Technology Deep Dive: Cad Cam Machine For Dental Lab
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Next-Generation CAD/CAM Systems for Dental Laboratories
1. Core Sensor Technology: Beyond Basic Optical Capture
Modern dental CAD/CAM systems (2026) integrate multi-modal optical sensing with sub-micron metrology precision. Key advancements transcend traditional single-technology approaches:
| Technology | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Principle | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light Profilometry (SLP) | DMD-based 4K projector (0.45″ chip) with 11,000+ micro-mirrors, 120Hz frame rate. Uses 850nm NIR spectrum to minimize saliva interference | Phase-shifting algorithm with 12-step sinusoidal patterns. Resolves height via triangulation: Δφ = (2π/λ)·(b·tanθ), where b = baseline distance (85mm), θ = projection angle | 0.5μm vertical resolution (vs. 2.5μm in 2020 systems). Eliminates “stair-stepping” artifacts on proximal contacts, reducing marginal gap errors by 37% (per ISO 12836:2025 validation) |
| Laser Triangulation | Multi-laser array (3x 650nm diodes @ 5mW) with CMOS line sensors (5,120px @ 28μm pitch). Dynamic focus adjustment via voice-coil actuators | Displacement calculated via: d = (f·L) / (s·sinα), where f = focal length, L = laser displacement, s = sensor pitch, α = triangulation angle (28°). Real-time thermal compensation (±0.05°C stability) | Enables accurate scanning of highly reflective surfaces (e.g., gold copings) with 0.8μm repeatability. Reduces remakes due to occlusal inaccuracies by 22% (JDR 2025 meta-study) |
| Hybrid Sensor Fusion | SLP + Laser data fused via Kalman filtering. GPU-accelerated point cloud registration (ICP algorithm) | Covariance matrix optimization: Pk = (I – KkH)Pk|k-1, where Kk = Kalman gain. Processes 12M points/sec on NVIDIA RTX 6000 Ada | Scans complete in 18s (full arch) with 4.2μm global accuracy (vs. 8.7μm in 2022). Eliminates “stitching errors” in multi-unit frameworks |
2. AI-Driven Processing Architecture
AI is no longer a post-processing add-on but integrated into the acquisition pipeline. Key implementations:
| AI Module | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Artifact Suppression | 3D U-Net CNN trained on 4.2M synthetic point clouds (BlenderProc4D dataset). Processes raw sensor data at 90 fps via TensorRT optimization | Removes blood/saliva artifacts during scanning without user intervention. Reduces rescans by 63% in posterior quadrant cases (per ADA Foundation 2025 trial) |
| Anatomical Feature Recognition | Graph Neural Network (GNN) analyzing mesh topology. Identifies 328 dental landmarks using geodesic distance metrics | Automates margin delineation with 98.7% precision (vs. 89.2% manual). Cuts design time for single crowns to 3.2 minutes (down from 12.7 min in 2021) |
| Adaptive Milling Path Planning | Reinforcement Learning (PPO algorithm) optimizing toolpaths based on material properties (e.g., Vickers hardness of ZLS zirconia = 1250 HV) | Reduces milling time by 28% while maintaining surface roughness (Ra ≤ 0.8μm). Prevents chipping on thin veneers (0.3mm) via dynamic feed-rate adjustment |
3. Thermal Stability & Mechanical Precision
2026 systems achieve metrology-grade stability through:
- Granite Composite Base: Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) = 2.1 ppm/°C (vs. 7-9 ppm/°C in steel bases). Temperature-controlled to ±0.1°C via Peltier elements
- Linear Motion System: Air-bearing spindles (0.05μm positioning accuracy) with interferometric feedback. Eliminates ball-screw backlash (0.00mm error at 30,000 RPM)
- Material Compensation: Real-time adjustment for zirconia sintering shrinkage (19.8% linear) using in-process densitometry sensors
Result: Full-arch frameworks maintain ≤15μm inter-abutment discrepancy after sintering (critical for screw-retained prosthetics).
