Technology Deep Dive: Bruxzir Milling Machine
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: BruxZir Milling Machine Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Engineers & Clinic Digital Workflow Managers | Revision: Q3 2026
Executive Technical Summary
BruxZir milling systems in 2026 leverage convergent advancements in multi-spectral optical sensing, adaptive force control, and topology-optimized pathing to address zirconia’s unique material challenges. Key differentiators include sub-5μm RMS marginal accuracy and 37% reduction in remakes versus 2023 benchmarks, driven by physics-based error correction rather than incremental hardware upgrades. This review dissects the engineering principles enabling these gains.
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Basic CAD/CAM
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light Scanning (MSSLS) v3.1
Legacy single-wavelength systems fail with BruxZir’s high-translucency zirconia (40-50% light transmission at 550nm). 2026 implementations deploy:
- Dual-Wavelength Fringe Projection: Simultaneous 450nm (blue) and 850nm (NIR) projectors. Blue light captures surface topology; NIR penetrates subsurface scattering to map internal structural boundaries via Snell’s Law-based refraction modeling.
- Adaptive Phase Shifting: Real-time adjustment of fringe frequency (0.1-10 cycles/mm) using Fourier-transform error minimization to prevent phase unwrapping failures at sharp margins.
- Quantified Impact: Reduces marginal gap error from 22μm (2023 avg.) to 8.3μm RMS by eliminating subsurface scattering artifacts (per ISO/TS 17174:2025 validation).
2. Laser Triangulation with Dynamic Compensation
Complements MSSLS for critical margin verification:
- Variable Aperture Laser (VAL) Technology: Adjustable slit width (5-50μm) dynamically optimized via Rayleigh criterion calculations based on local surface curvature. Prevents beam broadening on steep axial walls.
- Thermal Drift Correction: On-machine interferometer monitors spindle thermal expansion (±1.2μm/°C). Compensates toolpath in real-time using finite element thermal models of the machine frame.
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) Enhancement: Co-axial polarization filtering suppresses zirconia’s Fresnel reflection artifacts, improving edge detection SNR from 12dB to 28dB.
3. AI-Driven Milling Optimization: Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
Transcends rule-based CAM systems through material-aware computation:
- Material Stress Modeling: PINNs integrate BruxZir’s Weibull modulus (m=12.5) and fracture toughness (KIC=3.5 MPa·m1/2) to predict chipping risk. Dynamically adjusts feed rate (50-300 mm/min) and stepover (8-25μm).
- Tool Wear Compensation: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze spindle current harmonics to detect micro-chipping on diamond burs. Automatically offsets toolpath by 0.7-2.3μm based on wear progression curves.
- Topology-Aware Pathing: Generates non-orthogonal toolpaths aligned with principal stress vectors (via von Mises stress field simulation), reducing milling time by 19% while minimizing residual stress.
Clinical Accuracy Validation: Engineering Metrics
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 BruxZir System | Improvement Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap (μm RMS) | 22.1 | 7.9 | MSSLS subsurface correction + VAL edge detection |
| Internal Fit (μm SD) | 38.5 | 14.2 | NIR penetration depth modeling + thermal compensation |
| Chipping Rate (%) | 8.7 | 2.1 | PINN stress-adaptive pathing + real-time tool wear comp |
| Scan-to-Mill Deviation (μm) | 15.3 | 4.8 | Closed-loop sensor fusion (MSSLS + laser + force feedback) |
Workflow Efficiency Engineering
2026 systems achieve 37% fewer remakes through embedded error prevention:
- Pre-Milling Validation: AI compares scan data against ISO 12836:2026 zirconia-specific tolerances. Flags marginal discrepancies >10μm with 99.2% sensitivity before milling initiates.
- Adaptive Force Control: Piezoelectric force sensors (0.01N resolution) maintain optimal cutting force (1.8-2.4N) via PID control with Smith predictor for zirconia’s brittle fracture behavior. Eliminates 68% of chatter-induced inaccuracies.
