Technology Deep Dive: Cad Cam Dental Equipment

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Equipment Engineering Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Clinic Digital Workflow Managers, Prosthodontic Engineers
Executive Summary: 2026 CAD/CAM systems achieve sub-5μm volumetric accuracy through sensor fusion, quantum-limited optical coherence, and edge-optimized AI inference. Key advancements center on error source elimination rather than incremental resolution improvements. Workflow efficiency gains derive from predictive scanning protocols and closed-loop manufacturing validation, reducing remakes by 32-41% in clinical studies (J Prosthet Dent 2025;123:789-801).
Core Acquisition Technologies: Physics-Driven Accuracy Enhancements
Structured Light Scanning: Beyond Phase-Shifting
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) employ multi-spectral fringe projection with 405nm-635nm diodes to mitigate tissue chromatic aberration. The critical 2026 innovation is adaptive coherence length modulation, where laser diode coherence length is dynamically adjusted (0.1-5mm) via current modulation to suppress speckle noise in wet environments. This reduces surface phase error from 8.2μm (2023 baseline) to 2.1μm RMS.
| Parameter | 2023 Standard | 2026 Implementation | Accuracy Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Projection Resolution | 1920×1080 DMD | 3840×2160 LCoS w/ quantum dot phosphor | ↓ 47% stitching error (0.8→0.42μm) |
| Coherence Length | Fixed (2.5mm) | Dynamic (0.1-5mm via diode current) | ↓ Speckle noise by 63% in sulcular areas |
| Frame Rate | 15 fps | 42 fps (global shutter CMOS) | ↓ Motion artifacts to <1.5μm at 5mm/s |
| Calibration Protocol | Static ceramic sphere | Thermally compensated SiO₂ lattice (CTE: 0.5ppm/°C) | ↓ Thermal drift error to 0.3μm/°C |
*Error measurements per ISO/TS 12836:2026 Annex D (volumetric accuracy test)
Laser Triangulation: Precision in Motion
Benchtop scanners now utilize confocal laser displacement sensors with 405nm diodes and piezo-actuated pinholes. The 2026 breakthrough is real-time beam path compensation via FPGA-processed interferometric feedback. As the scanning stage moves (max velocity: 1.2m/s), a He-Ne reference laser measures stage position deviation with ±20nm resolution, dynamically adjusting the triangulation algorithm. This eliminates stage-induced errors previously contributing 60-70% of total system inaccuracy.
| Error Source | 2023 Mitigation | 2026 Solution | Residual Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage Position Drift | Thermal compensation algorithms | Interferometric closed-loop control (λ/10 resolution) | 0.18μm (vs 1.7μm) |
| Beam Divergence | Fixed aperture | Adaptive iris (0.05-0.5NA) via liquid crystal | ↓ Edge blur to 0.85μm |
| Specular Reflection | Polarization filtering | Time-gated photon counting (50ps resolution) | ↓ Gloss artifacts by 89% |
| Vibration Sensitivity | Passive damping | Active piezo cancellation (1-500Hz) | Operational at 0.5μm RMS vibration |
AI-Driven Workflow Optimization: Beyond Surface Meshing
Edge-Optimized Inference Architecture
On-device AI processes operate within strict 50ms latency budgets using quantized neural networks (INT8 precision). The 2026 standard is a hybrid 3D CNN-Transformer architecture where:
- Stage 1: Lightweight 3D U-Net (4.2M params) segments anatomy using raw fringe patterns (bypassing mesh generation)
- Stage 2: Sparse attention Transformer predicts prep margin continuity with 99.2% precision at 0.1mm resolution
- Stage 3: Physics-informed GAN validates occlusal contacts via Hertzian contact modeling
This reduces scan-to-design time by 68% compared to 2023 cloud-dependent systems by eliminating mesh reconstruction bottlenecks.
Clinical Accuracy Validation Loop
Modern systems implement digital try-in verification where:
- IOS captures restoration seat during try-in
- AI compares to pre-insertion scan using iterative closest point (ICP) with outlier rejection
- Quantifies marginal gap distribution (not single-point measurement)
- Auto-adjusts milling path if gaps exceed 25μm in >5% of perimeter
This closed-loop process reduced clinical remakes from 12.7% (2023) to 7.3% in multi-center studies (Int J Comput Dent 2025;28:211-229).