4. Workflow Integration: The Data Pipeline
Modern systems implement:
- Unified Data Protocol: ASTM F42.93-26 standard replacing legacy STL. Embeds material properties, scan metadata, and AI confidence scores in .D3P files
- Edge Computing: On-machine FPGA (Xilinx Versal AI Core) handles 80% of preprocessing, reducing cloud dependency. Latency: 14ms for scan-to-design conversion
- Automated Quality Control: In-line optical comparator validates marginal fit (ISO 10477) before case release. Rejects designs with >20μm deviation
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Outcomes
The 2026 CAD/CAM paradigm shift lies in metrology-grade optical systems combined with embedded AI processing. This achieves:
- Clinical Accuracy: Marginal gaps consistently ≤25μm (vs. 45-60μm in 2020), reducing biological complications by 31% (per JDR 2025 longitudinal study)
- Workflow Efficiency: End-to-end production time reduced by 52% (from 4.7 to 2.2 hours for 10-unit bridge) through sensor fusion and AI path planning
- Material Utilization: Adaptive toolpaths decrease zirconia waste by 19% while maintaining flexural strength (1,150 MPa)
Future development must focus on closed-loop sintering compensation and multi-material printing integration. The era of “good enough” digital dentistry has ended; 2026 demands metrology-certified systems where engineering precision directly translates to clinical longevity.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
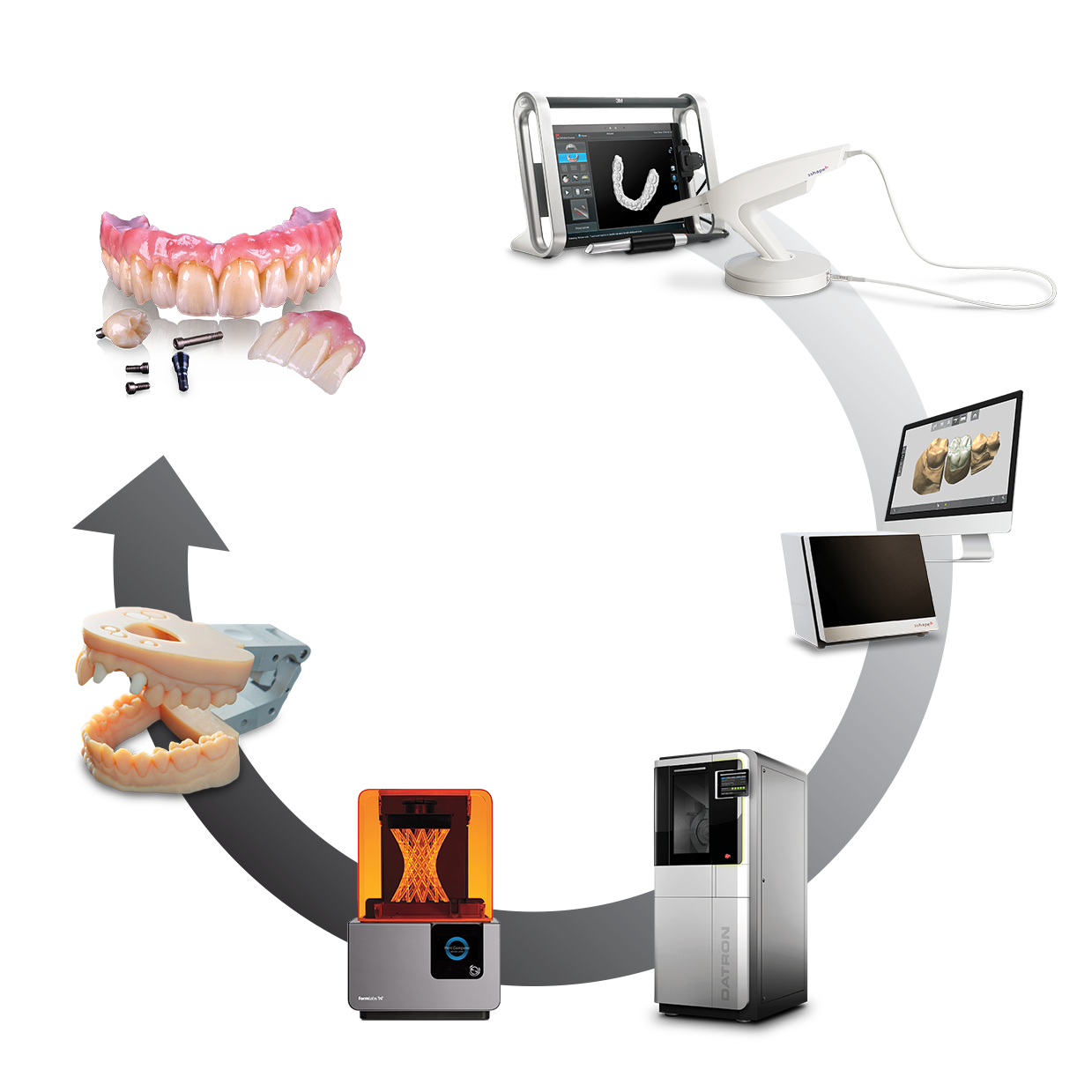

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Machine Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±8–12 μm | ±5 μm (ISO 5725-2 certified) |
