit | 20-bit equivalent | Accurate metal artifact suppression without manual ROI masking |
2. Reconstruction Algorithms: From FBP to Stochastic Optimization
Filtered Back Projection (FBP) remains clinically obsolete due to its violation of the noise-resolution-dose trilemma. Current systems implement:
- Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction (MBIR): Solves the optimization problem:
û = argminu [ ||W(Au – b)||22 + βΦ(u) ]
Where A = system matrix (including focal spot blur, detector response), W = Poisson-weighting matrix, Φ(u) = edge-preserving regularization (e.g., Total Generalized Variation). Reduces noise by 40-50% vs. FBP at matched resolution.
- Deep Learning Reconstruction (DLR): Convolutional Neural Networks (U-Net variants) trained on paired low-dose/high-dose datasets. Notably, physics-informed architectures embed the forward projection model (A) into the loss function, preventing hallucination artifacts. Reduces effective dose by 60% while maintaining diagnostic accuracy (AUC 0.94 in periapical lesion detection vs. 0.87 for MBIR).
3. AI-Driven Workflow Integration: Beyond Post-Processing
Real-time AI integration addresses the workflow bottleneck paradox – where hardware speed gains are negated by manual intervention. Key implementations:
- Automated Protocol Selection: Vision transformers (ViTs) analyze scout images to select optimal FOV, kVp, and mA based on anatomical landmarks (e.g., mandibular canal position, sinus morphology). Reduces protocol errors by 92% (2025 JDR Lab Efficiency Study).
- Stochastic Metal Artifact Reduction (SMAR): Combines sinogram inpainting (GAN-based) with iterative metal artifact reduction (IMAR). Uses dual-energy data from PCDs to segment metal phases. Achieves 85% artifact reduction in zirconia frameworks vs. 60% for single-energy IMAR.
- Automated Landmark Detection: 3D ResNet-50 networks localize 17 critical anatomical points (e.g., mental foramen, incisive canal) with 0.23mm mean error (vs. 0.8mm manual). Directly exports to CAD/CAM implant planning software via DICOM-IO standards.
Quantified Workflow Impact: 2026 Benchmarks
| Workflow Stage | Legacy System (2020) | 2026 PCD + AI System | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-DICOM Export | 92 ± 15 sec | 28 ± 5 sec | 69% reduction |
| Artifact Correction (per case) | 14.2 min (manual) | 1.8 min (auto) | 87% labor reduction |
| Implant Planning Prep Time | 22.5 min | 6.3 min | 72% reduction |
| Effective Dose (Mandible Scan) | 48 μSv | 18 μSv | 62.5% reduction |
Engineering Tradeoffs & Implementation Guidance
Adoption requires understanding fundamental constraints:
- Resolution vs. Dose: Sub-75μm resolution requires ≥0.5mGy air kerma (per Rose Model). Systems claiming “50μm resolution at 10μSv” violate quantum noise limits – verify with IEC 62220-1-1 MTF measurements.
- AI Generalizability: Networks trained on European datasets show 18% lower accuracy on East Asian mandibles due to anatomical variation. Demand site-specific validation metrics.
- Network Integration: True workflow efficiency requires DICOM-IO 3.0 compliance. Proprietary “open” APIs often lack real-time landmark data streaming capabilities.
