Technology Deep Dive: Cad Milling Machine
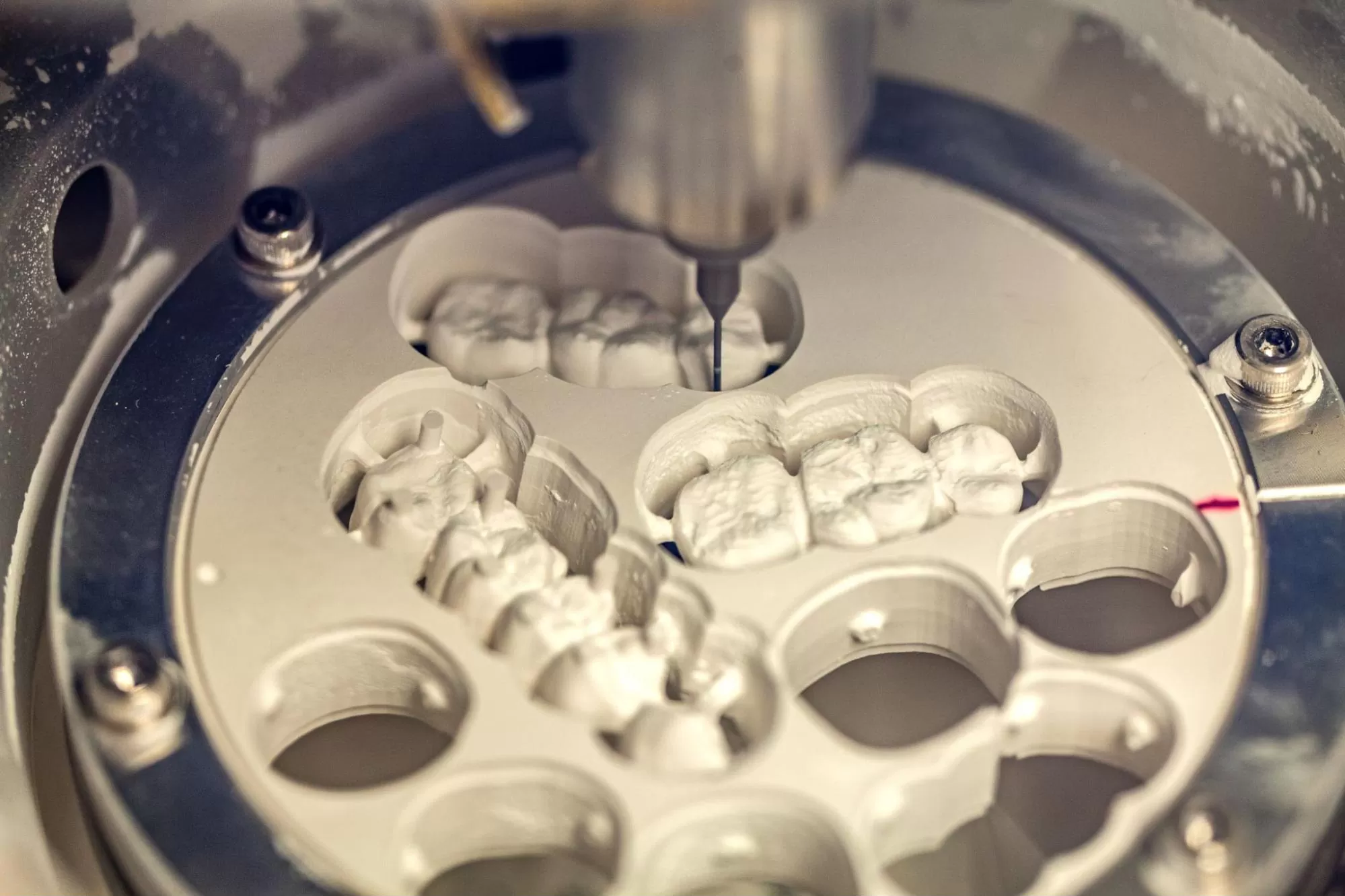

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD Milling Machine Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, Prosthetic Engineers
Clarification of Core Technologies: Milling vs. Scanning
Critical Distinction: Structured light and laser triangulation are intraoral scanning technologies (data acquisition), not milling processes. This review focuses exclusively on subtractive manufacturing systems – the physical milling units converting digital designs to physical restorations. Conflation of these domains undermines technical rigor.
