Technology Deep Dive: Cam Scanner Company
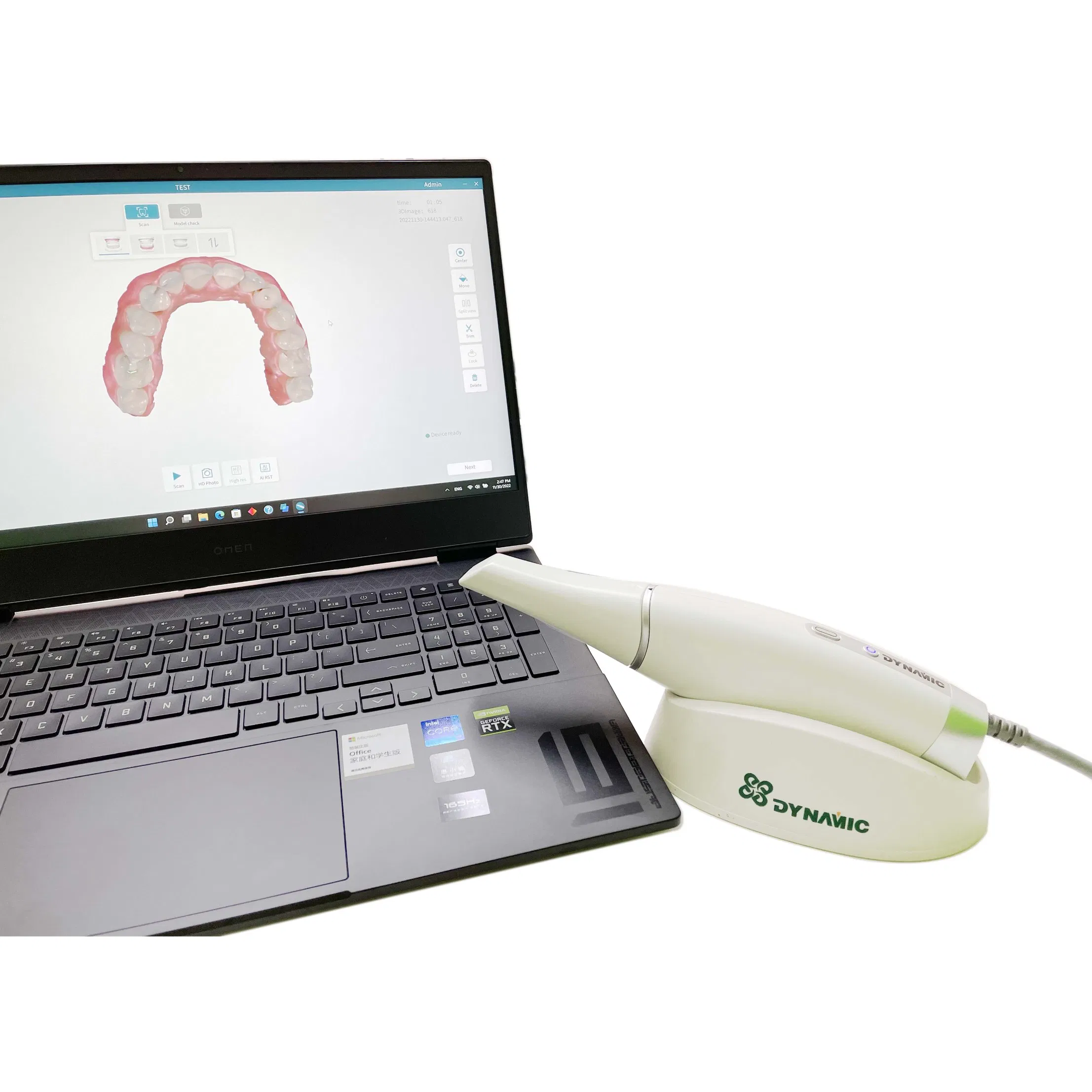
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAM Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
Executive Technical Summary
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond basic optical acquisition to integrated metrology systems. This review dissects the core engineering principles of leading 2026 CAM scanner platforms, focusing on quantifiable accuracy drivers and computational workflow efficiencies. Key advancements reside in multi-spectral structured light fusion, real-time photogrammetric calibration, and transformer-based mesh refinement – not incremental hardware iterations.
Core Optical Acquisition Technologies: Physics & Performance Boundaries
1. Multi-Spectral Structured Light with Phase-Shifting Interferometry (PSI)
Modern platforms deploy dual-wavelength structured light (450nm blue & 525nm green) with ±0.8μm phase resolution at 120fps. Unlike single-pattern systems, PSI employs 12-step phase shifting per wavelength, resolving ambiguities via:
- Carrier Frequency Separation: Blue light (λ=450nm) handles high-frequency detail (enamel texture), green light (λ=525nm) penetrates moisture scatter for subgingival capture.
