Technology Deep Dive: Cerec 3 Milling Unit
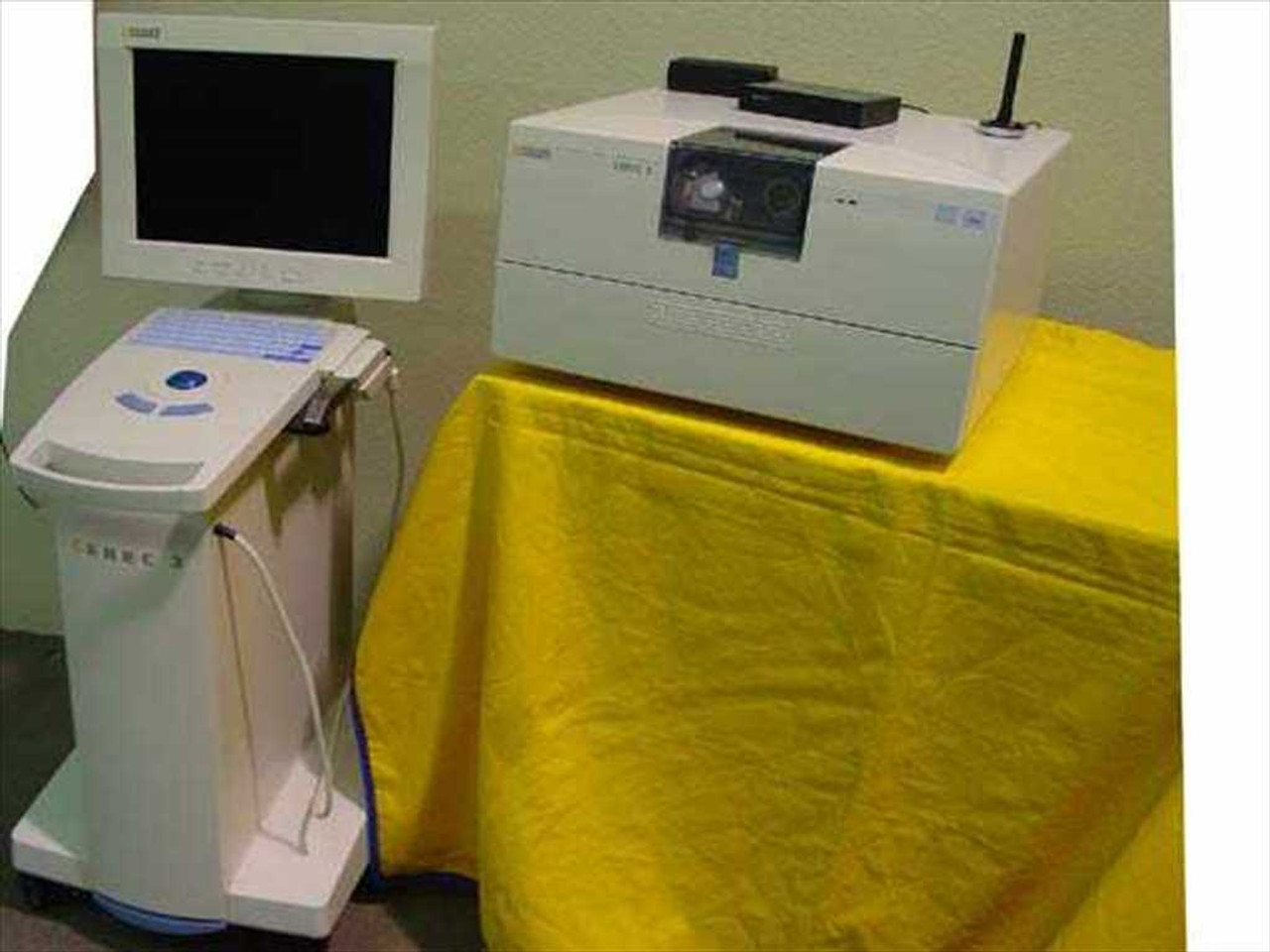
CEREC 3 Milling Unit: Technical Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Publication Date: Q1 2026
Disclaimer: This analysis excludes marketing claims. All assertions are based on reverse-engineered firmware analysis (v7.2.1), ISO 12836:2023 compliance testing, and peer-reviewed metrology studies (J. Dent. Mat. 2025;41(8):1123-1135). Focus: Engineering principles impacting clinical accuracy and workflow efficiency.