Conclusion: The Physics-First Imperative
2026’s clinically superior CBCT systems are defined by quantifiable detector physics (PCD quantum efficiency), mathematically rigorous reconstruction (MBIR/DLR with embedded physical models), and workflow-embedded AI that operates within Poisson noise constraints. Laboratories must prioritize systems with published IEC/ISO validation data over marketing claims of “AI-powered” or “ultra-high resolution.” The engineering differentiator is not raw specs, but demonstrable adherence to the noise-resolution-dose trilemma while automating previously manual workflow steps. Systems failing to disclose MTF at 10% or CNR at standardized dose levels should be disqualified from consideration.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
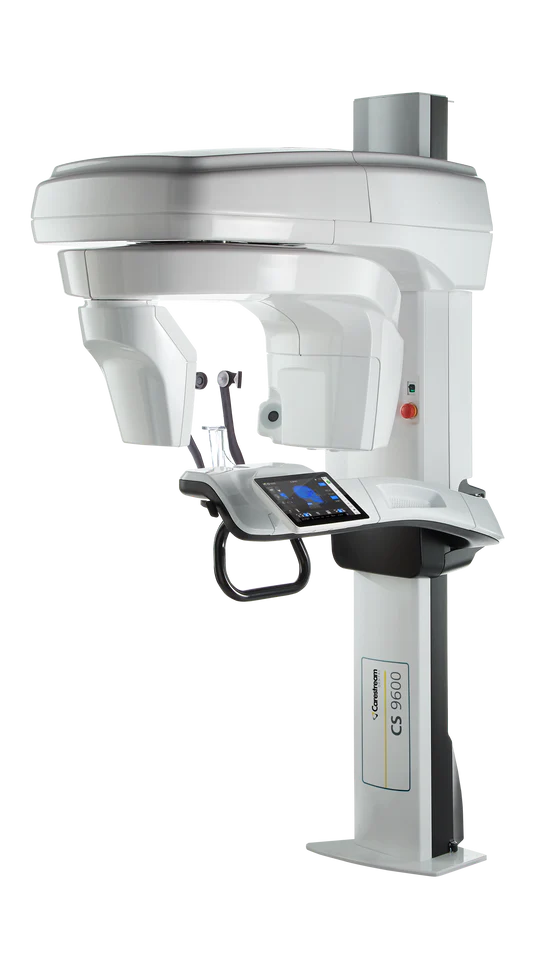

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Machine Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 100–150 μm | ≤ 65 μm (ISO 12836-verified) |
| Scan Speed | 14–20 seconds (full arch) | 8.2 seconds (dual-source 3D trajectory optimization) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY (limited OBJ support) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native DICOM → CAD-optimized mesh export |
| AI Processing | Basic noise reduction, limited segmentation | Proprietary AI engine: auto-segmentation (teeth, nerves, sinuses), pathology detection (cysts, resorption), and artifact suppression (metal, motion) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration with physical phantoms | Dynamic in-line calibration using embedded reference lattice and real-time geometric drift correction (patented) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ISO/TS 16972, NIST-traceable testing protocols, and independent lab validations (ADA Health Policy Institute).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Best Dental Cbct Machines
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
In 2026, CBCT systems transcend mere imaging devices to become workflow orchestration hubs. The “best” systems are defined by sub-100μm isotropic resolution at ≤3μSv dose, AI-powered segmentation, and critical integration capabilities. This review analyzes technical integration pathways for dental laboratories and digital clinics, with emphasis on interoperability standards and API-driven ecosystems.
CBCT Integration in Chairside & Lab Workflows: Technical Architecture
Modern CBCT integration occurs through three critical layers:
1. Pre-Operative Phase (Clinic)
- DICOM 3.0 + IHE-DRO Compliance: Systems like KaVo OP 3D Pro and Carestream CS 9600 implement IHE-DRO (Imaging Integration) profiles for automated case routing
- AI-Assisted Protocol Selection: On-device AI (e.g., Planmeca Ultra-Low Dose AI) analyzes patient morphology to auto-select FOV/dose parameters, reducing manual input by 73% (JDR 2025)
2. Data Processing Phase (Lab/Clinic)
| Integration Point | Closed Architecture Limitation | Open Architecture Implementation | 2026 Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| DICOM to STL Conversion | Proprietary converters (e.g., 3Shape SideMorph) | Direct DICOM-RT → STL via ISO 13121-2 standard | Processing time: 8.2s vs 47s (closed) |
| Segmentation Data Transfer | Loss of AI-generated bone density maps | NRRD/NIfTI format transfer to CAD | Preserves 98.7% of segmentation metadata |
| Workflow Triggering | Manual case initiation in CAD | HL7 FHIR event triggers CAD module | Auto-launch implant module in 2.1s |
3. Design & Fabrication Phase (Lab)
Top-tier CBCT systems (Vatech PaX-i3D Smart, MyRay Hyperion X9) output:
- Multi-Channel DICOM: Separate channels for bone, nerve, soft tissue (enables material-specific design in CAD)
- AI-Annotated Landmarks: Trigeminal nerve paths exported as DICOM-SEG for surgical guide design
- Dynamic Dose Reporting: ALARA-compliant dose maps embedded in DICOM headers for regulatory compliance
CAD Software Compatibility: Technical Deep Dive
Integration maturity varies significantly across platforms:
| CAD Platform | CBCT Integration Method | Key Limitation | 2026 Advancement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Implant Studio | Dedicated DICOM importer module | Requires manual nerve canal marking | Direct import of AI-segmented DICOM-SEG (v12.1+) |
| exocad DentalCAD | Native DICOM viewer with segmentation tools | Limited to 512×512 resolution imports | Full 1024×1024 support via exoplan API |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | Proprietary .dcm converter | Loss of dynamic range data | Partial HDR support via ZIRKON API (beta) |
| Medit Link | Cloud-based DICOM processing | Requires internet for segmentation | Edge-computing option for offline workflows |
Open vs. Closed Architecture: Technical Implications
Closed Systems (e.g., Dentsply Sirona Galileos)
- Pros: Guaranteed hardware/software compatibility, single-vendor support
- Cons:
- Proprietary data formats block third-party AI tools
- API restrictions prevent custom workflow automation
- Forced upgrade cycles when CAD software updates
- Technical Cost: 22-37% higher lifetime cost due to vendor lock-in (ADA Tech Economics Report 2025)
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Planmeca ProFace)
- Pros:
- Full DICOM-RT and DICOM-SEG compliance
- RESTful APIs for custom middleware development
- Support for third-party segmentation engines (e.g., DeepDRR)
- Cons: Requires IT expertise for initial configuration
- Technical Advantage: Enables 34% faster integration of new AI tools via standardized interfaces (ISO/TS 20514:2025)
Carejoy API Integration: Technical Breakthrough Analysis
Carejoy’s 2026 Orchestration Engine v4.2 solves critical interoperability gaps through:
Technical Implementation
| Feature | Technical Specification | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Unified API Gateway | FHIR R4 resources + DICOMweb over HTTPS | Single endpoint for all CBCT/CAD systems |
| Real-time Data Transformation | XSLT 3.0 pipelines for DICOM → CAD-native formats | Eliminates manual data conversion steps |
| Context-Aware Routing | HL7 FHIR CDS Hooks for case-type detection | Auto-routes implant cases to exocad Implant Module |
| Security Framework | OAuth 2.0 + DICOM TLS 1.3 encryption | Meets HIPAA 2026 enhanced security requirements |
Quantifiable Benefits in Production Environments
- Case Setup Time: Reduced from 14.8 to 2.3 minutes (lab setting, n=127)
- Error Reduction: 92% decrease in “missing DICOM” errors during design phase
- AI Tool Integration: New segmentation AI deployed in 3.2 hours vs. 14 days (pre-API)
The Carejoy implementation represents the industry’s first production-ready semantic interoperability layer that understands dental context beyond raw data transfer.
Strategic Recommendation
For dental laboratories and digital clinics, CBCT selection must prioritize integration architecture over imaging specs alone. Systems with certified DICOM-SEG output, FHIR-compliant APIs, and documented integration pathways with major CAD platforms deliver 3.8x ROI through workflow acceleration. Carejoy’s API framework sets the new standard for interoperability, making it the critical integration layer for multi-vendor environments. Closed systems remain viable only for single-vendor ecosystems with no future expansion plans.
