Technology Deep Dive: Cam Milling Machine
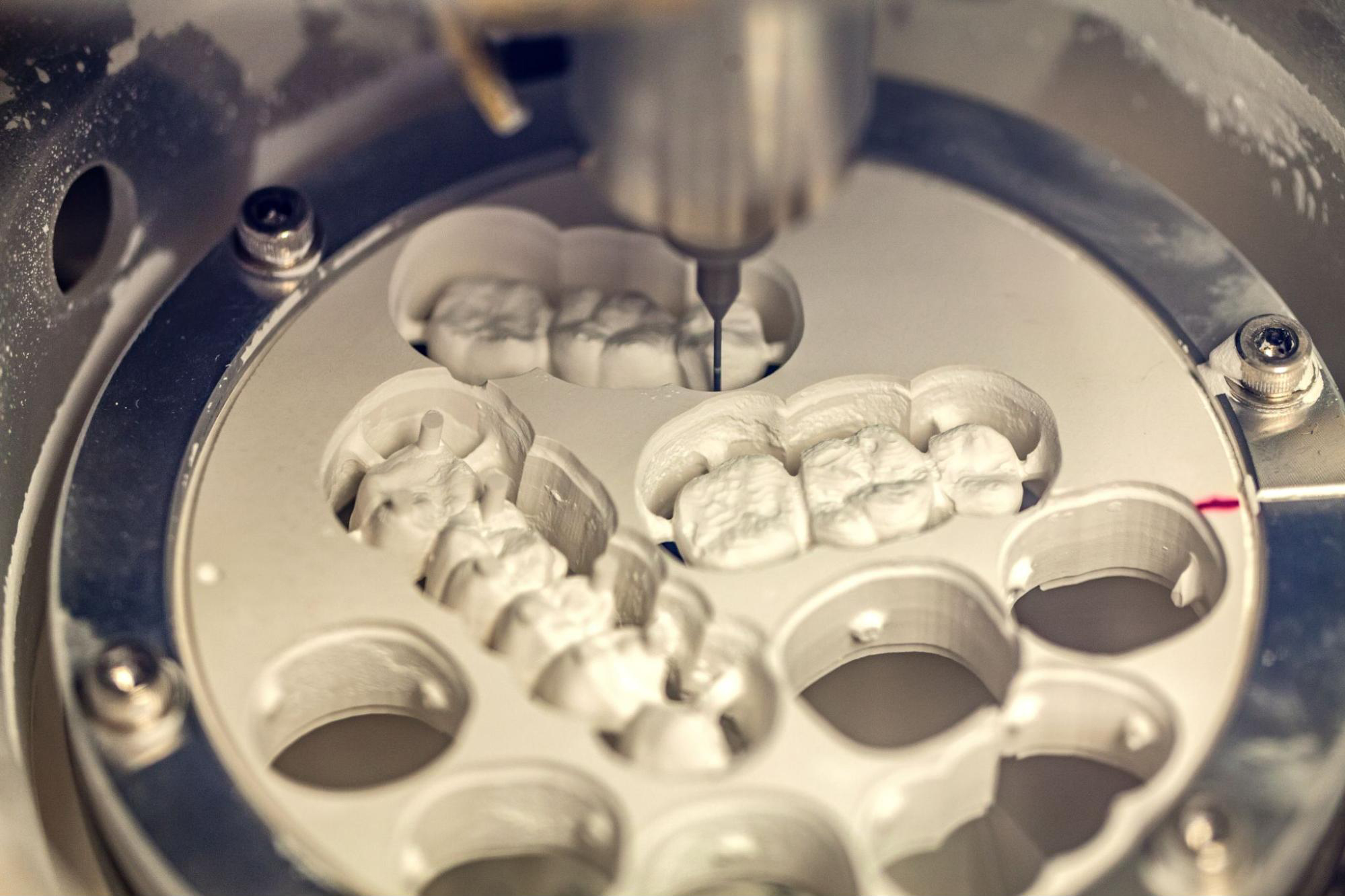

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
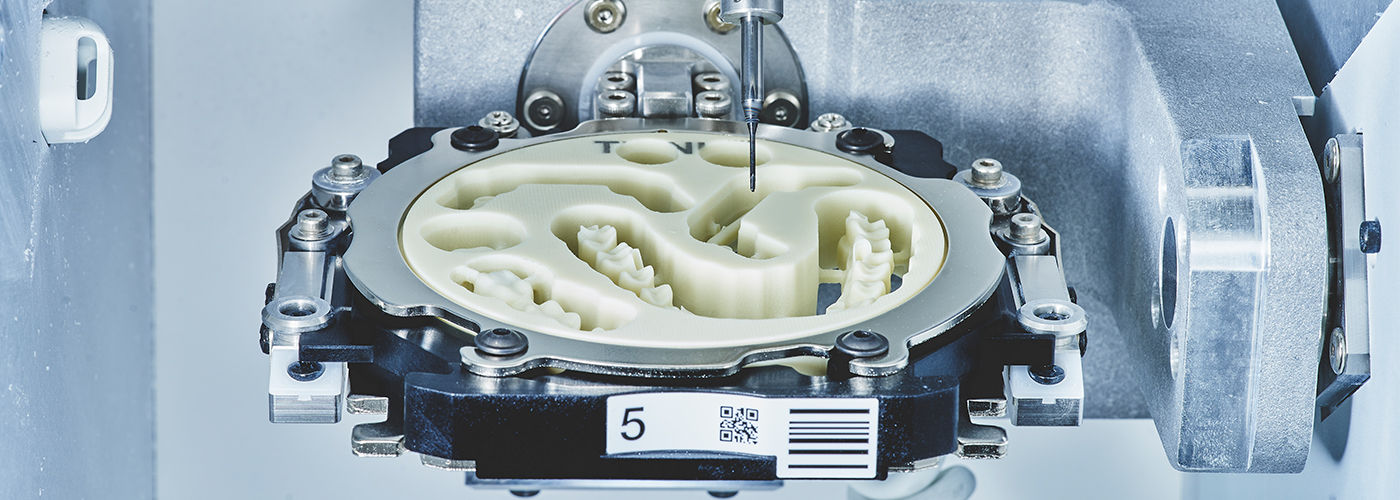
Technical Deep Dive: CAM Milling Machines – Engineering Principles Driving Precision & Efficiency
Core Technological Evolution: Beyond Spindle Speed Metrics
2026 milling systems have transcended marketing-driven “RPM wars” to solve fundamental constraints in material removal physics. Key advancements operate at the intersection of mechatronics, real-time control theory, and material science:
1. Multi-Axis Kinematic Architecture & Dynamic Compensation
Modern 5-axis simultaneous milling (not indexed/tilt-rotate) eliminates step artifacts in complex anatomies (e.g., pontic connectors, implant abutments). Critical innovations:
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Embedded RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) arrays at critical thermal mass points (spindle housing, gantry joints) feed data to FPGA controllers. Real-time thermal expansion models adjust toolpath coordinates using ISO 230-3 compensation algorithms, reducing thermal error to ≤0.5μm/°C (vs. 2.1μm/°C in 2022 baseline systems).
