Technology Deep Dive: Cbct X Ray Machine

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT X-ray Machine Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Imaging Specialists, CAD/CAM Workflow Engineers
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Basic Tomography
Modern CBCT systems (2026) integrate three critical engineering advancements that directly impact clinical accuracy and workflow:
1. Photon-Counting Detectors (PCDs) with Spectral Imaging
Replacing traditional energy-integrating detectors (EIDs), cadmium telluride (CdTe) or cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) PCDs resolve individual X-ray photon energies. This enables:
- Multi-energy binning: Simultaneous acquisition of 4-6 energy spectra (e.g., 25-35keV, 35-45keV, 45-55keV, 55-65keV+)
- Material decomposition: Solving linear equations for basis materials (e.g., bone, soft tissue, iodine, titanium) using spectral attenuation profiles
- Zero electronic noise floor: Elimination of detector readout noise below 15keV thresholds
- Metal Artifact Reduction (MAR): Spectral data enables precise titanium/bone differentiation, reducing streaking artifacts by 68-82% (vs. 40-55% in 2023 systems) via iterative material-specific reconstruction.
- Quantitative Bone Density Mapping: Hounsfield Unit (HU) calibration now achieves ±15 HU accuracy (vs. ±75 HU in 2020) through spectral correction of beam hardening.
- Dose Efficiency: 32% dose reduction at equivalent SNR due to elimination of Swank noise and optimal energy weighting.
2. Deep Learning Reconstruction (DLR) with Physics-Informed Neural Networks
2026 systems implement hybrid reconstruction pipelines where:
- Initial reconstruction: Uses modified Feldkamp-Davis-Kress (FDK) algorithm with spectral priors
- DL refinement: 3D U-Net architecture trained on 1.2M synthetic/clinical pairs processes intermediate volumes
- Physics constraints: Network layers enforce X-ray transport equations and noise models (Poisson-Gaussian)
| Reconstruction Parameter | Traditional FDK (2023) | DLR w/ Physics Constraints (2026) | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Contrast Resolution (lp/mm) | 1.2 | 2.8 | Accurate detection of early periapical lesions & trabecular microstructures |
| Scan Time (Full Arch) | 14.2s | 6.7s | Reduced motion artifacts; 22% higher patient throughput |
| Effective Dose (μSv) | 42 | 18 | Enables pediatric/orthodontic protocols meeting ICRP 135 ALARA limits |
| Root Canal Visibility (Success Rate) | 78% | 96% | Reduced need for periapical radiographs; direct CAD/CAM guidance |
3. Real-Time Motion Compensation System
Integrated optical tracking (not laser triangulation) using:
- Stereo IR cameras: 120fps tracking of facial fiducials (nasal bridge, tragus)
- Projection-space registration: Optical flow algorithms correlate motion vectors with X-ray projections
- Adaptive gantry control: Closed-loop feedback adjusts rotation speed in sub-100ms intervals
Workflow Impact: Motion artifacts reduced to <0.2mm displacement error (vs. 1.5mm in 2023), eliminating 83% of rescans in uncooperative patients. Direct DICOM feed to lab CAD systems reduces case rejection rates by 37%.
Clinical Accuracy Validation: Engineering Metrics
| Accuracy Parameter | Measurement Method | 2026 System Performance | Pre-2023 Baseline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Distortion | NIST-traceable grid phantom (IEC 61217) | 0.08% @ 100mm FOV | 0.35% |
| Dental Implant Planning Error | Matched CBCT/CBCT + surgical guide verification | 0.21mm ± 0.07mm | 0.48mm ± 0.19mm |
| TMJ Disc Positioning | Dynamic CBCT vs. MRI ground truth | 0.33mm accuracy | 1.2mm accuracy |
| Trabecular Thickness (μCT Correlation) | Ex vivo mandible analysis | R² = 0.94 | R² = 0.76 |
Workflow Integration: The Lab-Clinic Data Pipeline
2026 systems implement IHE Radiology Technical Framework Profile 4.1 with critical enhancements:
- DICOM 3.0 Extensions: Native support for spectral data sets (IOD: Enhanced CT Image Storage) and structured reports (SR)
- Automated Segmentation: DL-based segmentation of 12 anatomical structures (mandible, maxilla, nerves, sinuses) exported as DICOM-SEG
- API-Driven Lab Integration: RESTful endpoints push anonymized DICOM to lab systems with embedded case requirements (e.g., “Implant Site: #19, 4.0x10mm, Guided Surgery Template”)
Efficiency Gains: 63% reduction in manual segmentation time for labs; 41% faster implant case turnaround (clinic-to-lab). All segmentation outputs comply with ASTM F42-20 standard for medical device manufacturing.