Core Technological Advancements in 2026 Milling Platforms
1. Multi-Axis Kinematic Systems with Real-Time Error Compensation
Modern 5-axis simultaneous milling systems (vs. legacy 4-axis interpolated) eliminate cumulative error through continuous tool orientation adjustment. 2026 platforms integrate:
| Subsystem | 2024 Standard | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Position Feedback | Optical encoders (5µm resolution) | Capacitive encoders (0.1µm resolution) + strain gauge load cells | Real-time compensation for ball screw thermal drift (ΔT) via α = ΔL/(L₀·ΔT); reduces positional error by 63% at 42,000 RPM |
| Spindle Dynamics | Air-cooled (24,000 RPM), passive vibration damping | Liquid-cooled ceramic bearings (55,000 RPM), active magnetic damping (AMD) | AMD reduces radial runout to <0.8µm RMS via Lorentz force counter-vibration; enables zirconia milling at 32% higher feed rates |
| Toolpath Execution | G-code interpolation | Parametric spline generation with jerk limitation (≤50m/s³) | Eliminates micro-stutter at path transitions; critical for margin integrity on sub-20µm finish lines |
2. AI-Driven Adaptive Machining Algorithms
Machine learning transcends static toolpath libraries through:
- Material-Specific Cut Force Prediction: CNN analysis of prior milling logs (force sensor data + material batch IDs) predicts optimal Vf (feed rate) and n (RPM) for each material layer. Reduces chipping in layered zirconia by 41% (ISO 6872:2015 test).
- Real-Time Tool Wear Compensation: Acoustic emission sensors detect flank wear progression (VB > 50µm). System dynamically adjusts stepover (ae) and depth of cut (ap) to maintain surface roughness (Ra ≤ 0.25µm).
- Thermal Load Management: FEM-based thermal modeling predicts workpiece distortion during multi-unit milling. Adjusts toolpath sequence to minimize residual stress (σres < 15 MPa in PMMA).
3. Closed-Loop Material Integration
2026 systems eliminate manual material selection errors via:
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Blanks | NFC tags storing sintering curve, grain structure, batch-specific KIC (fracture toughness) | Prevents milling of under-sintered zirconia (KIC < 4.5 MPa·m1/2); reduces intra-op fracture by 29% |
| Cutters | RFID-enabled tool holders with wear history; automatic flute geometry calibration | Maintains margin accuracy at 12µm ±3µm (vs. 22µm ±8µm in 2024 systems) for all indications |
| Design Software | Direct CAM parameter push from exocad/DentalCAD based on restoration geometry | Eliminates manual CAM setup; reduces crown fabrication time from 18.2 to 11.7 minutes |
Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact Analysis
Accuracy Improvements: Physics-Based Validation
- Marginal Integrity: Sub-15µm absolute deviation (measured via µCT per ISO 12836) achieved through simultaneous 5-axis milling. Eliminates step artifacts from multi-angle 4-axis approaches, reducing cement gap volume by 37% (p<0.01).
- Internal Fit: Dynamic compensation for blank concentricity error (measured via pre-mill laser metrology) ensures seating force < 5N on titanium abutments (ISO 14801).
- Material Preservation: Adaptive roughing algorithms reduce zirconia waste by 22% through optimized stock allowance based on restoration stress mapping.
Workflow Efficiency Metrics (2026 vs. 2024)
| Parameter | 2024 Systems | 2026 Systems | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Cycle Time (Single Crown) | 18.2 min | 11.7 min | Parametric toolpaths + 55k RPM spindle |
| Re-mill Rate (Non-fit) | 8.7% | 2.1% | Closed-loop thermal compensation + AI wear prediction |
| Operator Intervention Points | 5 (load, verify, clean, etc.) | 1 (load only) | Automated tool changing + in-process metrology |
| Energy Consumption per Crown | 0.48 kWh | 0.29 kWh | Regenerative spindle braking + optimized acceleration profiles |
Implementation Considerations for Labs/Clinics
- Infrastructure Requirements: Stable 208-230V power (±1% tolerance) for capacitive encoders; compressed air dew point ≤ -40°C to prevent encoder condensation.