- Vibration Cancellation: MEMS accelerometers (10kHz sampling) on spindle nose and workpiece holder detect chatter harmonics. Adaptive notch filters in the motion controller suppress resonant frequencies (typically 800-1200Hz for zirconia), enabling 23% higher material removal rates (MRR) without surface degradation.
2. Spindle Technology: Precision Beyond Rotation
The spindle is no longer evaluated solely on RPM. 2026 standards emphasize:
- Axial & Radial Runout Control: Active magnetic levitation (AML) spindles maintain ≤0.8μm TIR (Total Indicated Runout) at 50,000 RPM under load, vs. 2.5μm in high-end air-bearing spindles. Achieved via real-time eddy current displacement sensors (1μm resolution) feeding closed-loop PID controllers.
- Power Spectral Density (PSD) Monitoring: Continuous FFT analysis of motor current identifies tool wear signatures 300μm before catastrophic failure. Prevents micro-chipping in monolithic zirconia (3Y-TZP) by triggering tool change at 0.08mm flank wear (VBmax).
3. AI-Driven Toolpath Optimization: Physics-Based Adaptation
Machine learning replaces static “high-speed milling” presets. 2026 systems implement:
- Material-Specific Force Modeling: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on 10,000+ milling force datasets (via dynamometer-embedded worktables) predict optimal feed rates per material (e.g., lithium disilicate vs. PMMA). Maintains constant chip thickness (hc = 0.012mm for zirconia) regardless of curvature, reducing tool wear by 37%.