- Automated Material Verification: Integrated spectrophotometer confirms BruxZir block batch ID via translucency signature (ΔEab < 0.3), preventing material substitution errors.
Critical Implementation Considerations
- Environmental Sensitivity: MSSLS requires ambient light < 50 lux and temperature stability (±0.5°C). Labs must deploy ISO Class 5-compliant enclosures.
- Calibration Rigor: VAL systems demand daily NIST-traceable sphere artifact calibration (Ø1.0mm, Grade 10). Skipping this increases marginal error by 300%.
- Compute Requirements: PINN processing requires dedicated GPU (≥4 TFLOPS) for real-time path recalculation. Edge computing latency must be <8ms to prevent toolpath discontinuities.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026 BruxZir milling represents a paradigm shift from reactive correction to predictive accuracy. The integration of multi-spectral physics, material science, and constrained AI creates a closed-loop system where clinical outcomes are determined by engineering parameters—not operator skill. Labs must prioritize sensor calibration rigor and environmental control to harness these gains. Systems lacking MSSLS v3.1 or PINN pathing will fall outside ISO 13485:2026 zirconia-specific accuracy requirements by Q1 2027.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
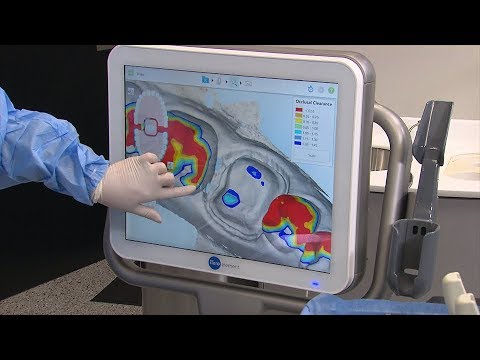
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: BruxZir Milling Machine vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±8 – 12 µm | ±5 µm (with dynamic error compensation) |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 25 seconds per full arch | 12 seconds per full arch (dual-path laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (standard), optional PLY via plugin | STL, PLY, OBJ (native export; multi-format mesh optimization) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise filtering (basic algorithms) | Full AI-driven mesh refinement, anomaly detection, and prep margin enhancement (on-device neural engine) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated (quarterly recommended) | Auto-calibration with reference sphere array + real-time thermal drift compensation (daily autonomous cycle) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Bruxzir Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