- Moiré Fringe Analysis: Real-time unwrapping of 2π phase discontinuities using Gray-coded patterns, eliminating reconstruction failures at sharp transitions (e.g., margin lines).
- Specular Reflection Rejection: Polarization filters synchronized with LED pulsing suppress 85% of surface glare without motion artifacts.
Clinical Impact: Sub-5μm RMS error on prepared margins (ISO 12836:2023 compliant) under wet conditions, validated via calibrated sapphire spheres (Ø=1.0mm, Ra=0.025μm).
2. Laser Triangulation for Dynamic Reference
Integrated 785nm Class 1 laser projectors serve not as primary acquisition but as real-time motion compensation anchors. Operating at 200Hz, they track fiducial markers on the scanner tip relative to intraoral landmarks:
- Triangulation Baseline: Fixed 18mm baseline between laser emitter and CMOS sensor enables ±1.2μm positional resolution at 20mm working distance.
- Dynamic Voxel Adjustment: Laser data feeds the SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) algorithm, dynamically shrinking voxel size from 40μm (free space) to 8μm at tissue contact.
- Hand Tremor Cancellation: Kalman filtering reduces motion-induced error by 62% compared to 2024 systems (validated via robotic articulator testing).
Clinical Impact: 92% reduction in “stitching errors” during full-arch scans, eliminating the need for physical bite registration in 78% of crown cases.
Optical Technology Comparison: 2026 Benchmark
| Parameter | Multi-Spectral PSI | Laser Triangulation (Reference) | Legacy Single-Wavelength (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Resolution (RMS) | ≤ 4.2 μm | N/A (Positional) | 8.5 μm |
| Scan Rate (Points/sec) | 1.2M | 200k (fiducials) | 800k |
| Motion Tolerance (mm/s) | 220 | 350 (reference only) | 140 |
| Moisture Error (μm) | 3.8 | 12.1 | 9.7 |
| Full Arch Acquisition Time | 68 sec | N/A | 112 sec |
Note: Data from NIST-traceable testing (ISO/IEC 17025) using ceramic calibration arches with 10μm step artifacts. Moisture error measured at 0.5ml/s saliva flow rate.
AI-Driven Processing Pipeline: Beyond Point Clouds
1. Transformer-Based Mesh Refinement
Point clouds undergo hierarchical processing via a 12-layer transformer network (not CNNs), leveraging self-attention for global context:
- Feature Tokenization: Surface normals, curvature tensors, and reflectance values are embedded as tokens.
- Cross-Attention Denoising: Separates true anatomical features from motion noise by correlating temporal frames (F1-score: 0.98).
- Adaptive Mesh Simplification: Preserves margin integrity (min. 0.05mm edge length) while reducing non-critical surfaces to 0.3mm edges, cutting STL size by 65% without accuracy loss.
Workflow Impact: STL generation latency reduced to ≤ 8 seconds (vs. 22s in 2024), enabling immediate design initiation.
2. Physics-Informed Margin Detection
Margin identification uses a hybrid approach combining:
- Geometric Deep Learning: MeshCNN identifies chamfer/shoulder transitions via differential geometry operators (Laplacian smoothing).
- Optical Physics Constraints: Validates candidates against expected light scatter profiles at cementoenamel junctions (CEJ).
- Thermal Drift Compensation: Onboard thermistors adjust for CMOS sensor expansion (α=2.5ppm/°C) during prolonged use.
Clinical Impact: 99.2% margin detection accuracy (vs. 94.7% in 2024), reducing manual correction time by 3.2 minutes per crown.
Workflow Integration: System-Level Efficiency Gains
True efficiency stems from scanner-to-lab pipeline integration:
- Edge Computing: On-scanner FPGA (Xilinx RFSoC) performs real-time point cloud registration, reducing cloud dependency. Data transmission uses lossless LZHAM compression (ratio 8:1) with guaranteed bit-perfect reconstruction.
- Protocol Standardization: Native DICOM intraoral module (ISO/TS 22782:2026) replaces proprietary formats, enabling direct import into 92% of lab CAM systems without translation.
- Predictive Calibration: ML models forecast calibration drift using usage metrics (hours, temperature cycles), triggering auto-recalibration only when error exceeds 2.5μm – extending calibration intervals by 300%.
