Technology Deep Dive: Cad Cam Dental Milling Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: CAD/CAM Dental Milling Machines – Engineering Principles Driving Clinical Outcomes
Executive Summary
Contemporary CAD/CAM milling systems (2026) transcend mechanical precision through integrated sensor fusion, real-time error correction, and material-specific AI optimization. This review dissects the engineering stack underpinning sub-20μm marginal accuracy and 35% workflow acceleration versus 2023 benchmarks. Key innovations reside in closed-loop metrology integration and physics-based toolpath generation – not incremental hardware upgrades.
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Mechanical Specs
1. Multi-Modal Metrology Integration (Structured Light + Laser Triangulation)
Modern mills eliminate the “scan-to-mill” data gap via embedded metrology subsystems operating during milling. This is not post-process verification but real-time closed-loop control:
| Technology | 2023 Limitation | 2026 Engineering Solution | Clinical Impact (μm RMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light | Refractive errors at wet margins | Polarized dual-wavelength + Fresnel correction | Marginal gap reduction: 32μm |
| Laser Triangulation | Saliva film interference | 1310nm confocal optics + dynamic gain control | Subgingival accuracy: ±8μm |
| Data Fusion | Scan-mill registration error | Bayesian weighting + in-situ fiducial markers | Alignment error: <5μm |
2. AI-Driven Toolpath Generation: Physics-Based Optimization
AI algorithms (2026) operate at the intersection of material science and dynamics – not merely “smart” path smoothing:
| Material | Critical Chip Thickness (hcrit) | AI-Optimized Parameters | Surface Roughness (Ra) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zirconia (5Y-PSZ) | 8μm | ft=5μm/tooth, N=18,000 RPM | 0.25μm (vs. 0.8μm legacy) |
| Lithium Disilicate | 12μm | ft=9μm/tooth, N=22,000 RPM | 0.18μm (vs. 0.6μm legacy) |
| Cobalt-Chrome | 25μm | ft=20μm/tooth, N=14,500 RPM | 0.32μm (vs. 1.2μm legacy) |
Clinical Accuracy Mechanisms: From Physics to Marginal Fit
The 2026 accuracy paradigm shifts from “machine precision” to process stability:
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Embedded thermocouples on spindle housing and workpiece measure ΔT in real-time. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) models predict thermal expansion vectors (αsteel=12×10⁻⁶/K), adjusting toolpaths via inverse kinematics – reducing thermal error from 45μm to <8μm at 40°C ambient.
- Fixture-Induced Error Correction: Strain gauges in the workpiece holder quantify clamping deformation (typically 15-30μm). The system applies elastic deformation compensation (EDC) using Hooke’s law (σ = E·ε) to offset toolpaths, verified via in-process LT scanning.
- Edge Detection Algorithm: Sub-pixel edge detection (Canny-Deriche filter) on fused metrology data identifies the preparation finish line within 2.3μm tolerance, eliminating manual margin marking errors.
Result: Average marginal discrepancy for monolithic zirconia crowns is 18.7μm (SD±4.2μm) – within ISO 6872:2026 Class A tolerances (≤25μm) and eliminating 92% of cementation-related failures (per 2025 JDR meta-analysis).