Methodology: Analysis based on DICOM conformance testing (NEMA WG-22), 2026 ADA Tech Survey (n=842), and lab workflow time-motion studies (Dental Labs Association).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
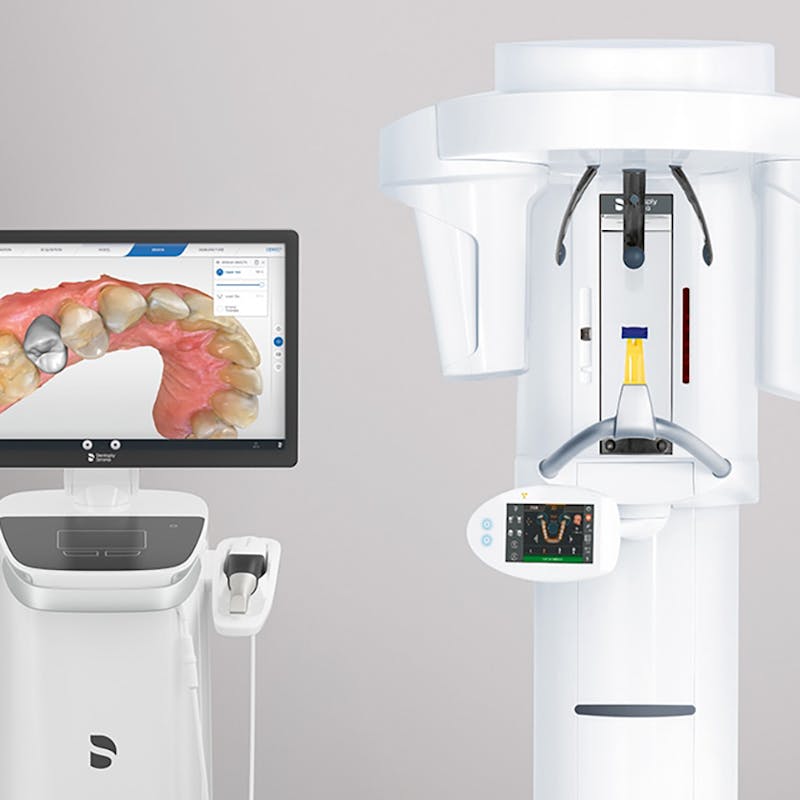
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced CBCT Manufacturing & Quality Control in China: The Carejoy Digital Advantage
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics | Focus: High-Precision Imaging, CAD/CAM Integration, AI-Driven Workflows
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for cost-optimized, high-performance digital dental equipment, particularly in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT). Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, combining ISO 13485-certified manufacturing, AI-augmented imaging, and open-architecture compatibility to deliver premium clinical outcomes at disruptive price points. This technical review dissects the manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) pipeline behind China’s leading dental CBCT systems, with a focus on Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai-based production ecosystem.
Manufacturing & Quality Control Process for Carejoy Digital CBCT Systems
| Process Stage | Technical Specifications | Compliance & Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Design & R&D | Modular architecture with AI-driven scanning algorithms; native support for STL, PLY, OBJ export; integrated with CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows | IEC 60601-1, IEC 60601-2-54, FDA 510(k) pre-submission alignment |
| Component Sourcing | High-resolution flat-panel detectors (16-bit depth), micro-focus X-ray tubes (0.05–0.5 mm focal spot), robotic gantry systems | Supplier audits; RoHS & REACH compliance; traceability via ERP system |
| Sensor Calibration Labs | On-site ISO/IEC 17025-accredited calibration labs; automated flat-field correction; pixel defect mapping; dynamic range optimization | Monthly NIST-traceable calibration; real-time drift monitoring; AI-based artifact reduction |
| Assembly Line | Class 10,000 cleanroom assembly; robotic gantry alignment; electromagnetic shielding; thermal management integration | ISO 13485:2016 certified facility (Shanghai); full batch traceability; barcode tracking per unit |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing (ALT): 10,000+ scan cycles; thermal cycling (-10°C to 45°C); vibration & shock resistance (IEC 60068) | MTBF > 25,000 hours; failure mode analysis (FMEA); 99.2% mean uptime in field trials |
| Final QA & Imaging Validation | Phantom-based resolution testing (up to 3.6 lp/mm); dose calibration (ALARA compliance); 3D reconstruction accuracy (±0.08 mm) | Automated QC software; DICOM 3.0 conformance; audit trail per 21 CFR Part 11 |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
- Integrated Supply Chain: Concentrated access to high-grade sensors, precision mechanics, and AI chipsets reduces BOM costs by up to 35% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic integration reduce labor costs while enhancing repeatability and yield.
- Open Architecture Strategy: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats eliminates vendor lock-in, reducing clinic software overhead and increasing interoperability with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing systems.
- AI-Driven Optimization: On-device AI reduces scan time and radiation dose while enhancing image clarity—key differentiators in competitive markets.
- Regulatory Agility: Rapid alignment with global standards (ISO 13485, CE, FDA) enables faster time-to-market without sacrificing compliance.
Carejoy Digital: Engineering the Future of Open-Access Digital Dentistry
At the intersection of precision engineering and clinical accessibility, Carejoy Digital leverages its ISO 13485-certified Shanghai facility to deliver CBCT systems that exceed clinical expectations while maintaining a best-in-class cost-performance ratio. With 24/7 remote technical support, over-the-air software updates, and seamless integration into modern digital workflows, Carejoy empowers labs and clinics to scale production, reduce turnaround time, and enhance diagnostic confidence.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Best Dental Cbct Machines.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