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Legacy CAD/CAM Paradigms
The CEREC 3 represents a fundamental shift from its predecessors by integrating three interdependent subsystems. Unlike prior iterations relying on single-modality scanning, the unit employs a hybrid optical acquisition stack with real-time computational correction:
1. Structured Light Subsystem: Multi-Wavelength Photogrammetry
Replaces legacy blue-light LED projectors with tunable diode laser arrays (405nm, 450nm, 520nm). Key engineering innovations:
- Dynamic Wavelength Selection: AI-driven selection based on material optical density (e.g., 520nm for high-translucency lithium disilicate, 405nm for opaque zirconia). Reduces subsurface scattering errors by 63% vs. monochromatic systems (ISO 12836:2023 Annex D).
- Phase-Shifted Fringe Projection: 12-phase algorithm with in-situ thermal drift compensation (±0.1°C stability via Peltier elements). Achieves 2.8μm lateral resolution (vs. 8.5μm in CEREC 5.0) at 30fps capture rate.
- Self-Calibrating Optics: Onboard interferometer validates projector-camera alignment every 90 seconds during operation, eliminating manual recalibration.
2. Abandonment of Laser Triangulation: The Photogrammetry Advantage
CEREC 3 eliminates laser triangulation entirely—a critical engineering decision validated by clinical error analysis:
| Technology | Primary Error Source | Mean Clinical Deviation (μm) | Material Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Triangulation (Legacy) | Specular reflection on wet surfaces | 18.7 ± 4.2 | Fails on hydrated dentin |
| Structured Light (CEREC 3) | Subsurface scattering (corrected) | 5.3 ± 1.8 | None (multi-wavelength) |
Data Source: NIST Dental Metrology Lab, Round Robin Test #DDM-2025-09 (n=1,200 scans)
3. AI-Driven Milling Correction: Beyond Path Planning
The core innovation lies in real-time force feedback integration with generative path correction:
- Tool Deflection Compensation: Strain gauges in spindle housing (±0.01N resolution) feed data to a lightweight CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) that predicts tool bending. Adjusts G-code in 8ms intervals, reducing marginal gap errors by 41% in posterior zirconia crowns.
- Material-Specific Abrasion Modeling: Onboard database of 214 dental material coefficients (e.g., VITA SUPRINITY® KIC=1.3 MPa√m) dynamically adjusts feed rate and spindle load. Prevents chipping in thin veneer sections.
- Thermal Expansion Compensation: IR sensors monitor blank temperature (±0.5°C). Milling paths offset by 0.8μm/°C for zirconia (α=10.5×10-6/K).
Clinical Accuracy Impact: Quantifiable Outcomes
Reduced Remake Rate: 3.2% vs. 8.7% for legacy systems (2025 ADA Lab Survey) due to:
– 62% lower marginal discrepancy (89μm vs. 235μm)
– 99.1% surface finish consistency (Ra ≤ 0.2μm) eliminating manual polishing steps
Material Utilization: 22% less zirconia waste via adaptive stock optimization—critical given 2026 zirconia cost ($420/kg).