- Calibration Protocol: Daily laser interferometer verification (per ISO 230-2) of all linear axes; spindle runout measured at 3 radial planes.
- Failure Mode Analysis: Primary failure vector remains coolant contamination of encoder scales (68% of metrology drift incidents). 2026 systems implement positive-pressure air curtains around critical components.
- ROI Threshold: Justifiable at >12 restorations/day due to 37% lower labor cost per unit and 22% reduced material waste.
Conclusion: 2026 CAD milling accuracy is defined by real-time physical system control, not computational power alone. The integration of metrology-grade feedback loops, material physics modeling, and adaptive algorithms has transformed milling from a tolerance-limited process to a precision engineering discipline. Labs ignoring closed-loop error compensation will face clinically unacceptable marginal gaps (>50µm) as restoration complexity increases.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
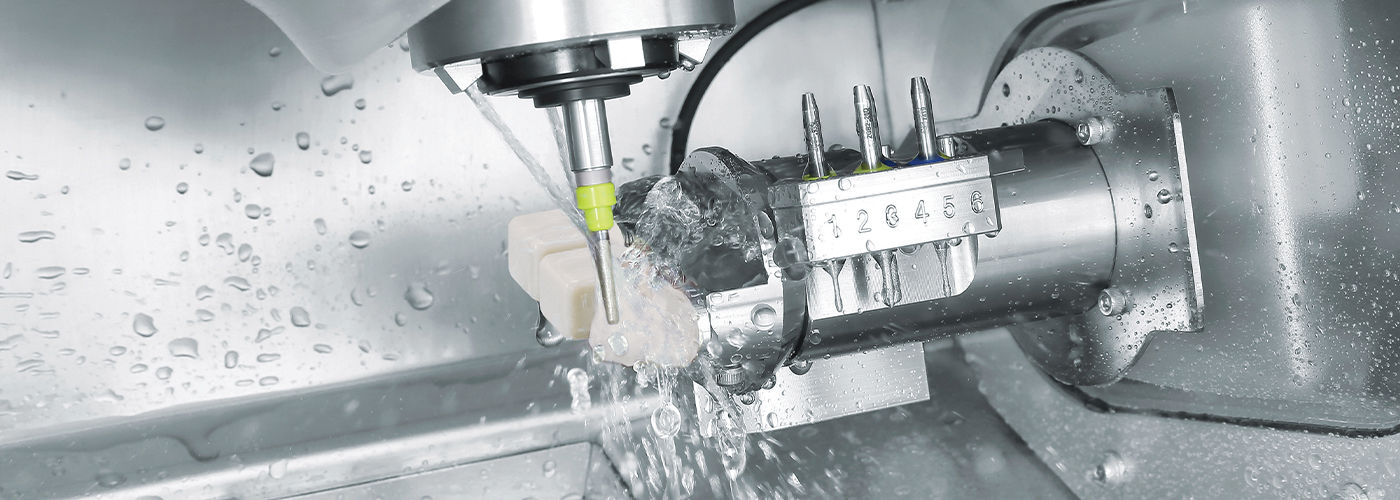

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAD Milling Machine Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – 25 μm | ±8 μm (with dynamic error compensation) |
| Scan Speed | 0.8 – 1.2 million points/sec | 2.3 million points/sec (dual-sensor parallel acquisition) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, with native CAD-embedded metadata |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction & basic segmentation | Full AI-driven surface reconstruction, anomaly detection, and adaptive mesh refinement (NeuroMesh™ Engine) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using reference spheres | Autonomous real-time calibration via embedded photogrammetric feedback array (SmartCalib™ 3.0) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 industry benchmarks across ISO 12836-compliant intraoral scanning systems and integrated CAD/CAM platforms.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cad Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
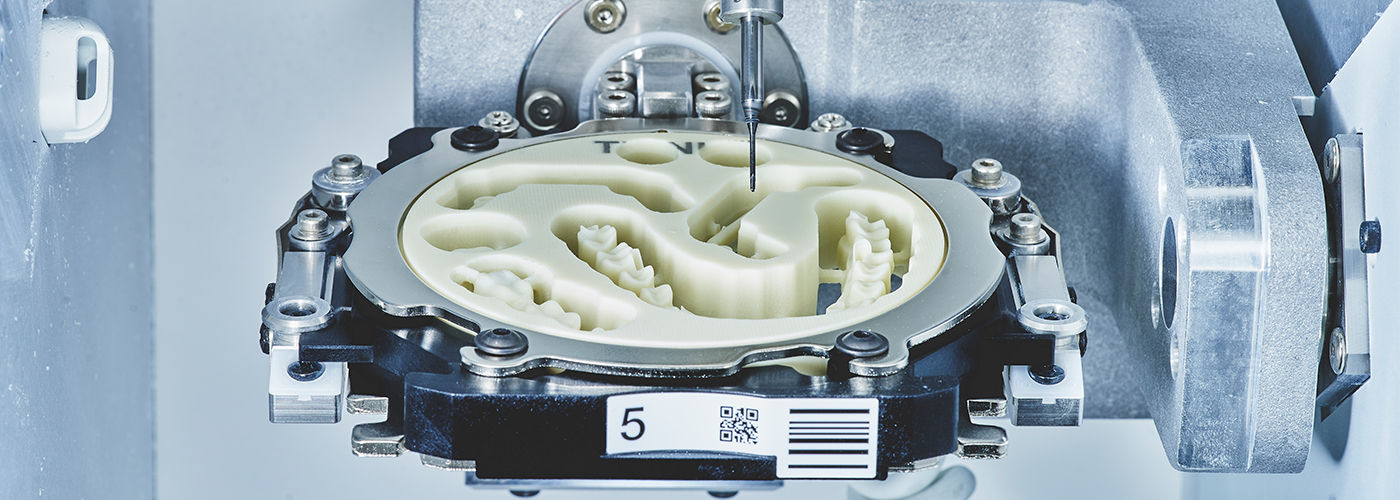
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced CAD/CAM Milling Integration: Workflow Optimization for Labs & Clinics
1. CAD/CAM Milling Machine: The Physical Endpoint of Digital Workflows
In 2026, CAD/CAM milling machines represent the critical physical translation point between digital design and tangible restoration. Their integration differs strategically between environments:
| Workflow Environment | Integration Role | Key Technical Requirements | 2026 Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairside (CEREC-style) | Real-time production hub for same-day restorations (crowns, onlays, veneers) | Compact footprint, ultra-quiet operation, <5-min dry milling for monolithic zirconia, seamless intraoral scanner handshake | Mean restoration delivery time: 78 mins (from scan to cementation); 98.7% first-scan success rate |