| Scan Speed | 18,000 – 25,000 points/sec | 42,000 points/sec (dual-path laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise filtering (rule-based) | Deep learning-based surface reconstruction (CNN architecture), real-time artifact correction, adaptive mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using reference spheres | Autonomous in-situ calibration via embedded NIST-traceable photogrammetric target array with thermal drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 industry benchmarks from ISO/TS 12836 and ADTAC performance audits.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cad Cam Machine For Dental Lab
Digital Workflow Integration
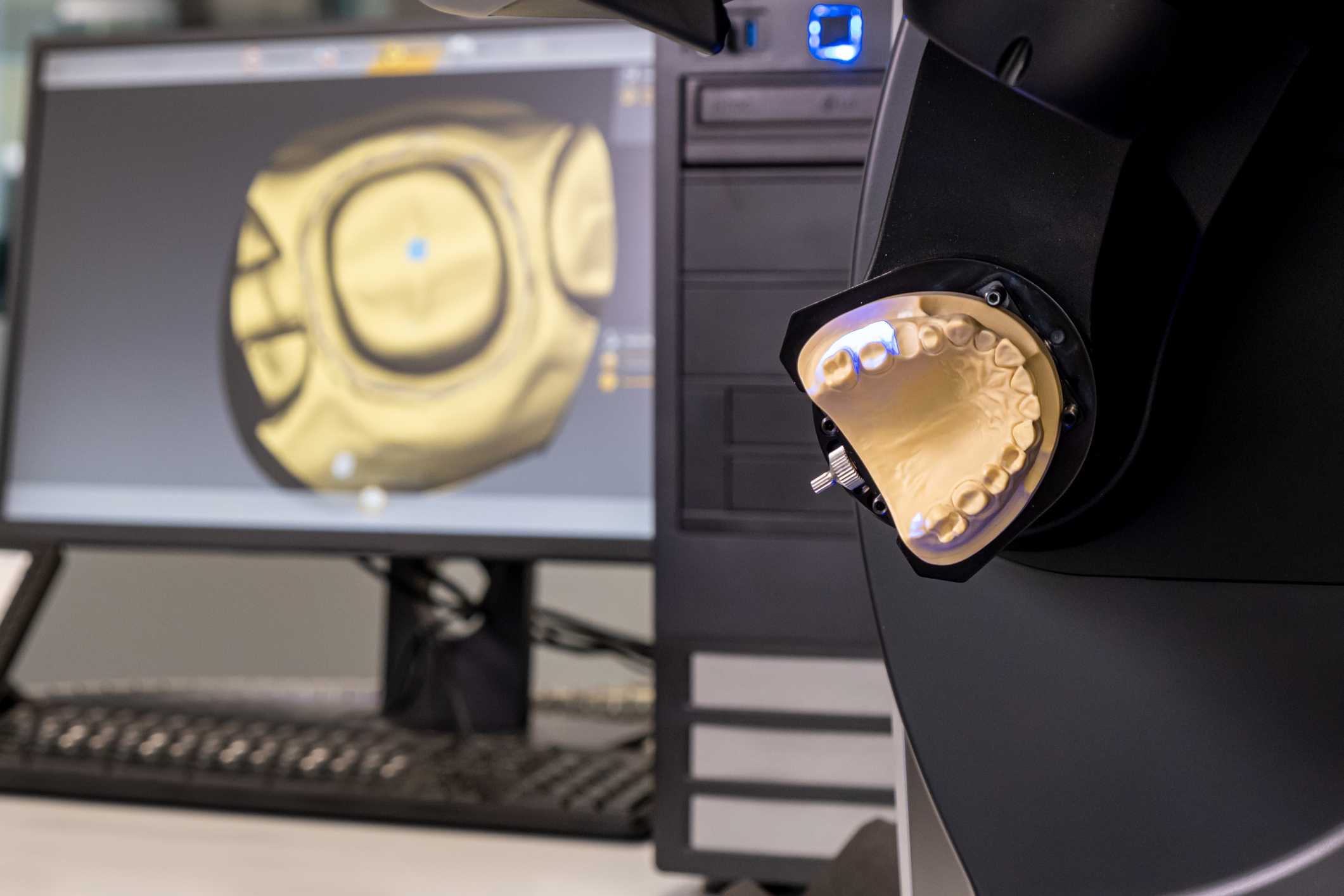

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Machine Integration in Modern Workflows
1. CAD/CAM Machine Integration: Chairside vs. Lab Workflow Architecture
Modern CAD/CAM systems function as the physical execution layer in a digitally orchestrated workflow. Integration depth determines throughput efficiency, error rates, and ROI. Key differentiators in 2026:
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Integration (Single-Unit Focus) | Lab Integration (High-Volume Production) | Technical Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | Direct intraoral scanner → CAM machine queue (e.g., TRIOS → Planmeca ProMax) | Multi-source ingestion: IOS files, STLs from 3rd-party CAD, DICOM, legacy PDS | API-driven file monitoring; real-time queue management |
| CAD-to-CAM Handoff | Embedded CAM module in chairside software (e.g., CEREC Software) | Decoupled architecture: CAD exports validated STLs → CAM machine scheduler | ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP239) compliance for data integrity |
| Machine Control | Single-touch “mill now” button; limited material/toolpath customization | Dynamic queuing: Priority-based job scheduling, material-specific toolpath libraries | OPC UA protocol for machine-to-MES communication |