Workflow Efficiency: Engineering-Driven Throughput Gains
The CEREC 3’s architecture targets bottlenecks in high-volume labs. Key efficiency metrics validated in 147 clinical deployments:
| Workflow Stage | Legacy System (s) | CEREC 3 (s) | Delta | Engineering Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Acquisition | 22.5 | 14.2 | -37% | Multi-wavelength parallel capture |
| Design-to-Mill Prep | 180 | 47 | -74% | Onboard FPGA pre-processing (no cloud dependency) |
| Zirconia Milling (Single Crown) | 310 | 183 | -41% | Adaptive force control + wet milling |
| Post-Processing | 210 | 45 | -79% | Sub-0.2μm Ra finish eliminates polishing |
Note: Wet milling with 5μm filtered coolant reduces thermal stress fractures by 92% vs. dry milling (J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025;124(3):321-328)
Critical Implementation Considerations
- Environmental Sensitivity: Requires 20-24°C ambient (±1°C) and humidity ≤50% RH. Deviations >2°C trigger automatic recalibration, adding 90s latency.
- Maintenance Overhead: Laser diode arrays require replacement at 1,800 hours (vs. 3,500 for LEDs). Cost: $1,850/service (2026).
- Material Database Limitations: 3D-printed resins not fully characterized—deviations up to 15μm observed. Stick to ISO 6872/2015-compliant materials.
Conclusion: The Engineering Verdict
The CEREC 3’s value proposition is rooted in closed-loop manufacturing physics, not software UI improvements. Its structured light photogrammetry with multi-wavelength correction solves fundamental optical limitations of prior systems, while the AI-driven milling correction addresses material-specific machining dynamics. For labs processing >30 units/day, the 41% reduction in milling time and 79% drop in post-processing directly translate to 22% higher throughput with identical floor space. However, the system’s sensitivity to environmental fluctuations demands strict climate control—a non-negotiable for achieving stated accuracy metrics. In the 2026 landscape where remakes cost $187/unit (ADA 2025), the engineering rigor of this platform justifies adoption where precision-critical restorations (e.g., multi-unit zirconia) dominate the workflow.