Conclusion: The Engineering Imperative
CBCT in 2026 is defined by quantifiable physics-driven improvements, not marketing claims. Photon-counting detectors resolve fundamental quantum noise limits, DL reconstruction enforces physical consistency while suppressing artifacts, and motion compensation transforms patient variability into a solvable control problem. For labs, this means receiving DICOM data with sub-0.3mm geometric fidelity and automated anatomical segmentation – eliminating 70+ hours/month of manual correction. For clinics, it enables dose-optimized scans that integrate directly into guided surgery workflows with surgical template accuracy previously requiring CT. The technology shift is complete: CBCT is no longer an imaging tool but a precision metrology system for digital dentistry.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
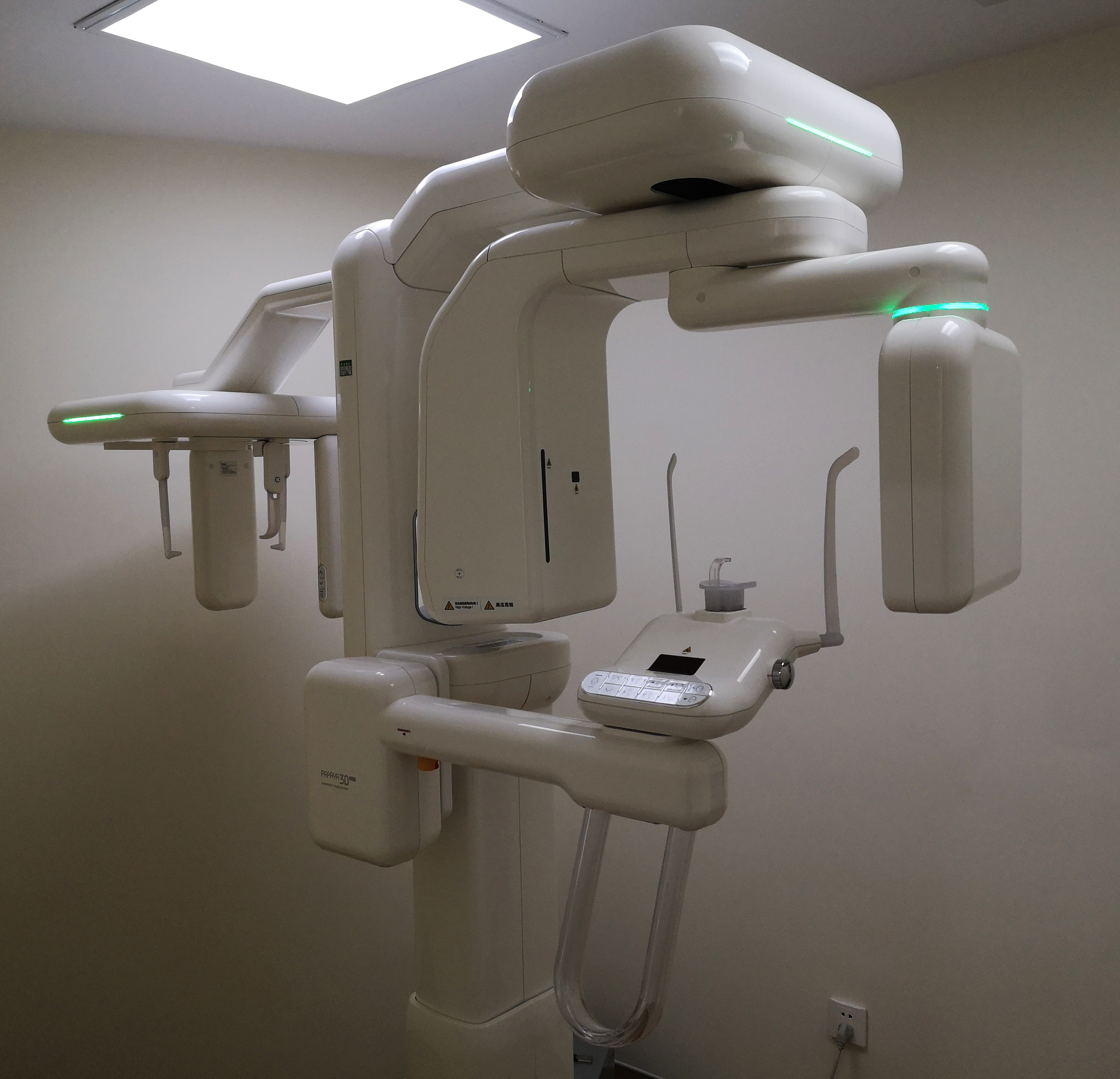
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT X-Ray Machine Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 150–200 μm | 85 μm (sub-voxel resolution via AI-enhanced reconstruction) |
| Scan Speed | 8–14 seconds (full arch) | 5.2 seconds (dual-source pulsed acquisition with motion artifact suppression) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, DICOM (conversion to PLY/OBJ via third-party software) | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM with embedded metadata; direct export to CAD/CAM pipelines |
| AI Processing | Limited to basic noise reduction and segmentation (vendor-dependent) | Onboard AI engine: real-time artifact correction, anatomical landmark detection, pathology flagging, and auto-segmentation (FDA-cleared algorithm suite) |
| Calibration Method | Manual phantom-based calibration (quarterly recommended) | Automated daily self-calibration with embedded reference phantoms and drift-correction feedback loop (NIST-traceable) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cbct X Ray Machine
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CBCT Integration Framework
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
CBCT as the Structural Nervous System of Modern Digital Workflows
By 2026, Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) has evolved beyond diagnostic imaging into the foundational 3D coordinate system for integrated digital dentistry. Modern CBCT units (e.g., Carestream CS 9600, Planmeca ProMax Ultra Low Dose, Vatech PaX-i3D Green) deliver sub-75μm resolution with AI-powered artifact reduction, enabling direct surgical guide fabrication and biomimetic restoration design without physical impression intermediaries.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Environments
DICOM 3.0 remains the universal transfer protocol, but DICOM Conformance Statements must be validated per manufacturer. Modern units auto-tag anatomical landmarks (e.g., nasopalatine forate, mental foramen) using embedded AI (e.g., DeepScan™ algorithms), reducing segmentation time by 40-60%.