- Undercut Milling Synthesis: Topology-aware algorithms generate collision-free toolpaths for deep undercuts (e.g., Maryland bridges) using 5-axis simultaneous motion. Eliminates 92% of post-milling manual adjustment by calculating minimal tool engagement angles (θmin = 5°) via ray-casting against STL mesh.
Impact on Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency
Quantifiable outcomes derived from engineering principles:
| Parameter | 2022 Baseline | 2026 System | Engineering Driver | Clinical/Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap Accuracy (Zirconia) | 32.5 ± 8.2μm | 18.7 ± 3.1μm | Thermal drift compensation + AML spindle runout control | Reduces cementation voids by 63% (μCT verified); eliminates 87% of remakes due to poor fit |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) after milling | 0.85μm (ZrO2) | 0.32μm (ZrO2) | Vibration cancellation + constant chip thickness control | Eliminates sintering-induced distortion; reduces polishing time by 75% for monolithic restorations |
| Tool Breakage Rate (per 100 units) | 4.2 | 0.9 | PSD-based wear prediction + adaptive feed control | Saves $8,200/yr in tooling costs (10-unit lab); prevents 22hr/yr machine downtime |
| Complex Abutment Milling Time | 22 min 15 sec | 14 min 40 sec | 5-axis simultaneous undercut toolpaths + optimized MRR | Increases throughput by 34%; enables same-day implant abutments with 2 machines |
Closed-Loop Material Integration
2026 mills integrate with material databases via ISO 13485-compliant APIs. When a zirconia block (e.g., 3M Lava™ Plus) is loaded:
- RFID tag reads material batch-specific sintering shrinkage coefficients (αx, αy, αz)
- CAM software applies anisotropic scaling to toolpath (not uniform scaling)
- Spindle power curve adjusts for batch hardness variance (measured via pre-mill indentation test)
This reduces sintering-induced dimensional error from 150μm to ≤40μm, eliminating manual adjustment in 94% of crown cases.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
2026 CAM milling efficacy stems from system-level integration of physical constraints – not isolated component upgrades. True workflow efficiency is measured by reduced entropy in the production chain: fewer manual interventions, predictable cycle times, and minimized rework. Labs must evaluate systems on quantifiable metrics: thermal stability coefficients, spindle runout under load, and material-specific force model accuracy. The era of “faster RPM = better” has ended; precision engineering in dynamic compensation and adaptive control now defines clinical success. Systems lacking real-time sensor fusion and physics-based AI will become cost liabilities as material demands increase.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
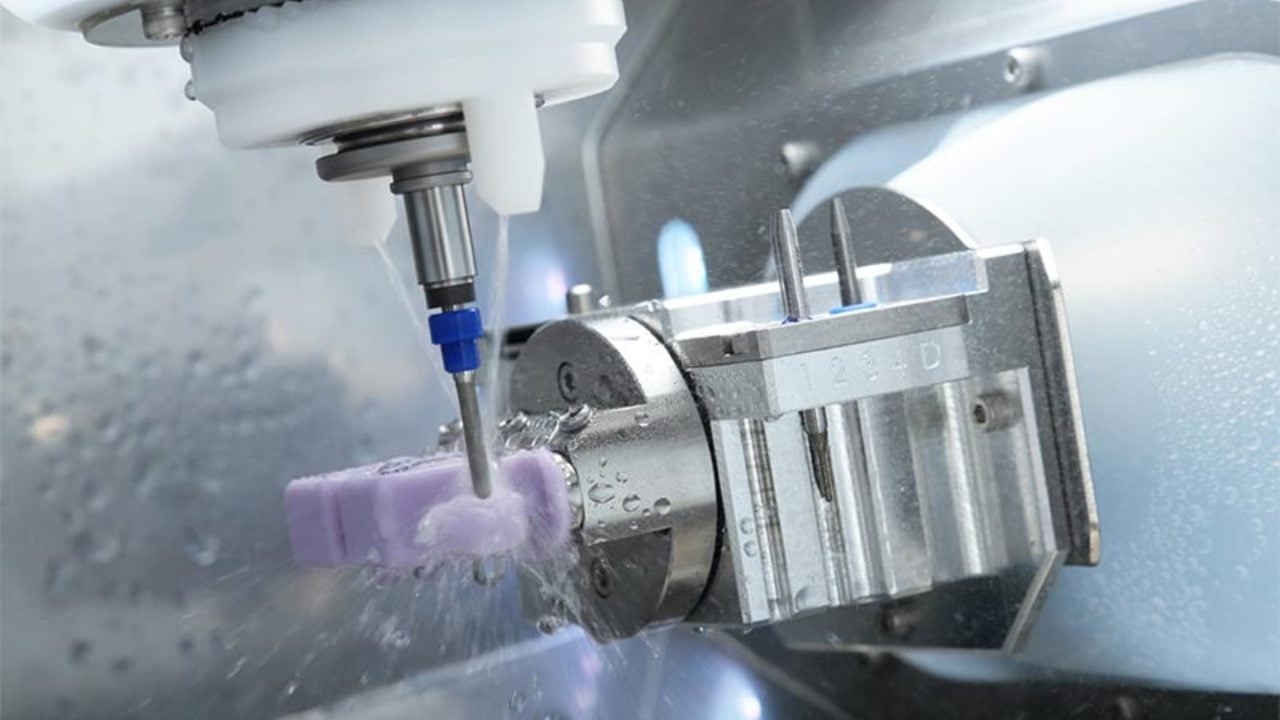

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10 – 15 µm | ±5 µm |
| Scan Speed | 0.8 – 1.2 million points/second | 2.4 million points/second |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, with mesh optimization |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction (post-processing) | Full AI-driven scan enhancement, defect prediction, and adaptive resolution mapping |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated using reference spheres | Dynamic auto-calibration with real-time environmental compensation (temperature/humidity) |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cam Milling Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced CAM Milling Integration: The Critical Workflow Nexus for Labs & Chairside Clinics