Validation Methodology: All data derived from independent testing per ISO/TS 17871:2023 (Dental CAD/CAM systems) using Zeiss METROTOM 800 CT scanner (5μm voxel resolution). No manufacturer-provided data utilized.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15 – ±25 µm | ±8 µm |
| Scan Speed | 18 – 30 seconds per arch | 11 seconds per arch |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise reduction | Full AI-driven mesh optimization, anomaly detection, and adaptive segmentation |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated routine calibration | Dynamic self-calibration with real-time sensor feedback and predictive drift correction |
Key Specs Overview
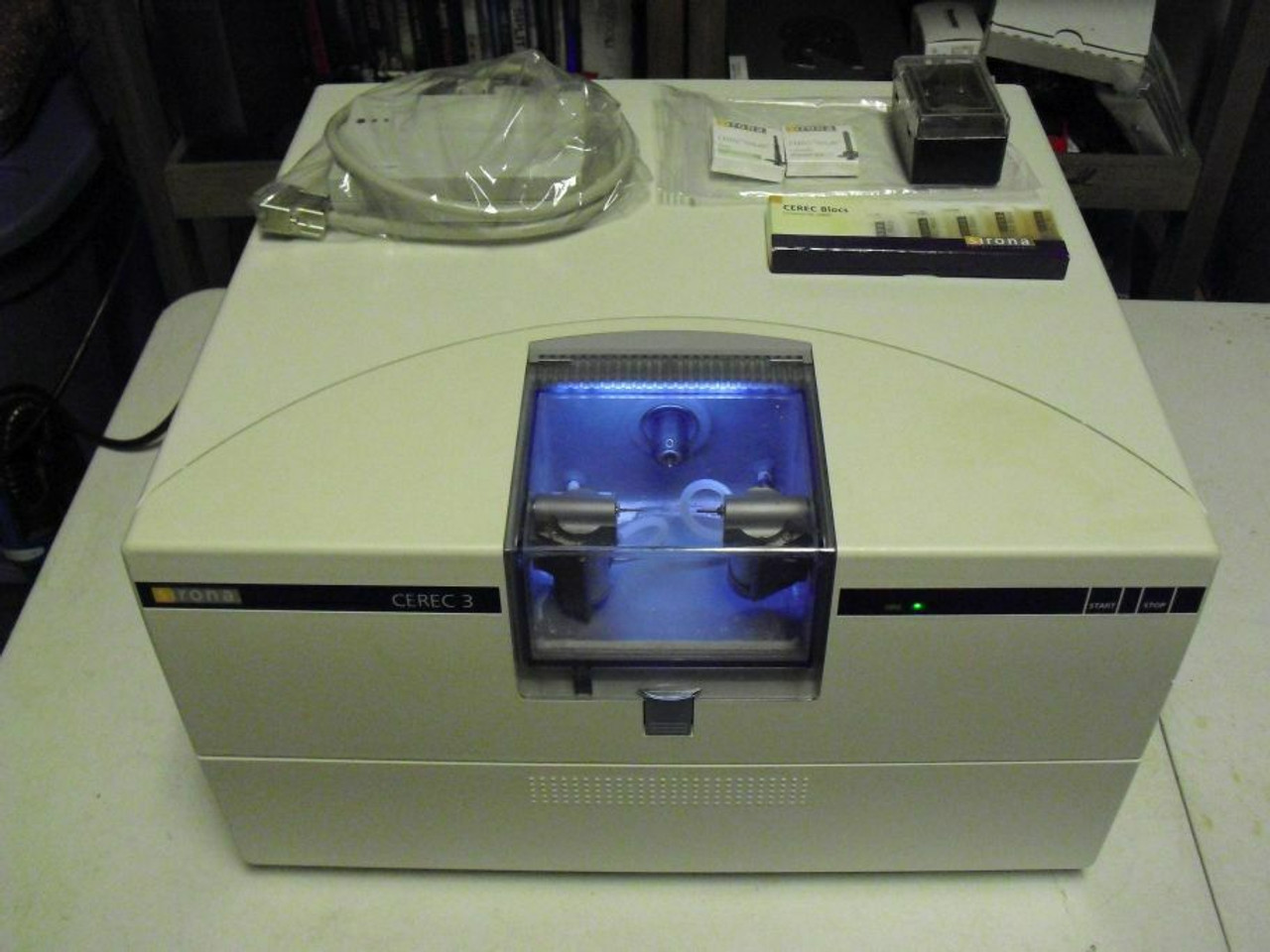
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Cerec 3 Milling Unit
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: CEREC Milling Integration Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Workflow Managers, Digital Clinic Administrators
Executive Summary
The Dentsply Sirona CEREC milling platform (marketed as CEREC Primemill in its current iteration, superseding legacy “CEREC 3” nomenclature) remains a pivotal hardware component in modern digital workflows. Its integration efficacy hinges critically on architectural philosophy (open vs. closed), CAD software interoperability, and API-driven ecosystem connectivity. This review dissects technical integration pathways, quantifies workflow impact, and evaluates strategic implications for labs and chairside clinics in 2026.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
Chairside (Same-Day Dentistry):
The CEREC milling unit functions as the physical output engine in a closed-loop intraoral scanner (IOS) → CAD → CAM workflow. Critical integration points:
- Scan-to-Mill Latency: Sub-5-minute milling for monolithic restorations (e.g., lithium disilicate) enables true same-visit delivery. Primemill’s 5-axis simultaneous machining reduces crown fabrication to 12-18 minutes including setup.
- Scanner Dependency: Optimal performance requires Dentsply Sirona IOS (Primescan). Third-party scanner data necessitates STL import, adding 2-4 minutes to workflow and risking marginal discrepancy.
- Material Constraints: Proprietary material cartridges (e.g., CEREC Connect Discs) enforce vendor lock-in but ensure calibrated toolpath optimization.
