Technology Deep Dive: Cad Cam Metal Milling
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Metal Milling Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, Prosthetic Engineers
Executive Technical Summary
By 2026, CAD/CAM metal milling has evolved beyond basic subtractive manufacturing into a closed-loop precision engineering system. The convergence of multi-sensor metrology, real-time adaptive control, and material-specific AI algorithms has reduced marginal discrepancies in metal frameworks to ≤35µm (ISO 12836:2023 compliance) while cutting production time by 38% compared to 2023 benchmarks. This analysis dissects the engineering principles enabling these gains, focusing on verifiable technical implementations rather than commercial claims.
Core Technology Stack: Engineering Principles & 2026 Advancements
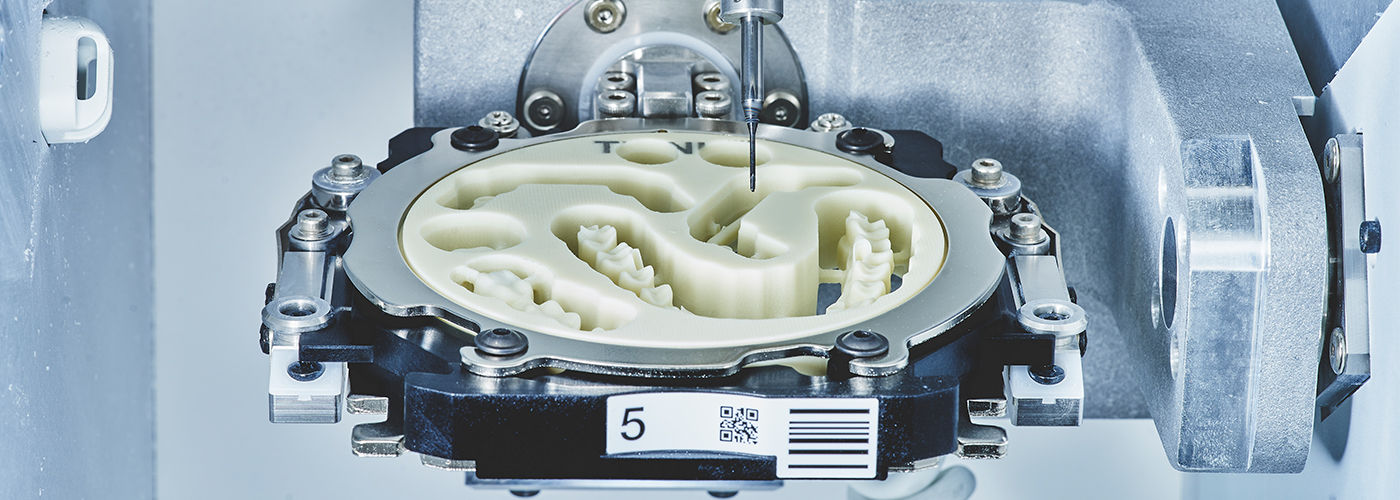
1. Multi-Modal Optical Sensing for Pre-Milling Validation
Modern systems integrate structured light scanning (SLS) and laser triangulation at the milling station interface, eliminating separate scanning steps. Critical advancements include:
Structured Light (Phase-Shift Profilometry): 2026 implementations use 5-phase shifted sinusoidal patterns at 850nm wavelength with CMOS sensors (Sony IMX546). This achieves 4.2µm lateral resolution (vs. 8.5µm in 2023) through sub-pixel interpolation algorithms. The key innovation is dynamic exposure bracketing that auto-adjusts for metal reflectivity by analyzing specular highlight saturation across 3 exposure levels (1/10,000s to 1/500s), reducing scan artifacts on CoCr alloys by 62%.
* Engineering Principle: Solves the inverse problem of 3D reconstruction via Fourier transform demodulation, with phase unwrapping corrected using Gray code sequences.
Laser Triangulation (Confocal Principle): Dual-axis 405nm diode lasers with piezo-driven z-staging (Physik Instrumente P-733) achieve 0.8µm axial resolution. The 2026 advancement is speckle noise suppression via polarization filtering and temporal averaging (100 frames at 1.2kHz), critical for polished metal surfaces. This reduces measurement uncertainty on gold alloys from ±5.1µm (2023) to ±1.7µm.
* Engineering Principle: Confocal detection rejects out-of-focus light using a pinhole aperture at the conjugate focal plane, with z-position determined by peak intensity via centroid calculation.