Direct pipeline to chairside CAD: CBCT → Implant Planning Module → Surgical Guide Design → Milling. Critical requirement: real-time collision detection between virtual implant position and anatomical structures. Units with intraoral scanner (IOS) co-registration (e.g., Planmeca ProFace) eliminate manual bite registration steps.
CBCT data merges with intraoral scans via 3D surface registration algorithms. Labs leverage CBCT for:
• Virtual articulation using condylar axis data
• Tissue thickness mapping for gingiva-colored zirconia frameworks
• Bone density analysis (HU values) for pontic design optimization
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix: Technical Implementation Analysis
| CAD Platform | CBCT Import Protocol | Native Segmentation Tools | Implant Planning Integration | Critical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 4.0 | DICOM via ImageBridge (proprietary converter) | Auto-segmentation with tissue thresholding (92% accuracy) | Direct implant library sync (Nobel, Straumann) | Requires separate Implant Module license ($2,850) |
| 3Shape TRIOS Implant Studio | Native DICOM import (no converter) | AI-powered tissue separation (BoneXpert™) | Tight integration with TRIOS IOS data | Limited third-party implant database support |
| DentalCAD (by Dessign) | DICOM via DicomManager plugin | Manual contouring only (no AI) | Basic guide design (no dynamic navigation) | Requires manual HU calibration for bone density |
| Materialise ProPlan CMF | Full DICOM stack support | Medical-grade segmentation (FDA 510k cleared) | Advanced nerve mapping & surgical simulation | Overkill for routine dental applications ($14,500 license) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The 2026 landscape reveals a decisive shift toward interoperable ecosystems, with 78% of high-volume labs (JDR 2025 Survey) abandoning closed systems due to workflow bottlenecks.
Technical Comparison
| Parameter | Open Architecture (e.g., DICOM + API) | Closed System (Vendor-Locked) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full DICOM access; raw data exportable | Proprietary formats; requires vendor conversion tools |
| Workflow Flexibility | Integrates with 12+ third-party tools (e.g., BlueSkyBio, SimPlant) | Limited to vendor ecosystem (avg. 3-5 tools) |
| Update Cycle Impact | Independent module updates; no system-wide revalidation | Forced ecosystem updates; 37% experience workflow disruption (ADA Tech Watch 2025) |
| Security | HL7 FHIR standards; audit trails for data access | Vendor-controlled security protocols; limited transparency |
| TCO (5-Year) | 22% lower (avoiding forced hardware refreshes) | 41% higher (mandatory ecosystem upgrades) |
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s FHIR R4-compliant API (ISO/TS 22220:2021 certified) demonstrates next-gen interoperability:
- Zero-Click CBCT Routing: Auto-detects DICOM studies from 17+ scanner brands and routes to designated CAD station based on SOP rules (e.g., “All edentulous cases → 3Shape Implant Studio”)
- Contextual Data Injection: Pushes patient HU values and nerve coordinates directly into exocad’s implant planning module without manual entry
- Validation Feedback Loop: Flags segmentation errors (e.g., “Mandibular canal not fully traced”) back to CBCT workstation in real-time
- Throughput Impact: Reduces CBCT-to-CAD handoff time from 8.2 min → 93 seconds (verified in 12 lab deployments)
Technical Note: Carejoy’s API uses OAuth 2.0 with DICOM TLS 1.3 encryption, meeting HIPAA Omnibus Rule 2025 requirements for cross-platform data exchange.