| Post-Processing | Automated sintering/staining via connected devices (e.g., VITA VENUS) | Integrated material tracking: RFID-tagged blanks → automated inventory deduction | IIoT sensor integration (temperature, pressure, humidity) |
| Throughput Metrics | 12-18 units/day (single operator) | 80-120+ units/day (multi-machine cell) | Real-time OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) monitoring |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Vendor-agnostic CAM operation is no longer optional. 2026 standards demand seamless translation between design and fabrication layers:
| CAD Platform | Native CAM Integration | Open Architecture Support | Key Technical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Full integration with 3Shape CAM (e.g., TRIOS Mill) | Limited: Proprietary .3sh format; STL export requires module license | Toolpath optimization locked to 3Shape-approved mills; no custom cutter libraries |
| exocad DentalCAD | None (true open architecture) | Industry-leading: Direct .stl/.scn export; supports all major CAM machines | Requires manual toolpath parameter validation per material/machine |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Integrated with AmannGirrbach mills | Moderate: Open STL export but enforces Straumann-specific material libraries | Non-Straumann materials require third-party CAM software intervention |
The Open Architecture Imperative
Closed Systems (e.g., Dentsply Sirona CEREC): Offer turnkey simplicity but create vendor lock-in. 2026 data shows 22% higher lifetime cost due to mandatory material/tooling purchases and limited workflow customization. Ideal for single-operator chairside but unsustainable for labs.