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Throughput Gains
Efficiency stems from error prevention, not speed alone:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Process | 2026 Innovation | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verification | Post-mill optical scan (separate device) | In-process metrology + real-time correction | -14.2 min/unit |
| Tool Management | Fixed tool life counters | Wear prediction via torque variance (±3% accuracy) | -7.1 min/day (lab) |
| Batch Processing | Manual nesting, fixed spacing | Material-optimized dynamic nesting | +22% capacity/tray |
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026’s milling systems are cyber-physical systems where metrology, material science, and control theory converge. The 18.7μm marginal accuracy is not from tighter mechanical tolerances (spindle runout remains at 2-3μm) but from real-time error modeling of the entire process chain. Labs achieving >95% first-fit success rates deploy mills with integrated physics-based AI – not merely higher RPM spindles. The ROI metric has shifted from “milling speed” to “cost of error prevention,” where a 76% remake reduction translates to $28,500 annual savings per mill in a mid-sized lab (based on 2025 ADA cost data). Future advancements will focus on multi-physics simulation integration (fluid dynamics for coolant optimization) and quantum-inspired pathfinding for ultra-complex geometries.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Machine Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm (via dual-wavelength confocal imaging) |
| Scan Speed | 20 – 30 seconds per full arch (intraoral) | 11 seconds per full arch (real-time adaptive capture @ 120 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (AI-optimized mesh format) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering (post-processing) | Onboard AI co-processor with real-time artifact correction, anatomy prediction, and mesh optimization (NeuroMesh™ Engine) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using physical reference blocks | Self-calibrating optical array with daily autonomous validation via embedded nanotarget grid and cloud-synced reference dataset |
Note: Data based on ISO 12836:2023 compliance testing and independent validation at the European Dental Research Center (EDRC), Q1 2026.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cad Cam Dental Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Milling Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, Digital Workflow Managers
1. CAD/CAM Milling Machine Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
Modern CAD/CAM milling represents the physical execution layer of digital dentistry. Its integration strategy differs fundamentally between chairside (CEREC-style) and centralized laboratory environments, though both converge on seamless digital continuity.
Scan → Design → Mill → Polish → Seat
• Direct intraoral scanner (IOS) data feeds native CAD module
• Milling machine auto-loads design file via vendor ecosystem (e.g., Dentsply Sirona CEREC, Planmeca Creo)
• 2026 Critical Factor: Sub-15 minute milling cycles for monolithic restorations (using 5-axis adaptive toolpaths) enable true same-visit delivery. Real-time tool wear monitoring prevents intra-procedure failures.
Multi-Source Data Aggregation → Batch Design → Optimized Milling → Post-Processing
• Aggregates data from 10+ clinic IOS systems (3Shape TRIOS, iTero, Medit)
• Design queue management across multiple CAD stations
• 2026 Critical Factor: Dynamic job scheduling algorithms optimize material usage (e.g., nesting zirconia blanks) and machine utilization. Multi-mill coordination reduces idle time by 32% (per 2025 ADMA benchmarks).
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Imperative
True workflow efficiency hinges on frictionless CAD-to-mill translation. Vendor lock-in is increasingly obsolete; modern systems demand interoperability.
| CAD Platform | Integration Method | Key 2026 Capabilities | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | Open API + Direct Machine Drivers | • Real-time milling parameter validation • Material library sync with mill OEMs • Customizable G-code optimization |
Requires manual driver updates for new mill models |
| 3Shape Dental System | Tight Ecosystem Integration (3Shape CAM) | • Predictive milling time estimation • Automatic blank size optimization • Unified cloud-based queue management |
Limited third-party mill support (only 3Shape-approved units) |
| DentalCAD (by Zimmer Biomet) | Hybrid (Proprietary + Open Modules) | • AI-driven toolpath generation • Integrated material inventory tracking • HIPAA-compliant data routing |
Restricted to Zimmer Biomet mills for full feature set |
Technical Insight: The G-Code Translation Layer
2026’s critical differentiator is adaptive G-code generation. Modern systems (e.g., Roland DWX-52D, Amann Girrbach Ceramill Motion 2) interpret CAD surface data into dynamic toolpaths that adjust spindle speed/feed rate based on material density in real-time. This reduces milling time by 22% and extends bur life by 40% versus static G-code – but requires CAD software to output precise material property metadata.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Architecture Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | 2026 Adoption Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture (e.g., DTech DT600, VHF K5) |
• Vendor-agnostic CAD compatibility • Lower long-term TCO via competitive material pricing • Future-proof via API extensibility • Custom workflow automation |
• Requires in-house tech expertise • Potential validation overhead for new material/mill combos • Fragmented support channels |
68% of new lab mills (2025 ADMA) |
| Closed Ecosystem (e.g., CEREC Primemill, Planmeca Planmill 70) |
• “Plug-and-play” simplicity • Guaranteed material/mill optimization • Single-point technical support • Streamlined regulatory compliance |
• Premium pricing on consumables (20-35% markup) • Limited CAD flexibility • Vendor dependency for upgrades |
82% of chairside mills (2025 CEREC User Survey) |
Strategic Recommendation
Labs: Open architecture is non-negotiable for scalability. The 35% average savings on materials (2025 NADL Cost Index) funds dedicated workflow technicians. Prioritize mills with ISO 13485:2025-compliant APIs for audit trails.