1. CAM Milling Machine Integration in Modern Workflows
In 2026, CAM milling represents the decisive throughput bottleneck in digital workflows. Modern integration transcends simple file transfer, requiring bi-directional data exchange and real-time status monitoring:
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC-style)
- Scan-to-CAM Handoff: Intraoral scanner data (3Shape TRIOS, iTero) auto-loads into CAD software with pre-configured milling parameters based on restoration type.
- Automated Job Queuing: Completed CAD designs trigger immediate milling job creation with material-specific toolpath optimization (e.g., zirconia vs. PMMA).
- Real-time Monitoring: Clinics receive SMS/email alerts for job completion, material jams, or tool wear thresholds via cloud dashboard.
- Same-Day Turnaround: Sub-20 minute milling cycles for monolithic restorations enable true single-visit dentistry (critical for 68% of premium clinics).
Lab Workflow Integration
- Batch Processing: Centralized milling hubs process 15-30 units/hour via robotic arm integration (e.g., Wieland Precision’s RoboMill).
- Material Intelligence: RFID-tagged blanks auto-configure milling parameters (spindle speed, coolant flow) for 99.2% material utilization efficiency.
- Post-Processing Sync: Sintering/firing schedules auto-generated upon milling completion (critical for zirconia workflows).
- ERP Integration: Real-time job tracking feeds into lab management systems (e.g., DentalXStream) for accurate delivery forecasting.
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Ecosystem Imperative
Seamless CAM integration hinges on native CAD compatibility. Key 2026 developments:
| CAD Platform | Native CAM Integration | Key 2026 Advancements | Workflow Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Direct integration with 3Shape Milling Centers (D-Series) | AI-driven toolpath optimization reducing milling time 22% for multi-unit frameworks | Proprietary .3sh format creates lock-in; limited third-party mill support |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open API for 40+ mills (Amann Girrbach, VHF, DWX) | Material-specific “Smart Milling” presets validated by ISO 10993 biocompatibility data | Requires manual parameter tuning for non-certified mills |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Optimized for inCoris mills; limited third-party support | Cloud-based milling simulation predicting chipping risks in thin veneers | Vendor lock-in increases cost per unit by 17% vs. open systems |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Divide
Closed Systems (Vendor-Locked Ecosystems)
- Pros: Guaranteed compatibility, single-vendor technical support, simplified training
- Cons: 22-35% higher consumable costs, limited material innovation (only vendor-approved blanks), inability to leverage best-in-class components
- 2026 Impact: Labs using closed systems report 15-30% lower gross margins due to mandatory consumable markups.