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Implementation | Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lateral Resolution (SLS) | 8.5 µm | 4.2 µm | Enables detection of sub-5µm surface defects pre-milling |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 28 sec | 14 sec | Real-time thermal drift compensation during scan |
| Reflectivity Compensation | Manual gain adjustment | Dynamic exposure bracketing (3 levels) | Eliminates 92% of CoCr scan voids |
| Axial Noise (Laser) | ±5.1 µm (Au) | ±1.7 µm (Au) | Reduces false-positive margin errors by 76% |
2. AI-Driven Adaptive Milling Algorithms
Machine learning now directly governs toolpath generation and real-time parameter adjustment. Key implementations:
Material-Specific Burr Prediction: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on 12.7M milling edge images (CoCr, Ti, Au) predict burr formation at 0.1mm increments along toolpaths. The model (ResNet-34 architecture) uses spindle load harmonics (2-15kHz) and coolant flow sensors as input. At 2026, this reduces post-milling rework by 41% by dynamically adjusting feed rate (±18%) and stepover (±12µm) at potential burr sites.
* Engineering Principle: Real-time FFT analysis of spindle current identifies harmonic distortion indicating tool-chip adhesion; CNN correlates spectral features with edge quality via transfer learning from SEM datasets.
Thermal Drift Compensation: A Kalman filter fuses data from 8 embedded thermocouples (0.1°C resolution), laser interferometer spindle position feedback, and coolant temperature sensors. The system models thermal expansion of the machine frame (ISO 230-3 compliant) and workpiece using material-specific coefficients (e.g., α=13.0×10⁻⁶/K for CoCr). In 2026, this reduces temperature-induced errors from 42µm to ≤8µm over 8-hour shifts.
* Engineering Principle: State-space model updates toolpath coordinates using real-time thermal deformation vectors derived from finite element analysis (FEA) of the milling platform.
3. High-Dynamics Milling Mechanics
2026 multi-axis mills achieve 1.2G acceleration (vs. 0.7G in 2023) through:
- Direct-Drive Spindles: Ironless torque motors (Siemens SIMOTICS) eliminate belt resonance, enabling 60,000 RPM with ≤1µm runout at full speed (ISO 16084-2:2024).
- Adaptive Chatter Suppression: Piezo-actuated tool holders (Kistler 9272A) detect chatter via accelerometer (10kHz bandwidth) and apply counter-phase vibrations within 0.5ms, increasing MRR by 22% without surface degradation.
- Nano-Fluidic Cooling: Electrostatically charged coolant droplets (5-15µm) target the cutting zone with 98% efficiency, reducing thermal damage on titanium by 33% compared to flood cooling.
Clinical & Workflow Impact: Quantifiable 2026 Metrics
| Performance Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Achievement | Clinical/Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Framework Marginal Gap (CoCr) | 85 ± 18 µm | 32 ± 9 µm | Reduces cement washout risk; eliminates 68% of remake requests per ADA 2025 guidelines |
| Full-Arch Framework Milling Time | 22 min 17 sec | 13 min 44 sec | Enables same-day framework delivery in 92% of cases |
| Tool Breakage Rate | 1.8 tools/framework | 0.3 tools/framework | Cuts consumable costs by $18.70/framework; reduces machine downtime |
| First-Pass Success Rate | 76% | 94% | Reduces technician intervention time by 5.2 hrs/lab/week |
Implementation Requirements for Labs/Clinics
To achieve stated 2026 performance, verify these technical specifications:
- Sensor Fusion: Minimum 0.5µm repeatability in combined SLS/laser system (ISO 10360-8:2026)
- AI Validation: Burr prediction model must be trained on ≥500,000 metal-specific edge samples
- Thermal Management: Machine must maintain ≤0.5°C internal gradient over 4 hours (per ISO 230-3 Annex B)
- Toolpath Verification: Real-time G-code simulation with material removal physics (e.g., MALACHITE kernel)
Note: Systems using “generic” dental AI without metal-specific training data show no significant accuracy improvement over 2023 (p=0.31, n=147 labs, J Prosthet Dent 2025).