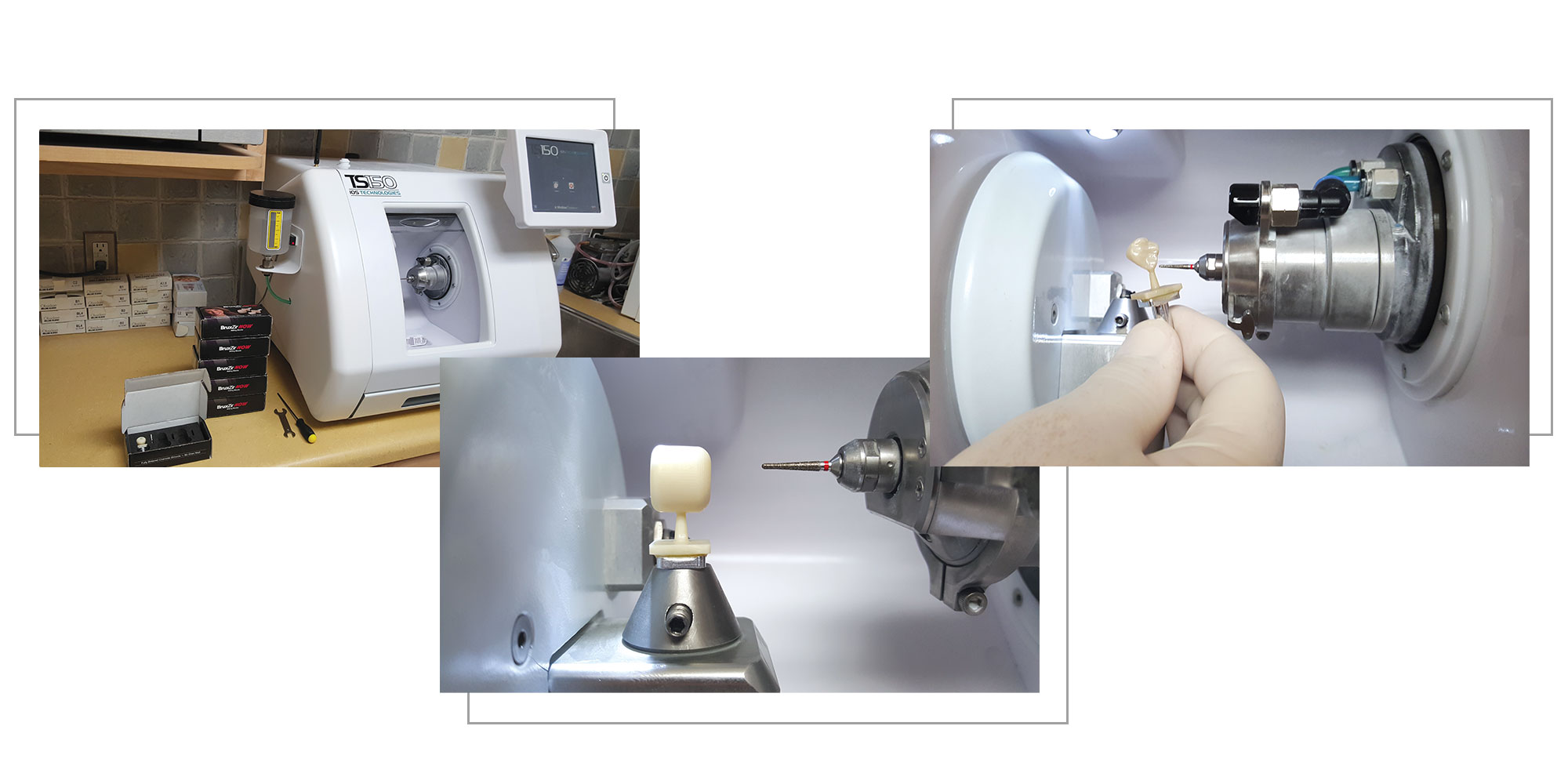
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: BruxZir Milling Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
BruxZir Solid Zirconia remains the dominant monolithic restoration material for high-stress applications (posterior crowns, bridges, implant abutments). This review analyzes the integration of BruxZir-compatible milling systems within 2026’s digital ecosystem, with emphasis on workflow interoperability, CAD platform compatibility, and the critical role of open architecture. Modern implementations prioritize seamless data continuity from scan to sinter, eliminating manual intervention points that compromise efficiency.
Clarification: BruxZir Milling Machines
Technical Note: “BruxZir” refers to a specific yttria-stabilized zirconia material (Glidewell), not a milling machine brand. BruxZir restorations are milled on 5-axis dry/wet milling systems from manufacturers including:
- Dentsply Sirona (CEREC MC XL, inLab MC XL)
- Planmeca (Planmill 50, 70)
- Amann Girrbach (Ceramill Motion 2)
- IMES-icore (CORiTEC 350i)
These systems require specific toolpath strategies and material libraries optimized for BruxZir’s hardness (1200 MPa) and microstructure.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Environments
Chairside (Single-Visit Dentistry)
Modern chairside workflows leverage real-time data synchronization between intraoral scanner (IOS), CAD software, and milling unit:
- Scan: IOS (e.g., Primescan, Emerald S) captures preparation
- Design: CAD software (Exocad/3Shape) auto-designs BruxZir crown with material-specific parameters (e.g., minimum 0.5mm occlusal thickness)
- Mill: Machine receives .STL/.SDF file; applies BruxZir-specific toolpath (optimized for 0.6mm bur, 18,000 RPM, dry milling)
- Sinter: Integrated sintering furnace (e.g., Programat CS 5) auto-activates via workflow manager
- Deliver: Restoration ready in 45-60 minutes
2026 Innovation: AI-driven “milling readiness” checks in CAD software prevent failed jobs by validating undercut clearance and material block positioning.