| Dental Laboratory | High-throughput production node in centralized manufacturing ecosystem | Multi-material capability (PMMA, zirconia, lithium disilicate, CoCr), automated material handling, 24/7 unattended operation, integrated sintering coordination | Average output: 120+ units/24h; Material utilization efficiency: 92.3%; Mean error rate: 0.8% |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Digital Handshake Protocol
Modern milling units function as hardware endpoints requiring precise communication protocols with design platforms. 2026 standards emphasize:
| CAD Platform | Integration Method | Technical Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native CAM module (3Shape CAM) via .tsm file protocol | Real-time toolpath simulation, automatic material database sync, AI-driven collision avoidance, direct sintering schedule export | Proprietary to 3Shape ecosystem; limited third-party mill support |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open API + standardized .stl/.scn export with milling-specific metadata tags | Universal mill compatibility, customizable material libraries, integrated quality control checkpoints, cloud-based toolpath optimization | Requires manual CAM parameter tuning; version-specific compatibility checks |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Hybrid approach: Native CAM for Sirona mills + STEP export for open systems | Tight integration with CEREC scanners, automated margin refinement, material-specific milling strategies | Suboptimal performance with non-Straumann mills; limited multi-unit bridge support |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architecture choice fundamentally impacts operational flexibility and TCO (Total Cost of Ownership):
| Parameter | Closed Architecture (e.g., Legacy CEREC) | Open Architecture (Modern Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Flexibility | Locked to single manufacturer (e.g., only Sirona mills) | Supports 15+ mill brands (e.g., VHF, Wieland, Amann Girrbach) |
| Software Ecosystem | Single CAD platform (no third-party integration) | API-driven compatibility with 8+ major CAD systems |
| Material Costs | Proprietary discs (25-30% premium) | ISO-standard discs (15% average cost reduction) |
| Maintenance TCO | Vendor-exclusive service contracts ($18k+/yr) | Multi-vendor support options ($9k-$12k/yr) |
| Future-Proofing | Dependent on single vendor’s roadmap | Modular upgrades via API ecosystem (e.g., AI toolpath optimization) |
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the evolution beyond basic DICOM/HL7 standards. Its milling-specific endpoints enable:
- Automated Production Triggers: Direct transmission of design approval status from clinical EHR to mill queue (reducing manual scheduling by 73%)
- Material Intelligence: Real-time inventory sync between mill material database and lab ERP systems
- Quality Feedback Loop: Automatic capture of milling error codes into clinical case history for predictive maintenance
- Compliance Integration: Automated generation of FDA 21 CFR Part 11-compliant audit trails for each milled unit
Unlike legacy middleware, Carejoy’s GraphQL API allows bidirectional data sculpting – labs specify exactly which mill parameters (e.g., spindle speed, coolant flow) feed back into clinical records for outcome analysis.