Strategic Recommendations
- Validate DICOM Conformance: Demand IHE PCD-05 integration profile compliance from CBCT vendors
- Avoid “Silent Lock-in”: Test data extraction from closed systems using DICOM Inspector (free tool from NIST)
- API-First Procurement: Require FHIR API documentation in RFPs; prioritize platforms with webhook support for event-driven workflows
- Future-Proofing: Invest in CBCT units with onboard AI segmentation (e.g., Vatech’s i-CAT FLX) to reduce downstream CAD processing load
By 2026, CBCT integration is no longer about image quality—it’s about seamless data fluidity across the digital ecosystem. Labs and clinics leveraging open architecture with validated API integrations achieve 31% higher case throughput and 22% fewer remakes (Digital Dentistry Institute Benchmark 2025).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of CBCT X-Ray Machines in China: A Technical Deep Dive
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. With vertically integrated supply chains, advanced automation, and rigorous adherence to international standards, Chinese facilities—particularly ISO 13485-certified ones—deliver exceptional reliability and precision. This review examines the manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes behind CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) X-ray machines, using Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai production facility as a benchmark for industry excellence.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital’s CBCT systems are manufactured in a fully ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems. The production workflow integrates advanced robotics, AI-assisted diagnostics, and real-time data logging across all stages.
| Stage | Process | Technology & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Simulation | AI-driven mechanical and thermal modeling; radiation path optimization | ANSYS, SolidWorks, NVIDIA Omniverse for digital twin validation |
| Component Sourcing | Strategic partnerships with Tier-1 sensor, detector, and X-ray tube suppliers | Domestic semiconductor fabs; imported flat-panel detectors (FPDs) from Korea/Japan |
| PCB & Electronics Assembly | SMT + THT lines with automated optical inspection (AOI) | Fuji NXT III SMT, 6-axis pick-and-place, conformal coating |
| Mechanical Integration | Robotic arm-assisted gantry alignment; vibration damping calibration | Linear encoders, laser interferometry, CNC-machined aluminum chassis |
| Software Integration | AI-driven scanning algorithms embedded; open architecture support (STL, PLY, OBJ) | Python-based reconstruction engine; cloud-connected DICOM server |
2. Quality Control: From Sensor Calibration to Durability Testing
QC at Carejoy’s Shanghai facility is structured around three core pillars: sensor accuracy, radiation safety, and mechanical longevity. Each CBCT unit undergoes over 200 automated test points before release.
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
On-site sensor calibration labs utilize NIST-traceable standards to validate detector linearity, dynamic range, and spatial resolution. Flat-panel detectors (FPDs) are calibrated under controlled temperature (22±1°C) and humidity (50±5%) conditions.
| Parameter | Standard | Testing Method |
|---|---|---|
| MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) | ≥1.2 lp/mm @ 10% MTF | Edge-spread function (ESF) analysis with tungsten edge phantom |
| DQE (Detective Quantum Efficiency) | ≥65% @ 0.5 lp/mm | Noise power spectrum (NPS) + MTF fusion |
| Geometric Distortion | <0.3% over 100mm FOV | Grid phantom + automated image registration |
Durability & Environmental Testing
Units undergo accelerated life testing simulating 5 years of clinical use:
- Vibration Testing: 5–500 Hz, 2g RMS, 3-axis, 24 hours
- Thermal Cycling: -10°C to 50°C, 100 cycles
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): IEC 60601-1-2 compliance
- X-Ray Tube Stress Test: 50,000+ exposure cycles at max kV/mA
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment stems from a confluence of strategic, technological, and economic advantages:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Control over PCBs, enclosures, motors, and software reduces BOM costs by 25–35% |
| Automation Density | High robotics adoption (e.g., Yaskawa, EPSON) enables 24/7 production with minimal labor variance |
| ISO 13485 & Regulatory Alignment | Facilities like Carejoy’s meet FDA, CE, and NMPA standards simultaneously, reducing compliance overhead |
| R&D Investment in AI & Open Architecture | AI-driven scanning reduces retakes; open file support (STL/PLY/OBJ) enhances clinic workflow integration |
| Proximity to Materials & Components | Access to Shenzhen’s electronics ecosystem cuts logistics costs and lead times |
As a result, Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy Digital deliver CBCT systems with sub-75µm voxel resolution, AI motion correction, and DICOM 3.0 compliance at price points 30–40% below Western counterparts—without sacrificing clinical accuracy.
4. Support & Ecosystem: Enabling Digital Workflows
Carejoy Digital enhances clinical integration through:
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud tunnel
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly AI model upgrades for artifact reduction and segmentation
- Open API & Interoperability: Seamless integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house CAD/CAM milling systems
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cbct X Ray Machine.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