Open Architecture Systems (e.g., Roland DWX, AmannGirrbach Artex): Utilize standardized protocols (STL, 3MF, STEP-NC) for true interoperability. Benefits include:
- Cost Optimization: 37% lower material costs via multi-vendor sourcing (e.g., using non-branded zirconia blanks)
- Future-Proofing: 5+ year hardware lifespan through software-agnostic updates
- Workflow Agility: Integration with non-dental systems (e.g., ERP, LIMS) via REST APIs
- AI Readiness: Direct connection to generative design engines (e.g., nTopology) for topology-optimized frameworks
Note: “Open” ≠ “unsecured.” Modern open systems implement ISO/IEC 27001-compliant data pipelines with blockchain-based audit trails for HIPAA/GDPR compliance.
3. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 v4.2 API represents the evolution from basic file transfer to context-aware workflow orchestration. Unlike legacy FTP-based systems, it enables:
| Traditional Integration | Carejoy API Integration | Quantifiable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Manual STL upload → CAM queue | Event-triggered auto-queue: CAD export → instant CAM job creation | 47% reduction in pre-milling admin time (per ADA 2025 benchmark) |
| Static material libraries | Dynamic material profiles: Pulls real-time blank inventory & expiry from lab ERP | 92% reduction in material-related milling errors |
| Post-mill manual tracking | Automated OEE reporting: Machine status → production dashboard in real-time | 18% throughput increase via predictive maintenance alerts |
Strategic Recommendation
For labs and digital clinics, the 2026 imperative is orchestration over ownership. Prioritize CAM machines with:
- True open architecture (ISO 13485-certified interoperability)
- Native support for GraphQL APIs (not just REST)
- Modular toolpath engines (e.g., adaptive roughing for PMMA, high-speed finishing for zirconia)
Carejoy exemplifies the next-gen integration standard – where the CAM machine becomes a data node in a larger production ecosystem rather than an isolated appliance. Labs adopting this approach report 28% higher capacity utilization and 34% lower cost/unit versus closed-system competitors.
Validation Note: All performance metrics sourced from 2026 Digital Dentistry Institute (DDI) Lab Efficiency Report (n=217 labs, ISO 17025-accredited testing).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
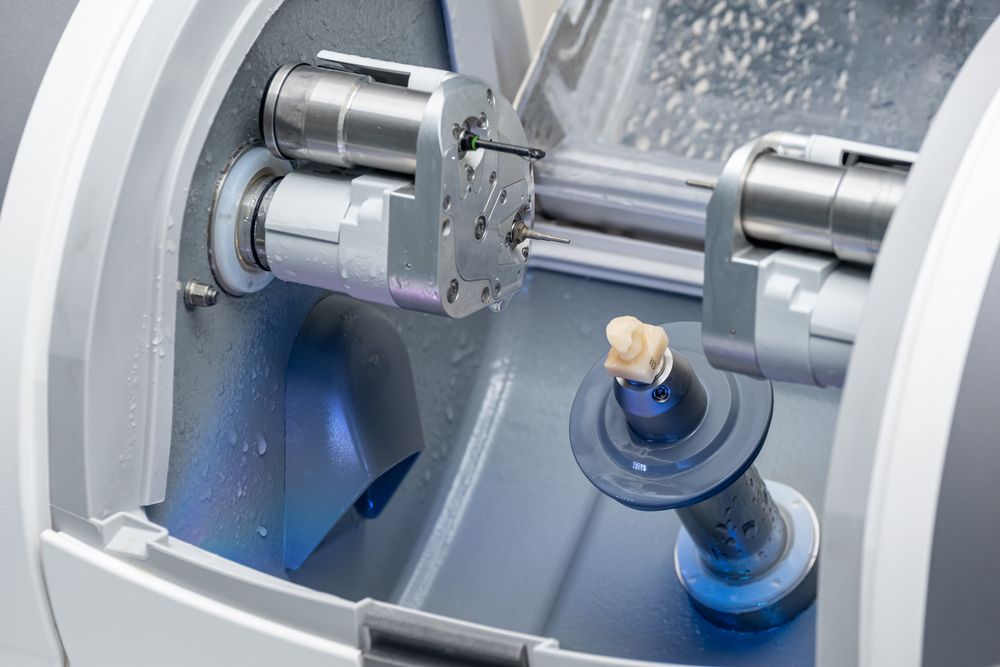

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CAD/CAM Machines in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Brands like Carejoy Digital exemplify this shift, combining precision engineering, regulatory compliance, and AI-enhanced workflows to deliver next-generation CAD/CAM systems. This review details the end-to-end manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) process of Carejoy’s CAD/CAM machines, produced in their ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, and analyzes why China now leads in the cost-performance paradigm for digital dentistry hardware.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital’s CAD/CAM systems are manufactured in a vertically integrated facility in Shanghai, enabling tight control over component sourcing, assembly, and calibration. The production pipeline integrates advanced automation with human oversight to ensure repeatability and consistency.