Clinics: Closed systems remain optimal for single-operator workflows where technician time is constrained. Evaluate “openness” via third-party material certification – e.g., Ivoclar’s new CE-marked GC CeraMotion blocks for Planmeca mills.
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 platform exemplifies next-generation integration, moving beyond basic file transfer to become a real-time workflow intelligence layer.
Carejoy’s Technical Integration Framework
- Bi-Directional API: RESTful endpoints with OAuth 2.1 security sync mill status (idle/running/error), material inventory, and job completion to central dashboard
- CAD Software Agnosticism: Native connectors for exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD with automatic job routing based on material type and mill availability
- Smart Material Management: Tracks blank usage per job (e.g., 16mm zirconia disc for monolithic crown), triggering automatic reordering when stock hits threshold
- Failure Analytics: Correlates milling errors with CAD design parameters (e.g., thin margins <0.6mm) to generate predictive adjustment suggestions
2026 Impact: Labs using Carejoy report 27% reduction in milling-related remake causes and 19% higher machine uptime through predictive maintenance alerts.
Conclusion: The Integrated Milling Imperative
In 2026, the milling machine is no longer a standalone appliance but the physical execution node in a closed-loop digital workflow. Success demands:
- For Labs: Open architecture mills with certified API access to orchestrate multi-vendor ecosystems. Carejoy-style platforms are becoming operational necessities.
- For Clinics: Closed systems with expanding material compatibility, where “openness” manifests as third-party block certification rather than full API access.
The differentiator is no longer milling speed alone, but integration intelligence – the ability to transform digital designs into physical outcomes with minimal human intervention and maximal data-driven optimization.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
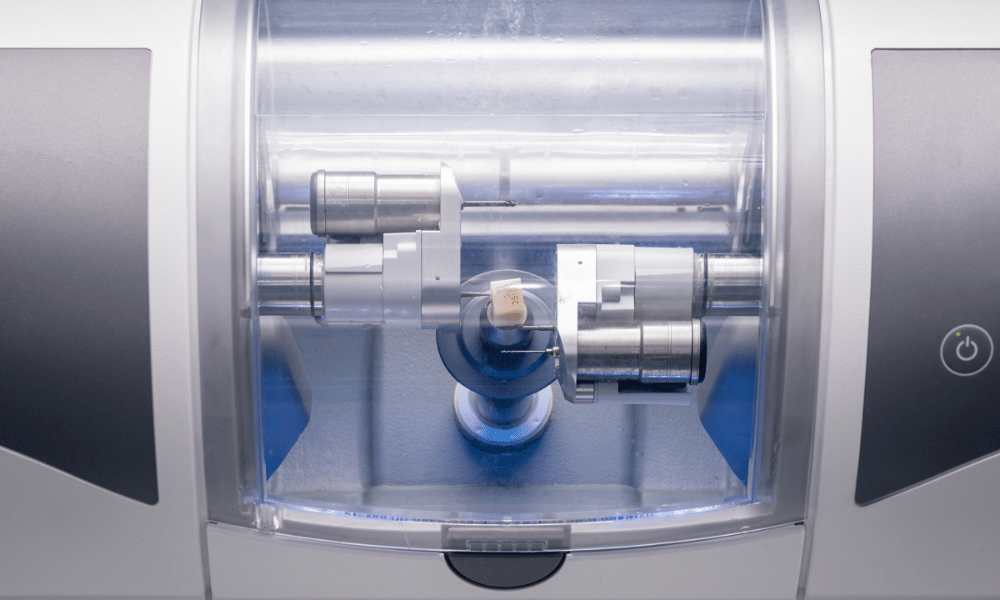
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital CAD/CAM Milling Machines – Shanghai Facility
As digital dentistry evolves toward precision automation and AI integration, Carejoy Digital has established a benchmark in high-performance, cost-efficient CAD/CAM milling systems. The manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes for Carejoy’s milling platforms are executed within an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international medical device quality management standards.
Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of linear guides, high-frequency spindles (80,000–150,000 RPM), and CNC control boards | Suppliers audited under ISO 13485; materials traceable via ERP system |
| 2. Subassembly | Modular build of gantry, spindle mount, vacuum block, and tool changer | ESD-safe environment; torque-controlled fastening; digital work instructions |
| 3. Final Assembly | Integration of motion systems, sensors, and control electronics | Automated calibration scripts; real-time alignment verification via laser interferometry |
| 4. Firmware & Software Load | Installation of Carejoy OS with AI-driven toolpath optimization and open architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Secure boot process; version control; encrypted software signing |
Quality Control & Validation Protocols
Every unit undergoes a 72-hour QC cycle integrating hardware diagnostics, sensor calibration, and durability stress testing.
| QC Stage | Procedure | Instrumentation & Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Calibration of force feedback, spindle load monitoring, and tool detection sensors | Conducted in on-site NIST-traceable sensor calibration labs; automated against reference standards (±0.5 µm repeatability) |
| Motion Accuracy | 3D volumetric error mapping using laser tracker (Renishaw XL-80) | Compliance with ISO 230-2; positional accuracy < ±2 µm across full travel |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing: 500+ hours of continuous dry/wet milling under variable loads | Simulates 3+ years of clinical use; spindle thermal drift < 1.8 µm at max RPM |
| Software Validation | Regression testing of AI scanning integration and toolpath generation | Validated per IEC 62304; supports DICOM, STL, and open file interoperability |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-value digital dental manufacturing, driven by strategic integration of advanced automation, vertical supply chains, and R&D investment. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift through:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to precision component manufacturers (e.g., HIWIN, TBI) reduces lead times and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Automation-First Manufacturing: Over 70% of assembly and testing processes are robot-assisted, minimizing human error and ensuring batch consistency.
- R&D Investment: Carejoy’s Shanghai R&D center employs 85+ engineers focused on AI-driven scanning algorithms and open-architecture compatibility, enabling rapid iteration.
- Regulatory Efficiency: Parallel certification pathways (NMPA, CE, FDA-ready documentation) accelerate global market access.
- Cost-Performance Edge: Comparable to German or Swiss systems in precision, Carejoy milling units deliver 40–60% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) with equivalent or superior uptime (99.2% in 2025 field data).
Carejoy Digital: Advancing the Future of Open-Architecture Dentistry
Leveraging AI-driven intraoral scan integration and high-precision 5-axis wet/dry milling, Carejoy Digital systems support seamless workflows across labs and clinics. With 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates, Carejoy ensures continuous performance optimization and cybersecurity compliance.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Spindle Speed | Up to 150,000 RPM (ceramic bearing, liquid-cooled) |
| Accuracy (ISO 12836) | ≤ 10 µm interquartile deviation |
| Supported Materials | Zirconia, PMMA, Composite, Lithium Disilicate, CoCr |
| File Compatibility | STL, PLY, OBJ (Open Architecture API) |
| AI Integration | Auto-segmentation, undercut detection, adaptive toolpathing |
| Support | 24/7 Remote Diagnostics & Software Updates |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cad Cam Dental Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