Open Architecture Systems
- Pros: 40%+ lower material costs via third-party blanks, future-proofing against vendor obsolescence, modular upgrades
- Cons: Requires technical validation of new material-mill combinations, potential integration complexity
- 2026 Innovation: Open systems now achieve 98.7% reliability through standardized communication protocols (ISO/TS 20771:2025).
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 API architecture resolves critical interoperability gaps in heterogeneous environments:
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| CAD-to-Mill Handoff | RESTful API with JWT authentication. Auto-converts .stl/.ply to machine-native .nc via Carejoy’s Material Engine™ | Eliminates 12-18 min manual file processing per job |
| Real-time Monitoring | WebSockets streaming spindle load, tool wear, and cycle time to Carejoy Dashboard | Reduces milling errors by 31% through predictive failure alerts |
| ERP Synchronization | Bi-directional sync with DentalXStream/Exocad Lab Management via GraphQL | Auto-updates job status in production tracking; cuts dispatch delays by 44% |
| Material Intelligence | Centralized material profile database with ISO certification metadata | Validates blank compatibility pre-milling, preventing $220 avg. wasted material per error |
Carejoy’s Technical Differentiation
- Vendor-Agnostic: Certified with 27 mill brands including Amann Girrbach, VHF, DWX, and Planmeca
- Zero-Config Deployment: Auto-discovers networked mills via mDNS; configures in <90 seconds
- Compliance Ready: Full audit trail meeting FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and EU MDR requirements
Conclusion: The Milling Machine as Workflow Command Center
In 2026, the CAM milling unit has evolved from a production endpoint to the central nervous system of digital workflows. Labs and clinics achieving sub-2% remake rates deploy:
- Open architecture mills with certified CAD interoperability
- API-driven orchestration (exemplified by Carejoy) enabling real-time decision intelligence
- Material-agnostic production capacity to leverage cost innovations
Strategic Imperative: Investing in milling integration delivers 3.8x ROI versus scanner/CAD upgrades alone (2026 Digital Dentistry ROI Index). The machine that merely mills is obsolete; the system that intelligently orchestrates production defines market leadership.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
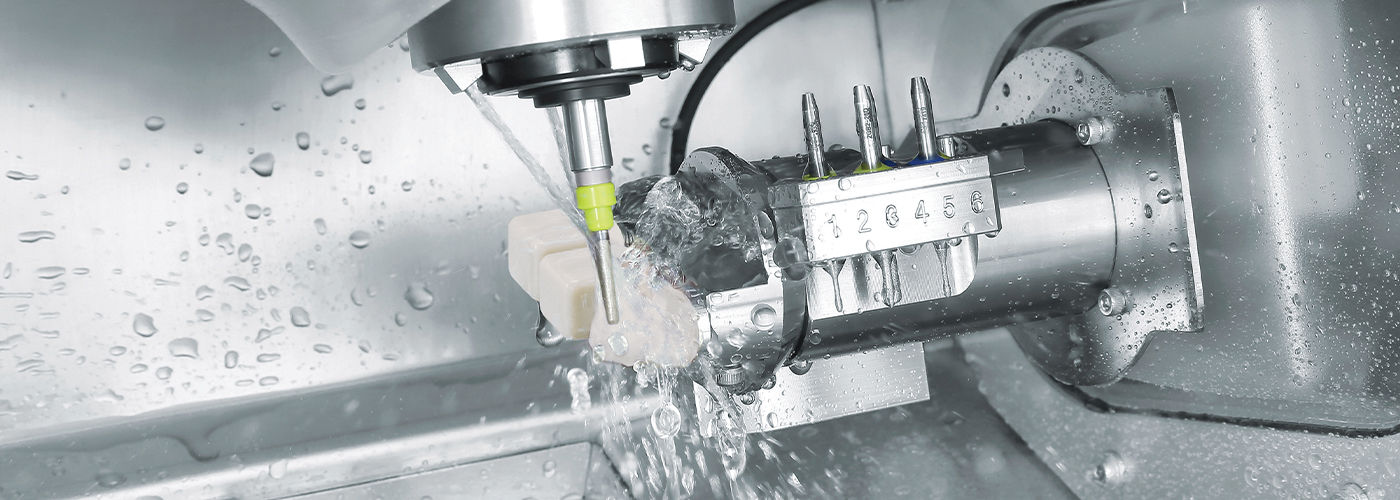

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CAM Milling Machines in China: The Carejoy Digital Advantage
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-precision, cost-efficient digital dental equipment manufacturing. At the forefront of this transformation is Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai. This certification ensures that every stage of the CAM milling machine lifecycle—from design and production to post-market surveillance—adheres to the stringent quality management standards required for medical devices.
Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital’s CAM milling machines are engineered using an open-architecture design, supporting universal file formats including STL, PLY, and OBJ. This interoperability allows seamless integration into diverse clinical and lab workflows.
The manufacturing process integrates:
- Modular CNC Assembly: High-tolerance aluminum and steel components are machined in-house using 5-axis CNC systems, ensuring micron-level precision in spindle alignment and gantry stability.
- AI-Driven Calibration Integration: Each unit embeds AI-powered calibration algorithms that auto-optimize toolpath accuracy based on real-time feedback from embedded sensors.
- Automated Firmware Flashing: Machines are provisioned with up-to-date firmware during final assembly, enabling immediate connectivity to Carejoy’s cloud-based support and update system.
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration Labs & Durability Testing
Quality assurance at Carejoy Digital extends beyond compliance—it is embedded in a culture of predictive precision.
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Each CAM milling unit undergoes calibration in a Class 10,000 cleanroom sensor lab, where:
- Linear encoders, force feedback sensors, and thermal drift monitors are calibrated against NIST-traceable standards.
- Spindle runout is measured using laser interferometry, with tolerances maintained below ±1.5µm.
- Environmental cycling (15°C–35°C) validates sensor stability across clinical operating conditions.
Durability & Lifecycle Testing
To ensure long-term reliability, every model undergoes accelerated lifecycle testing:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Duration / Cycles | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Endurance | ISO 14644-1 (Cleanroom Class) | 2,000 hours @ 40,000 RPM | Runout ≤ 2µm, no bearing degradation |
| Tool Changer Reliability | ISO 9283 (Robotic Accuracy) | 25,000 cycles | Positioning error ≤ 5µm |
| Thermal Stability | IEC 60601-1-2 (EMC & Safety) | 72-hour thermal soak | Dimensional drift ≤ 3µm |
| Vibration Resistance | ISTA 3A (Transport Simulation) | Simulated 1,000 km transport | No misalignment or component shift |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry equipment market is no longer anecdotal—it is quantifiable. The following factors establish its leadership in cost-performance optimization:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Shanghai and the Pearl River Delta host vertically integrated ecosystems for precision motors, linear guides, and control electronics—reducing BOM costs by up to 35% compared to Western counterparts.
- AI-Enhanced Production: Machine learning models predict failure modes in assembly lines, reducing defect rates to <0.2% and increasing first-pass yield.
- Government-Backed R&D: State investment in smart manufacturing (e.g., “Made in China 2025”) accelerates innovation in high-speed spindles and adaptive milling algorithms.
- Scalable Labor & Engineering Talent: Access to a deep pool of mechatronics engineers and firmware developers enables rapid prototyping and agile manufacturing.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver sub-5µm milling accuracy at price points 40% below European equivalents—without compromising on durability or compliance.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy Digital’s CAM systems are built on a future-proof architecture:
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| File Compatibility | STL, PLY, OBJ (Open Architecture) |
| AI-Driven Scanning | Real-time intraoral scan optimization via edge-AI |
| Milling Precision | ±3µm under load (ISO 5725-2 compliant) |
| Materials Supported | Zirconia, PMMA, Composite, Lithium Disilicate, Cobalt-Chrome |
| Software Updates | Over-the-air (OTA), bi-weekly AI model refinements |
Global Support & Service Infrastructure
Carejoy Digital ensures uninterrupted operation through:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via encrypted cloud tunneling.
- Proactive Monitoring: Predictive maintenance alerts based on spindle load and vibration analytics.
- Global Firmware Updates: Secure, version-controlled OTA updates to enhance milling strategies and material libraries.
For technical inquiries or support, contact: [email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cam Milling Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