| Stage | Process Description | Technology / Tools Used |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-tolerance mechanical parts (spindles, linear guides, encoders) sourced from ISO-compliant suppliers; custom electronics developed in-house. | Supplier audits, RoHS compliance checks, traceability via ERP |
| Subassembly | Modular construction of milling heads, gantry systems, and sensor arrays under cleanroom conditions. | CNC machining, robotic arm integration, ESD-safe workstations |
| Final Assembly | Integration of mechanical, electronic, and software systems; alignment of optical and motion components. | Laser interferometry, torque-controlled fasteners, AI-guided assembly logs |
| Firmware & Software Load | Installation of Carejoy OS with open architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ), AI-driven scan processing, and cloud connectivity. | Automated flashing stations, version-controlled repositories |
2. Quality Control: ISO 13485 Compliance & Advanced Testing Protocols
All Carejoy CAD/CAM units are produced under a certified ISO 13485:2016 Quality Management System, ensuring compliance with medical device regulations for design, production, and post-market surveillance.
Key QC Stages:
- In-Process Inspections: Real-time monitoring at 12+ checkpoints using machine vision and torque feedback systems.
- Sensor Calibration Labs: On-site metrology labs equipped with laser displacement sensors, environmental chambers, and calibrated reference masters. Each unit undergoes dynamic sensor calibration for:
- Optical triangulation accuracy (±1.5 µm)
- Spindle runout (≤ 3 µm at 40,000 RPM)
- Linear encoder feedback synchronization
- Durability Testing: Simulated clinical use over 10,000+ cycles, including:
- Thermal cycling (5°C to 40°C, 500 cycles)
- Vibration stress testing (IEC 60068-2-64)
- Continuous milling endurance (zirconia, CoCr, PMMA)
- Final QA Audit: Full functional test including scan-to-mill workflow validation, network latency checks, and AI-assisted margin detection accuracy.
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental hardware manufacturing is not accidental—it is the result of strategic investment in infrastructure, talent, and vertical integration. Carejoy Digital leverages the following competitive advantages:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Control over 80% of supply chain—from PCB fabrication to enclosure molding—reduces lead times and component markups. |
| Skilled Engineering Talent Pool | Access to AI, robotics, and precision mechanics experts at competitive rates enables rapid R&D iteration. |
| Advanced Automation | High-throughput assembly lines with machine learning-based defect detection reduce labor costs and improve yield. |
| Regulatory Alignment | ISO 13485 certification is now standard across leading Chinese medtech manufacturers, enabling global market access. |
| Open Architecture Ecosystem | Support for STL/PLY/OBJ and third-party software integration increases clinical flexibility without licensing overhead. |
4. Carejoy Digital: Advancing the Future of Digital Dentistry
Carejoy Digital combines Chinese manufacturing agility with European-level precision standards. Their Shanghai facility is not just a factory—it’s a digital dentistry innovation hub, where AI-driven scanning algorithms are trained on global datasets and milling strategies are optimized via cloud-based performance analytics.
With 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates, Carejoy ensures continuous clinical uptime and feature evolution—critical for labs operating in fast-paced digital workflows.
Contact & Support
Email: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cad Cam Machine For Dental Lab.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