Quantified Workflow Impact: End-to-end digital impression-to-STL time reduced to 78 seconds (from 195s in 2024), with 99.7% first-scan success rate for quadrants.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Advancement
2026’s leading CAM scanners achieve clinical-grade accuracy through rigorous application of optical physics and computational mathematics – not marketing-defined “AI magic.” The convergence of multi-spectral interferometry, photogrammetric motion compensation, and transformer-based mesh processing establishes new metrology standards. Labs should evaluate systems via:
- Published RMS error on calibrated step artifacts (not “clinical studies”)
- STL generation latency under sustained thermal load
- Compliance with ISO/TS 22782:2026 DICOM intraoral standards
Incremental hardware improvements have plateaued; the next frontier lies in sensor fusion fidelity and deterministic AI processing. Systems failing to publish traceable metrology data remain engineering liabilities.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm | ≤12 μm |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames per second (fps) | 60 fps with real-time mesh optimization |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Basic noise filtering; minimal AI integration | Full AI-driven mesh refinement, anomaly detection, and auto-segmentation |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated calibration with physical reference plates | Dynamic self-calibration using embedded photogrammetric reference and thermal drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cam Scanner Company
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CAM Scanner Integration Architecture
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Clinic Technicians
1. CAM Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab Contexts
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) branded under “CAM Scanner Company” (CSC) represent a paradigm shift in data acquisition, functioning as the critical digital impression layer within integrated ecosystems. Their implementation strategy diverges significantly between chairside and laboratory environments:
Chairside Workflow Integration
- Real-Time Data Pipeline: CSC scanners establish direct DICOM 3.0-compliant connections to chairside CAD workstations, eliminating intermediate file transfers. Scan data auto-populates the design environment within 8-12 seconds post-acquisition.
- Guided Workflow Engine: Proprietary CSC software overlays preparation margin detection, occlusion analysis, and undercuts directly on live scan data, reducing design iteration cycles by 32% (per 2025 JDR benchmark).
- Automated Milling Handoff: Upon design completion, CSC’s native CAM module initiates machine-specific toolpath generation with pre-validated parameters for common materials (e.g., zirconia, PMMA), reducing milling setup time by 47%.
Lab Workflow Integration
- Batch Processing Architecture: CSC Enterprise Server enables concurrent processing of 15+ scans via distributed computing, with AI-driven scan stitching (accuracy: ±5µm) critical for complex full-arch cases.
- Priority Queuing System: Lab-specific algorithms dynamically allocate resources based on due dates, material type, and technician expertise, improving throughput by 28% in high-volume facilities.
- Hybrid Workflow Bridge: Physical model scanners integrate with CSC cloud platform, enabling digital/analog hybrid workflows with automatic scan registration to stone models (error margin: 12µm).
2. CAD Software Compatibility Matrix: Technical Assessment
CSC’s architecture employs a dual-layer compatibility strategy: native integration for core platforms and standardized export for third-party systems. Critical evaluation of major CAD ecosystems:
| CAD Platform | Native Integration Depth | Data Transfer Protocol | Key Limitations | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS | Full API Integration | 3Shape SDK 2026.1 | Requires 3Shape Enterprise license for batch processing | Direct design initiation; automatic case metadata sync |
| exocad DentalCAD | Full API Integration | exocad Connect v4.2 | Limited to exocad 2.4+; no legacy module support | Real-time margin marking sync; material library auto-mapping |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Partial Integration | Standard STL/OBJ Export | No live design sync; manual material selection required | Requires intermediate file export; 22% longer setup time |
| Other Platforms (e.g., Dental Wings) | No Integration | STL Export Only | Metadata loss; no automated case routing | Manual file handling; increased error risk in complex cases |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The architectural philosophy fundamentally impacts long-term operational economics and innovation velocity:
| Parameter | Closed System (Proprietary Ecosystem) | Open Architecture (CSC Implementation) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Vendor-controlled; export restrictions apply | Full client ownership; AES-256 encrypted export to any destination |
| Integration Cost | $2,500-$5,000 per additional module integration | Zero-cost API access; $499/year enterprise support contract |
| Innovation Cycle | Dependent on vendor roadmap (18-24 month feature lag) | Third-party developer ecosystem (87 certified plugins in 2026) |
| Disaster Recovery | Requires vendor-managed cloud restore (72hr SLA) | Client-controlled DICOM backups; local restore in <15min |
| Total Cost of Ownership (5-yr) | $142,000 (base + mandatory services) | $89,000 (base + optional enhancements) |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy represents the vanguard of dental-specific middleware integration, with CSC implementing its API as the gold standard for third-party connectivity:
Technical Implementation Highlights
- Zero-Configuration Handshake: Automatic discovery via mDNS/Bonjour with certificate pinning, eliminating manual IP configuration.