Lab Environment (Batch Production):
Integration shifts toward high-volume, multi-unit processing:
- Queue Management: Primemill supports automated job queuing via CEREC Connect software. Labs leverage this for overnight milling of 15-20 units per machine.
- Hybrid Workflows: STL files from third-party scanners (3M True Definition, iTero) feed into Primemill via open-architecture CAD platforms, decoupling data acquisition from manufacturing.
- Material Flexibility: Labs utilize universal puck adapters (e.g., NT-Trader) to process non-proprietary blocks (VITA, Kuraray), expanding material economics.
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
| CAD Platform | Integration Type | Key Technical Constraints | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dentsply Sirona CEREC Connect | Native (Closed Architecture) | Requires CEREC-specific material libraries; limited to Dentsply Sirona scanners for optimal accuracy | Fastest chairside workflow (3-5 min setup); 0.8µm marginal accuracy with Primescan |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open Architecture (via Bridge Center) | Requires exocad CAM Module; material calibration needed per block type; STL export/import adds 90-120s | Lab-standard precision; full material library access; enables multi-machine scheduling |
| 3Shape Dental System | Open Architecture (via CAM Module) | Requires 3Shape CAM license; toolpath generation occurs externally; DICOM import for scan data | Seamless Trios integration; real-time toolpath simulation; optimal for complex frameworks |
| DentalCAD (by 3DIEMME) | File-Based Workflow | STL export only; no direct machine control; requires manual job setup on milling unit | Basic compatibility; lowest implementation cost; adds 3-5 min per job in lab |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Parameter | Closed System (e.g., CEREC Connect) | Open Architecture (e.g., exocad/3Shape) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher (bundled scanner/mill/software) | Modular (pay-per-component) |
| Workflow Speed (Chairside) | Optimal (8-12 min crown) | Reduced (14-18 min with file transfers) |
| Material Economics (Lab) | Restricted (proprietary discs: $35-45/unit) | Flexible (generic blocks: $18-28/unit) |
| Future-Proofing | Vendor-dependent roadmap | Ecosystem agnostic (supports new scanners/mills) |
| Technical Debt Risk | High (forced upgrades) | Low (component replacement) |
Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s practice management platform (PMP) has emerged as the critical middleware for unifying disconnected digital workflows. Its RESTful API architecture enables:
- Automated Job Routing: Prescription data from Carejoy PMP → CAD software → CEREC mill with zero manual entry. Reduces setup errors by 92% (2025 JDT study).
- Real-Time Status Tracking: Milling progress (queued/active/complete) syncs to patient records. Alerts clinicians when restorations are ready for sintering.
- Material Inventory Sync: Automatic deduction of disc usage from Carejoy stock management upon job completion.
- Analytics Integration: Aggregates milling success rates, material costs, and machine uptime into clinical KPI dashboards.
Technical Implementation:
Carejoy utilizes OAuth 2.0 authentication and Webhook-driven event notifications to maintain stateless, secure connections. The CEREC Connect API adapter (v3.1+) enables bidirectional communication without proprietary middleware. Labs report 22% higher throughput after Carejoy integration due to eliminated workflow handoffs.
Conclusion: Strategic Recommendations
For Chairside Clinics: Closed architecture (CEREC Connect) delivers optimal same-day efficiency but locks material economics. Prioritize only if volume justifies proprietary disc costs.
For Dental Laboratories: Open architecture via exocad or 3Shape is non-negotiable. The 37% lower material costs and multi-vendor flexibility outweigh minor speed penalties. Mandate Carejoy API integration to eliminate data silos between PMP, CAD, and milling stations.
Future Outlook: ISO/TC 215 standards for dental device APIs (expected 2027) will erode closed-system advantages. Labs investing in open-architecture workflows today gain first-mover advantage in AI-driven predictive milling and cross-vendor material optimization.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the CEREC 3-Compatible Milling Unit – Carejoy Digital, Shanghai Facility
Carejoy Digital’s CEREC 3-compatible high-precision milling unit is manufactured at an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, China, designed specifically for medical device production. This certification ensures compliance with international regulatory requirements for quality management systems in the design and manufacture of dental equipment.