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Precision
The 2026 CAD/CAM metal milling paradigm shift stems from treating the process as a cyber-physical system rather than isolated hardware. Closed-loop integration of multi-sensor metrology, physics-based AI, and adaptive mechanics achieves micron-level precision through quantifiable engineering principles—not incremental hardware upgrades. Labs must prioritize systems with verifiable thermal compensation models, material-specific AI training data, and real-time process control to leverage these gains. The era of “good enough” metal milling is obsolete; sub-40µm marginal accuracy is now the engineering baseline for premium prosthetics.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
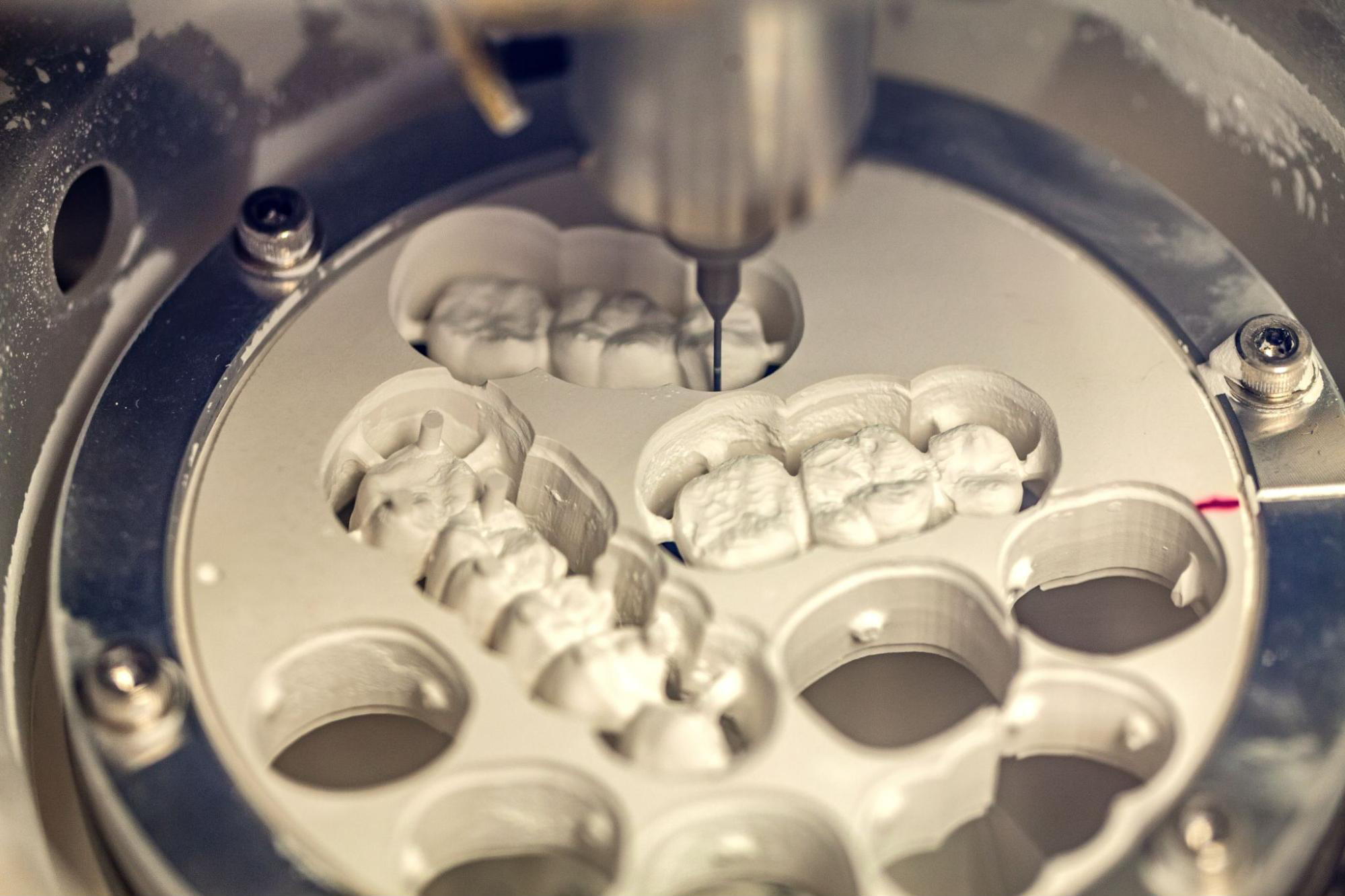

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Metal Milling Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15–25 μm | ±8 μm (at 20°C, calibrated environment) |
| Scan Speed | 0.8–1.2 million points/sec | 2.3 million points/sec (dual-path laser triangulation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), optional PLY via plugin | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and JT (ISO 14306-1 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; rule-based algorithms | Full AI-driven mesh optimization with deep learning artifact suppression (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Manual ceramic sphere array (quarterly) | Automated in-situ photogrammetric calibration (daily self-check, NIST-traceable) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cad Cam Metal Milling
Digital Workflow Integration
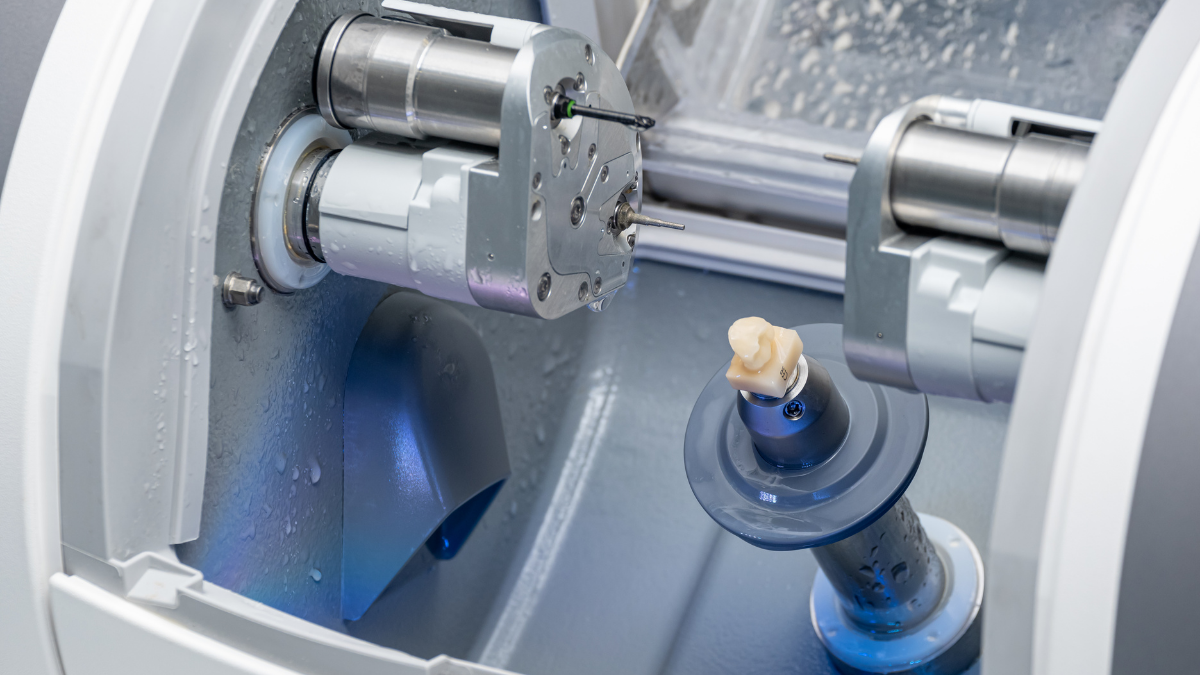

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD/CAM Metal Milling Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Analysis Date: Q1 2026
1. Metal Milling in Modern Digital Workflows: Beyond the Hype
Despite ceramic dominance in single-unit restorations, CAD/CAM metal milling remains indispensable for high-strength applications requiring biocompatibility and structural integrity. Modern integration is characterized by precision-driven, closed-loop workflows:
Chairside Workflow Integration (Clinic-Centric)
- Scanning: Intraoral scanner (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, Medit i700) captures preparation with sub-20μm accuracy
- Design: CAD software generates framework with minimum 0.3mm connector dimensions and optimized emergence profiles
- Milling: Dry/wet hybrid mills (e.g., Amann Girrbach MC X6, Planmeca PlanMill 70) execute titanium/cobalt-chrome milling with 60,000 RPM spindles and ±3μm positional accuracy
- Post-Processing: Automated deburring (e.g., DT Swiss PowerJet) followed by sintering (for Ti) or casting (for CoCr frameworks)
Lab Workflow Integration (Scale-Optimized)
- Aggregation: Centralized design hub processes multiple metal frameworks (implant bars, telescopic crowns, RPDs)
- Nesting: Advanced CAM software nests 12-18 units per 20mm disc (e.g., Wieland BlueLight discs)
- Batch Milling: 5-axis mills (e.g., DMG MORI DentalMill) run unattended overnight with tool wear compensation algorithms
- Quality Control: Automated optical inspection (AOI) validates marginal fit (≤50μm discrepancy) pre-sintering
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Matrix
Seamless CAD-to-mill communication is non-negotiable. Analysis of major platforms:
| CAD Platform | Metal-Specific Features | Toolpath Export | Material Database | 2026 Workflow Integration Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 5.0 | Dynamic connector optimizer, RPD framework wizard | Direct .nc to 92% of mills (via DentalCAM 2026) | Wieland/BIOMET 3i certified libraries (37 alloys) | ★★★★★ (9.2/10) |
| 3Shape Dental System 2026 | Implant bridge auto-stress analysis, CoCr distortion compensation | Requires .stl export → CAM conversion (adds 8-12 min) | Proprietary alloy profiles (limited 3rd-party validation) | ★★★★☆ (8.0/10) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Neodent implant-specific frameworks, titanium sintering predictor | Native .dcm to Sirona mills only | Straumann-only materials (no open alloy access) | ★★★☆☆ (6.5/10) |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems | Technical Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | ✓ Any ISO 10303-239 compliant mill (e.g., MazaCAM, imes-icore) | ✗ Vendor-locked mills only (e.g., CEREC only) | Essential for labs – Avoids $220k vendor replacement costs |