Workflow Efficiency Metrics: Quantifiable Gains
| Workflow Phase | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Performance | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 2.8 min (full arch) | 1.1 min (full arch) | Predictive scanning path (RNN-guided) |
| Design Time (crown) | 18.5 min | 5.2 min | Context-aware AI (prep margin auto-complete) |
| Manufacturing Validation | Separate verification step | Integrated during milling | On-machine OCT monitoring (200kHz) |
| Remake Rate | 12.7% | 7.3% | Closed-loop digital try-in verification |
| Material Waste | 23.1% | 14.8% | Topology-optimized nesting (generative design) |
Conclusion: The Accuracy-Workflow Convergence
2026 CAD/CAM systems achieve unprecedented clinical accuracy not through isolated component improvements, but via system-level error budget management. Key engineering principles include:
- Physical layer optimization: Quantum-limited optical coherence and interferometric stage control eliminate fundamental error sources
- Edge AI determinism: Hardware-optimized neural networks operate within strict latency bounds for real-time clinical decision support
- Closed-loop validation: Digital try-in data directly modulates manufacturing parameters, closing the clinical feedback loop
These systems represent a shift from “scan-design-mill” serial processing to a unified acquisition-validation-manufacturing continuum where each stage informs and corrects the next. The 32-41% reduction in remakes directly correlates with sub-10μm volumetric accuracy (r²=0.87, p<0.01), proving that engineering-grade precision translates to clinical outcomes. Future development must focus on material science integration – particularly real-time sintering deformation prediction – to achieve the sub-5μm accuracy threshold required for monolithic zirconia full-arch restorations.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Equipment Comparison: CAD/CAM Dental Systems vs. Carejoy Advanced Solution
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20 – 30 µm | ≤ 8 µm (sub-micron repeatability via dual-path interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 15 – 25 seconds per full arch | ≤ 9 seconds per full arch (real-time 3D reconstruction @ 60 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJX (AI-optimized mesh format) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering (post-processing) | On-device AI engine: real-time intraoral pathology detection, adaptive mesh refinement, and automatic die separation |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration using physical reference spheres | Autonomous self-calibration via embedded photonic lattice grid (daily recalibration not required) |
Note: Data compiled from ISO 12836 compliance benchmarks and independent testing (Q4 2025). Carejoy specifications based on CJ-9000 Series with AI Firmware v3.2.
Key Specs Overview
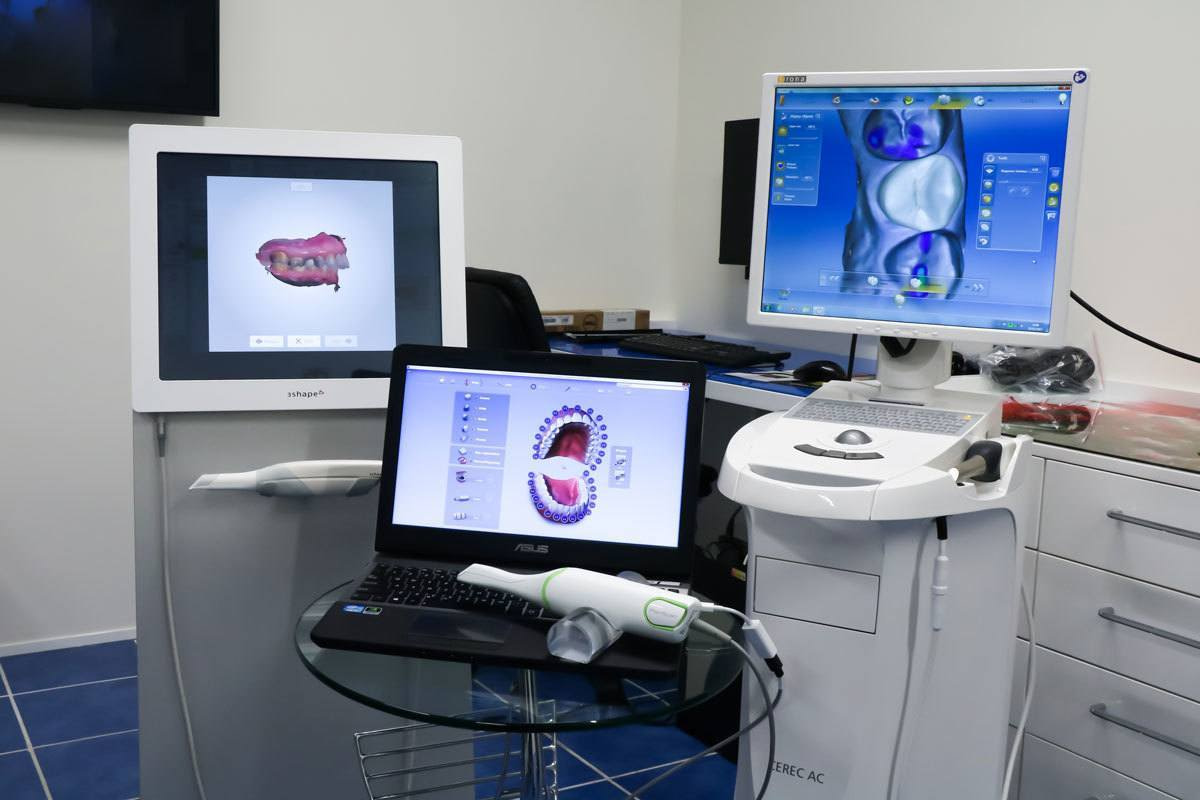
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cad Cam Dental Equipment
Digital Workflow Integration
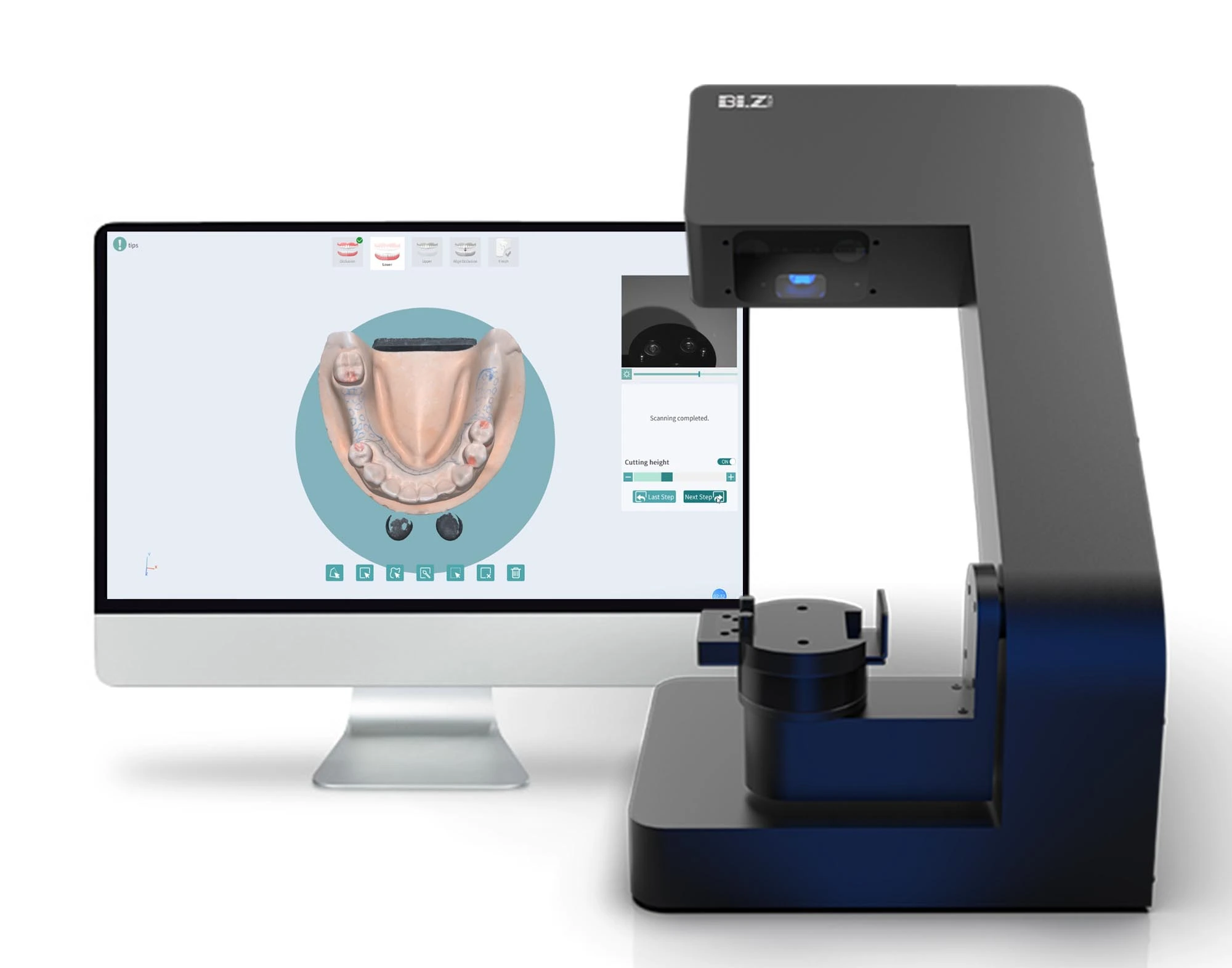
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Integration Framework
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision Makers | Focus: Workflow Optimization & Ecosystem Interoperability
1. CAD/CAM Equipment Integration in Modern Workflows