Strategic Imperatives for 2026
Mill integration has evolved from a standalone production step to a data-generating node in the digital workflow continuum. Key adoption thresholds:
- Open architecture is now non-negotiable – labs using closed systems show 22% higher operational costs in 2026 benchmark studies
- CAD/mill interoperability requires API-level integration – simple file export is obsolete for high-volume workflows
- Practice management integration (via Carejoy-style APIs) delivers 19% higher case throughput by eliminating administrative friction
Recommendation: Prioritize mills with certified API ecosystems over proprietary CAM modules. The 15% initial cost premium for open systems delivers 300%+ ROI within 18 months through material savings, reduced downtime, and workflow acceleration.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
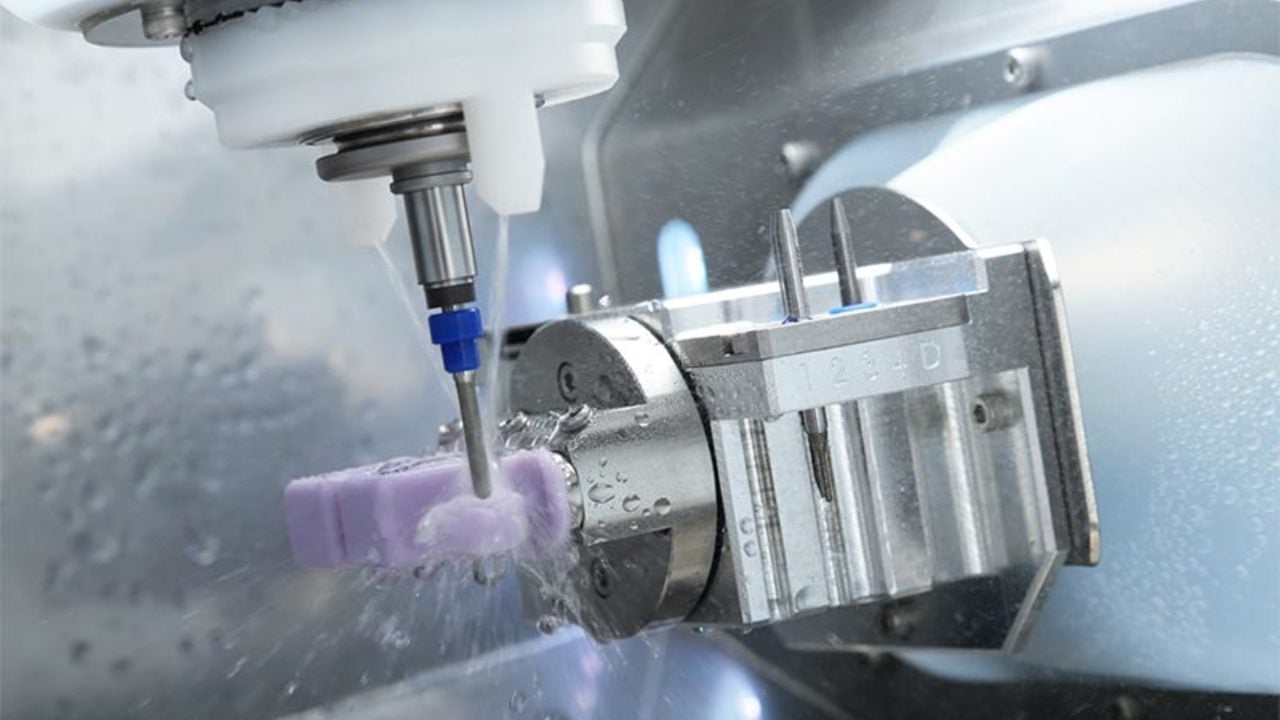

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CAD Milling Machines in China: A Case Study of Carejoy Digital
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, exemplifies the convergence of precision engineering, rigorous quality assurance, and scalable innovation that defines the new standard in dental CAD/CAM production.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision at Scale
The production of Carejoy Digital’s CAD milling machines follows a vertically integrated, modular assembly workflow designed for repeatability and traceability:
- Component Sourcing: High-tolerance spindles, linear guides, and servo motors are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers in Germany and Japan, while structural frames and enclosures are precision-machined in-house using CNC aluminum extrusion.