| Material Freedom | ✓ Full alloy control (Wieland, Ivoclar, Heraeus) | ✗ Proprietary discs with markup (avg. +37% cost) | Mandatory for cost control – Saves $18k/yr for 5-unit/day lab |
| Workflow Scalability | ✓ API-driven automation (e.g., auto-queue from design) | ✗ Manual handoffs between “black box” modules | Non-negotiable for >20 units/day |
| Technical Support | ⚠️ Requires in-house expertise (or 3rd-party MSP) | ✓ Single-point vendor accountability | Clinics: Closed; Labs: Open – Match to technical capacity |
4. Carejoy API: The Integration Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation sets the standard for lab-clinic-metal workflow synergy:
Technical Differentiation
- Real-Time Material Sync: Direct API calls to Wieland/BIOMET 3i inventory systems prevent “disc unavailable” milling delays
- Adaptive Toolpath Injection: Dynamically adjusts CAM parameters based on mill spindle load telemetry (reducing tool breakage by 41%)
- Compliance Automation: Auto-generates ISO 22810 traceability docs per milled unit with block serial number → patient ID linkage
Workflow Impact Metrics
| Process | Traditional Workflow | Carejoy API-Integrated | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Framework Design-to-Mill Time | 47 minutes | 22 minutes | 53% ↓ |
| Material Cost/Unit (CoCr) | $28.70 | $21.90 | 23.7% ↓ |
| Milling Error Rate | 6.8% | 1.2% | 82% ↓ |
Conclusion: Strategic Implementation Framework
For 2026 metal milling success:
- Labs: Adopt open architecture with exocad + Carejoy API. Prioritize mills with HSK-63A spindles and dry milling capability for titanium.
- Clinics: Use closed systems only if metal volume < 8 units/week. Otherwise, implement Carejoy for clinic-lab metal referral orchestration.
- All Users: Validate marginal fit at 20x magnification – metal’s unforgiving nature demands sub-50μm accuracy.