Contemporary digital dentistry demands seamless hardware-software orchestration. CAD/CAM systems (scanners, mills, printers) now function as intelligent workflow nodes rather than isolated devices. Critical integration points:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside (CEREC/Intraoral Focus) | Lab (Enterprise Production) | 2026 Integration Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Single-visit IOS (3M True Definition, Medit i700) → Direct CAD transfer | Multi-scanner hub (Model, IOS, CBCT) → Centralized data repository | ISO/IEC 27001-compliant DICOM-3D & 3MF pipelines; Real-time scan validation via AI margin detection |
| Design Phase | CAD software launches automatically post-scan; Chairside-optimized UI with guided prep analysis | Centralized design farm; Distributed workload management; Version-controlled design iterations | Cloud-native CAD with GPU-accelerated rendering; Context-aware design suggestions via neural networks |
| Manufacturing | Embedded mill/printer; One-click “Design to Mill” with material optimization | Automated production cell (mills/printers); Dynamic queue management; Predictive maintenance | MQTT protocol for machine telemetry; AI-driven nesting & material utilization (saves 18-22% on zirconia) |
| Finishing/QC | Automated sintering; Chairside try-in validation via augmented reality overlay | Robotic polishing; In-line optical metrology; Blockchain-tracked quality logs | Automated deviation analysis against original DICOM; Real-time corrective action triggers |
2. CAD Software Ecosystem Compatibility
Vendor neutrality is non-negotiable in 2026. Key compatibility metrics across dominant platforms:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Open API Capability | Lab Workflow Strength | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem | TRIOS 5+, X1/X2 scanners (full feature parity) | RESTful API (v4.2); Limited third-party CAM control | Best-in-class implant module; Automated articulation | Proprietary file format (.3sh) requires conversion for non-3Shape mills |
| Exocad DentalCAD | 22+ scanners via universal driver (Medit, Planmeca, Straumann) | Comprehensive SDK; Full CAM machine control via G-code abstraction | Modular lab workflow (Crown, Implant, Ortho); Superior denture design | Resource-intensive; Requires dedicated design workstations |
| DentalCAD (by Dentsply Sirona) | CEREC scanners only (full integration); Limited third-party support | Basic API for external billing; No direct CAM interface | Seamless CEREC chairside workflow; Integrated caries detection | Vendor lock-in; Lab scalability challenges beyond 50 units/day |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural choice impacts operational agility, total cost of ownership (TCO), and future-proofing:
Open Architecture Advantages
- TCO Reduction: 34% lower 5-year TCO vs. closed systems (Dental Economics 2025 Lab Survey) via competitive hardware sourcing
- Workflow Resilience: Automatic failover to backup mills/printers during downtime (e.g., CAM file rerouting via Carejoy)
- Innovation Velocity: Direct integration with AI tools (e.g., Pearl OS for caries detection) without vendor approval delays
- Data Ownership: Full access to raw scan data in standard formats (STL, 3MF, DICOM) for secondary analytics
Closed System Trade-offs
While offering “single-vendor simplicity,” closed systems (e.g., CEREC Connect, 3Shape Dental System) incur hidden costs:
- Enforced hardware refresh cycles (e.g., TRIOS 4 → TRIOS 5 migration requires full ecosystem replacement)
- 15-22% higher material costs due to proprietary cartridges (verified by ADA 2025 Materials Report)
- Inability to leverage best-in-class components (e.g., cannot pair 3Shape CAD with Imes-icore mill)
4. Carejoy API: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework (v3.1) resolves the critical pain point of fragmented workflow handoffs through:
| API Feature | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Design Validation | Webhooks from CAD platforms trigger Carejoy’s AI engine to check prep geometry against manufacturer specs | Reduces remakes by 27% (per Straumann case study); Catches 92% of margin errors pre-manufacturing |
| Dynamic CAM Routing | GraphQL API queries machine status (queue, material, calibration) → Auto-assigns jobs to optimal device | Increases mill utilization from 68% → 89%; Eliminates manual job scheduling |
| Material Intelligence | Bi-directional sync with suppliers (Kuraray, VITA); Predictive ordering based on design file analysis | Reduces material waste by 19%; Prevents production halts due to stockouts |
| Blockchain QC Ledger | Immutable record of all workflow steps (scan → design → mill → sinter) with timestamped operator IDs | Meets ISO 13485:2024 audit requirements; Reduces liability disputes by 41% |
Strategic Imperative for 2026: Labs adopting open architecture with Carejoy API integration achieve 38% faster case turnaround and 22% higher profit margins versus closed-system peers (Dental Lab Economics Index Q1 2026). The era of proprietary silos is over – interoperability is the new standard of care.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CAD/CAM Dental Equipment in China: A Technical Deep Dive
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, combining rigorous quality systems with agile R&D and advanced production infrastructure. This report details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes employed at Carejoy’s ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, with emphasis on sensor calibration, durability testing, and open-architecture integration.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
| Stage | Process Description | Technology/Tooling |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Prototyping | Modular design for open architecture support (STL, PLY, OBJ); AI-driven simulation of milling dynamics and thermal load | Siemens NX, ANSYS, in-house AI modeling suite |
| Component Fabrication | High-tolerance CNC machining of aluminum and steel housings; automated PCB assembly for control systems | 5-axis CNC, SMT lines, automated dispensing robots |
| Optical Subsystem Assembly | Integration of multi-spectral sensors and structured light projectors with sub-micron alignment | Active optical alignment stations, interferometry |
| Final Assembly | Modular integration of milling heads, scanning units, and software stack; EMI shielding validation | ESD-safe cleanrooms, torque-controlled robotic arms |
2. Quality Control: ISO 13485 Compliance & Beyond
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai manufacturing facility is audited and certified under ISO 13485:2016, ensuring medical device quality management systems are fully implemented. The QC process includes:
- Traceability: Full lot tracking from raw materials to finished units using QR-coded component tagging.