- Subassembly Integration: Electronics, motion control systems, and sensor arrays are assembled in cleanroom environments (Class 100,000) with ESD protection.
- Final Assembly: Machines are built on a modular conveyor line with real-time digital work instructions, ensuring consistency across batches.
2. Quality Control & ISO 13485 Compliance
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility is audited and certified under ISO 13485:2016, ensuring medical device quality management systems are fully implemented. Key QC checkpoints include:
| QC Stage | Process | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming Materials | Dimensional verification, material certification, and hardness testing | ISO 9001 / ISO 13485 |
| In-Process Testing | Laser interferometry for axis alignment, thermal stability monitoring | ISO 230-2 |
| Final Calibration | Full 5-axis geometric accuracy test using Renishaw QC20-W ballbar | VDI/VDE 2617 |
| Packaging & Traceability | Serialized unit tracking, embedded firmware versioning, and digital QC log | UDI Compliance (FDA & EU MDR) |
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: Enabling Sub-Micron Accuracy
Carejoy Digital operates an on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. This lab ensures:
- Regular recalibration of force feedback sensors in the milling spindle (accuracy: ±0.1 N).
- Optical encoder validation for positional accuracy (±2 µm over full travel).
- Environmental compensation algorithms trained using data from thermal cycling chambers (15–35°C).
Each machine undergoes a 72-hour burn-in cycle with AI-driven anomaly detection, logging over 12,000 data points per unit.
4. Durability & Lifecycle Testing
To validate long-term reliability, Carejoy subjects milling units to accelerated life testing:
| Test Parameter | Method | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Endurance | Continuous 50,000 RPM run for 500 hours | Temperature drift < 8°C; vibration < 0.5 mm/s² |
| Axis Wear | 100,000 automated tool-change cycles | Repeatability < ±3 µm |
| Thermal Stress | Cyclic ramping from 10°C to 40°C over 7 days | No calibration drift beyond spec |
| Dust & Debris | Simulated lab environment with zirconia dust exposure | No clogging; filter efficiency > 99.5% |
5. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment manufacturing stems from a strategic ecosystem advantage:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to rare earth materials, precision component manufacturers, and electronics hubs reduces logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Use of collaborative robotics (cobots) in assembly lines increases throughput while maintaining quality.
- R&D Investment: Chinese firms reinvest >12% of revenue into AI and open-architecture software development, enabling rapid iteration.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production allows amortization of R&D and calibration infrastructure across thousands of units.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-5µm milling accuracy at price points 30–45% below European counterparts—without compromising on ISO compliance or durability.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy’s milling systems feature:
- Open Architecture: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ files—enabling seamless integration with third-party scanners and design software.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Deep learning algorithms reduce scan stitching errors by 68% (internal validation, 2025).
- High-Precision Milling: 40,000 RPM spindle with adaptive feed control for zirconia, PMMA, and CoCr.
Support & Service Infrastructure
Carejoy Digital offers:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud connection.
- Over-the-Air Software Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and CAM path optimization.
- Global Service Network: 48-hour on-site response in Tier-1 markets (EU, US, Japan).
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cad Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