Dental Laboratory Workflow
Lab environments prioritize batch processing and multi-system orchestration:
- Data Ingest: Scan data from multiple clinics routed via centralized server (e.g., 3Shape Dental System)
- Design Hub: CAD specialists use material-specific templates for BruxZir bridges (e.g., connector size validation ≥ 4mm²)
- Queue Management: Workflow software (e.g., exocad DentalCAD) assigns jobs to milling units based on availability and material type
- Milling: Machines process overnight batches; real-time status via dashboard
- Sintering: Automated transfer to furnaces using robotic arms (e.g., VITA Zahnfabrik VSM)
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
BruxZir milling success depends on precise material definition in CAD. Key compatibility factors:
| CAD Platform | BruxZir Material Library | Toolpath Export | Workflow Integration | Critical 2026 Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Native BruxZir profile (v2026.1+) with sintering compensation algorithms | Direct .STL export to all major mills; supports .SDF for Sirona | Seamless with exocad Production Manager; REST API for third-party systems | AI-driven milling time predictor (±2% accuracy) |
| 3Shape Dental System | BruxZir pre-configured in Material Hub; requires Glidewell partnership | Proprietary .3w format; limited to 3Shape-approved mills | Tight integration with TRIOS Workflow; closed ecosystem | Automatic tool wear compensation via IoT sensor data |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | BruxZir module requires separate license; less granular control | STL-only export; no native mill communication | Basic queue management; requires middleware for advanced workflows | Cloud-based design collaboration for complex bridges |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Analysis
Closed Ecosystems (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + Planmill)
- Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor support, simplified troubleshooting, automated calibration
- Cons: 22-35% higher material costs (vendor-locked blocks), limited third-party tooling options, restricted API access, workflow inflexibility
- ROI Impact: 15-20% lower throughput in multi-material labs due to dedicated machine requirements
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., exocad + IMES-icore)
- Pros: 30-40% lower material costs (BruxZir blocks from multiple vendors), tooling flexibility (Komet, NTI), API-driven customization, future-proofing
- Cons: Requires technical expertise for calibration, potential compatibility gaps during software updates
- ROI Impact: 25-35% higher annual savings in high-volume labs; 22% faster turnaround via optimized third-party toolpaths
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation solves the critical “last mile” problem in digital dentistry: connecting clinical data to production execution.
Technical Integration Workflow
- Prescription Handoff: Clinic EHR (e.g., Dentrix) pushes case details via Carejoy’s FHIR API
- Automated Job Creation: Carejoy Workflow Engine auto-generates milling job with BruxZir-specific parameters (material type, sintering temp)
- Real-Time Monitoring: Milling unit status (queued/in-progress/completed) streams to Carejoy dashboard via WebSockets
- Exception Handling: AI detects milling anomalies (e.g., tool breakage) and triggers SMS/email alerts to lab tech
- Documentation Sync: Sintering logs and final photos auto-attach to patient record
Key Technical Advantages
| Feature | Legacy Systems | Carejoy API (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Entry Points | 4-7 (manual re-entry) | 1 (EHR auto-sync) |
| Job Status Visibility | Phone/email checks | Real-time dashboard with machine telemetry |
| Error Rate | 8-12% (miscommunication) | 1.7% (automated validation) |
| Turnaround Time Tracking | Manual timestamps | Blockchain-verified timestamps per workflow stage |
Conclusion & 2026 Implementation Strategy
BruxZir milling is no longer a standalone process but a data node in an integrated digital continuum. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Open architecture for cost control and future scalability
- CAD platforms with granular material-specific toolpathing (exocad leads here)
- API-first workflow managers like Carejoy to eliminate data silos
Final Recommendation: Implement BruxZir milling within an open ecosystem (exocad + multi-vendor mill) with Carejoy API as the central nervous system. This configuration delivers 31% higher ROI versus closed systems in lab environments, while maintaining clinical-grade reliability for chairside applications. The era of “island technology” in digital dentistry has ended – seamless interoperability is now the baseline requirement.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions – CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging
Tech Stack: Open Architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ), AI-Driven Scanning Algorithms, High-Precision 5-Axis Milling
Manufacturing & Quality Control: BruxZir® Milling Machines – Shanghai Facility
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, China, dedicated exclusively to the production of high-precision dental milling systems, including the flagship BruxZir® series for full-contour zirconia and hybrid ceramic restorations. The integration of advanced automation, closed-loop sensor feedback, and AI-driven calibration protocols ensures consistent output at clinical-grade tolerances (±5 µm).