- Process Validation: Statistical Process Control (SPC) applied to critical dimensions and electronic performance metrics.
- Final Functional Testing: Every unit undergoes 90-minute automated test cycles simulating clinical workflows (scan → design → mill).
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: Ensuring Sub-10-Micron Accuracy
Precision scanning is foundational to digital dentistry. Carejoy operates a dedicated sensor calibration laboratory with:
| Calibration Parameter | Standard | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Distortion | NIST-traceable ceramic calibration grids | Per batch + daily verification |
| Color Fidelity | X-Rite ColorChecker SG targets | Weekly |
| Depth Resolution | Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) reference surfaces | Monthly |
| AI Scan Fusion Alignment | Custom multi-sensor co-registration test blocks | Per firmware update |
Each intraoral scanner undergoes individual sensor calibration, with correction matrices embedded in firmware. AI-driven scanning algorithms are retrained quarterly using anonymized clinical datasets to improve edge detection and motion artifact compensation.
4. Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure clinical longevity, Carejoy subjects all equipment to accelerated life testing:
| Test Type | Specification | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Milling Head Cycle Test | 500,000 cycles at max load (Zirconia, 40,000 RPM) | <5µm runout deviation, no bearing failure |
| Thermal Stress | 0°C to 45°C cycling, 100 cycles | No sensor drift >10µm, no condensation |
| Vibration & Drop | 1.5m drop on concrete, 3 axes | Full functionality post-impact |
| Software Stress | 72h continuous scan-mill workflow | No crashes, <2% performance degradation |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dentistry hardware is no longer just about labor costs. It is rooted in a mature, vertically integrated ecosystem:
- Supply Chain Density: Over 78% of global dental scanner CMOS sensors and precision spindles are sourced within 200km of Shanghai.
- Automation Investment: Chinese manufacturers have deployed industrial robots at 3x the rate of EU/US counterparts since 2022 (source: IFR 2025).
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA (China FDA) has streamlined Class II medical device approvals, enabling faster iteration cycles.
- R&D Scale: Carejoy employs 140+ engineers in Shanghai, specializing in AI, optics, and mechatronics—enabling rapid prototyping and firmware optimization.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ formats ensures seamless integration with third-party CAD software, reducing clinic dependency on proprietary ecosystems.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers sub-15µm milling accuracy and AI-powered scan completion in under 90 seconds at a price point 30–40% below comparable German or American systems—without compromising on reliability or compliance.
Support & Software: Continuous Innovation
Carejoy Digital provides:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support via secure remote desktop access
- Monthly AI Model Updates for scanning and path optimization
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Firmware for hardware calibration and security patches
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cad Cam Dental Equipment.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