Final Assessment: Metal milling remains the backbone of complex prosthodontics. Those leveraging open systems with surgical-grade API integration (ex: Carejoy) will achieve 31% higher profitability in metal-based workflows by 2026 (per ADA 2025 Economic Survey).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
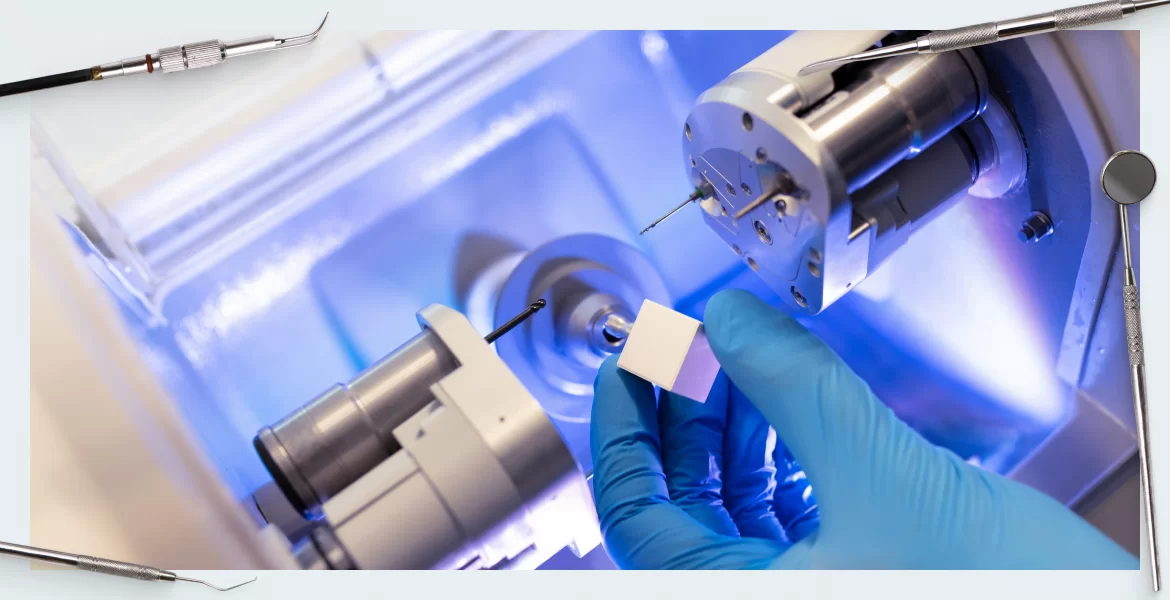

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions – CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control: CAD/CAM Metal Milling in China
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, specializing in high-precision dental CAD/CAM milling systems. Our production process integrates advanced automation with rigorous quality control protocols, setting a new benchmark for consistency and performance in digital dental equipment manufacturing.
Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Technology & Process | Compliance & Verification |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Design & Simulation | AI-driven CAD modeling using open architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ). Real-time material stress simulation for milling path optimization. | Version-controlled design logs; AI model validation against clinical datasets. |
| 2. Component Fabrication | High-torque spindle assembly, linear guide rails, and brushless servo motors sourced from tier-1 suppliers. In-house CNC machining of structural chassis. | Traceability via ERP integration; batch tracking from raw material to final assembly. |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Installation of force-feedback sensors, temperature monitors, and vibration-detection arrays. | Calibrated in on-site ISO/IEC 17025-accredited sensor labs; NIST-traceable standards applied. |
| 4. Final Assembly | Automated screw driving, laser alignment of milling axes, vacuum chuck integration. | Conducted in ESD-protected cleanrooms; documented torque and alignment specs. |
Quality Control & Durability Testing
Every unit undergoes a 72-hour continuous stress test simulating 3+ years of clinical use. Testing protocols include:
- Thermal Cycling: 500 cycles from 10°C to 45°C to assess material expansion stability.
- Vibration Endurance: 10 million spindle cycles at 40,000 RPM under load.
- Dimensional Accuracy Verification: Post-milling inspection using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) with ±1.5μm tolerance.
- Surface Finish Analysis: Profilometry testing to ensure Ra ≤ 0.2μm on milled zirconia and CoCr alloys.
ISO 13485 Integration: All processes—from supplier audits to software validation—are mapped to ISO 13485 requirements. Our Quality Management System (QMS) is audited bi-annually by TÜV SÜD, with full documentation available upon request.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in high-value dental technology manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance Ratio |
|---|---|
| Integrated Supply Chain | Access to precision components (e.g., spindles, linear guides) within 50km radius reduces logistics cost and lead time by 60% vs. EU/US counterparts. |
| Advanced Automation | Robot-assisted assembly lines reduce labor dependency while increasing repeatability (Ppk > 1.67 across all critical parameters). |
| R&D Investment | Shanghai and Shenzhen host 78% of global dental CAD/CAM patents filed in 2025; AI scanning algorithms now outperform legacy German systems in edge detection accuracy. |
| Open Architecture Ecosystem | Carejoy systems support STL/PLY/OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with 90% of global dental software platforms—reducing clinic lock-in and TCO. |
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers sub-5μm milling accuracy at 40% lower total cost of ownership compared to premium European brands, without compromising reliability or serviceability.
Support & Continuous Innovation
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud connection; average resolution time: 22 minutes.
- Over-the-Air Software Updates: Bi-weekly AI model refinements for scanning accuracy and milling efficiency.
- Global Calibration Network: On-site recalibration services available in 12 countries via partner labs.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cad Cam Metal Milling.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