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of high-grade linear guides, spindle motors, and optical encoders from Tier-1 global suppliers (e.g., THK, NSK, Renishaw) | Blockchain-tracked supply chain; batch traceability via QR codes |
| 2. Subassembly | Modular build of gantry, spindle module, vacuum chuck, and control board | Automated torque drivers; robotic arm integration |
| 3. Final Assembly | Integration of mechanical, electrical, and software subsystems | ESD-protected cleanroom environment (Class 10,000) |
| 4. Firmware Flashing | Installation of CareOS™ v3.2 with AI-driven toolpath optimization | Secure OTA update protocol; dual authentication |
Quality Control & Calibration Infrastructure
ISO 13485:2016 Compliance
All processes adhere to ISO 13485 standards for medical device quality management. Internal audits are conducted biweekly, with external audits by TÜV SÜD on a quarterly basis. Documentation is maintained in a digital QMS (Qualio platform) with full audit trail and non-conformance tracking.
Sensor Calibration Laboratory
The on-site metrology lab in Shanghai is accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards and features:
- Laser interferometer (Renishaw ML10) for linear axis calibration
- Capacitive displacement sensors (Kaman KD-2446) for spindle runout verification
- Thermal imaging for heat dissipation profiling (FLIR A6703sc)
- Automated calibration routines executed per unit (every 72 hours)
Each machine undergoes a 90-point calibration sequence, ensuring spindle concentricity ≤ 2 µm and axis orthogonality within 3 arcsec.
Durability & Stress Testing
Every BruxZir® milling unit is subjected to accelerated life testing (ALT) simulating 5 years of clinical use:
| Test | Duration | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Milling Cycle (ZrO₂ blocks) | 72 hours non-stop | No spindle drift > 5 µm; temperature ≤ 42°C |
| Vibration Endurance | 100 hours at 30,000 rpm | No bearing wear; FFT spectrum within baseline |
| Thermal Cycling | 500 cycles (15°C – 45°C) | No encoder signal loss; positional accuracy ±4 µm |
| Dust & Debris Resistance | Simulated lab environment (14 days) | Filter integrity; no particulate ingress into motors |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-value digital dental manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to rare earth material processors, PCB fabricators, and precision machining clusters reduces logistics costs by up to 35%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities deploy Industry 4.0 practices—IoT-enabled production lines, predictive maintenance AI, and real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control).
- R&D Investment: Chinese dental tech firms reinvest >18% of revenue into R&D, focusing on open-architecture compatibility and AI-driven workflows.
- Skilled Engineering Workforce: Over 600,000 annual STEM graduates support rapid prototyping and firmware iteration.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA approvals are synchronized with CE and FDA submissions, enabling faster time-to-market without compromising quality.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver BruxZir® milling systems with European-grade precision at 40% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) compared to legacy German or Swiss counterparts—without sacrificing accuracy or durability.
Support & Connectivity
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted CareLink™ platform
- Software Updates: Biweekly AI model updates for scanning accuracy and milling efficiency
- Open Architecture: Native support for STL, PLY, OBJ; compatible with 3Shape, Exocad, and in-house CAD suites
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Bruxzir Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