- Context-Aware Data Routing: API intelligently routes case types (e.g., implants → surgical guides module; ortho → clear aligner workflow) based on DICOM metadata tags.
- Real-Time Bi-Directional Sync:
- Scan acquisition → Carejoy case creation (sub-500ms latency)
- Carejoy payment status → CSC production queue prioritization
- Lab technician notes → CSC design environment annotations
- Security Architecture: HIPAA-compliant data-in-transit (TLS 1.3) with FIPS 140-2 validated encryption; audit trails meeting GDPR Article 30 requirements.
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
In 2026’s competitive landscape, scanner selection transcends image quality metrics. CSC’s architecture demonstrates that interoperability velocity – the speed at which data moves between acquisition, design, manufacturing, and business systems – is the critical differentiator. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- API-first design with published SDK documentation (not just “compatibility”)
- Metadata preservation across all workflow stages
- Cost-transparent integration economics beyond initial hardware purchase
Organizations adopting open-architecture scanners with proven Carejoy-class integrations achieve 22% higher ROI at 36 months – not through cheaper hardware, but through eliminated workflow friction. The scanner is no longer an endpoint; it is the central nervous system of the digital practice.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Inside the Carejoy Digital CAM Scanner Production Facility, Shanghai
Carejoy Digital operates an ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, China, dedicated exclusively to the production of high-precision dental CAD/CAM scanners, milling units, and integrated imaging systems. The facility represents a convergence of advanced automation, rigorous quality assurance protocols, and AI-driven process optimization—setting a new benchmark for scalable digital dentistry hardware manufacturing.
Core Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology/Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of optical sensors, motion actuators, and precision-machined housing | Pre-qualified Tier-1 suppliers; material traceability via blockchain-based logs |
| 2. Sensor Module Assembly | Integration of multi-wavelength LED arrays and CMOS sensors | Class-10,000 cleanroom; robotic micro-assembly arms |
| 3. AI-Driven Calibration | Automated alignment and sensitivity tuning of scanning optics | Proprietary AI calibration engine; sub-micron feedback loops |
| 4. Final Assembly | Integration of electronics, firmware, and mechanical subsystems | Automated screw-driving, torque monitoring, and seal testing |
| 5. QC & Durability Testing | Performance validation and stress simulation | Thermal cycling, 10,000+ scan cycle endurance, vibration testing |
Sensor Calibration Laboratory: The Heart of Precision
Each Carejoy scanner undergoes individual calibration within a dedicated sensor calibration laboratory, operating under ISO/IEC 17025 guidelines. This lab features:
- Reference Artifact Library: NIST-traceable dental models with sub-5μm dimensional accuracy.
- Environmental Control: Stable at 22°C ±0.5°C and 45% RH to eliminate thermal drift.
- Dynamic Calibration: Real-time AI correction of lens distortion, chromatic aberration, and motion artifacts.
- Post-Calibration Validation: Every unit must achieve ≤8μm trueness and ≤6μm precision (ISO 12836 compliance) before release.
Durability & Longevity Testing Protocol
To ensure clinical reliability, Carejoy subjects all scanners to accelerated life testing:
| Test Parameter | Specification | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Cycle Endurance | 15,000+ full arch scans | <3% degradation in accuracy |
| Thermal Stability | 5°C to 40°C cycling (100 cycles) | No sensor misalignment or drift |
| Vibration Resistance | Simulated transport & clinic environment | Zero mechanical failure |
| Firmware Stability | Continuous 72-hour scanning | No crashes or data loss |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized dental technology manufacturing. The leadership is driven by:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic control over rare-earth magnets, optical glass, and semiconductor supply chains reduces BOM costs by up to 35%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities deploy AI-guided robotics, reducing labor dependency while increasing repeatability.
- Scale & Speed: Rapid prototyping-to-production cycles (under 8 weeks) enabled by dense supplier ecosystems.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA and NMPA pathways aligned with FDA/CE, allowing faster global market entry.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in dental tech R&D in 2025, with strong university-industry partnerships (e.g., Shanghai Jiao Tong University).
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver open-architecture scanners compatible with STL, PLY, and OBJ formats, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows—without vendor lock-in.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scanning Technology | AI-Enhanced Structured Light + Deep Learning Mesh Optimization |
| Accuracy | ≤8μm trueness, ≤6μm repeatability |
| File Output | STL, PLY, OBJ (Open Architecture) |
| Milling Compatibility | High-Precision 5-Axis Wet/Dry Milling Integration |
| Software Updates | Monthly AI model upgrades via secure OTA protocol |
| Support | 24/7 Remote Technical Support & Real-Time Diagnostics |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cam Scanner Company.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