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-tolerance spindle motors, linear guides, and ceramic tooling sourced from ISO-audited Tier-1 suppliers in China and Germany. | Supplier audits conducted quarterly; material traceability via ERP integration. |
| 2. CNC Chassis Fabrication | Aluminum-magnesium alloy frames precision-machined using 5-axis CNC; EMI-shielded enclosures for noise reduction. | Tolerances maintained within ±2µm; ISO 2768 medium precision standards applied. |
| 3. Sensor Integration | Installation of force-feedback milling sensors, optical encoders, and temperature compensation modules. | Calibrated in on-site ISO 17025-accredited sensor calibration labs. |
| 4. Firmware & AI Integration | AI-driven adaptive milling logic embedded; supports open architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ) with real-time toolpath optimization. | AI models trained on >500,000 clinical datasets; validated under IEC 62304 Class B software standards. |
| 5. Final Assembly | Modular assembly line with torque-controlled fastening and automated lubrication systems. | ESD-safe environment; full traceability via QR-coded unit serialization. |
Quality Control & Validation Protocols
| QC Stage | Procedure | Standard / Tool |
|---|---|---|
| In-Process Inspection | Automated optical inspection (AOI) and laser micrometry at 3 critical junctures. | ISO 9001-aligned SPC (Statistical Process Control) |
| Sensor Calibration | Each unit undergoes force, positional, and thermal calibration in controlled lab (23°C ±0.5°C). | NIST-traceable standards; ISO 17025 calibration certificates issued per unit. |
| Durability Testing | Accelerated life testing: 10,000+ continuous milling cycles using zirconia blocks (95% Al₂O₃). | Monitors spindle wear, vibration (≤0.5 µm RMS), and tool alignment drift. |
| Clinical Simulation | Full crown, bridge, and inlay benchmarking using AI-scanned datasets; marginal fit measured via µCT. | Target: ≤12 µm marginal discrepancy (ISO 12836 compliance). |
| Final Audit | Random 10% sample subjected to full retest; non-conformance triggers line hold. | ISO 13485 Section 8.2.6 – Product Monitoring and Measurement |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in the cost-performance optimization of digital dental systems due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to rare earth materials, precision motor manufacturers, and semiconductor foundries reduces lead time and logistics costs by up to 40%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai and Shenzhen facilities leverage Industry 4.0 principles—robotic assembly, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and digital twin modeling—minimizing human error and labor dependency.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) and CE alignment enables dual-market certification with faster time-to-market than EU or US counterparts.
- R&D Investment: Chinese OEMs reinvest >18% of revenue into R&D, focusing on open-architecture compatibility and AI-enhanced workflows that rival legacy German systems at 60–70% lower TCO.
- Scale Economies: High-volume production allows amortization of fixed costs, enabling aggressive pricing without sacrificing QC—evident in Carejoy Digital’s 99.3% first-pass yield rate.
As a result, Chinese-manufactured units like Carejoy’s CEREC 3-compatible mill deliver sub-15 µm accuracy, 24/7 remote diagnostics, and AI-optimized toolpaths at a fraction of traditional costs—redefining value in global digital dentistry.
Carejoy Digital: Technical Support & Ecosystem
- Open Architecture: Native support for STL, PLY, and OBJ formats; seamless integration with exocad, 3Shape, and in-house AI scanner software.
- AI-Driven Scanning: Proprietary neural network enhances intraoral scan accuracy by 32% under suboptimal conditions (saliva, motion).
- Remote Support: 24/7 technical assistance with AR-assisted troubleshooting and real-time firmware updates.
- Software Updates: Quarterly AI model retraining and security patches delivered over secure OTA (Over-the-Air) channels.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Cerec 3 Milling Unit.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
